|
TAMK
Tampere University of Applied Sciences ( fi, Tampereen ammattikorkeakoulu, TAMK) is a university of applied sciences (a polytechnic) in the region of Pirkanmaa, Finland. Together with Tampere University, TAMK constitutes the Tampere higher education community. Founded in 1996, TAMK merged with the Pirkanmaa University of Applied Sciences in 2010. Its campuses are located in Tampere, Ikaalinen, Mänttä-Vilppula and Virrat. TAMK's main campus is located in the city of Tampere, away from the city centre. There are three other smaller campuses in Tampere: Mediapolis, Music Academy, and Proakatemia. TAMK has almost 10,000 students divided among over 40 degree programmes, of which seven are conducted in English. Schools TAMK comprises five schools: * School of Built Environment and Bioeconomy * School of Business and Media * School of Industrial Engineering *School of Pedagogic Innovations and Culture *School of Social Services and Health Care Academic collaboration TAMK has ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamk Logo
Tampere University of Applied Sciences ( fi, Tampereen ammattikorkeakoulu, TAMK) is a Ammattikorkeakoulu, university of applied sciences (a Institute of technology, polytechnic) in the region of Pirkanmaa, Finland. Together with Tampere University, TAMK constitutes the Tampere higher education community. Founded in 1996, TAMK merged with the Pirkanmaa University of Applied Sciences in 2010. Its campuses are located in Tampere, Ikaalinen, Mänttä-Vilppula and Virrat. TAMK's main campus is located in the city of Tampere, away from the city centre. There are three other smaller campuses in Tampere: Mediapolis, Music Academy, and Proakatemia. TAMK has almost 10,000 students divided among over 40 degree programmes, of which seven are conducted in English. Schools TAMK comprises five schools: * School of Built Environment and Bioeconomy * School of Business and Media * School of Industrial Engineering *School of Pedagogic Innovations and Culture *School of Social Services and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamk Sisaankaynti
Tampere University of Applied Sciences ( fi, Tampereen ammattikorkeakoulu, TAMK) is a university of applied sciences (a polytechnic) in the region of Pirkanmaa, Finland. Together with Tampere University, TAMK constitutes the Tampere higher education community. Founded in 1996, TAMK merged with the Pirkanmaa University of Applied Sciences in 2010. Its campuses are located in Tampere, Ikaalinen, Mänttä-Vilppula and Virrat. TAMK's main campus is located in the city of Tampere, away from the city centre. There are three other smaller campuses in Tampere: Mediapolis, Music Academy, and Proakatemia. TAMK has almost 10,000 students divided among over 40 degree programmes, of which seven are conducted in English. Schools TAMK comprises five schools: * School of Built Environment and Bioeconomy * School of Business and Media * School of Industrial Engineering *School of Pedagogic Innovations and Culture *School of Social Services and Health Care Academic collaboration TA ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
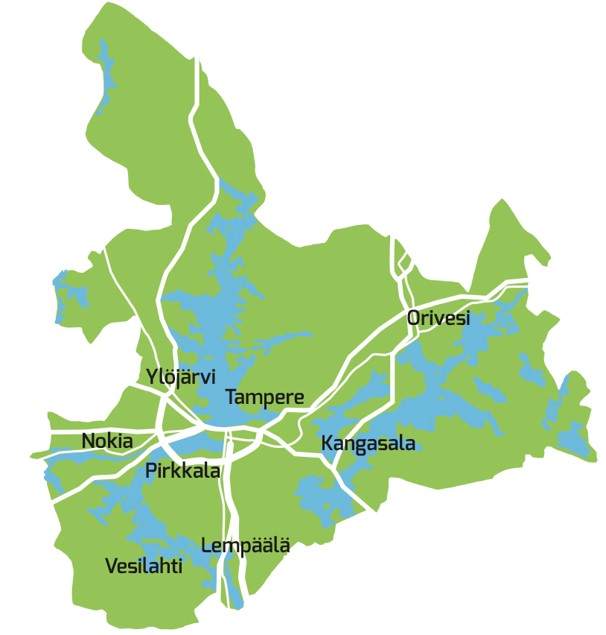
Tampere
Tampere ( , , ; sv, Tammerfors, ) is a city in the Pirkanmaa region, located in the western part of Finland. Tampere is the most populous inland city in the Nordic countries. It has a population of 244,029; the urban area has a population of 341,696; and the metropolitan area, also known as the Tampere sub-region, has a population of 393,941 in an area of . Tampere is the second-largest urban area and third most-populous individual municipality in Finland, after the cities of Helsinki and Espoo, and the most populous Finnish city outside the Greater Helsinki area. Today, Tampere is one of the major urban, economic, and cultural hubs in the whole inland region. Tampere and its environs belong to the historical province of Satakunta. The area belonged to the Häme Province from 1831 to 1997, and over time it has often been considered to belong to Tavastia as a province. For example, in '' Uusi tietosanakirja'' published in the 1960s, the Tampere sub-region is presented as p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahjalal University Of Science And Technology
Shahjalal University of Science and Technology (SUST) is a Public university, public research university, research based university in Sylhet, Bangladesh. It is the List of universities in Bangladesh#Public universities, 8th oldest university of the country and the first university to adopt American credit system. The university is known for its pioneering research and education in the physical sciences and engineering. In 2016, SUST ranked as the top research university in Bangladesh (610th in the world) by SCImago Institutions Rankings, Scopus-SCImago institution ranking. In 2017, the university had highest research expenditure among all universities in Bangladesh. Following the success of SUST, twelve more Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics, STEM List of universities in Bangladesh#Science and Technology universities, universities have been established in the country by the Government of Bangladesh. History Shahjalal University of Science and Technology was es ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Educational Institutions Established In 1996
Education is a purposeful activity directed at achieving certain aims, such as transmitting knowledge or fostering skills and character traits. These aims may include the development of understanding, rationality, kindness, and honesty. Various researchers emphasize the role of critical thinking in order to distinguish education from indoctrination. Some theorists require that education results in an improvement of the student while others prefer a value-neutral definition of the term. In a slightly different sense, education may also refer, not to the process, but to the product of this process: the mental states and dispositions possessed by educated people. Education originated as the transmission of cultural heritage from one generation to the next. Today, educational goals increasingly encompass new ideas such as the liberation of learners, skills needed for modern society, empathy, and complex vocational skills. Types of education are commonly divided into formal, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universities And Colleges In Finland
A university () is an institution of higher (or tertiary) education and research which awards academic degrees in several academic disciplines. Universities typically offer both undergraduate and postgraduate programs. In the United States, the designation is reserved for colleges that have a graduate school. The word ''university'' is derived from the Latin ''universitas magistrorum et scholarium'', which roughly means "community of teachers and scholars". The first universities were created in Europe by Catholic Church monks. The University of Bologna (''Università di Bologna''), founded in 1088, is the first university in the sense of: *Being a high degree-awarding institute. *Having independence from the ecclesiastic schools, although conducted by both clergy and non-clergy. *Using the word ''universitas'' (which was coined at its foundation). *Issuing secular and non-secular degrees: grammar, rhetoric, logic, theology, canon law, notarial law.Hunt Janin: "The university ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Science Without Borders
Science is a systematic endeavor that builds and organizes knowledge in the form of testable explanations and predictions about the universe. Science may be as old as the human species, and some of the earliest archeological evidence for scientific reasoning is tens of thousands of years old. The earliest written records in the history of science come from Ancient Egypt and Mesopotamia in around 3000 to 1200 BCE. Their contributions to mathematics, astronomy, and medicine entered and shaped Greek natural philosophy of classical antiquity, whereby formal attempts were made to provide explanations of events in the physical world based on natural causes. After the fall of the Western Roman Empire, knowledge of Greek conceptions of the world deteriorated in Western Europe during the early centuries (400 to 1000 CE) of the Middle Ages, but was preserved in the Muslim world during the Islamic Golden Age and later by the efforts of Byzantine Greek scholars who brought Greek man ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
The China Programme For Educational Cooperation
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the most frequently used word in the English language; studies and analyses of texts have found it to account for seven percent of all printed English-language words. It is derived from gendered articles in Old English which combined in Middle English and now has a single form used with pronouns of any gender. The word can be used with both singular and plural nouns, and with a noun that starts with any letter. This is different from many other languages, which have different forms of the definite article for different genders or numbers. Pronunciation In most dialects, "the" is pronounced as (with the voiced dental fricative followed by a schwa) when followed by a consonant sound, and as (homophone of pronoun ''thee'') when followed by a v ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nordplus
The Nordic Council of Ministers is an Intergovernmental organisation, intergovernmental forum established after the Helsinki Treaty. The purpose of the Nordic Council of Ministers is to complement the Nordic Council and promote Nordic cooperation. Structure The governments of the Nordic countries each have a Minister for Nordic Cooperation (other), Minister for Nordic Cooperation. This responsibility often goes to the Minister of Foreign Affairs or another ministerial post that the Nordic country has a special desire for cooperation. These Ministers for Nordic Cooperation delegate meetings for other Ministers to discuss avenues for cooperation in the minister's respective fields, thus the Ministers for Cooperation set up Ministerial Councils. Hence the name, Council of Ministers. Cooperation with other International Organizations The Council and the Council of Ministers are involved in various forms of cooperation with neighbouring areas, amongst them being th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Erasmus +
Desiderius Erasmus Roterodamus (; ; English: Erasmus of Rotterdam or Erasmus;''Erasmus'' was his baptismal name, given after St. Erasmus of Formiae. ''Desiderius'' was an adopted additional name, which he used from 1496. The ''Roterodamus'' was a scholarly name meaning "from Rotterdam", though the Latin genitive would be . 28 October 1466 – 12 July 1536) was a Dutch philosopher and Catholic theologian who is considered one of the greatest scholars of the northern Renaissance.Gleason, John B. "The Birth Dates of John Colet and Erasmus of Rotterdam: Fresh Documentary Evidence", Renaissance Quarterly, The University of Chicago Press on behalf of the Renaissance Society of America, Vol. 32, No. 1 (Spring, 1979), pp. 73–76www.jstor.org/ref> As a Catholic priest, he was an important figure in classical scholarship who wrote in a pure Latin style. Among humanists he was given the sobriquet "Prince of the Humanists", and has been called "the crowning glory of the Christian humanists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pirkanmaa University Of Applied Sciences
Pirkanmaa (; sv, Birkaland; la, Birkaria, link=no), also known as ''Tampere Region'' in government documents, is a region of Finland. It borders the regions of Satakunta, South Ostrobothnia, Central Finland, Päijät-Häme, Kanta-Häme and Southwest Finland. Most of the water area in the Kokemäki River watershed is located in the Pirkanmaa region, although Lake Vanajavesi is partly in the Kanta-Häme region. The region got its name from Pirkkala, which in the Middle Ages comprised most of present-day Pirkanmaa. Tampere is the regional center and capital of Pirkanmaa, and at the same time the largest city in the region. The total population of Pirkanmaa was 529,100 on 30 June 2022, which makes it the second largest among Finland's regions after Uusimaa. The population density is well over twice the Finnish average, and most of its population is largely concentrated in the Tampere sub-region. Economy The Gross domestic product (GDP) of the region was 18.3 billion € in 2016, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.png)
.jpg)