|
Synanthedon Exitiosa
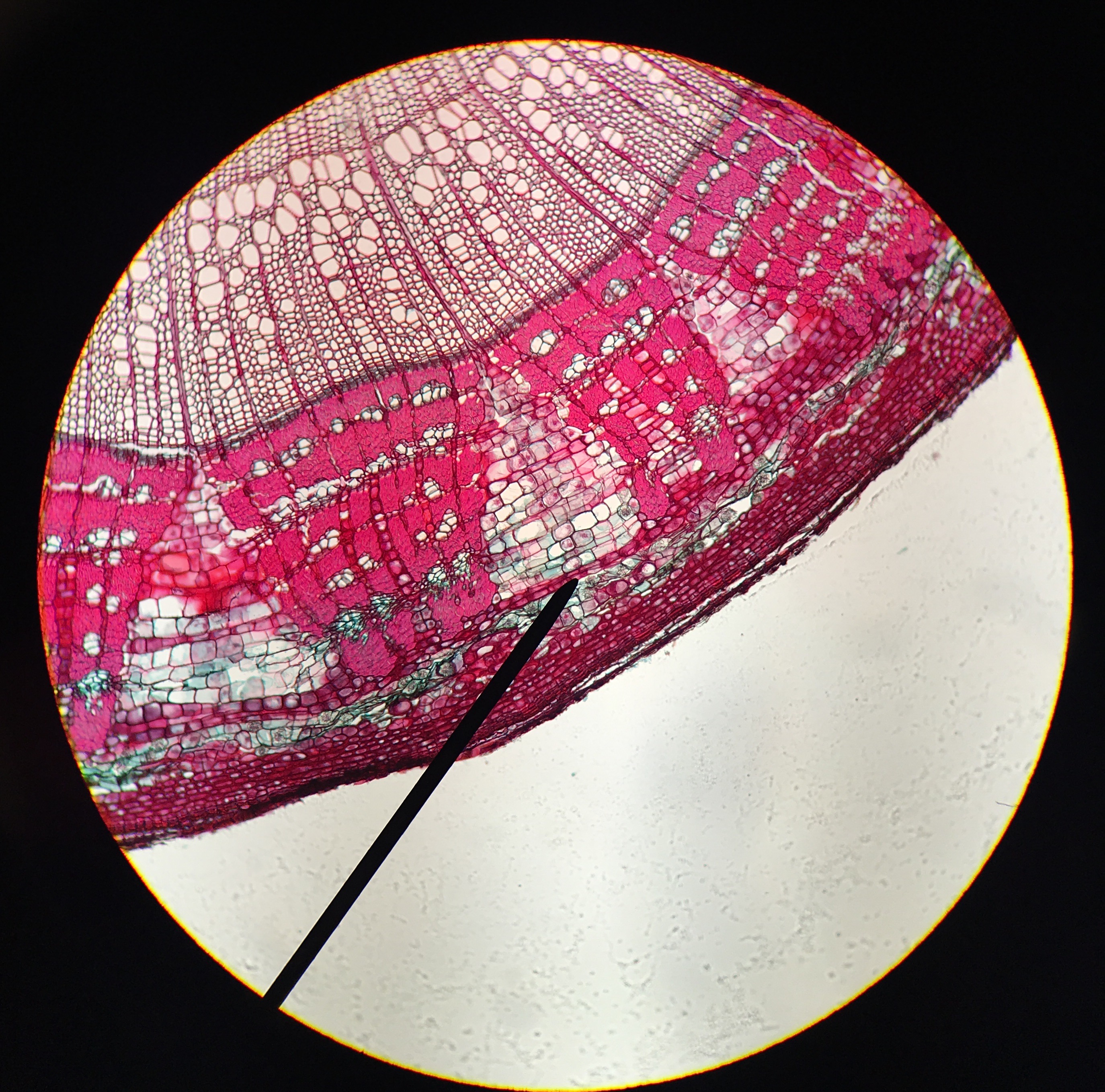
''Synanthedon exitiosa'', the peachtree borer, is a species of moth in the family Sesiidae that is native to North America.Strickland, J. S''Synanthedon exitiosa''.Featured Creatures. Department of Entomology and Nematology. University of Florida IFAS. Updated October 2014. The adult female of the species has a wingspan of about 3.5 centimeters. It is dark metallic blue in color with an orange band around the abdomen. It has opaque forewings and clear hindwings. The male is smaller and more slender, and both pairs of wings are clear. The larva is up to 3.5 centimeters long and white with a brown head. The host plants are trees and shrubs of the genus ''Prunus'', such as peach, cherry, and apricot. The female lays eggs around the base of the trunk and the larvae bore into it. They feed on the cambium A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Say
Thomas Say (June 27, 1787 – October 10, 1834) was an American entomologist, conchologist, and herpetologist. His studies of insects and shells, numerous contributions to scientific journals, and scientific expeditions to Florida, Georgia, the Rocky Mountains, Mexico, and elsewhere made him an internationally known naturalist. Say has been called the father of American descriptive entomology and American conchology. He served as librarian for the Academy of Natural Sciences of Philadelphia, curator at the American Philosophical Society (elected in 1817), and professor of natural history at the University of Pennsylvania. Early life and education Born in Philadelphia into a prominent Quaker family, Thomas Say was the great-grandson of John Bartram, and the great-nephew of William Bartram. His father, Dr. Benjamin Say, was brother-in-law to another Bartram son, Moses Bartram. The Say family had a house, "The Cliffs" at Gray's Ferry, adjoining the Bartram family farms in King ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of which have yet to be described. Most species of moth are nocturnal, but there are also crepuscular and diurnal species. Differences between butterflies and moths While the butterflies form a monophyletic group, the moths, comprising the rest of the Lepidoptera, do not. Many attempts have been made to group the superfamilies of the Lepidoptera into natural groups, most of which fail because one of the two groups is not monophyletic: Microlepidoptera and Macrolepidoptera, Heterocera and Rhopalocera, Jugatae and Frenatae, Monotrysia and Ditrysia.Scoble, MJ 1995. The Lepidoptera: Form, function and diversity. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press; 404 p. Although the rules for distinguishing moths from butterflies are not well est ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sesiidae
The Sesiidae or clearwing moths are a diurnality, diurnal moth family (biology), family in the order Lepidoptera known for their Batesian mimicry in both appearance and behaviour of various Hymenoptera. The family consists of 165 genus, genera spread over two subfamilies, containing in total 1525 species and 49 subspecies, most of which occur in the tropics, though there are many species in the Holarctic region as well, including over a hundred species known to occur in Europe. Morphology Sesiidae are characterized by their hymenopteriform Batesian mimicry, frequently of identifiable species. Most species of Sesiidae have wings with areas where scale (insect anatomy), scales are nearly completely absent, resulting in partial, marked transparency. Forewings are commonly elongated and narrow in the basal half. In many species, the abdomen is elongated, with an anal tuft, and striped or ringed yellow, red or white, sometimes very brightly so. Legs are long, thin and frequently co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Larva
A larva (; plural larvae ) is a distinct juvenile form many animals undergo before metamorphosis into adults. Animals with indirect development such as insects, amphibians, or cnidarians typically have a larval phase of their life cycle. The larva's appearance is generally very different from the adult form (''e.g.'' caterpillars and butterflies) including different unique structures and organs that do not occur in the adult form. Their diet may also be considerably different. Larvae are frequently adapted to different environments than adults. For example, some larvae such as tadpoles live almost exclusively in aquatic environments, but can live outside water as adult frogs. By living in a distinct environment, larvae may be given shelter from predators and reduce competition for resources with the adult population. Animals in the larval stage will consume food to fuel their transition into the adult form. In some organisms like polychaetes and barnacles, adults are im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shrub
A shrub (often also called a bush) is a small-to-medium-sized perennial woody plant. Unlike herbaceous plants, shrubs have persistent woody stems above the ground. Shrubs can be either deciduous or evergreen. They are distinguished from trees by their multiple stems and shorter height, less than tall. Small shrubs, less than 2 m (6.6 ft) tall are sometimes termed as subshrubs. Many botanical groups have species that are shrubs, and others that are trees and herbaceous plants instead. Some definitions state that a shrub is less than and a tree is over 6 m. Others use as the cut-off point for classification. Many species of tree may not reach this mature height because of hostile less than ideal growing conditions, and resemble a shrub-sized plant. However, such species have the potential to grow taller under the ideal growing conditions for that plant. In terms of longevity, most shrubs fit in a class between perennials and trees; some may only last about fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prunus
''Prunus'' is a genus of trees and shrubs, which includes (among many others) the fruits plums, cherries, peaches, nectarines, apricots, and almonds. Native to the North American temperate regions, the neotropics of South America, and the paleotropics of Asia and Africa, 430 different species are classified under ''Prunus''. Many members of the genus are widely cultivated for their fruit and for decorative purposes. ''Prunus'' fruit are drupes, or stone fruits. The fleshy mesocarp surrounding the endocarp is edible while the endocarp itself forms a hard, inedible shell called the pyrena ("stone" or "pit"). This shell encloses the seed (or "kernel") which is edible in many species (such as almonds) but poisonous in others (such as apricots). Besides being eaten off the hand, most ''Prunus'' fruit are also commonly used in processing, such as jam production, canning, drying, and seeds for roasting. Botany Members of the genus can be deciduous or evergreen. A few species have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties), nectarines. The specific name ''persica'' refers to its widespread cultivation in Persia (modern-day Iran), from where it was transplanted to Europe. It belongs to the genus '' Prunus'', which includes the cherry, apricot, almond, and plum, in the rose family. The peach is classified with the almond in the subgenus '' Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera by the corrugated seed shell ( endocarp). Due to their close relatedness, the kernel of a peach stone tastes remarkably similar to almond, and peach stones are often used to make a cheap version of marzipan, known as persipan. Peaches and nectarines are the same species, though they are regarded commercially as different fruits. The skin of nectarine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus '' Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit). Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet '' Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The name 'cherry' also refers to the cherry tree and its wood, and is sometimes applied to almonds and visually similar flowering trees in the genus ''Prunus'', as in "ornamental cherry" or " cherry blossom". Wild cherry may refer to any of the cherry species growing outside cultivation, although ''Prunus avium'' is often referred to specifically by the name "wild cherry" in the British Isles. Botany True cherries ''Prunus'' subg. ''Cerasus'' contains species that are typically called cherries. They are known as true cherries and distinguished by having a single winter bud per axil, by having the flowers in small corymbs or umbels of several together (occasionally solitary, e.g. ''P. serrula''; some species with short racemes, e.g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apricot
An apricot (, ) is a fruit, or the tree that bears the fruit, of several species in the genus '' Prunus''. Usually, an apricot is from the species '' P. armeniaca'', but the fruits of the other species in ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca'' are also called apricots. Etymology ''Apricot'' first appeared in English in the 16th century as ''abrecock'' from the Middle French ''aubercot'' or later ''abricot'', from Spanish '' albaricoque'' and Catalan ''a(l)bercoc'', in turn from Arabic الْبَرْقُوق (al-barqūq, "the plums"), from Byzantine Greek βερικοκκίᾱ (berikokkíā, "apricot tree"), derived from late Greek ''πραικόκιον'' (''praikókion'', "apricot") from Latin '' ersica ("peach")praecocia'' (''praecoquus'', "early ripening"). Species Apricots are species belonging to ''Prunus'' sect. ''Armeniaca''. The taxonomic position of '' P. brigantina'' is disputed. It is grouped with plum species according to chloroplast DNA sequences, but more closel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cambium
A cambium (plural cambia or cambiums), in plants, is a tissue layer that provides partially undifferentiated cells for plant growth. It is found in the area between xylem and phloem. A cambium can also be defined as a cellular plant tissue from which phloem, xylem, or cork grows by division, resulting (in woody plants) in secondary thickening. It forms parallel rows of cells, which result in secondary tissues. There are several distinct kinds of cambium found in plant stems and roots: * Cork cambium, a tissue found in many vascular plants as part of the periderm. * Unifacial cambium, which ultimately produces cells to the interior of its cylinder. * Vascular cambium, a lateral meristem in the vascular tissue of plants. Uses The cambium of many species of woody plants are edible; however, due to its vital role in the homeostasis and growth of woody plants, this may result in death of the plant if enough cambium is removed at once. The cambium can generally be eaten raw or c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Pest Insects
A pest is any animal or plant harmful to humans or human concerns. The term is particularly used for creatures that damage crops, livestock, and forestry or cause a nuisance to people, especially in their homes. Humans have modified the environment for their own purposes and are intolerant of other creatures occupying the same space when their activities impact adversely on human objectives. Thus, an elephant is unobjectionable in its natural habitat but a pest when it tramples crops. Some animals are disliked because they bite or sting; snakes, wasps, ants, bed bugs, fleas and ticks belong in this category. Others enter the home; these include houseflies, which land on and contaminate food, beetles, which tunnel into the woodwork, and other animals that scuttle about on the floor at night, like cockroaches, which are often associated with unsanitary conditions. Agricultural and horticultural crops are attacked by a wide variety of pests, the most important being insects, mites ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |





.jpg)

.jpg)