|
Theodor Frølich
Theodor Christian Brun Frølich (29 September 1870 – 14 August 1947) was a Norwegian physician and Professor of Pediatrics at the University of Oslo. In 1938 he was nominated for the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for his pioneering contributions to the study of the treatment of Scurvy and to the development of Vitamin C. Biography Theodor Frølich was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was the son of ''Hofmarskalk'' (Lord Steward of the Household) Theodor Christian Brun Frølich (1834–1904) and Bodil Christina (Stina) Grønn (1834–1901). In 1897 he married (Clara Constance Rosalie) Aimée Thaulow Knutsen (1873–1948). Their son was the fencer Jens Frølich (1914–1938), who competed in the individual and team foil events at the 1936 Summer Olympics. Their grandsons were jazz musicians Theodor Christian Frølich «Totti» Bergh (1935–2012) and his brother ''Johs. Bergh'' (1932–2001). Early career After examen artium from Gjertsen's Skole ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
University Of Oslo
The University of Oslo ( no, Universitetet i Oslo; la, Universitas Osloensis) is a public research university located in Oslo, Norway. It is the highest ranked and oldest university in Norway. It is consistently ranked among the top universities in the world and as one of the leading universities of Northern Europe; the Academic Ranking of World Universities ranked it the 58th best university in the world and the third best in the Nordic countries. In 2016, the Times Higher Education World University Rankings listed the university at 63rd, making it the highest ranked Norwegian university. Originally named the Royal Frederick University, the university was established in 1811 as the de facto Norwegian continuation of Denmark-Norway's common university, the University of Copenhagen, with which it shares many traditions. It was named for King Frederick VI of Denmark and Norway, and received its current name in 1939. The university was commonly nicknamed "The Royal Freder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larvik
Larvik () is a town and municipality in Vestfold in Vestfold og Telemark county, Norway. The administrative centre of the municipality is the city of Larvik. The municipality of Larvik has about 46,364 inhabitants. The municipality has a 110 km coastline, only shorter than that of neighbouring Sandefjord. The city achieved market town status in 1671. Larvik was established as a municipality on 1 January 1838 (see formannskapsdistrikt). The city of Stavern, and the rural municipalities of Brunlanes, Hedrum, and Tjølling were forcefully merged into the municipality of Larvik on 1 January 1988. On 1 January 2018, neighboring Lardal was merged into Larvik as part of a nationwide municipal reform. After the merge, Larvik is the largest municipality in Vestfold by area, and the second-most populous municipality in the Vestfold district. Larvik is known as the hometown of Thor Heyerdahl. It is also home to '' Bøkeskogen'', the northernmost beech tree forest in the world. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Den Norske Legeforening
The Norwegian Medical Association ( no, Den norske lægeforening (1886–2008), spelled ''Den norske legeforening'' since 2008) is the main Norwegian medical association and trade union, and was founded in 1886. It has 32 555 members (as of 2016) or about 96% of all Norwegian doctors. Marit Hermansen is the current president of the association. It is affiliated with the Federation of Norwegian Professional Associations. The association publishes the ''Journal of the Norwegian Medical Association The ''Journal of the Norwegian Medical Association'' ( no, Tidsskrift for den Norske Legeforening) is a biweekly peer-reviewed medical journal published by the Norwegian Medical Association. It was established in 1881, five years before the Norweg ...'', established in 1881. Governance: *Executive Committee (9 members) *County Divisions (19) *Occupational branches (7) *Specialty Branches (59) References External links Official website Trade unions in Norway Medical associations b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Det Norske Medicinske Selskab
The Norwegian Medical Society ( no, Det norske medicinske Selskab, la, Societas Medica Norvegica) is a medical organisation in Norway. It has its roots in an informal group created in 1826, which subscribed to and shared foreign medical journals. In 1833 it was formally inaugurated as ''Lægeforeningen i Christiania'', the physician's association in Christiania. The name Norwegian Medical Society was taken in 1847. From 1826 to 1837 it published Norway's first medical journal, ''Eyr'', named after Eir. From 1840 to 1939 it published the journal ''Norsk Magazin for Lægevidenskaben'', and since 2004 the journal ''Michael Quarterly''. It also hosts symposia and debates. See also *Norwegian Medical Association The Norwegian Medical Association ( no, Den norske lægeforening (1886–2008), spelled ''Den norske legeforening'' since 2008) is the main Norwegian medical association and trade union, and was founded in 1886. It has 32 555 members (as of 2016) o ... References Me ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Carapichea Ipecacuanha
''Carapichea ipecacuanha'' is a species of flowering plant in the family Rubiaceae. It is native to Costa Rica, Nicaragua, Panama, Colombia, and Brazil. Its common name, ipecacuanha (), is derived from the Tupi ''ipega'kwãi'', or "road-side sick-making plant". The plant has been discussed under a variety of synonyms over the years by various botanists. The roots were used to make syrup of ipecac, a powerful emetic, a longtime over-the-counter medicine no longer approved for medical use in the West for lack of evidence of safety and efficacy. An example of emetic compound from the roots is emetine. Description Ipecacuanha is a slow-growing plant, which reduces its commercial appeal as a crop plant. It is seldom cultivated in South America but it has been cultivated in India and elsewhere. The root of ipecacuanha has been used in preparation of the medicament, the syrup, is simple or divided into a few branches, flexuous, and composed of rings of various size. It is somewha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
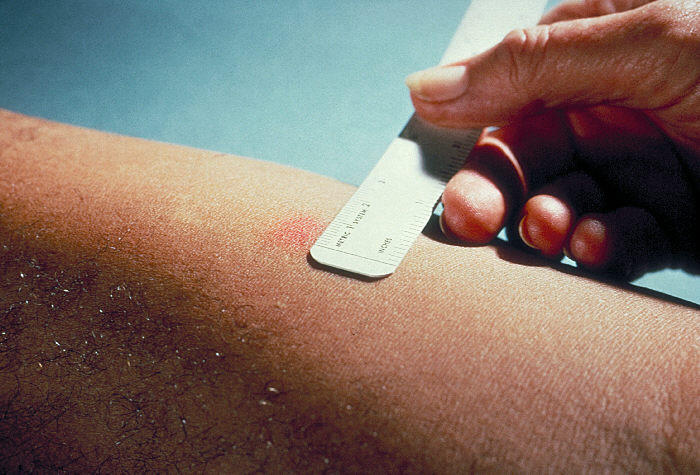
Tuberculin Skin Test
The Mantoux test or Mendel–Mantoux test (also known as the Mantoux screening test, tuberculin sensitivity test, Pirquet test, or PPD test for purified protein derivative) is a tool for screening for tuberculosis (TB) and for tuberculosis diagnosis. It is one of the major tuberculin skin tests used around the world, largely replacing multiple-puncture tests such as the tine test. The Heaf test, a form of tine test, was used until 2005 in the UK, when it was replaced by the Mantoux test. The Mantoux test is endorsed by the American Thoracic Society and Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. It was also used in the USSR and is now prevalent in most of the post-Soviet states. History Tuberculin is a glycerol Glycerol (), also called glycerine in British English and glycerin in American English, is a simple triol compound. It is a colorless, odorless, viscous liquid that is sweet-tasting and non-toxic. The glycerol backbone is found in lipids know ... extract ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, in which case it is known as latent tuberculosis. Around 10% of latent infections progress to active disease which, if left untreated, kill about half of those affected. Typical symptoms of active TB are chronic cough with hemoptysis, blood-containing sputum, mucus, fever, night sweats, and weight loss. It was historically referred to as consumption due to the weight loss associated with the disease. Infection of other organs can cause a wide range of symptoms. Tuberculosis is Human-to-human transmission, spread from one person to the next Airborne disease, through the air when people who have active TB in their lungs cough, spit, speak, or sneeze. People with Latent TB do not spread the disease. Active infection occurs more often in people wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) and wrinkles on the face. It is used to prevent and treat scurvy. Vitamin C is an essential nutrient involved in the repair of tissue, the formation of collagen, and the enzymatic production of certain neurotransmitters. It is required for the functioning of several enzymes and is important for immune system function. It also functions as an antioxidant. Most animals are able to synthesize their own vitamin C. However, apes (including humans) and monkeys (but not all primates), most bats, some rodents, and certain other animals must acquire it from dietary sources. There is some evidence that regular use of supplements may reduce the duration of the common cold, but it does not appear to prevent infection. It is unclear whether s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antiscorbutic
Scurvy is a disease resulting from a lack of vitamin C (ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding from the skin may occur. As scurvy worsens there can be poor wound healing, personality changes, and finally death from infection or bleeding. It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C in the diet before symptoms occur. In modern times, scurvy occurs most commonly in people with mental disorders, unusual eating habits, alcoholism, and older people who live alone. Other risk factors include intestinal malabsorption and dialysis. While many animals produce their own vitamin C, humans and a few others do not. Vitamin C is required to make the building blocks for collagen. Diagnosis is typically based on physical signs, X-rays, and improvement after treatment. Treatment is with vitamin C supplements taken by mouth. Improvement o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Axel Holst
Axel Holst (6 September 1860 – 26 April 1931) was a Norwegian Professor of Hygiene and Bacteriology at the University of Oslo. He was most known for his contributions to the study of the treatment of Beriberi and Scurvy. Biography Holst was born in Christiania (now Oslo), Norway. He was the son of Axel Holst (1826–80) and Anna Mathilde Charlotte Flemming (1832–97). He was the brother of the linguist Clara Holst and grandson of Frederik Holst. Both his father and grandfather were physicians. Holst attended Christiania Cathedral School (1877). He studied at Royal Frederick University (now University of Oslo) gaining his cand.med. in 1884. In 1887, he was awarded the Crown Prince's gold medal (''Kronprinsens gullmedalje''). He was granted his doctorate in 1892 involving the bacterium streptococcus. He was an assistant at the National Institute of Pathological Anatomy from 1885-89. During 1890-1892, he studied at various European laboratories including visits ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diabetes
Diabetes, also known as diabetes mellitus, is a group of metabolic disorders characterized by a high blood sugar level (hyperglycemia) over a prolonged period of time. Symptoms often include frequent urination, increased thirst and increased appetite. If left untreated, diabetes can cause many health complications. Acute complications can include diabetic ketoacidosis, hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state, or death. Serious long-term complications include cardiovascular disease, stroke, chronic kidney disease, foot ulcers, damage to the nerves, damage to the eyes, and cognitive impairment. Diabetes is due to either the pancreas not producing enough insulin, or the cells of the body not responding properly to the insulin produced. Insulin is a hormone which is responsible for helping glucose from food get into cells to be used for energy. There are three main types of diabetes mellitus: * Type 1 diabetes results from failure of the pancreas to produce enough insulin due ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)