|
Tape-automated Bonding
Tape-automated bonding (TAB) is a process that places bare semiconductor chips (dies) like integrated circuits onto a flexible circuit board (FPC) by attaching them to fine conductors in a polyamide or polyimide (like trade names Kapton or UPILEX) film carrier. This FPC with the die(s) (TAB inner lead bonding, ILB) can be mounted on the system or module board or assembled inside a package (TAB outer lead bonding, OLB). Typically the FPC includes from one to three conductive layers and all inputs and outputs of the semiconductor die are connected simultaneously during the TAB bonding. Tape automated bonding is one of the methods needed for achieving chip-on-flex (COF) assembly and it is one of the first roll-to-roll processing (also called R2R, reel-to-reel) type methods in the electronics manufacturing. Process The TAB mounting is done such that the bonding sites of the die, usually in the form of bumps or balls made of gold, solder or anisotropic conductive material, are connec ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blob Top
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering. Design Electronic packaging can be organized by levels: * Level 0 - "Chip", protecting a bare semiconductor die from contamination and damage. * Level 1 - C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frances Hugle
Frances Sarnat Hugle (August 13, 1927 – May 24, 1968) was an American scientist, engineer, and inventor who contributed to the understanding of semiconductors, integrated circuitry, and the unique electrical principles of microscopic materials. She also invented techniques, processes, and equipment for practical (high volume) fabrication of microscopic circuitry, integrated circuits, and microprocessors which are still in use today. In 1962, Hugle co-founded Siliconix, one of Silicon Valley's first semiconductor houses. She is the only woman included in the "Semiconductor Family Tree." Early life and education Frances Betty Sarnat (Sarnatzky) was born on August 13, 1927, in Chicago, Illinois, to Nathan Sarnat (Sarnatzky) and Lylian Steinfeld. Sarnat attended Hyde Park High School on Chicago's south side, where she participated in many of the school's science clubs, including the chemistry, physics and biology clubs. In the spring of 1944, just before her graduation, she was sel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flip Chip
Flip chip, also known as controlled collapse chip connection or its abbreviation, C4, is a method for interconnecting dies such as semiconductor devices, IC chips, integrated passive devices and microelectromechanical systems (MEMS), to external circuitry with solder bumps that have been deposited onto the chip pads. The technique was developed by General Electric's Light Military Electronics Department, Utica, New York. The solder bumps are deposited on the chip pads on the top side of the wafer during the final wafer processing step. In order to mount the chip to external circuitry (e.g., a circuit board or another chip or wafer), it is flipped over so that its top side faces down, and aligned so that its pads align with matching pads on the external circuit, and then the solder is reflowed to complete the interconnect. This is in contrast to wire bonding, in which the chip is mounted upright and fine wires are welded onto the chip pads and lead frame contacts to interconnect t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
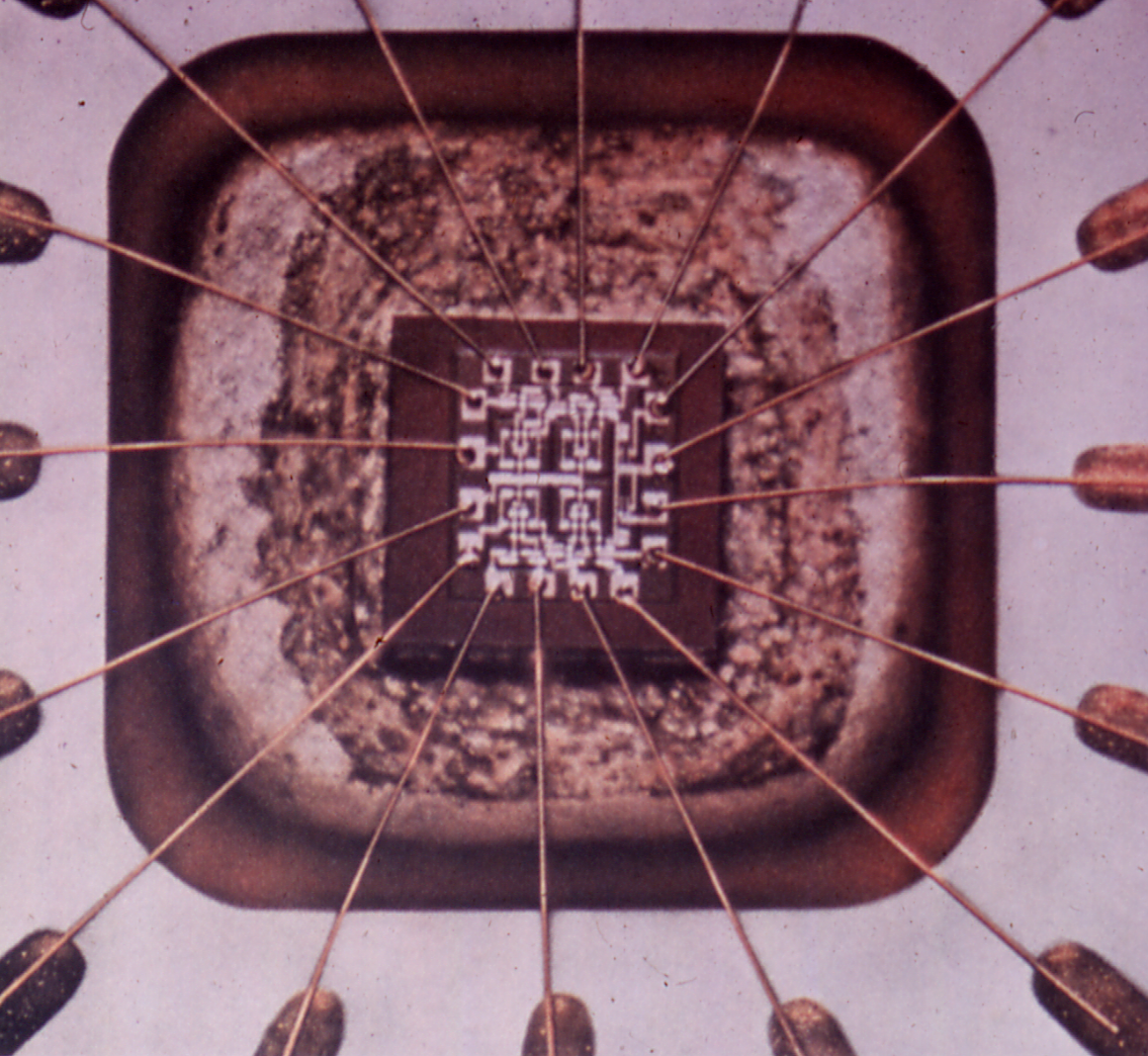
Lead Frame
A lead frame (pronounced ) is the metal structure inside a chip package that carries signals from the die to the outside. The lead frame consists of a central die pad, where the die is placed, surrounded by leads, metal conductors leading away from the die to the outside world. The end of each lead closest to the die ends in a bond pad. Small bond wires connect the die to each bond pad. Mechanical connections fix all these parts into a rigid structure, which makes the whole lead frame easy to handle automatically. Manufacturing Lead frames are manufactured by removing material from a flat plate of copper, copper-alloy, or iron-nickel alloy like alloy 42. Two processes used for this are etching (suitable for high density of leads), or stamping (suitable for low density of leads). The mechanical bending process can be applied after both techniques. The die is glued or soldered to the die pad inside the lead frame, and then bond wires are attached between the die and the bond p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
SIM Card
file:SIM-Karte von Telefónica O2 Europe - Standard und Micro.jpg, A typical SIM card (mini-SIM with micro-SIM cutout) file:Sim card.png, A smart card taken from a Global System for Mobile Communications, GSM mobile phone file:Simkarte NFC SecureElement.jpg, T-Mobile nano-SIM card with NFC capabilities in the SIM tray of an iPhone 6s file:Tf sim both sides.png, A TracFone Wireless SIM card has no distinctive carrier markings and is only marked as a "SIM card" A SIM card (full form Subscriber Identity Module or Subscriber Identification Module) is an integrated circuit (IC) intended to securely store the international mobile subscriber identity (IMSI) number and its related key, which are used to identify and authenticate subscribers on mobile telephony devices (such as mobile phones and computers). Technically the actual physical card is known as a universal integrated circuit card (UICC); this smart card is usually made of PVC with embedded contacts and semiconductors, with the S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electronic Packaging
Electronic packaging is the design and production of enclosures for electronic devices ranging from individual semiconductor devices up to complete systems such as a mainframe computer. Packaging of an electronic system must consider protection from mechanical damage, cooling, radio frequency noise emission and electrostatic discharge. Product safety standards may dictate particular features of a consumer product, for example, external case temperature or grounding of exposed metal parts. Prototypes and industrial equipment made in small quantities may use standardized commercially available enclosures such as card cages or prefabricated boxes. Mass-market consumer devices may have highly specialized packaging to increase consumer appeal. Electronic packaging is a major discipline within the field of mechanical engineering. Design Electronic packaging can be organized by levels: * Level 0 - "Chip", protecting a bare semiconductor die from contamination and damage. * Level 1 - ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wire Bonding
Wire bonding is the method of making interconnections between an integrated circuit (IC) or other semiconductor device and its packaging during semiconductor device fabrication. Although less common, wire bonding can be used to connect an IC to other electronics or to connect from one printed circuit board (PCB) to another. Wire bonding is generally considered the most cost-effective and flexible interconnect technology and is used to assemble the vast majority of semiconductor packages. Wire bonding can be used at frequencies above 100 GHz. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
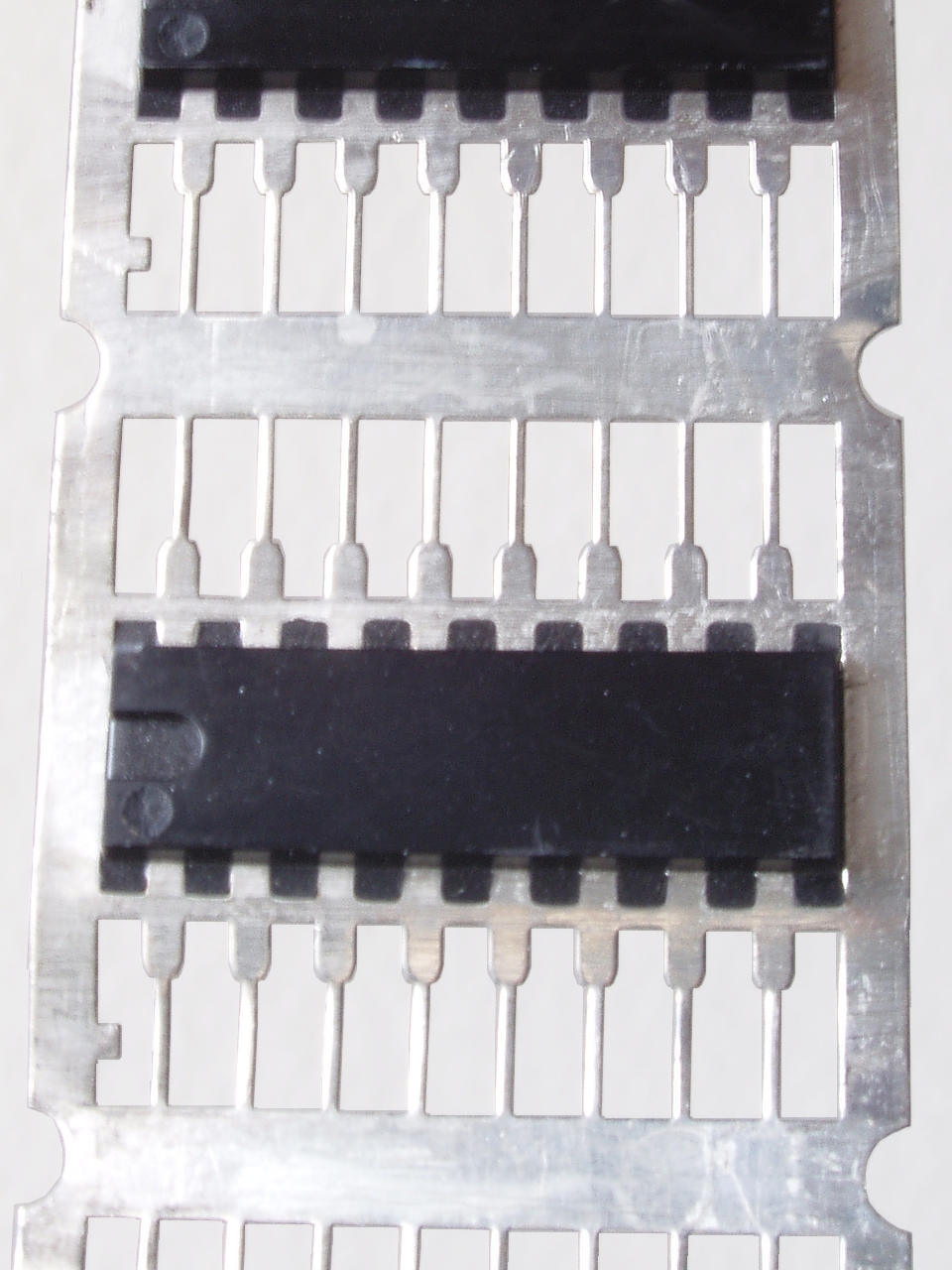
Example Of A TAB Tape After Assembly
Example may refer to: * '' exempli gratia'' (e.g.), usually read out in English as "for example" * .example, reserved as a domain name that may not be installed as a top-level domain of the Internet ** example.com, example.net, example.org, example.edu, second-level domain names reserved for use in documentation as examples * HMS ''Example'' (P165), an Archer-class patrol and training vessel of the Royal Navy Arts * ''The Example'', a 1634 play by James Shirley * ''The Example'' (comics), a 2009 graphic novel by Tom Taylor and Colin Wilson * Example (musician), the British dance musician Elliot John Gleave (born 1982) * ''Example'' (album), a 1995 album by American rock band For Squirrels See also * * Exemplar (other), a prototype or model which others can use to understand a topic better * Exemplum, medieval collections of short stories to be told in sermons * Eixample The Eixample (; ) is a district of Barcelona between the old city (Ciutat Vella) and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermosonic Bonding
Thermosonic bonding is widely used to wire bond silicon integrated circuits into computers. Alexander Coucoulas was named "Father of Thermosonic Bonding" by George Harman, the world's foremost authority on wire bonding, where he referenced Coucoulas's leading edge publications in his book, ''Wire Bonding In Microelectronics''.Coucoulas, A., Trans. Metallurgical Society Of AIME, "Ultrasonic Welding of Aluminum Leads to Tantalum Thin Films", 1966, pp. 587–589. abstract https://sites.google.com/site/coucoulasthermosonicbondaltaCoucoulas, A., "Hot Work Ultrasonic Bonding – A Method Of Facilitating Metal Flow By Restoration Processes", Proc. 20th IEEE Electronic Components Conf. Washington, D.C., May 1970, pp. 549–556.https://sites.google.com/site/hotworkultrasonicbonding Owing to the well proven reliability of thermosonic bonds, it is extensively used to connect the central processing units (CPUs), which are encapsulated silicon integrated circuits that serve as the "brains" of to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
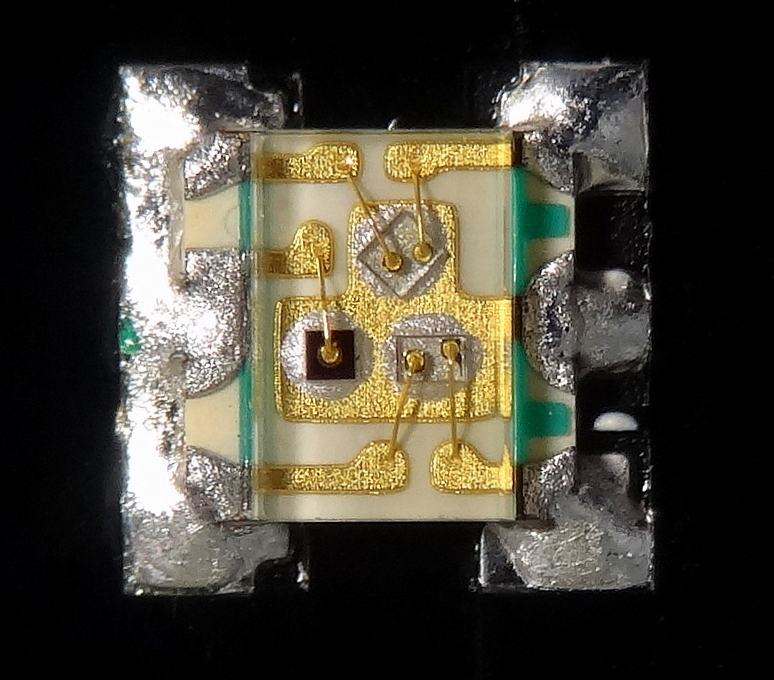
Integrated Circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny MOSFETs (metal–oxide–semiconductor field-effect transistors) integrate into a small chip. This results in circuits that are orders of magnitude smaller, faster, and less expensive than those constructed of discrete electronic components. The IC's mass production capability, reliability, and building-block approach to integrated circuit design has ensured the rapid adoption of standardized ICs in place of designs using discrete transistors. ICs are now used in virtually all electronic equipment and have revolutionized the world of electronics. Computers, mobile phones and other home appliances are now inextricable parts of the structure of modern societies, made possible by the small size and low cost of ICs such as modern computer ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermocompression Bonding
Thermocompression bonding describes a wafer bonding technique and is also referred to as diffusion bonding, pressure joining, thermocompression welding or solid-state welding. Two metals, e.g. gold-Gold, gold (Au), are brought into atomic contact applying force and heat simultaneously. The diffusion requires atomic contact between the surface physics, surfaces due to the atomic Motion (physics), motion. The atoms migrate from one crystal lattice to the other one based on Wavelength#Crystals, crystal lattice vibration. This atomic interaction sticks the Interface (chemistry), interface together. The diffusion process is described by the following three processes: * surface diffusion * grain boundary diffusion * bulk diffusion This method enables internal structure protecting device packages and direct electrical interconnect structures without additional steps beside the surface mounting process. Overview The most established materials for Vapor-compression evaporation#Thermocompr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)