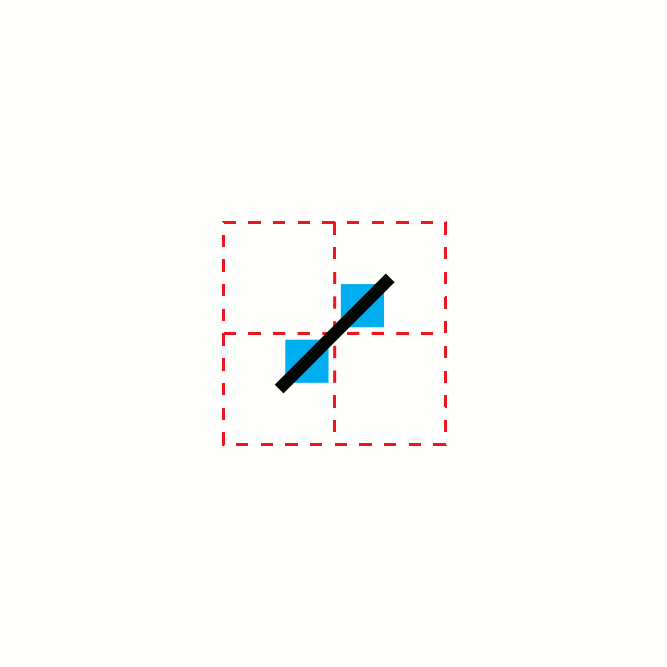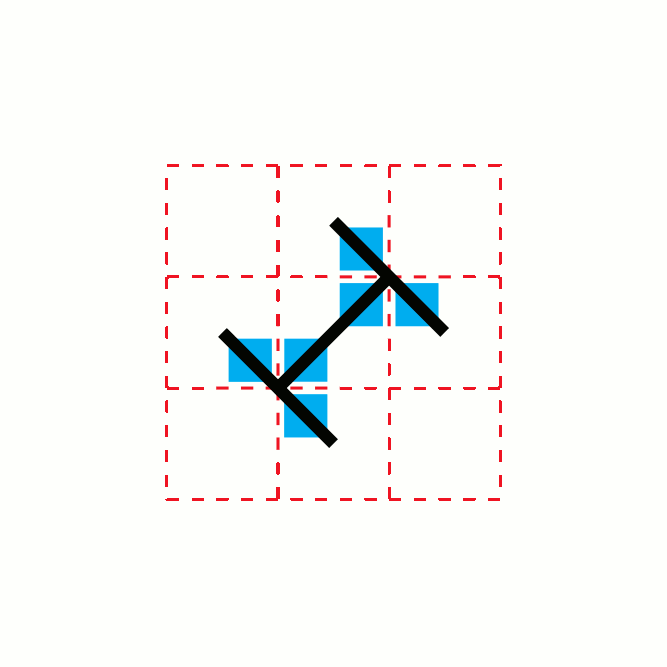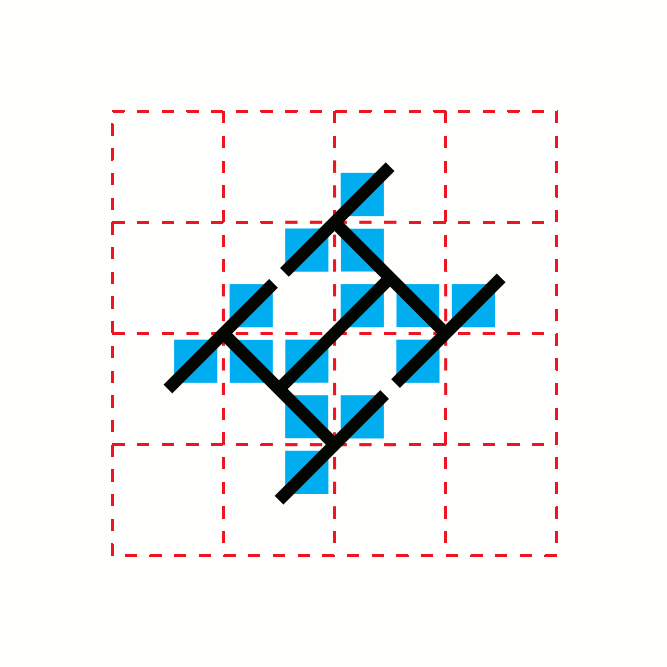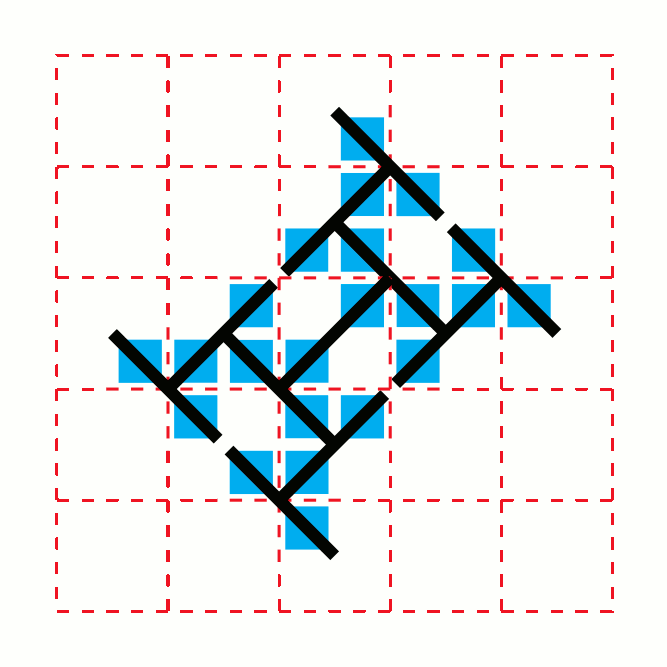|
T-square (fractal)
In mathematics, the T-square is a two-dimensional fractal. It has a boundary of infinite length bounding a finite area. Its name comes from the drawing instrument known as a T-square.Dale, Nell; Joyce, Daniel T.; and Weems, Chip (2016). ''Object-Oriented Data Structures Using Java'', p.187. Jones & Bartlett Learning. . "Our resulting image is a fractal called a T-square because with it we can see shapes that remind us of the technical drawing instrument of the same name." Algorithmic description It can be generated from using this algorithm: # Image 1: ## Start with a square. (The black square in the image) # Image 2: ## At each convex corner of the previous image, place another square, centered at that corner, with half the side length of the square from the previous image. ## Take the union of the previous image with the collection of smaller squares placed in this way. # Images 3–6: ## Repeat step 2. The method of creation is rather similar to the ones used to cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal Dimension
In mathematics, more specifically in fractal geometry, a fractal dimension is a ratio providing a statistical index of complexity comparing how detail in a pattern (strictly speaking, a fractal pattern) changes with the scale at which it is measured. It has also been characterized as a measure of the space-filling capacity of a pattern that tells how a fractal scales differently from the space it is embedded in; a fractal dimension does not have to be an integer. The essential idea of "fractured" dimensions has a long history in mathematics, but the term itself was brought to the fore by Benoit Mandelbrot based on his 1967 paper on self-similarity in which he discussed ''fractional dimensions''. In that paper, Mandelbrot cited previous work by Lewis Fry Richardson describing the counter-intuitive notion that a coastline's measured length changes with the length of the measuring stick used ( see Fig. 1). In terms of that notion, the fractal dimension of a coastline quantifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toothpick Sequence
In geometry, the toothpick sequence is a sequence of 2-dimensional patterns which can be formed by repeatedly adding line segments ("toothpicks") to the previous pattern in the sequence. The first stage of the design is a single "toothpick", or line segment. Each stage after the first is formed by taking the previous design and, for every exposed toothpick end, placing another toothpick centered at a right angle on that end. This process results in a pattern of growth in which the number of segments at stage oscillates with a fractal pattern between and . If denotes the number of segments at stage , then values of for which is near its maximum occur when is near a power of two, while the values for which it is near its minimum occur near numbers that are approximately times a power of two. The structure of stages in the toothpick sequence often resemble the T-square fractal, or the arrangement of cells in the Ulam–Warburton cellular automaton. All of the bounded region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Fractals By Hausdorff Dimension
According to Benoit Mandelbrot, "A fractal is by definition a set for which the Hausdorff-Besicovitch dimension strictly exceeds the topological dimension." Presented here is a list of fractals, ordered by increasing Hausdorff dimension, to illustrate what it means for a fractal to have a low or a high dimension. Deterministic fractals Random and natural fractals See also * Fractal dimension * Hausdorff dimension * Scale invariance Notes and references Further reading * * * * External links The fractals on MathworldOther fractals on Paul Bourke's websiteFractals on mathcurve.com* ttps://web.archive.org/web/20060923100014/http://library.thinkquest.org/26242/full/index.html Fractals unleashedIFStile - software that computes the dimension of the boundary of self-affine tiles {{DEFAULTSORT:Fractals By Hausdorff Dimension Hausdorff Dimension Hausdorff Dimension In mathematics, Hausdorff dimension is a measure of ''roughness'', or more specifically, fractal dimension, that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sierpiński Triangle
The Sierpiński triangle (sometimes spelled ''Sierpinski''), also called the Sierpiński gasket or Sierpiński sieve, is a fractal attractive fixed set with the overall shape of an equilateral triangle, subdivided recursively into smaller equilateral triangles. Originally constructed as a curve, this is one of the basic examples of self-similar sets—that is, it is a mathematically generated pattern that is reproducible at any magnification or reduction. It is named after the Polish mathematician Wacław Sierpiński, but appeared as a decorative pattern many centuries before the work of Sierpiński. Constructions There are many different ways of constructing the Sierpinski triangle. Removing triangles The Sierpinski triangle may be constructed from an equilateral triangle by repeated removal of triangular subsets: # Start with an equilateral triangle. # Subdivide it into four smaller congruent equilateral triangles and remove the central triangle. # Repeat step 2 with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
V4 Ban1 Inc1
V4 or V-4 may refer to: Science and technology * LNER Class V4, a British steam locomotive * V4 engine, a V engine with four cylinders in two banks of two cylinders * Visual area V4, in the visual cortex * Klein four-group, in mathematics * V.4, an ITU-T recommendation for data transmission * ATC code V04 ''Diagnostic agents'', a subgroup of the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical Classification System * The V4 JavaScript JavaScript (), often abbreviated as JS, is a programming language that is one of the core technologies of the World Wide Web, alongside HTML and CSS. As of 2022, 98% of Website, websites use JavaScript on the Client (computing), client side ... engine for QML * V4, one of six precordial leads in electrocardiography Other uses * Visegrád Group, an alliance of four Central European states - Czech Republic, Hungary, Poland and Slovakia * ''Rheinbote'' or V-4, a German World War II four-stage missile * Saint Kitts & Nevis (ITU prefix) * Vieques Air Link (IATA ai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chaos Game
In mathematics, the term chaos game originally referred to a method of creating a fractal, using a polygon and an initial point selected at random inside it. The fractal is created by iteratively creating a sequence of points, starting with the initial random point, in which each point in the sequence is a given fraction of the distance between the previous point and one of the vertices of the polygon; the vertex is chosen at random in each iteration. Repeating this iterative process a large number of times, selecting the vertex at random on each iteration, and throwing out the first few points in the sequence, will often (but not always) produce a fractal shape. Using a regular triangle and the factor 1/2 will result in the Sierpinski triangle, while creating the proper arrangement with four points and a factor 1/2 will create a display of a "Sierpinski Tetrahedron", the three-dimensional analogue of the Sierpinski triangle. As the number of points is increased to a number N, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fractal
In mathematics, a fractal is a geometric shape containing detailed structure at arbitrarily small scales, usually having a fractal dimension strictly exceeding the topological dimension. Many fractals appear similar at various scales, as illustrated in successive magnifications of the Mandelbrot set. This exhibition of similar patterns at increasingly smaller scales is called self-similarity, also known as expanding symmetry or unfolding symmetry; if this replication is exactly the same at every scale, as in the Menger sponge, the shape is called affine self-similar. Fractal geometry lies within the mathematical branch of measure theory. One way that fractals are different from finite geometric figures is how they scale. Doubling the edge lengths of a filled polygon multiplies its area by four, which is two (the ratio of the new to the old side length) raised to the power of two (the conventional dimension of the filled polygon). Likewise, if the radius of a filled s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |