Antiscorbutic on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Scurvy is a
File:Scorbutic tongue (cropped).jpg, A child presenting a "scorbutic tongue" due to
 Vitamins are essential to the production and use of enzymes that are involved in ongoing processes throughout the human body.
Vitamins are essential to the production and use of enzymes that are involved in ongoing processes throughout the human body.
"Scott and Scurvy"
Retrieved 2016-05-31.
 In 2009, a handwritten household book authored by a Cornishwoman in 1707 was discovered in a house in Hasfield,
In 2009, a handwritten household book authored by a Cornishwoman in 1707 was discovered in a house in Hasfield,
second edition (1757)
Lind explained the details of his clinical trial and concluded "the results of all my experiments was, that oranges and lemons were the most effectual remedies for this distemper at sea." However, the experiment and its results occupied only a few paragraphs in a work that was long and complex and had little impact. Lind himself never actively promoted lemon juice as a single 'cure'. He shared medical opinion at the time that scurvy had multiple causes – notably hard work, bad water, and the consumption of salt meat in a damp atmosphere which inhibited healthful perspiration and normal excretion – and therefore required multiple solutions. Lind was also sidetracked by the possibilities of producing a concentrated 'rob' of lemon juice by boiling it. This process destroyed the vitamin C and was therefore unsuccessful. During the 18th century, scurvy killed more British sailors than wartime enemy action. It was mainly by scurvy that George Anson, in his celebrated voyage of 1740–1744, lost nearly two-thirds of his crew (1,300 out of 2,000) within the first 10 months of the voyage. The Royal Navy enlisted 184,899 sailors during the
 The surgeon-in-chief of
The surgeon-in-chief of
disease
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury. Diseases are often known to be medical conditions that a ...
resulting from a lack of vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
(ascorbic acid). Early symptoms of deficiency include weakness, feeling tired and sore arms and legs. Without treatment, decreased red blood cells, gum disease, changes to hair, and bleeding from the skin may occur. As scurvy worsens there can be poor wound
A wound is a rapid onset of injury that involves laceration, lacerated or puncture wound, punctured skin (an ''open'' wound), or a bruise, contusion (a ''closed'' wound) from blunt force physical trauma, trauma or compression. In pathology, a '' ...
healing, personality changes, and finally death from infection or bleeding.
It takes at least a month of little to no vitamin C in the diet before symptoms occur. In modern times, scurvy occurs most commonly in people with mental disorder
A mental disorder, also referred to as a mental illness or psychiatric disorder, is a behavioral or mental pattern that causes significant distress or impairment of personal functioning. Such features may be persistent, relapsing and remitti ...
s, unusual eating habits, alcoholism
Alcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol (drug), alcohol that results in significant Mental health, mental or physical health problems. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word ''alcoholism'', it is not a recognize ...
, and older people who live alone. Other risk factors include intestinal malabsorption and dialysis. While many animals produce their own vitamin C, humans and a few others do not. Vitamin C is required to make the building blocks for collagen. Diagnosis is typically based on physical signs, X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
, and improvement after treatment.
Treatment is with vitamin C supplements taken by mouth. Improvement often begins in a few days with complete recovery in a few weeks. Sources of vitamin C in the diet include citrus fruit
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
and a number of vegetables, including red peppers, broccoli, and tomatoes. Cooking often decreases the residual amount of vitamin C in foods.
Scurvy is rare compared to other nutritional deficiencies. It occurs more often in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
in association with malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
. Rates among refugees
A refugee, conventionally speaking, is a displaced person who has crossed national borders and who cannot or is unwilling to return home due to well-founded fear of persecution.
are reported at 5 to 45 percent. Scurvy was described as early as the time of ancient Egypt. It was a limiting factor in long-distance sea travel, often killing large numbers of people. During the Age of Sail, it was assumed that 50 percent of the sailors would die of scurvy on a major trip. A Scottish surgeon in the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
, James Lind
James Lind (4 October 1716 – 13 July 1794) was a Scottish doctor. He was a pioneer of naval hygiene in the Royal Navy. By conducting one of the first ever clinical trials, he developed the theory that citrus fruits cured scurvy.
Lind ...
, is generally credited with proving that scurvy can be successfully treated with citrus fruit
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
in 1753. Nevertheless, it was not until 1795 that health reformers such as Gilbert Blane
Sir Gilbert Blane of Blanefield, 1st Baronet FRSE FRS MRCP (29 August 174926 June 1834) was a Scottish physician who instituted health reform in the Royal Navy. He saw action against both the French and Spanish fleets, and later served as a C ...
persuaded the Royal Navy to routinely give lemon juice to its sailors.
Signs and symptoms
Early symptoms are malaise andlethargy
Lethargy is a state of tiredness, sleepiness, weariness, fatigue, sluggishness or lack of energy. It can be accompanied by depression, decreased motivation, or apathy. Lethargy can be a normal response to inadequate sleep, overexertion, overwo ...
. After one to three months, patients develop shortness of breath and bone pain. Myalgias may occur because of reduced carnitine
Carnitine is a quaternary ammonium compound involved in metabolism in most mammals, plants, and some bacteria. In support of energy metabolism, carnitine transports long-chain fatty acids into mitochondria to be oxidized for energy production, an ...
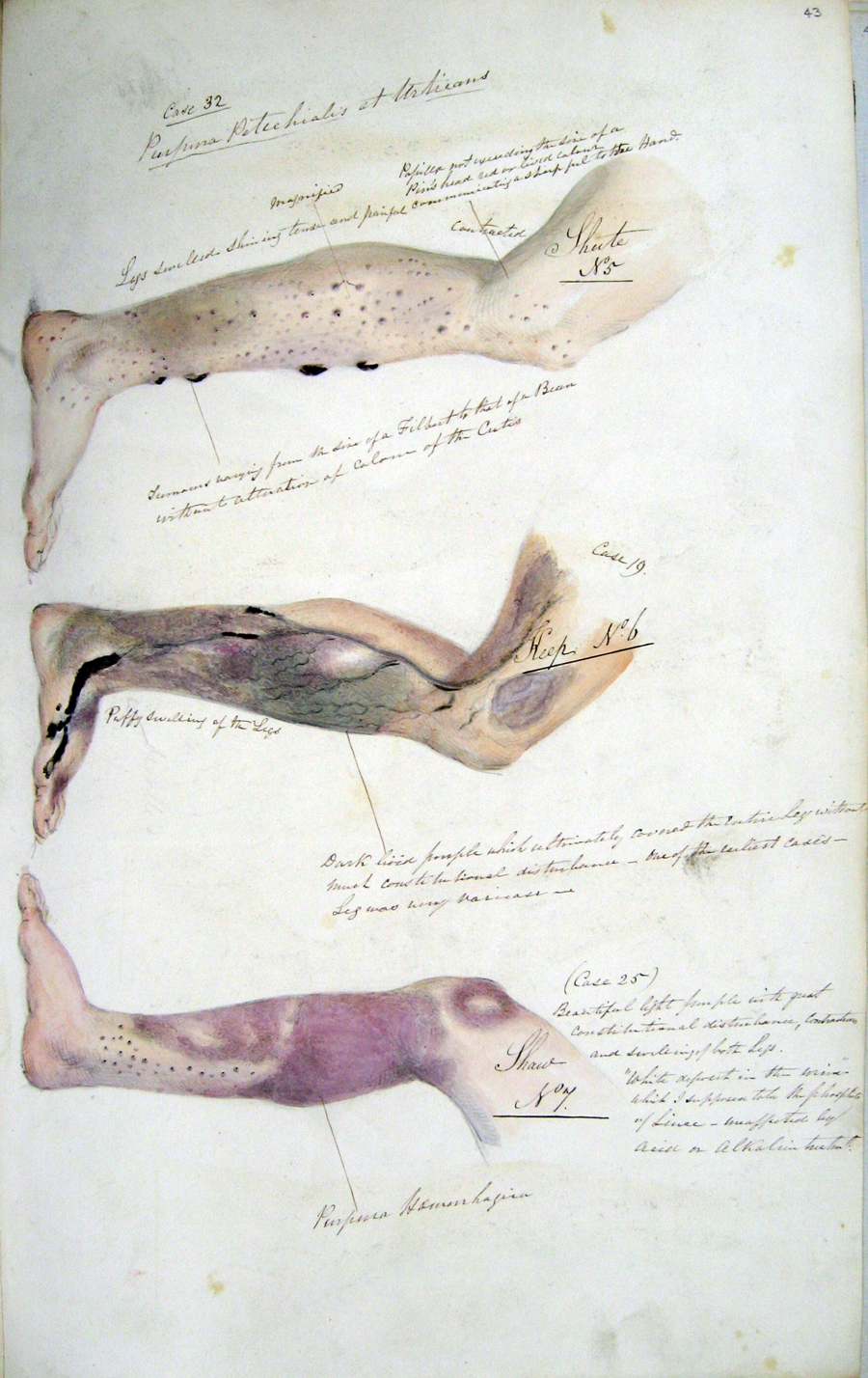
production. Other symptoms include skin changes with roughness, easy bruising and petechiae, gum disease
Periodontal disease, also known as gum disease, is a set of inflammatory conditions affecting the tissues surrounding the teeth. In its early stage, called gingivitis, the gums become swollen and red and may bleed. It is considered the main caus ...
, loosening of teeth, poor wound healing, and emotional changes (which may appear before any physical changes). Dry mouth and dry eyes similar to Sjögren's syndrome may occur. In the late stages, jaundice
Jaundice, also known as icterus, is a yellowish or greenish pigmentation of the skin and sclera due to high bilirubin levels. Jaundice in adults is typically a sign indicating the presence of underlying diseases involving abnormal heme meta ...
, generalised edema, oliguria
Oliguria or hypouresis is the low output of urine specifically more than 80 ml/day but less than 400ml/day.Boon et al, Davidson's Principles & Practice of Medicine (20th Ed), p475 The decreased output of urine may be a sign of dehydration, kidney ...
, neuropathy
Peripheral neuropathy, often shortened to neuropathy, is a general term describing disease affecting the peripheral nerves, meaning nerves beyond the brain and spinal cord. Damage to peripheral nerves may impair sensation, movement, gland, or o ...
, fever, convulsions, and eventual death are frequently seen.
vitamin C
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
deficiency.
File:ASM-30-325-g001.jpg, A child with scurvy in flexion posture.
File:ASM-30-325-g002.jpg, Photo of the chest cage with scorbutic rosaries.
Cause
Scurvy, including subclinical scurvy, is caused by a deficiency of dietary vitamin C since humans are unable to metabolically synthesize vitamin C. Provided the diet contains sufficient vitamin C, the lack of workingL-gulonolactone oxidase
L-Gulonolactone oxidase ( ECbr>1.1.3.8 is an enzyme that produces vitamin C, but is non-functional in Haplorrhini (including humans), in some bats, and in guinea pigs. It catalyzes the reaction of L-gulono-1,4-lactone with oxygen to form L ...
(GULO) enzyme has no significance, and in modern Western societies, scurvy is rarely present in adults, although infants and elderly people are affected. Virtually all commercially available baby formulas contain added vitamin C, preventing infantile scurvy. Human breast milk contains sufficient vitamin C, if the mother has an adequate intake. Commercial milk is pasteurized
Pasteurization American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), or pasteurisation is a process of food preservation in which packaged and non-packaged foods (such as milk and fruit juices) are treated with mi ...
, a heating process that destroys the natural vitamin C content of the milk.
Scurvy is one of the accompanying diseases of malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues a ...
(other such micronutrient deficiencies are beriberi
Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, ...
and pellagra
Pellagra is a disease caused by a lack of the vitamin niacin (vitamin B3). Symptoms include inflamed skin, diarrhea, dementia, and sores in the mouth. Areas of the skin exposed to either sunlight or friction are typically affected first. Over t ...
) and thus is still widespread in areas of the world depending on external food aid.
Although rare, there are also documented cases of scurvy due to poor dietary choices by people living in industrialized nations.
Pathogenesis
 Vitamins are essential to the production and use of enzymes that are involved in ongoing processes throughout the human body.
Vitamins are essential to the production and use of enzymes that are involved in ongoing processes throughout the human body. Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C (also known as ascorbic acid and ascorbate) is a water-soluble vitamin found in citrus and other fruits and vegetables, also sold as a dietary supplement and as a topical 'serum' ingredient to treat melasma (dark pigment spots) an ...
is needed for a variety of biosynthetic pathways, by accelerating hydroxylation and amidation
In organic chemistry, an amide, also known as an organic amide or a carboxamide, is a compound with the general formula , where R, R', and R″ represent organic groups or hydrogen atoms. The amide group is called a peptide bond when it is p ...
reactions. In the synthesis of collagen, ascorbic acid is required as a cofactor for prolyl hydroxylase
Procollagen-proline dioxygenase, commonly known as prolyl hydroxylase, is a member of the class of enzymes known as alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases. These enzymes catalyze the incorporation of oxygen into organic substrates through a mec ...
and lysyl hydroxylase
Lysyl hydroxylases (or procollagen-lysine 5-dioxygenases) are alpha-ketoglutarate-dependent hydroxylases enzymes that catalyze the hydroxylation of lysine to hydroxylysine. Lysyl hydroxylases require iron and vitamin C as cofactors for their ...
. These two enzymes are responsible for the hydroxylation of the proline and lysine
Lysine (symbol Lys or K) is an α-amino acid that is a precursor to many proteins. It contains an α-amino group (which is in the protonated form under biological conditions), an α-carboxylic acid group (which is in the deprotonated −C ...
amino acids in collagen. Hydroxyproline
(2''S'',4''R'')-4-Hydroxyproline, or L-hydroxyproline ( C5 H9 O3 N), is an amino acid, abbreviated as Hyp or O, ''e.g.'', in Protein Data Bank.
Structure and discovery
In 1902, Hermann Emil Fischer isolated hydroxyproline from hydrolyzed gelati ...
and hydroxylysine
Hydroxylysine (Hyl) is an amino acid with the molecular formula C6H14N2O3. It was first discovered in 1921 by Donald Van Slyke
Donald Dexter Van Slyke (March 29, 1883 – May 4, 1971) was a Dutch American biochemist. His achievements include ...
are important for stabilizing collagen by cross-linking the propeptides in collagen.
Collagen is a primary structural protein in the human body, necessary for healthy blood vessels, muscle, skin, bone, cartilage, and other connective tissues.
Defective connective tissue leads to fragile capillaries, resulting in abnormal bleeding, bruising, and internal hemorrhaging.
Collagen is an important part of bone, so bone formation is also affected. Teeth loosen, bones break more easily, and once-healed breaks may recur.
Defective collagen fibrillogenesis impairs wound healing.
Untreated scurvy is invariably fatal.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is typically based on physical signs,X-rays
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nbs ...
, and improvement after treatment.
Differential diagnosis
Various childhood onset disorders can mimic the clinical and X-ray picture of scurvy such as: *Rickets
Rickets is a condition that results in weak or soft bones in children, and is caused by either dietary deficiency or genetic causes. Symptoms include bowed legs, stunted growth, bone pain, large forehead, and trouble sleeping. Complications ma ...
* Osteochondrodysplasias
Osteochondrodysplasia is a general term for a disorder of the development (dysplasia) of bone ("osteo") and cartilage ("chondro"). Osteochondrodysplasias are rare diseases. About 1 in 5,000 babies are born with some type of skeletal dysplasia. Non ...
especially osteogenesis imperfecta
Osteogenesis imperfecta (; OI), colloquially known as brittle bone disease, is a group of genetic disorders that all result in bones that break easily. The range of symptoms—on the skeleton as well as on the body's other organs—may be mi ...
* Blount's disease
Blount's disease (or Blount disease) is a growth disorder of the tibia (shin bone) which causes the lower leg to angle inward, resembling a bowleg. It is also known as "tibia vara".
Description and risk factors
Blount disease is a growth disorde ...
* Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis (OM) is an infection of bone. Symptoms may include pain in a specific bone with overlying redness, fever, and weakness. The long bones of the arms and legs are most commonly involved in children e.g. the femur and humerus, while the ...
Prevention
Scurvy can be prevented by a diet that includes uncooked vitamin C-rich foods such as amla,bell pepper
The bell pepper (also known as paprika, sweet pepper, pepper, or capsicum ) is the fruit of plants in the Grossum Group of the species ''Capsicum annuum''. Cultivars of the plant produce fruits in different colors, including red, yellow, orange ...
s (sweet peppers), blackcurrants, broccoli
Broccoli (''Brassica oleracea'' var. ''italica'') is an edible green plant in the cabbage family (family Brassicaceae, genus ''Brassica'') whose large flowering head, stalk and small associated leaves are eaten as a vegetable. Broccoli is cla ...
, chili peppers
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for ...
, guava
Guava () is a common tropical fruit cultivated in many tropical and subtropical regions. The common guava ''Psidium guajava'' (lemon guava, apple guava) is a small tree in the myrtle family ( Myrtaceae), native to Mexico, Central America, the ...
, kiwifruit
Kiwifruit (often shortened to kiwi in North American, British and continental European English) or Chinese gooseberry is the edible berry of several species of woody vines in the genus '' Actinidia''. The most common cultivar group of kiwi ...
, and parsley. Other sources rich in vitamin C are fruits such as lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
s, limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
* the Latin word for ''limit'' which refers to:
** Limes (Roman Empire)
(Latin, singular; plural: ) is a modern term used primarily for the Germanic border defence or delimiting ...
, oranges
An orange is a fruit of various citrus species in the family Rutaceae (see list of plants known as orange); it primarily refers to ''Citrus'' × ''sinensis'', which is also called sweet orange, to distinguish it from the related ''Citrus × ...
, papaya
The papaya (, ), papaw, () or pawpaw () is the plant species ''Carica papaya'', one of the 21 accepted species in the genus ''Carica'' of the family Caricaceae. It was first domesticated in Mesoamerica, within modern-day southern Mexico and ...
, and strawberries
The garden strawberry (or simply strawberry; ''Fragaria × ananassa'') is a widely grown hybrid species of the genus '' Fragaria'', collectively known as the strawberries, which are cultivated worldwide for their fruit. The fruit is widely ap ...
. It is also found in vegetables, such as brussels sprout
The Brussels sprout is a member of the Gemmifera cultivar group of cabbages (''Brassica oleracea''), grown for its edible buds. The leaf vegetables are typically 1.5–4.0 cm (0.6–1.6 in) in diameter and resemble miniature cabbages ...
s, cabbage
Cabbage, comprising several cultivars of ''Brassica oleracea'', is a leafy green, red (purple), or white (pale green) biennial plant grown as an annual vegetable crop for its dense-leaved heads. It is descended from the wild cabbage ( ''B.&nb ...
, potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
es, and spinach
Spinach (''Spinacia oleracea'') is a leafy green flowering plant native to central and western Asia. It is of the order Caryophyllales, family Amaranthaceae, subfamily Chenopodioideae. Its leaves are a common edible vegetable consumed either f ...
. Some fruits and vegetables not high in vitamin C may be pickled
Pickling is the process of preserving or extending the shelf life of food by either anaerobic fermentation in brine or immersion in vinegar. The pickling procedure typically affects the food's texture and flavor. The resulting food is called ...
in lemon juice
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culina ...
, which is high in vitamin C. Nutritional supplements which provide ascorbic acid well in excess of what is required to prevent scurvy may cause adverse health effects.
Some animal products, including liver
The liver is a major Organ (anatomy), organ only found in vertebrates which performs many essential biological functions such as detoxification of the organism, and the Protein biosynthesis, synthesis of proteins and biochemicals necessary for ...
, muktuk
Muktuk (transliterated in various ways, see below) is a traditional food of the peoples of the Arctic, consisting of whale skin and blubber. It is most often made from the bowhead whale, although the beluga and the narwhal are also used. It is ...
(whale skin), oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
s, and parts of the central nervous system, including the adrenal medulla, brain, and spinal cord, contain large amounts of vitamin C, and can even be used to treat scurvy. Fresh meat from animals, notably internal organs, contains enough vitamin C to prevent scurvy, and even partly treat it.
Scott's 1902 Antarctic expedition used lightly fried seal meat and liver, whereby complete recovery from incipient scurvy was reported to have taken less than two weeks.
Treatment
Scurvy will improve with doses of vitamin C as low as 10 mg per day though doses of around 100 mg per day are typically recommended. Most people make a full recovery within 2 weeks.History
Symptoms of scurvy have been recorded in Ancient Egypt as early as 1550 BCE. InAncient Greece
Ancient Greece ( el, Ἑλλάς, Hellás) was a northeastern Mediterranean civilization, existing from the Greek Dark Ages of the 12th–9th centuries BC to the end of classical antiquity ( AD 600), that comprised a loose collection of cult ...
, the physician Hippocrates
Hippocrates of Kos (; grc-gre, Ἱπποκράτης ὁ Κῷος, Hippokrátēs ho Kôios; ), also known as Hippocrates II, was a Greek physician of the classical period who is considered one of the most outstanding figures in the history of ...
(460-370 BCE) described symptoms of scurvy, specifically a "swelling and obstruction of the spleen
The spleen is an organ found in almost all vertebrates. Similar in structure to a large lymph node, it acts primarily as a blood filter. The word spleen comes .
."
In 406 CE, the Chinese monk Faxian
Faxian (法顯 ; 337 CE – c. 422 CE), also referred to as Fa-Hien, Fa-hsien and Sehi, was a Chinese Buddhist monk and translator who traveled by foot from China to India to acquire Buddhist texts. Starting his arduous journey about age 60, h ...
wrote that ginger
Ginger (''Zingiber officinale'') is a flowering plant whose rhizome, ginger root or ginger, is widely used as a spice
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices ...
was carried on Chinese ships to prevent scurvy.
The knowledge that consuming foods containing vitamin C is a cure for scurvy has been repeatedly forgotten and rediscovered into the early 20th century.Maciej Cegłowski, 2010-03-06"Scott and Scurvy"
Retrieved 2016-05-31.
Early modern era
In the 13th century, theCrusaders
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
frequently developed scurvy. In the 1497 expedition of Vasco da Gama, the curative effects of citrus fruit were already known and confirmed by Pedro Álvares Cabral
Pedro Álvares Cabral ( or ; born Pedro Álvares de Gouveia; c. 1467 or 1468 – c. 1520) was a Portuguese nobleman, military commander, navigator and explorer regarded as the European discoverer of Brazil. He was the first human in ...
and his crew in 1507.
The Portuguese planted fruit trees and vegetables in Saint Helena
Saint Helena () is a British overseas territory located in the South Atlantic Ocean. It is a remote volcanic tropical island west of the coast of south-western Africa, and east of Rio de Janeiro in South America. It is one of three constitu ...
, a stopping point for homebound voyages from Asia, and left their sick, who had scurvy and other ailments, to be taken home by the next ship if they recovered.
In 1500, one of the pilots of Cabral's fleet bound for India noted that in Malindi
Malindi is a town on Malindi Bay at the mouth of the Sabaki River, lying on the Indian Ocean coast of Kenya. It is 120 kilometres northeast of Mombasa. The population of Malindi was 119,859 as of the 2019 census. It is the largest urban cent ...
, its king offered the expedition fresh supplies such as lambs, chickens, and ducks, along with lemons and oranges, due to which "some of our ill were cured of scurvy".
Unfortunately, these travel accounts did not stop further maritime tragedies caused by scurvy, first because of the lack of communication between travelers and those responsible for their health, and because fruits and vegetables could not be kept for long on ships.
In 1536, the French explorer Jacques Cartier, exploring the St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
, used the local St. Lawrence Iroquoians
The St. Lawrence Iroquoians were an Iroquoian Indigenous people who existed from the 14th century to about 1580. They concentrated along the shores of the St. Lawrence River in present-day Quebec and Ontario, Canada, and in the American states o ...
' knowledge to save his men who were dying of scurvy. He boiled the needles of the arbor vitae tree (eastern white cedar
''Thuja occidentalis'', also known as northern white-cedar, eastern white-cedar, or arborvitae, is an evergreen coniferous tree, in the cypress family Cupressaceae, which is native to eastern Canada and much of the north-central and northeaste ...
) to make a tea that was later shown to contain 50 mg of vitamin C per 100 grams. Such treatments were not available aboard ship, where the disease was most common. Later, possibly inspired by this incident, several European countries experimented with preparations of various conifers, such as spruce beer
Spruce beer is a beverage flavored with the buds, needles, or essence of spruce trees. ''Spruce beer'' can refer to either alcoholic or non-alcoholic beverages.
A number of flavors are associated with spruce-flavored beverages, ranging from ...
, as cures for scurvy.
In February 1601, Captain James Lancaster
Sir James Lancaster (c. 1554 – 6 June 1618) was an English privateer and trader of the Elizabethan era.
Life and work
Lancaster came from Basingstoke in Hampshire. In his early life, he was a soldier and a trader in Portugal.
On 10 April 1 ...
, while sailing to Sumatra
Sumatra is one of the Sunda Islands of western Indonesia. It is the largest island that is fully within Indonesian territory, as well as the sixth-largest island in the world at 473,481 km2 (182,812 mi.2), not including adjacent i ...
, landed on the northern coast of Madagascar specifically to obtain lemons and oranges for his crew to stop scurvy. Captain Lancaster conducted an experiment using four ships under his command. One ship's crew received routine doses of lemon juice while the other three ships did not receive any such treatment. As a result, members of the non-treated ships started to contract scurvy, with many dying as a result.
During the Age of Exploration
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafari ...
(between 1500 and 1800), it has been estimated that scurvy killed at least two million sailor
A sailor, seaman, mariner, or seafarer is a person who works aboard a watercraft as part of its crew, and may work in any one of a number of different fields that are related to the operation and maintenance of a ship.
The profession of the s ...
s. Jonathan Lamb wrote: "In 1499, Vasco da Gama lost 116 of his crew of 170; In 1520, Magellan lost 208 out of 230;...all mainly to scurvy."
In 1579, the Spanish friar and physician Agustin Farfán published a book in which he recommended oranges and lemons for scurvy, a remedy that was already known in the Spanish Navy.
In 1593, Admiral Sir Richard Hawkins
Admiral Sir Richard Hawkins (or Hawkyns) (c. 1562 – 17 April 1622) was a 17th-century English seaman, explorer and privateer. He was the son of Admiral Sir John Hawkins.
Biography
He was from his earlier days familiar with ships and the s ...
advocated drinking orange and lemon juice as a means of preventing scurvy.
A 1609 book by Bartolomé Leonardo de Argensola recorded a number of different remedies for scurvy known at this time in the Moluccas, including a kind of wine mixed with cloves and ginger, and "certain herbs." The Dutch sailors in the area were said to cure the same disease by drinking lime juice.
In 1614, John Woodall
John Woodall (1570–1643) was an English military surgeon, Paracelsian chemist, businessman, linguist and diplomat. He made a fortune through the stocking of medical chests for the East India Company and later the armed forces of England. He i ...
, Surgeon General of the East India Company
The East India Company (EIC) was an English, and later British, joint-stock company founded in 1600 and dissolved in 1874. It was formed to trade in the Indian Ocean region, initially with the East Indies (the Indian subcontinent and Southea ...
, published ''The Surgion's Mate'' as a handbook for apprentice surgeons aboard the company's ships. He repeated the experience of mariners that the cure for scurvy was fresh food or, if not available, oranges, lemons, limes, and tamarinds
Tamarind (''Tamarindus indica'') is a leguminous tree bearing edible fruit that is probably indigenous to tropical Africa. The genus ''Tamarindus'' is monotypic, meaning that it contains only this species. It belongs to the family Fabaceae.
...
. He was, however, unable to explain the reason why, and his assertion had no impact on the prevailing opinion of the influential physicians of the age, that scurvy was a digestive complaint.
Apart from ocean travel, even in Europe, until the late Middle Ages, scurvy was common in late winter, when few green vegetables, fruits and root vegetables were available. This gradually improved with the introduction from the Americas of potatoes; by 1800, scurvy was virtually unheard of in Scotland, where it had previously been endemic.
18th century
 In 2009, a handwritten household book authored by a Cornishwoman in 1707 was discovered in a house in Hasfield,
In 2009, a handwritten household book authored by a Cornishwoman in 1707 was discovered in a house in Hasfield, Gloucestershire
Gloucestershire ( abbreviated Glos) is a county in South West England. The county comprises part of the Cotswold Hills, part of the flat fertile valley of the River Severn and the entire Forest of Dean.
The county town is the city of Gl ...
, containing a " for the Scurvy" amongst other largely medicinal and herbal recipes. The recipe consisted of extracts from various plants mixed with a plentiful supply of orange juice, white wine or beer.
In 1734, Leiden
Leiden (; in English and archaic Dutch also Leyden) is a city and municipality in the province of South Holland, Netherlands. The municipality of Leiden has a population of 119,713, but the city forms one densely connected agglomeration wit ...
-based physician Johann Bachstrom
Jan Fryderyk or Johann Friedrich Bachstrom (24 December 1688, near Rawitsch, now Rawicz, Poland - June 1742, Nieswiez, now Nyasvizh, Belarus) was a writer, scientist and Lutheran theologian who spent the last decade of his life in Leiden. His surn ...
published a book on scurvy in which he stated, "scurvy is solely owing to a total abstinence from fresh vegetable food, and greens; which is alone the primary cause of the disease", and urged the use of fresh fruit and vegetables as a cure.
It was not until 1747 that James Lind
James Lind (4 October 1716 – 13 July 1794) was a Scottish doctor. He was a pioneer of naval hygiene in the Royal Navy. By conducting one of the first ever clinical trials, he developed the theory that citrus fruits cured scurvy.
Lind ...
formally demonstrated that scurvy could be treated by supplementing the diet with citrus fruit, in one of the first controlled clinical experiments reported in the history of medicine. As a naval surgeon on HMS ''Salisbury'', Lind had compared several suggested scurvy cures: hard cider
Cider ( ) is an alcoholic beverage made from the fermented juice of apples. Cider is widely available in the United Kingdom (particularly in the West Country) and the Republic of Ireland. The UK has the world's highest per capita consumption, ...
, vitriol
Vitriol is the general chemical name encompassing a class of chemical compound comprising sulfates of certain metalsoriginally, iron or copper. Those mineral substances were distinguished by their color, such as green vitriol for hydrated iron( ...
, vinegar
Vinegar is an aqueous solution of acetic acid and trace compounds that may include flavorings. Vinegar typically contains 5–8% acetic acid by volume. Usually, the acetic acid is produced by a double fermentation, converting simple sugars to eth ...
, seawater
Seawater, or salt water, is water from a sea or ocean. On average, seawater in the world's oceans has a salinity of about 3.5% (35 g/L, 35 ppt, 600 mM). This means that every kilogram (roughly one liter by volume) of seawater has appro ...
, oranges
An orange is a fruit of various citrus species in the family Rutaceae (see list of plants known as orange); it primarily refers to ''Citrus'' × ''sinensis'', which is also called sweet orange, to distinguish it from the related ''Citrus × ...
, lemons
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culina ...
, and a mixture of balsam of Peru
Balsam of Peru or Peru balsam, also known and marketed by many other names, is a balsam derived from a tree known as ''Myroxylon balsamum'' var. ''pereirae''; it is found in El Salvador, where it is an endemic species.
Balsam of Peru is used i ...
, garlic
Garlic (''Allium sativum'') is a species of bulbous flowering plant in the genus ''Allium''. Its close relatives include the onion, shallot, leek, chive, Allium fistulosum, Welsh onion and Allium chinense, Chinese onion. It is native to South A ...
, myrrh, mustard seed and radish
The radish (''Raphanus raphanistrum'' subsp. ''sativus'') is an edible root vegetable of the family Brassicaceae that was domesticated in Asia prior to Roman times.
Radishes are grown and consumed throughout the world, being mostly eaten raw ...
root. In ''A Treatise on the Scurvy'' (1753) (Also archivesecond edition (1757)
Lind explained the details of his clinical trial and concluded "the results of all my experiments was, that oranges and lemons were the most effectual remedies for this distemper at sea." However, the experiment and its results occupied only a few paragraphs in a work that was long and complex and had little impact. Lind himself never actively promoted lemon juice as a single 'cure'. He shared medical opinion at the time that scurvy had multiple causes – notably hard work, bad water, and the consumption of salt meat in a damp atmosphere which inhibited healthful perspiration and normal excretion – and therefore required multiple solutions. Lind was also sidetracked by the possibilities of producing a concentrated 'rob' of lemon juice by boiling it. This process destroyed the vitamin C and was therefore unsuccessful. During the 18th century, scurvy killed more British sailors than wartime enemy action. It was mainly by scurvy that George Anson, in his celebrated voyage of 1740–1744, lost nearly two-thirds of his crew (1,300 out of 2,000) within the first 10 months of the voyage. The Royal Navy enlisted 184,899 sailors during the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (1754� ...
; 133,708 of these were "missing" or died from disease, and scurvy was the leading cause.
Although throughout this period sailors and naval surgeons were increasingly convinced that citrus fruits could cure scurvy, the classically trained physicians who determined medical policy dismissed this evidence as merely anecdotal, as it did not conform to their theories of disease. Literature championing the cause of citrus juice, therefore, had no practical impact. The medical theory was based on the assumption that scurvy was a disease of internal putrefaction brought on by faulty digestion caused by the hardships of life at sea and the naval diet. Although this basic idea was given different emphases by successive theorists, the remedies they advocated (and which the navy accepted) amounted to little more than the consumption of 'fizzy drinks' to activate the digestive system, the most extreme of which was the regular consumption of 'elixir of vitriol' – sulphuric acid taken with spirits and barley water, and laced with spices.
In 1764, a new and similarly inaccurate theory on scurvy appeared. Advocated by Dr David MacBride and Sir John Pringle, Surgeon General of the Army and later President of the Royal Society, this idea was that scurvy was the result of a lack of 'fixed air' in the tissues which could be prevented by drinking infusions of malt and wort
Wort () is the liquid extracted from the mashing process during the brewing of beer or whisky. Wort contains the sugars, the most important being maltose and maltotriose, that will be fermented by the brewing yeast to produce alcohol. Wort als ...
whose fermentation within the body would stimulate digestion and restore the missing gases. These ideas received wide and influential backing, when James Cook
James Cook (7 November 1728 Old Style date: 27 October – 14 February 1779) was a British explorer, navigator, cartographer, and captain in the British Royal Navy, famous for his three voyages between 1768 and 1779 in the Pacific Ocean an ...
set off to circumnavigate the world (1768–1771) in , malt and wort were top of the list of the remedies he was ordered to investigate. The others were beer, Sauerkraut
Sauerkraut (; , "sour cabbage") is finely cut raw cabbage that has been fermented by various lactic acid bacteria. It has a long shelf life and a distinctive sour flavor, both of which result from the lactic acid formed when the bacteria ferm ...
(a good source of vitamin C) and Lind's 'rob'. The list did not include lemons.
Cook did not lose a single man to scurvy, and his report came down in favour of malt and wort, although it is now clear that the reason for the health of his crews on this and other voyages was Cook's regime of shipboard cleanliness, enforced by strict discipline, as well as frequent replenishment of fresh food and greenstuffs. Another beneficial rule implemented by Cook was his prohibition of the consumption of salt fat skimmed from the ship's copper boiling pans, then a common practice elsewhere in the Navy. In contact with air, the copper formed compounds that prevented the absorption of vitamins by the intestines.
The first major long distance expedition that experienced virtually no scurvy was that of the Spanish naval officer Alessandro Malaspina
Alejandro Malaspina (November 5, 1754 – April 9, 1810) was a Tuscan explorer who spent most of his life as a Spanish naval officer. Under a Spanish royal commission, he undertook a voyage around the world from 1786 to 1788, then, from 1789 t ...
, 1789–1794. Malaspina's medical officer, Pedro González, was convinced that fresh oranges and lemons were essential for preventing scurvy. Only one outbreak occurred, during a 56-day trip across the open sea. Five sailors came down with symptoms, one seriously. After three days at Guam
Guam (; ch, Guåhan ) is an organized, unincorporated territory of the United States in the Micronesia subregion of the western Pacific Ocean. It is the westernmost point and territory of the United States (reckoned from the geographic cent ...
all five were healthy again. Spain's large empire and many ports of call made it easier to acquire fresh fruit.
Although towards the end of the century MacBride's theories were being challenged, the medical authorities in Britain remained committed to the notion that scurvy was a disease of internal 'putrefaction' and the Sick and Hurt Board, run by administrators, felt obliged to follow its advice. Within the Royal Navy, however, opinion – strengthened by first-hand experience of the use of lemon juice at the siege of Gibraltar and during Admiral Rodney's expedition to the Caribbean – had become increasingly convinced of its efficacy. This was reinforced by the writings of experts like Gilbert Blane
Sir Gilbert Blane of Blanefield, 1st Baronet FRSE FRS MRCP (29 August 174926 June 1834) was a Scottish physician who instituted health reform in the Royal Navy. He saw action against both the French and Spanish fleets, and later served as a C ...
and Thomas Trotter and by the reports of up-and-coming naval commanders.
With the coming of war in 1793, the need to eliminate scurvy acquired a new urgency. But the first initiative came not from the medical establishment but from the admirals. Ordered to lead an expedition against Mauritius, Rear Admiral Gardner was uninterested in the wort, malt and elixir of vitriol which were still being issued to ships of the Royal Navy, and demanded that he be supplied with lemons, to counteract scurvy on the voyage. Members of the Sick and Hurt Board, recently augmented by two practical naval surgeons, supported the request, and the Admiralty ordered that it be done. There was, however, a last minute change of plan, and the expedition against Mauritius was cancelled. On 2 May 1794, only and two sloops
A sloop is a sailboat with a single mast typically having only one headsail in front of the mast and one mainsail aft of (behind) the mast. Such an arrangement is called a fore-and-aft rig, and can be rigged as a Bermuda rig with triangular ...
under Commodore Peter Rainier sailed for the east with an outward bound convoy, but the warships were fully supplied with lemon juice and the sugar with which it had to be mixed.
In March 1795, it was reported that the ''Suffolk'' had arrived in India after a four-month voyage without a trace of scurvy and with a crew that was healthier than when it set out. The effect was immediate. Fleet commanders clamoured also to be supplied with lemon juice, and by June the Admiralty acknowledged the groundswell of demand in the navy and agreed to a proposal from the Sick and Hurt Board that lemon juice and sugar should in future be issued as a daily ration to the crews of all warships.
It took a few years before the method of distribution to all ships in the fleet had been perfected and the supply of the huge quantities of lemon juice required to be secured, but by 1800, the system was in place and functioning. This led to a remarkable health improvement among the sailors and consequently played a critical role in gaining the advantage in naval battles against enemies who had yet to introduce the measures.
Scurvy was not only a disease of seafarers. The only colonists of Australia suffered greatly because of the lack of fresh fruit and vegetables in the winter. There the disease was called Spring fever or Spring disease and described an often fatal condition associated with skin lesions, bleeding gums and lethargy. It was eventually identified as scurvy and the remedies already in use at sea implemented.
19th century
 The surgeon-in-chief of
The surgeon-in-chief of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who ...
's army at the Siege of Alexandria (1801)
The siege of Alexandria (17 August – 2 September 1801) was fought during the French Revolutionary Wars between French and British forces. It was the last action of the French campaign in Egypt and Syria (1798–1801). The French had occupied A ...
, Baron Dominique-Jean Larrey
Baron Dominique Jean Larrey (; 8 July 1766 – 25 July 1842) was a French surgeon and military doctor, who distinguished himself in the French Revolutionary Wars and the Napoleonic Wars. An important innovator in battlefield medicine and triage, h ...
, wrote in his memoirs that the consumption of horse meat
Horse meat forms a significant part of the culinary traditions of many countries, particularly in Eurasia. The eight countries that consume the most horse meat consume about 4.3 million horses a year. For the majority of humanity's early existen ...
helped the French to curb an epidemic of scurvy. The meat was cooked but was freshly obtained from young horses bought from Arabs, and was nevertheless effective. This helped to start the 19th-century tradition of horse meat consumption in France.
Lauchlin Rose patented a method used to preserve citrus juice without alcohol in 1867, creating a concentrated drink known as Rose's lime juice
Rose's lime juice, often known simply as Rose's, is a sweetened concentrated fruit juice patented in 1867. This was the world's first commercially produced fruit concentrate.
Background
In 1753, James Lind discovered that consuming citrus fruit ...
. The Merchant Shipping Act of 1867 required all ships of the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
and Merchant Navy to provide a daily lime
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a color between yellow and green
Lime may also refer to:
Botany ...
ration of one pound to sailors to prevent scurvy. The product became nearly ubiquitous, hence the term "limey
"Limey" (from lime / lemon) is a predominantly American slang nickname for a British person that has been around since the mid 19th century.Cochlearia officinalis'', also known as "common scurvygrass", acquired its common name from the observation that it cured scurvy, and it was taken on board ships in dried bundles or distilled extracts. Its very bitter taste was usually disguised with herbs and spices; however, this did not prevent scurvygrass drinks and sandwiches from becoming a popular fad in the UK until the middle of the nineteenth century, when citrus fruits became more readily available.
West Indian limes began to supplement lemons, when Spain's alliance with France against Britain in the Napoleonic Wars made the supply of Mediterranean lemons problematic, and because they were more easily obtained from Britain's Caribbean colonies and were believed to be more effective because they were more acidic. It was the acid, not the (then-unknown) Vitamin C that was believed to cure scurvy. In fact, the West Indian limes were significantly lower in Vitamin C than the previous lemons and further were not served fresh but rather as lime juice, which had been exposed to light and air, and piped through copper tubing, all of which significantly reduced the Vitamin C. Indeed, a 1918 animal experiment using representative samples of the Navy and Merchant Marine's lime juice showed that it had virtually no antiscorbutic power at all.
The belief that scurvy was fundamentally a nutritional deficiency, best treated by consumption of fresh food, particularly fresh citrus or fresh meat, was not universal in the 19th and early 20th centuries, and thus sailors and explorers continued to have scurvy into the 20th century. For example, the
Belgian Antarctic Expedition
The Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–1899 was the first expedition to winter in the Antarctic region. Led by Adrien de Gerlache de Gomery aboard the RV ''Belgica'', it was the first Belgian Antarctic expedition and is considered the firs ...
of 1897–1899 became seriously affected by scurvy when its leader, Adrien de Gerlache
Baron Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache de Gomery (; 2 August 1866 – 4 December 1934) was a Belgian officer in the Belgian Royal Navy who led the Belgian Antarctic Expedition of 1897–99.
Early years
Born in Hasselt in eastern Belgium as th ...
, initially discouraged his men from eating penguin and seal meat.
In the Royal Navy's Arctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar regions of Earth, polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenla ...
expeditions in the 19th century it was widely believed that scurvy was prevented by good hygiene on board ship, regular exercise, and maintaining the morale of the crew, rather than by a diet of fresh food. Navy expeditions continued to be plagued by scurvy even while fresh (not jerked or tinned) meat was well known as a practical antiscorbutic among civilian whalers and explorers in the Arctic. Criticism also focused on the fact that some of the men most affected by scurvy on Naval polar expeditions had apparently been heavy drinkers, with suggestions that this predisposed them to the condition. Even cooking fresh meat did not entirely destroy its antiscorbutic properties, especially as many cooking methods failed to bring all the meat to high temperature.
The confusion is attributed to a number of factors:
* while ''fresh'' citrus (particularly lemons) cured scurvy, lime ''juice'' that had been exposed to light, air and copper tubing did not – thus undermining the theory that citrus cured scurvy;
* fresh meat (especially organ meat and raw meat, consumed in arctic exploration) also cured scurvy, undermining the theory that fresh vegetable matter was essential to preventing and curing scurvy;
* increased marine speed via steam shipping, and improved nutrition on land, reduced the incidence of scurvy – and thus the ineffectiveness of copper-piped lime juice compared to fresh lemons was not immediately revealed.
In the resulting confusion, a new hypothesis was proposed, following the new germ theory of disease – that scurvy was caused by ptomaine
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease) ...
, a waste product of bacteria, particularly in tainted tinned meat.
Infantile scurvy emerged in the late 19th century because children were being fed pasteurized cow's milk, particularly in the urban upper class. While pasteurization killed bacteria, it also destroyed vitamin C. This was eventually resolved by supplementing with onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onion ...
juice or cooked potatoes. Native Americans helped save some newcomers from scurvy by directing them to eat wild onions Wild onion can refer to
* any uncultivated species in the genus ''Allium'', especially:
**'' Allium bisceptrum''
** ''Allium canadense''
** ''Allium tricoccum''
** '' Allium validum''
** '' Allium vineale''
* '' Asphodelus tenuifolius''
* ''Cyperus ...
.
20th century
By the early 20th century, whenRobert Falcon Scott
Captain Robert Falcon Scott, , (6 June 1868 – c. 29 March 1912) was a British Royal Navy officer and explorer who led two expeditions to the Antarctic regions: the ''Discovery'' expedition of 1901–1904 and the ill-fated ''Terra Nov ...
made his first expedition to the Antarctic
The Antarctic ( or , American English also or ; commonly ) is a polar region around Earth's South Pole, opposite the Arctic region around the North Pole. The Antarctic comprises the continent of Antarctica, the Kerguelen Plateau and other ...
(1901–1904), the prevailing theory was that scurvy was caused by "ptomaine poisoning
Foodborne illness (also foodborne disease and food poisoning) is any illness resulting from the spoilage of contaminated food by pathogenic bacteria, viruses, or parasites that contaminate food,
as well as prions (the agents of mad cow disease ...
", particularly in tinned meat. However, Scott discovered that a diet of fresh meat from Antarctic seals cured scurvy before any fatalities occurred. But while he saw fresh meat as a cure for scurvy, he remained confused about its underlying causes.
In 1907, an animal model which would eventually help to isolate and identify the "antiscorbutic factor" was discovered. Axel Holst and Theodor Frølich, two Norwegian
Norwegian, Norwayan, or Norsk may refer to:
*Something of, from, or related to Norway, a country in northwestern Europe
* Norwegians, both a nation and an ethnic group native to Norway
* Demographics of Norway
*The Norwegian language, including ...
physicians studying shipboard beriberi
Thiamine deficiency is a medical condition of low levels of thiamine (Vitamin B1). A severe and chronic form is known as beriberi. The two main types in adults are wet beriberi and dry beriberi. Wet beriberi affects the cardiovascular system, ...
contracted by ship's crews in the Norwegian Fishing Fleet, wanted a small test mammal to substitute for the pigeon
Columbidae () is a bird family consisting of doves and pigeons. It is the only family in the order Columbiformes. These are stout-bodied birds with short necks and short slender bills that in some species feature fleshy ceres. They primarily ...
s then used in beriberi research. They fed guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus ''Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ani ...
s their test diet of grains and flour, which had earlier produced beriberi in their pigeons, and were surprised when classic scurvy resulted instead. This was a serendipitous choice of animal. Until that time, scurvy had not been observed in any organism apart from humans and had been considered an exclusively human disease. Certain birds, mammals, and fish are susceptible to scurvy, but pigeons are unaffected, since they can synthesize ascorbic acid internally. Holst and Frølich found they could cure scurvy in guinea pigs with the addition of various fresh foods and extracts. This discovery of an animal experimental model for scurvy, which was made even before the essential idea of "vitamins" in foods had been put forward, has been called the single most important piece of vitamin C research.
In 1915, New Zealand troops in the Gallipoli Campaign had a lack of vitamin C in their diet which caused many of the soldiers to contract scurvy. It is thought that scurvy is one of many reasons that the Allied attack on Gallipoli failed.
Vilhjalmur Stefansson
Vilhjalmur Stefansson (November 3, 1879 – August 26, 1962) was an Arctic explorer and ethnologist. He was born in Manitoba, Canada.
Early life
Stefansson, born William Stephenson, was born at Arnes, Manitoba, Canada, in 1879. His parents had ...
, an arctic explorer who had lived among the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
, proved that the all-meat diet they consumed did not lead to vitamin deficiencies. He participated in a study in New York's Bellevue Hospital
Bellevue Hospital (officially NYC Health + Hospitals/Bellevue and formerly known as Bellevue Hospital Center) is a hospital in New York City and the oldest public hospital in the United States. One of the largest hospitals in the United States ...
in February 1928, where he and a companion ate only meat for a year while under close medical observation, yet remained in good health.
In 1927, Hungarian biochemist Albert Szent-Györgyi
Albert Imre Szent-Györgyi de Nagyrápolt ( hu, nagyrápolti Szent-Györgyi Albert Imre; September 16, 1893 – October 22, 1986) was a Hungarian biochemist who won the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine in 1937. He is credited with fi ...
isolated a compound he called " hexuronic acid". Szent-Györgyi suspected hexuronic acid, which he had isolated from adrenal glands, to be the antiscorbutic agent, but he could not prove it without an animal-deficiency model. In 1932, the connection between hexuronic acid and scurvy was finally proven by American researcher Charles Glen King of the University of Pittsburgh
The University of Pittsburgh (Pitt) is a public state-related research university in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania. The university is composed of 17 undergraduate and graduate schools and colleges at its urban Pittsburgh campus, home to the universit ...
. King's laboratory was given some hexuronic acid by Szent-Györgyi and soon established that it was the sought-after anti-scorbutic agent. Because of this, hexuronic acid was subsequently renamed ''ascorbic acid.''
21st century
Rates of scurvy in most of the world are low. Those most commonly affected aremalnourished
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
people in the developing world
A developing country is a sovereign state with a lesser developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreem ...
and the homeless. There have been outbreaks of the condition in refugee camps
A refugee camp is a temporary settlement built to receive refugees and people in refugee-like situations. Refugee camps usually accommodate displaced people who have fled their home country, but camps are also made for internally displaced peop ...
. Case reports in the developing world of those with poorly healing wounds have occurred.
Human trials
Notable human dietary studies of experimentally induced scurvy were conducted onconscientious objector
A conscientious objector (often shortened to conchie) is an "individual who has claimed the right to refuse to perform military service" on the grounds of freedom of thought, conscience, or religion. The term has also been extended to object ...
s during World War II in Britain and in the United States on Iowa state prisoner volunteers in the late 1960s. These studies both found that all obvious symptoms of scurvy previously induced by an experimental scorbutic diet with extremely low vitamin C content could be completely reversed by additional vitamin C supplementation of only 10 mg per day. In these experiments, no clinical difference was noted between men given 70 mg vitamin C per day (which produced blood levels of vitamin C of about 0.55 mg/dl, about of tissue saturation levels), and those given 10 mg per day (which produced lower blood levels). Men in the prison study developed the first signs of scurvy about 4 weeks after starting the vitamin C-free diet, whereas in the British study, six to eight months were required, possibly because the subjects were pre-loaded with a 70 mg/day supplement for six weeks before the scorbutic diet was fed.
Men in both studies, on a diet devoid or nearly devoid of vitamin C, had blood levels of vitamin C too low to be accurately measured when they developed signs of scurvy, and in the Iowa study, at this time were estimated (by labeled vitamin C dilution) to have a body pool of less than 300 mg, with daily turnover of only 2.5 mg/day.
In other animals
Most animals and plants are able to synthesize vitamin C through a sequence ofenzyme
Enzymes () are proteins that act as biological catalysts by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as products. A ...
-driven steps, which convert monosaccharides
Monosaccharides (from Greek '' monos'': single, '' sacchar'': sugar), also called simple sugars, are the simplest forms of sugar and the most basic units ( monomers) from which all carbohydrates are built.
They are usually colorless, water ...
to vitamin C. However, some mammals have lost the ability to synthesize vitamin C, notably simians and tarsiers. These make up one of two major primate
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians (monkeys and apes, the latter including huma ...
suborders, haplorrhini
Haplorhini (), the haplorhines ( Greek for "simple-nosed") or the "dry-nosed" primates, is a suborder of primates containing the tarsiers and the simians (Simiiformes or anthropoids), as sister of the Strepsirrhini ("moist-nosed"). The name is ...
, and this group includes human
Humans (''Homo sapiens'') are the most abundant and widespread species of primate, characterized by bipedalism and exceptional cognitive skills due to a large and complex brain. This has enabled the development of advanced tools, culture, ...
s. The strepsirrhini
Strepsirrhini or Strepsirhini (; ) is a Order (biology), suborder of primates that includes the Lemuriformes, lemuriform primates, which consist of the lemurs of Fauna of Madagascar, Madagascar, galagos ("bushbabies") and pottos from Fauna of A ...
(non-tarsier prosimians) can make their own vitamin C, and these include lemur
Lemurs ( ) (from Latin ''lemures'' – ghosts or spirits) are Strepsirrhini, wet-nosed primates of the Superfamily (biology), superfamily Lemuroidea (), divided into 8 Family (biology), families and consisting of 15 genera and around 100 exist ...
s, loris
Loris is the common name for the strepsirrhine mammals of the subfamily Lorinae (sometimes spelled Lorisinae) in the family Lorisidae. ''Loris'' is one genus in this subfamily and includes the slender lorises, ''Nycticebus'' is the genus conta ...
es, potto
The pottos are three species of strepsirrhine primate in the genus ''Perodicticus'' of the family Lorisidae. In some English-speaking parts of Africa, they are called "softly-softlys".
Etymology
The common name "potto" may be from Wolof (a t ...
s, and galago
Galagos , also known as bush babies, or ''nagapies'' (meaning "night monkeys" in Afrikaans), are small nocturnal primates native to continental, sub-Sahara Africa, and make up the family Galagidae (also sometimes called Galagonidae). They ar ...
s. Ascorbic acid is also not synthesized by at least two species of caviidae
Caviidae, the cavy family, is composed of rodents native to South America and includes the domestic guinea pig, wild cavies, and the largest living rodent, the capybara. They are found across South America in open areas from moist savanna to tho ...
, the capybara and the guinea pig
The guinea pig or domestic guinea pig (''Cavia porcellus''), also known as the cavy or domestic cavy (), is a species of rodent belonging to the genus ''Cavia'' in the family Caviidae. Breeders tend to use the word ''cavy'' to describe the ani ...
. There are known species of birds and fish that do not synthesize their own vitamin C. All species that do not synthesize ascorbate require it in the diet. Deficiency causes scurvy in humans, and somewhat similar symptoms in other animals.
Animals that can contract scurvy all lack the L-gulonolactone oxidase (GULO) enzyme, which is required in the last step of vitamin C synthesis. The genomes of these species contain GULO as pseudogenes, which serve as insight into the evolutionary past of the species.
Name
In babies, scurvy is sometimes referred to as ''Barlow's disease'', named after Thomas Barlow, a Britishphysician
A physician (American English), medical practitioner (Commonwealth English), medical doctor, or simply doctor, is a health professional who practices medicine, which is concerned with promoting, maintaining or restoring health through th ...
who described it in 1883. However, ''Barlow's disease'' may also refer to mitral valve prolapse (Barlow's syndrome), first described by John Brereton Barlow in 1966.
References
Further reading
* * * * * *External links
{{Authority control Animal diseases Vitamin deficiencies Vitamin C Nutritional anemias Collagen disease Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate Wikipedia neurology articles ready to translate