Heat capacity on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Heat capacity or thermal capacity is a
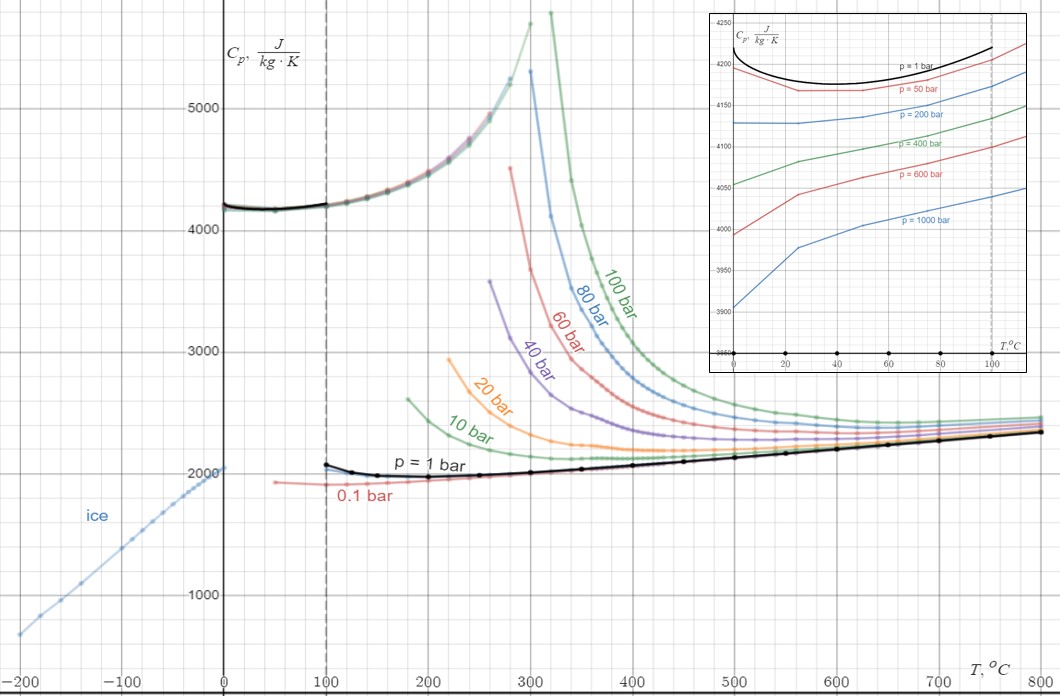 The variation can be ignored in contexts when working with objects in narrow ranges of temperature and pressure. For example, the heat capacity of a block of
The variation can be ignored in contexts when working with objects in narrow ranges of temperature and pressure. For example, the heat capacity of a block of
Heat capacity (Alternate title: thermal capacity)
. {{Authority control Physical quantities Thermodynamic properties
physical property
A physical property is any Property (philosophy), property that is Measurement, measurable, whose value describes a state of a physical system. The changes in the physical properties of a system can be used to describe its changes between momenta ...
of matter
In classical physics and general chemistry, matter is any substance that has mass and takes up space by having volume. All everyday objects that can be touched are ultimately composed of atoms, which are made up of interacting subatomic par ...
, defined as the amount of heat
In thermodynamics, heat is defined as the form of energy crossing the boundary of a thermodynamic system by virtue of a temperature difference across the boundary. A thermodynamic system does not ''contain'' heat. Nevertheless, the term is ...
to be supplied to an object to produce a unit change in its temperature
Temperature is a physical quantity that expresses quantitatively the perceptions of hotness and coldness. Temperature is measured with a thermometer.
Thermometers are calibrated in various temperature scales that historically have relied on ...
. The SI unit
The International System of Units, known by the international abbreviation SI in all languages and sometimes Pleonasm#Acronyms and initialisms, pleonastically as the SI system, is the modern form of the metric system and the world's most wid ...
of heat capacity is joule per kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ph ...
(J/K).
Heat capacity is an extensive property. The corresponding intensive property is the specific heat capacity, found by dividing the heat capacity of an object by its mass. Dividing the heat capacity by the amount of substance in moles yields its molar heat capacity. The volumetric heat capacity measures the heat capacity per volume
Volume is a measure of occupied three-dimensional space. It is often quantified numerically using SI derived units (such as the cubic metre and litre) or by various imperial or US customary units (such as the gallon, quart, cubic inch). Th ...
. In architecture
Architecture is the art and technique of designing and building, as distinguished from the skills associated with construction. It is both the process and the product of sketching, conceiving, planning, designing, and constructing buildings ...
and civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
, the heat capacity of a building is often referred to as its thermal mass.
Definition
Basic definition
The heat capacity of an object, denoted by , is the limit : where is the amount of heat that must be added to the object (of mass ''M'') in order to raise its temperature by . The value of this parameter usually varies considerably depending on the starting temperature of the object and the pressure applied to it. In particular, it typically varies dramatically withphase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ...
s such as melting or vaporization (see enthalpy of fusion and enthalpy of vaporization). Therefore, it should be considered a function of those two variables.
Variation with temperature
 The variation can be ignored in contexts when working with objects in narrow ranges of temperature and pressure. For example, the heat capacity of a block of
The variation can be ignored in contexts when working with objects in narrow ranges of temperature and pressure. For example, the heat capacity of a block of iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
weighing one pound
Pound or Pounds may refer to:
Units
* Pound (currency), a unit of currency
* Pound sterling, the official currency of the United Kingdom
* Pound (mass), a unit of mass
* Pound (force), a unit of force
* Rail pound, in rail profile
Symbols
* Po ...
is about 204 J/K when measured from a starting temperature ''T'' = 25 °C and ''P'' = 1 atm of pressure. That approximate value is adequate for temperatures between 15 °C and 35 °C, and surrounding pressures from 0 to 10 atmospheres, because the exact value varies very little in those ranges. One can trust that the same heat input of 204 J will raise the temperature of the block from 15 °C to 16 °C, or from 34 °C to 35 °C, with negligible error.
Heat capacities of a homogeneous system undergoing different thermodynamic processes
At constant pressure, ''δQ'' = ''dU'' + ''PdV'' ( isobaric process)
At constant pressure, heat supplied to the system contributes to both the work done and the change in internal energy, according to the first law of thermodynamics. The heat capacity is calledAt constant volume, ''dV'' = 0, ''δQ'' = ''dU'' ( isochoric process)
A system undergoing a process at constant volume implies that no expansion work is done, so the heat supplied contributes only to the change in internal energy. The heat capacity obtained this way is denoted The value of is always less than the value of ( < )Calculating ''CP'' and ''CV'' for an ideal gas
Mayer's relation: : : where : is the number of moles of the gas, : is the universal gas constant, : is the heat capacity ratio (which can be calculated by knowing the number ofdegrees of freedom
Degrees of freedom (often abbreviated df or DOF) refers to the number of independent variables or parameters of a thermodynamic system. In various scientific fields, the word "freedom" is used to describe the limits to which physical movement or ...
of the gas molecule).
Using the above two relations, the specific heats can be deduced as follows:
:
:
At constant temperature (
Isothermal process
In thermodynamics, an isothermal process is a type of thermodynamic process in which the temperature ''T'' of a system remains constant: Δ''T'' = 0. This typically occurs when a system is in contact with an outside thermal reservoir, and ...
)
No change in internal energy (as the temperature of the system is constant throughout the process) leads to only work done by the total supplied heat, and thus an infinite amount of heat is required to increase the temperature of the system by a unit temperature, leading to infinite or undefined heat capacity of the system.
At the time of phase change (
Phase transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states ...
)
Heat capacity of a system undergoing phase transition is infinite, because the heat is utilized in changing the state of the material rather than raising the overall temperature.
Heterogeneous objects
The heat capacity may be well-defined even for heterogeneous objects, with separate parts made of different materials; such as anelectric motor
An electric motor is an electrical machine that converts electrical energy into mechanical energy. Most electric motors operate through the interaction between the motor's magnetic field and electric current in a wire winding to generate forc ...
, a crucible with some metal, or a whole building. In many cases, the (isobaric) heat capacity of such objects can be computed by simply adding together the (isobaric) heat capacities of the individual parts.
However, this computation is valid only when all parts of the object are at the same external pressure before and after the measurement. That may not be possible in some cases. For example, when heating an amount of gas in an elastic container, its volume ''and pressure'' will both increase, even if the atmospheric pressure outside the container is kept constant. Therefore, the effective heat capacity of the gas, in that situation, will have a value intermediate between its isobaric and isochoric capacities and .
For complex thermodynamic systems with several interacting parts and state variables, or for measurement conditions that are neither constant pressure nor constant volume, or for situations where the temperature is significantly non-uniform, the simple definitions of heat capacity above are not useful or even meaningful. The heat energy that is supplied may end up as kinetic energy
In physics, the kinetic energy of an object is the energy that it possesses due to its motion.
It is defined as the work needed to accelerate a body of a given mass from rest to its stated velocity. Having gained this energy during its a ...
(energy of motion) and potential energy
In physics, potential energy is the energy held by an object because of its position relative to other objects, stresses within itself, its electric charge, or other factors.
Common types of potential energy include the gravitational potentia ...
(energy stored in force fields), both at macroscopic and atomic scales. Then the change in temperature will depends on the particular path that the system followed through its phase space between the initial and final states. Namely, one must somehow specify how the positions, velocities, pressures, volumes, etc. changed between the initial and final states; and use the general tools of thermodynamics
Thermodynamics is a branch of physics that deals with heat, work, and temperature, and their relation to energy, entropy, and the physical properties of matter and radiation. The behavior of these quantities is governed by the four laws o ...
to predict the system's reaction to a small energy input. The "constant volume" and "constant pressure" heating modes are just two among infinitely many paths that a simple homogeneous system can follow.
Measurement
The heat capacity can usually be measured by the method implied by its definition: start with the object at a known uniform temperature, add a known amount of heat energy to it, wait for its temperature to become uniform, and measure the change in its temperature. This method can give moderately accurate values for many solids; however, it cannot provide very precise measurements, especially for gases.Units
International system
The SI unit for heat capacity of an object is joule per kelvin (J/K or J⋅K−1). Since an increment of temperature of one degree Celsius is the same as an increment of one kelvin, that is the same unit as J/°C. The heat capacity of an object is an amount of energy divided by a temperature change, which has thedimension
In physics and mathematics, the dimension of a mathematical space (or object) is informally defined as the minimum number of coordinates needed to specify any point within it. Thus, a line has a dimension of one (1D) because only one coor ...
L2⋅M⋅T−2⋅Θ−1. Therefore, the SI unit J/K is equivalent to kilogram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially ...
meter squared per second squared per kelvin
The kelvin, symbol K, is the primary unit of temperature in the International System of Units (SI), used alongside its prefixed forms and the degree Celsius. It is named after the Belfast-born and University of Glasgow-based engineer and ph ...
(kg⋅m2⋅s−2⋅K−1 ).
English (Imperial) engineering units
Professionals inconstruction
Construction is a general term meaning the art and science to form objects, systems, or organizations,"Construction" def. 1.a. 1.b. and 1.c. ''Oxford English Dictionary'' Second Edition on CD-ROM (v. 4.0) Oxford University Press 2009 and ...
, civil engineering
Civil engineering is a professional engineering discipline that deals with the design, construction, and maintenance of the physical and naturally built environment, including public works such as roads, bridges, canals, dams, airports, sewa ...
, chemical engineering
Chemical engineering is an engineering field which deals with the study of operation and design of chemical plants as well as methods of improving production. Chemical engineers develop economical commercial processes to convert raw materials in ...
, and other technical disciplines, especially in the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., federal district, five ma ...
, may use the so-called English Engineering units
Some fields of engineering in the United States use a system of measurement of physical quantities known as the English Engineering Units. Despite its name, the system is based on United States customary units of measure; it is not used in Englan ...
, that include the pound
Pound or Pounds may refer to:
Units
* Pound (currency), a unit of currency
* Pound sterling, the official currency of the United Kingdom
* Pound (mass), a unit of mass
* Pound (force), a unit of force
* Rail pound, in rail profile
Symbols
* Po ...
(lb = 0.45359237 kg) as the unit of mass, the degree Fahrenheit or Rankine (°K, about 0.55556 °K) as the unit of temperature increment, and the British thermal unit
The British thermal unit (BTU or Btu) is a unit of heat; it is defined as the amount of heat required to raise the temperature of one pound of water by one degree Fahrenheit. It is also part of the United States customary units. The modern SI ...
(BTU ≈ 1055.06 J),
Published under the auspices of the ''Verein Deutscher Ingenieure'' (VDI).
as the unit of heat. In those contexts, the unit of heat capacity is 1 BTU/°R ≈ 1900 J/°K. The BTU was in fact defined so that the average heat capacity of one pound of water would be 1 BTU/°F. In this regard, with respect to mass, note conversion of 1 Btu/lb⋅°R ≈ 4,187 J/kg⋅°K and the calorie (below).
Calories
In chemistry, heat amounts are often measured incalorie
The calorie is a unit of energy. For historical reasons, two main definitions of "calorie" are in wide use. The large calorie, food calorie, or kilogram calorie was originally defined as the amount of heat needed to raise the temperature of ...
s. Confusingly, two units with that name, denoted "cal" or "Cal", have been commonly used to measure amounts of heat:
* The "small calorie" (or "gram-calorie", "cal") is 4.184 J, exactly. It was originally defined so that the heat capacity of 1 gram
The gram (originally gramme; SI unit symbol g) is a unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI) equal to one one thousandth of a kilogram.
Originally defined as of 1795 as "the absolute weight of a volume of pure water equal to ...
of liquid water would be 1 cal/°C.
* The "grand calorie" (also "kilocalorie", "kilogram-calorie", or "food calorie"; "kcal" or "Cal") is 1000 cal, that is, 4184 J, exactly. It was originally defined so that the heat capacity of 1 kg of water would be 1 kcal/°C.
With these units of heat energy, the units of heat capacity are
:: 1 cal/°C = 4.184 J/K
:: 1 kcal/°C = 4184 J/K
Physical basis
Negative heat capacity
Most physical systems exhibit a positive heat capacity; constant-volume and constant-pressure heat capacities, rigorously defined as partial derivatives, are always positive for homogeneous bodies.Landau, L. D.; Lifshitz, E. M. (reprinted 2011). ''Statistical Physics Part 1'', Ch.II §21, 3rd edition, Elsevier ISBN 978-0-7506-3372-7 However, even though it can seem paradoxical at first, there are some systems for which the heat capacity / is ''negative''. Examples include a reversibly and nearly adiabatically expanding ideal gas, which cools, < 0, while a small amount of heat > 0 is put in, or combusting methane with increasing temperature, > 0, and giving off heat, < 0. Others are inhomogeneous systems that do not meet the strict definition of thermodynamic equilibrium. They include gravitating objects such as stars and galaxies, and also somenano-scale
The nanoscopic scale (or nanoscale) usually refers to structures with a length scale applicable to nanotechnology, usually cited as 1–100 nanometers (nm). A nanometer is a billionth of a meter. The nanoscopic scale is (roughly speaking) a lo ...
clusters of a few tens of atoms close to a phase transition. A negative heat capacity can result in a negative temperature
Certain systems can achieve negative thermodynamic temperature; that is, their temperature can be expressed as a negative quantity on the Kelvin or Rankine scales. This should be distinguished from temperatures expressed as negative numbers ...
.
Stars and black holes
According to thevirial theorem
In mechanics, the virial theorem provides a general equation that relates the average over time of the total kinetic energy of a stable system of discrete particles, bound by potential forces, with that of the total potential energy of the system. ...
, for a self-gravitating body like a star or an interstellar gas cloud, the average potential energy ''U''pot and the average kinetic energy ''U''kin are locked together in the relation
:
The total energy ''U'' (= ''U''pot + ''U''kin) therefore obeys
:
If the system loses energy, for example, by radiating energy into space, the average kinetic energy actually increases. If a temperature is defined by the average kinetic energy, then the system therefore can be said to have a negative heat capacity.See e.g., Section 4 and onwards.
A more extreme version of this occurs with black holes. According to black-hole thermodynamics, the more mass and energy a black hole absorbs, the colder it becomes. In contrast, if it is a net emitter of energy, through Hawking radiation, it will become hotter and hotter until it boils away.
Consequences
According to theSecond Law of Thermodynamics
The second law of thermodynamics is a physical law based on universal experience concerning heat and energy interconversions. One simple statement of the law is that heat always moves from hotter objects to colder objects (or "downhill"), unles ...
, when two systems with different temperatures interact via a purely thermal connection, heat will flow from the hotter system to the cooler one (this can also be understood from a statistical point of view). Therefore, if such systems have equal temperatures, they are at thermal equilibrium. However, this equilibrium is stable only if the systems have ''positive'' heat capacities. For such systems, when heat flows from a higher temperature system to a lower temperature one, the temperature of the first decreases and that of the latter increases, so that both approach equilibrium. In contrast, for systems with ''negative'' heat capacities, the temperature of the hotter system will further increase as it loses heat, and that of the colder will further decrease, so that they will move farther from equilibrium. This means that the equilibrium is unstable.
For example, according to theory, the smaller (less massive) a black hole is, the smaller its Schwarzschild radius will be and therefore the greater the curvature
In mathematics, curvature is any of several strongly related concepts in geometry. Intuitively, the curvature is the amount by which a curve deviates from being a straight line, or a surface deviates from being a plane.
For curves, the can ...
of its event horizon will be, as well as its temperature. Thus, the smaller the black hole, the more thermal radiation it will emit and the more quickly it will evaporate.
See also
* Quantum statistical mechanics * Heat capacity ratio * Statistical mechanics *Thermodynamic equations
Thermodynamics is expressed by a mathematical framework of ''thermodynamic equations'' which relate various thermodynamic quantities and physical properties measured in a laboratory or production process. Thermodynamics is based on a fundamental ...
* Thermodynamic databases for pure substances
* Heat equation
* Heat transfer coefficient
* Heat of mixing
* Latent heat
* Material properties (thermodynamics)
* Joback method The Joback method (often named Joback/Reid method) predicts eleven important and commonly used pure component thermodynamic properties from molecular structure only.
Basic principles
Group-contribution method
The Joback method is a group-c ...
(estimation of heat capacities)
* Specific heat of melting (enthalpy of fusion)
* Specific heat of vaporization
The enthalpy of vaporization (symbol ), also known as the (latent) heat of vaporization or heat of evaporation, is the amount of energy (enthalpy) that must be added to a liquid substance to transform a quantity of that substance into a gas. T ...
(enthalpy of vaporization)
* Volumetric heat capacity
* Thermal mass
* R-value (insulation)
In the context of construction, the R-value is a measure of how well a two-dimensional barrier, such as a layer of insulation, a window or a complete wall or ceiling, resists the conductive flow of heat. R-value is the temperature difference pe ...
* Storage heater
* Frenkel line
* Table of specific heat capacities
References
Further reading
* Encyclopædia Britannica, 2015,Heat capacity (Alternate title: thermal capacity)
. {{Authority control Physical quantities Thermodynamic properties