|
Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are devices that detect light or other forms of electromagnetic radiation and convert it into an electrical signal. They are essential in a wide range of applications, from digital imaging and optical communication to scientific research and industrial automation. Photodetectors can be classified by their mechanism of detection, such as the photoelectric effect, photochemical reactions, or thermal effects, or by performance metrics like spectral response. Common types include photodiodes, phototransistors, and photomultiplier tubes, each suited to specific uses. Solar cells, which convert light into electricity, are also a type of photodetector. This article explores the principles behind photodetectors, their various types, applications, and recent advancements in the field. History The development of photodetectors began with the discovery of the photoelectric effect by Heinrich Hertz in 1887, later explained by Albert Einst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Responsivity
Responsivity is a measure of the input–output Gain (electronics), gain of a detector system. In the specific case of a photodetector, it measures the electrical output per optical input. A photodetector's responsivity is usually expressed in units of amperes or volts per watt of incident radiant flux, radiant power. For a system that responds linearly to its input, there is a unique responsivity. For nonlinear systems, the responsivity is the Derivative, local slope. Many common photodetectors respond linearly as a function of the incident power. Responsivity is a function of the wavelength of the incident Electromagnetic radiation, radiation and of the sensor's properties, such as the bandgap of the material of which the photodetector is made. One simple expression for the responsivity ''R'' of a photodetector in which an optical signal is converted into an electric current (known as a photocurrent) is : R=\eta\frac\approx\eta\frac where \eta is the quantum efficiency (the c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photodiode
A photodiode is a semiconductor diode sensitive to photon radiation, such as visible light, infrared or ultraviolet radiation, X-rays and gamma rays. It produces an electrical current when it absorbs photons. This can be used for detection and measurement applications, or for the generation of electrical power in solar cells. Photodiodes are used in a wide range of applications throughout the electromagnetic spectrum from visible light photocells to gamma ray spectrometers. Principle of operation A photodiode is a PIN diode, PIN structure or p–n junction. When a photon of sufficient energy strikes the diode, it creates an electron–electron hole, hole pair. This mechanism is also known as the inner photoelectric effect. If the absorption occurs in the junction's depletion region, or one diffusion length away from it, these carriers are swept from the junction by the built-in electric field of the depletion region. Thus holes move toward the anode, and electrons toward the cath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quantum Efficiency
The term quantum efficiency (QE) may apply to incident photon to converted electron (IPCE) ratio of a photosensitive device, or it may refer to the TMR effect of a magnetic tunnel junction. This article deals with the term as a measurement of a device's electrical sensitivity to light. In a charge-coupled device (CCD) or other photodetector, it is the ratio between the number of charge carriers collected at either terminal and the number of photons hitting the device's photoreactive surface. As a ratio, QE is dimensionless, but it is closely related to the responsivity, which is expressed in amps per watt. Since the energy of a photon is inversely proportional to its wavelength, QE is often measured over a range of different wavelengths to characterize a device's efficiency at each photon energy level. For typical semiconductor photodetectors, QE drops to zero for photons whose energy is below the band gap. A photographic film typically has a QE of much less than 10%, while CCD ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Specific Detectivity
Specific detectivity, or ''D*'', for a photodetector is a figure of merit used to characterize performance, equal to the reciprocal of noise-equivalent power (NEP), normalized per square root of the sensor's area and frequency bandwidth (reciprocal of twice the integration time). Specific detectivity is given by D^*=\frac, where A is the area of the photosensitive region of the detector, \Delta f is the bandwidth, and NEP the noise equivalent power in units It is commonly expressed in ''Jones'' units (cm \cdot \sqrt/ W) in honor of Robert Clark Jones who originally defined it.R. C. Jones, "Proposal of the detectivity D** for detectors limited by radiation noise," ''J. Opt. Soc. Am.'' 50, 1058 (1960), ) Given that noise-equivalent power can be expressed as a function of the responsivity \mathfrak (in units of A/W or V/W) and the noise spectral density S_n (in units of A/Hz^ or V/Hz^) as NEP=\frac, it is common to see the specific detectivity expressed as D^*=\frac. It is ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gallium Arsenide
Gallium arsenide (GaAs) is a III-V direct band gap semiconductor with a Zincblende (crystal structure), zinc blende crystal structure. Gallium arsenide is used in the manufacture of devices such as microwave frequency integrated circuits, monolithic microwave integrated circuits, infrared light-emitting diodes, laser diodes, solar cells and optical windows. GaAs is often used as a substrate material for the epitaxial growth of other III-V semiconductors, including indium gallium arsenide, aluminum gallium arsenide and others. History Gallium arsenide was first synthesized and studied by Victor Goldschmidt in 1926 by passing arsenic vapors mixed with hydrogen over gallium(III) oxide at 600 °C. The semiconductor properties of GaAs and other Compound semiconductor, III-V compounds were patented by Heinrich Welker at Siemens-Schuckert in 1951 and described in a 1952 publication. Commercial production of its monocrystals commenced in 1954, and more studies followed in the 195 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indium Phosphide
Indium phosphide (InP) is a binary semiconductor composed of indium and phosphorus. It has a face-centered cubic ("zincblende (crystal structure), zincblende") crystal structure, identical to that of gallium arsenide, GaAs and most of the List of semiconductor materials, III-V semiconductors. Manufacturing Indium phosphide can be prepared from the reaction of white phosphorus and indium iodide at 400 °C., also by direct combination of the purified elements at high temperature and pressure, or by thermal decomposition of a mixture of a trialkyl indium compound and phosphine. Applications The application fields of InP splits up into three main areas. It is used as the basis for optoelectronic components, high-speed electronics, and photovoltaics High-speed optoelectronics InP is used as a substrate for epitaxy, epitaxial optoelectronic devices based other semiconductors, such as indium gallium arsenide. The devices include pseudomorphic heterojunction bipolar transistors th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Cell
A solar cell, also known as a photovoltaic cell (PV cell), is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by means of the photovoltaic effect.Solar Cells chemistryexplained.com It is a type of photoelectric cell, a device whose electrical characteristics (such as Electric current, current, voltage, or Electrical resistance and conductance, resistance) vary when it is exposed to light. Individual solar cell devices are often the electrical building blocks of solar panel, photovoltaic modules, known colloquially as "solar panels". Almost all commercial PV cells consist of crystalline silicon, with a market share of 95%. Cadmium telluride thin-film solar cells account for the remainder. The common single-junction silicon solar cell can produce a maximum open-circuit voltage o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noise-equivalent Power
Noise-equivalent power (NEP) is a measure of the sensitivity of a photodetector or detector system. It is defined as the signal power that gives a signal-to-noise ratio of one in a one hertz output bandwidth. An output bandwidth of one hertz is equivalent to half a second of integration time.The factor of one half is explained by the Nyquist–Shannon sampling theorem. The units of NEP are watts per square root hertz. The NEP is equal to the noise amplitude spectral density (expressed in units of \mathrm/\sqrt or \mathrm/\sqrt) divided by the responsivity Responsivity is a measure of the input–output Gain (electronics), gain of a detector system. In the specific case of a photodetector, it measures the electrical output per optical input. A photodetector's responsivity is usually expressed in un ... (expressed in units of \mathrm/\mathrm or \mathrm/\mathrm, respectively). The fundamental equation is SNR = P/NEP. A smaller NEP corresponds to a more sensitive detector. For exa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Image Sensor
An image sensor or imager is a sensor that detects and conveys information used to form an image. It does so by converting the variable attenuation of light waves (as they refraction, pass through or reflection (physics), reflect off objects) into signal (electrical engineering), signals, small bursts of electric current, current that convey the information. The waves can be light or other electromagnetic radiation. Image sensors are used in electronics, electronic imaging devices of both analogue electronics, analog and digital electronics, digital types, which include digital cameras, camera modules, camera phones, optical mouse devices, medical imaging equipment, night vision equipment such as thermography, thermal imaging devices, radar, sonar, and others. As technological change, technology changes, electronic and digital imaging tends to replace chemical and analog imaging. The two main types of electronic image sensors are the charge-coupled device (CCD) and the active-pixel s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Refraction
In optics, the refractive index (or refraction index) of an optical medium is the ratio of the apparent speed of light in the air or vacuum to the speed in the medium. The refractive index determines how much the path of light is bent, or refracted, when entering a material. This is described by Snell's law of refraction, , where and are the angle of incidence and angle of refraction, respectively, of a ray crossing the interface between two media with refractive indices and . The refractive indices also determine the amount of light that is reflected when reaching the interface, as well as the critical angle for total internal reflection, their intensity (Fresnel equations) and Brewster's angle. The refractive index, n, can be seen as the factor by which the speed and the wavelength of the radiation are reduced with respect to their vacuum values: the speed of light in a medium is , and similarly the wavelength in that medium is , where is the wavelength of that light in v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
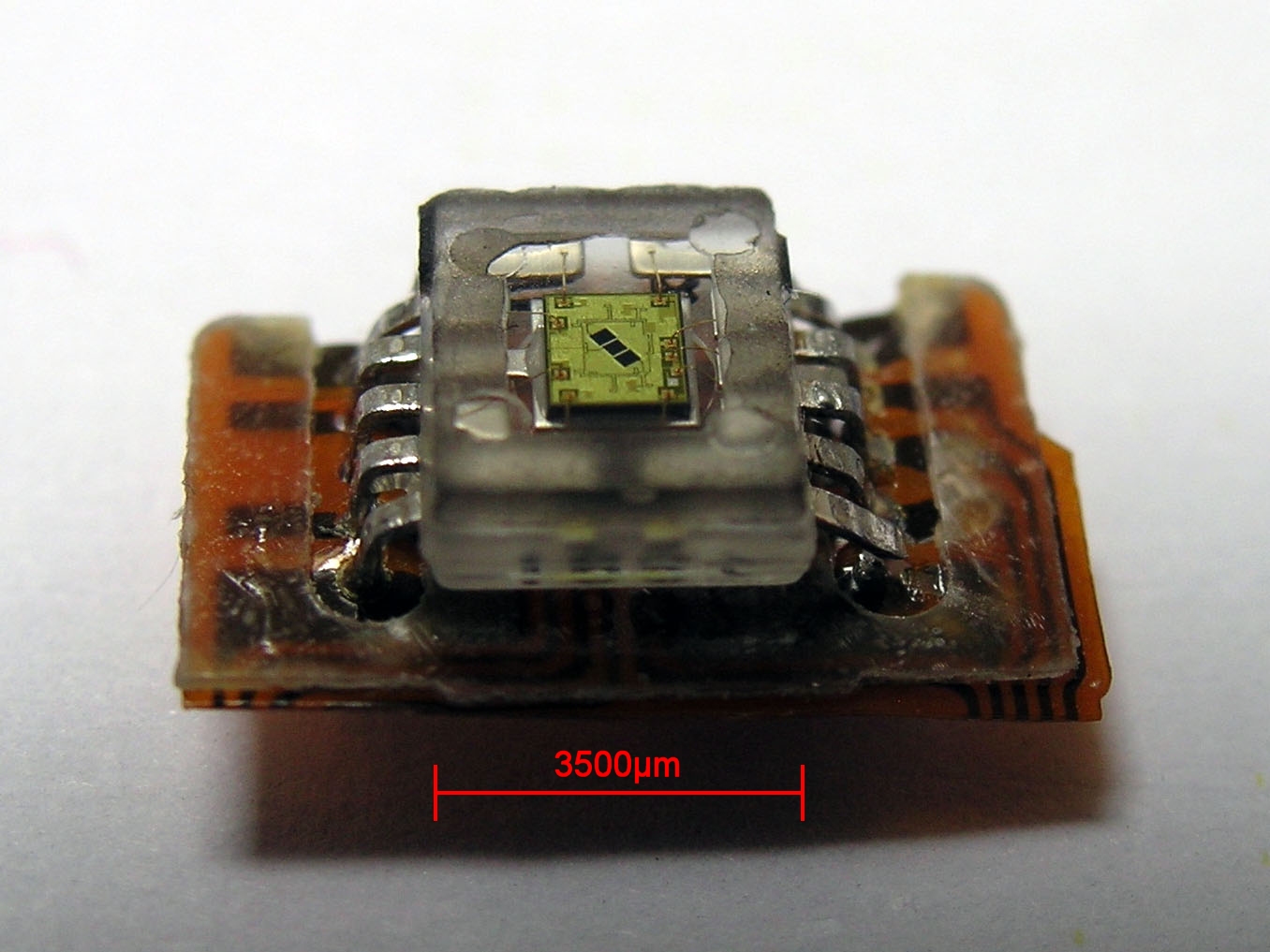
CD-ROM Photodetector
A CD-ROM (, compact disc read-only memory) is a type of read-only memory consisting of a pre-pressed optical compact disc that contains data computers can read, but not write or erase. Some CDs, called enhanced CDs, hold both computer data and audio with the latter capable of being played on a CD player, while data (such as software or digital video) is only usable on a computer (such as ISO 9660 format PC CD-ROMs). During the 1990s and early 2000s, CD-ROMs were popularly used to distribute software and data for computers and fifth generation video game consoles. DVDs as well as downloading started to replace CD-ROMs in these roles starting in the early 2000s, and the use of CD-ROMs for commercial software is now rare. History The earliest theoretical work on optical disc storage was done by independent researchers in the United States including David Paul Gregg (1958) and James Russel (1965–1975). In particular, Gregg's patents were used as the basis of the LaserDisc sp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |