|
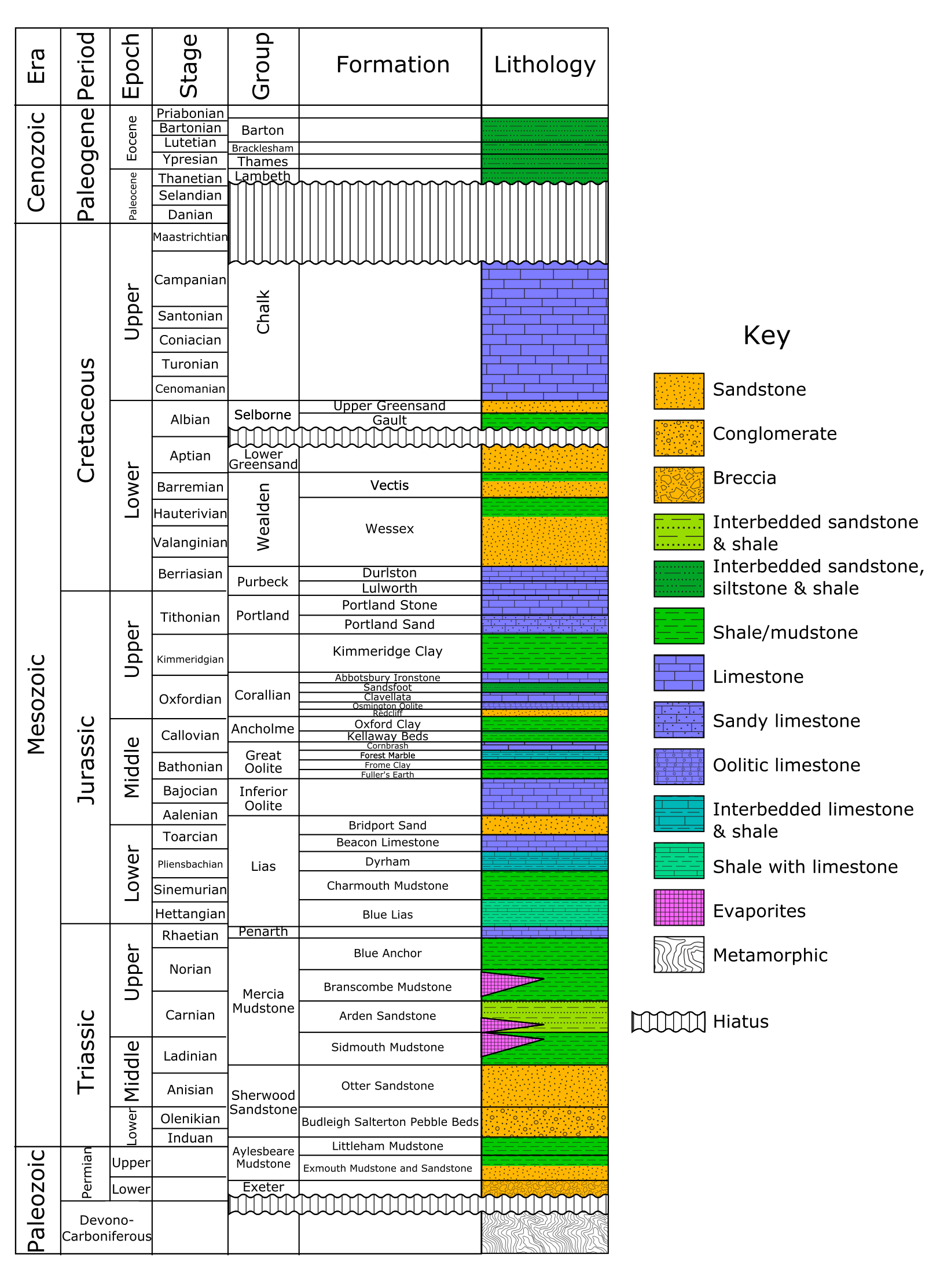
Stratigraphic Section
A stratigraphic section is a sequence of layers of rocks in the order they were deposited. It is based on the principle of original horizontality, which states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity. Biostratigraphers estimate the age of stratigraphic sections by using the faunal assemblages contained within rock samples from outcrop and drill cores.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. Geochronologists precisely date rocks within the stratigraphic section to provide better absolute bounds on the timing and rates of deposition. Magnetic stratigraphers look for signs of magnetic reversals in igneous rock units within the drill cores. Other scientists perform stable-isotope studies on the rocks to gain information about past climate. Stratigraphic sections can also be used to locate areas for water, coal, and hydrocarbon extraction, particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Blegny Mijn Geologisch Profiel
Blegny (, before 2001: Blégny; wa, Blegné) is a municipality of Wallonia located in the province of liège, Belgium. On January 1, 2006, Blegny had a total population of 12,799. The total area is 26.07 km² which gives a population density of 491 inhabitants per km². The municipality consists of the following districts A district is a type of administrative division that, in some countries, is managed by the local government. Across the world, areas known as "districts" vary greatly in size, spanning regions or counties, several municipalities, subdivisions o ...: Barchon, Housse, Mortier, Saint-Remy, Saive, and Trembleur (town centre). See also * List of protected heritage sites in Blegny References External links * * Municipalities of Liège Province {{Liege-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms when these minerals precipitate out of water containing dissolved calcium. This can take place through both biological and nonbiological processes, though biological processes, such as the accumulation of corals and shells in the sea, have likely been more important for the last 540 million years. Limestone often contains fossils which provide scientists with information on ancient environments and on the evolution of life. About 20% to 25% of sedimentary rock is carbonate rock, and most of this is limestone. The remaining carbonate rock is mostly dolomite, a closely related rock, which contains a high percentage of the mineral dolomite, . ''Magnesian limestone'' is an obsolete and poorly-defined term used variously for dolomite, for limes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wessex Basin
The Wessex Basin is a petroleum-bearing geological area located along the southern coast of England and extending into the English Channel. The onshore part of the basin covers approximately 20,000 km2 and the area that encompasses the English Channel is of similar size. The basin is a rift basin that was created during the Permian to early Cretaceous in response to movement of the African plate relative to the Eurasian plate. In the late Cretaceous, and again in the Cenozoic, the basin was inverted as a distant effect of the Alpine orogeny. The basin is usually divided into 3 main sub-basins including the Winterborne-Kingston Trough, Channel Basin, and Vale of Pewsey Basin. The area is also rich in hydrocarbons with several offshore wells in the area. With the large interest in the hydrocarbon exploration of the area, data became more readily available, which improved the understanding of the type of inversion tectonics that characterize this basin. Tectonic mechanisms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bouldnor Formation
The Bouldnor Formation is a geological formation in the Hampshire Basin of southern England. It is the youngest formation of the Solent Group and was deposited during the uppermost Eocene and lower Oligocene. Stratotype and occurrence The Bouldnor Formation was named after Bouldnor, a small hamlet east of Yarmouth, Isle of Wight. The formation is exposed along ''Bouldnor Cliff'' between Yarmouth and Hamstead occupying the core of the east-southeast-striking ''Bouldnor Syncline''. Yet the stratotype of the formation is found at ''Whitecliff Bay'' on the east side of the Isle of Wight. History The Bouldnor Formation was scientifically established 1985 by A. Insole and B. Daly, who also defined its members. The paleogene strata on the Isle of Wight had already been described in 1853 by Edward Forbes. Forbes was followed in 1921 by H.J.O. White, a geologist from the Geological Survey. Stratigraphy The Bouldnor-Formation is the topmost formation of the Solent Group before ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stratigraphic Section
A stratigraphic section is a sequence of layers of rocks in the order they were deposited. It is based on the principle of original horizontality, which states that layers of sediment are originally deposited horizontally under the action of gravity. Biostratigraphers estimate the age of stratigraphic sections by using the faunal assemblages contained within rock samples from outcrop and drill cores.Hine, Robert. “Biostratigraphy.” ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. Geochronologists precisely date rocks within the stratigraphic section to provide better absolute bounds on the timing and rates of deposition. Magnetic stratigraphers look for signs of magnetic reversals in igneous rock units within the drill cores. Other scientists perform stable-isotope studies on the rocks to gain information about past climate. Stratigraphic sections can also be used to locate areas for water, coal, and hydrocarbon extraction, particular ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, the fourth-largest country in the Americas, and the eighth-largest country in the world. It shares the bulk of the Southern Cone with Chile to the west, and is also bordered by Bolivia and Paraguay to the north, Brazil to the northeast, Uruguay and the South Atlantic Ocean to the east, and the Drake Passage to the south. Argentina is a federal state subdivided into twenty-three provinces, and one autonomous city, which is the federal capital and largest city of the nation, Buenos Aires. The provinces and the capital have their own constitutions, but exist under a federal system. Argentina claims sovereignty over the Falkland Islands, South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands, and a part of Antarctica. The earliest recorded human prese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salta Province
Salta () is a province of Argentina, located in the northwest of the country. Neighboring provinces are from the east clockwise Formosa, Chaco, Santiago del Estero, Tucumán and Catamarca. It also surrounds Jujuy. To the north it borders Bolivia and Paraguay and to the west lies Chile. History Before the Spanish conquest, numerous native peoples (now called Diaguitas and Calchaquíes) lived in the valleys of what is now Salta Province; they formed many different tribes, the Quilmes and Humahuacas among them, which all shared the Cacán language. The Atacamas lived in the Puna, and the Wichís (Matacos), in the Chaco region. The first conquistador to venture into the area was Diego de Almagro in 1535; he was followed by Diego de Rojas. Hernando de Lerma founded San Felipe de Lerma in 1582, following orders of the viceroy Francisco de Toledo, Count of Oropesa; the name of the city was soon changed to "San Felipe de Salta". By 1650, the city had around five hundred inhabitan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Strata
In geology and related fields, a stratum ( : strata) is a layer of rock or sediment characterized by certain lithologic properties or attributes that distinguish it from adjacent layers from which it is separated by visible surfaces known as either '' bedding surfaces'' or ''bedding planes''.Salvador, A. ed., 1994. ''International stratigraphic guide: a guide to stratigraphic classification, terminology, and procedure. 2nd ed.'' Boulder, Colorado, The Geological Society of America, Inc., 215 pp. . Prior to the publication of the International Stratigraphic Guide, older publications have defined a stratum as either being either equivalent to a single bed or composed of a number of beds; as a layer greater than 1 cm in thickness and constituting a part of a bed; or a general term that includes both ''bed'' and ''lamina''.Neuendorf, K.K.E., Mehl, Jr., J.P., and Jackson, J.A. , eds., 2005. ''Glossary of Geology'' 5th ed. Alexandria, Virginia, American Geological Institute. 779 pp. . ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Utah
Utah ( , ) is a state in the Mountain West subregion of the Western United States. Utah is a landlocked U.S. state bordered to its east by Colorado, to its northeast by Wyoming, to its north by Idaho, to its south by Arizona, and to its west by Nevada. Utah also touches a corner of New Mexico in the southeast. Of the fifty U.S. states, Utah is the 13th-largest by area; with a population over three million, it is the 30th-most-populous and 11th-least-densely populated. Urban development is mostly concentrated in two areas: the Wasatch Front in the north-central part of the state, which is home to roughly two-thirds of the population and includes the capital city, Salt Lake City; and Washington County in the southwest, with more than 180,000 residents. Most of the western half of Utah lies in the Great Basin. Utah has been inhabited for thousands of years by various indigenous groups such as the ancient Puebloans, Navajo and Ute. The Spanish were the first Europe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
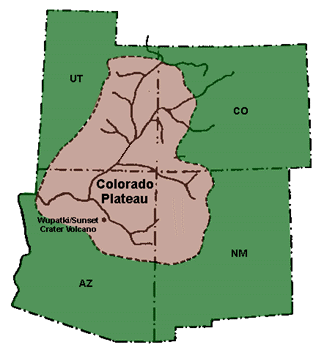
Colorado Plateau
The Colorado Plateau, also known as the Colorado Plateau Province, is a physiographic and desert region of the Intermontane Plateaus, roughly centered on the Four Corners region of the southwestern United States. This province covers an area of 336,700 km2 (130,000 mi2) within western Colorado, northwestern New Mexico, southern and eastern Utah, northern Arizona, and a tiny fraction in the extreme southeast of Nevada. About 90% of the area is drained by the Colorado River and its main tributaries: the Green, San Juan, and Little Colorado. Most of the remainder of the plateau is drained by the Rio Grande and its tributaries. The Colorado Plateau is largely made up of high desert, with scattered areas of forests. In the south-west corner of the Colorado Plateau lies the Grand Canyon of the Colorado River. Much of the Plateau's landscape is related to the Grand Canyon in both appearance and geologic history. The nickname "Red Rock Country" suggests the brightly colored ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jurassic
The Jurassic ( ) is a Geological period, geologic period and System (stratigraphy), stratigraphic system that spanned from the end of the Triassic Period million years ago (Mya) to the beginning of the Cretaceous Period, approximately Mya. The Jurassic constitutes the middle period of the Mesozoic, Mesozoic Era and is named after the Jura Mountains, where limestone strata from the period were first identified. The start of the Jurassic was marked by the major Triassic–Jurassic extinction event, associated with the eruption of the Central Atlantic magmatic province, Central Atlantic Magmatic Province. The beginning of the Toarcian Stage started around 183 million years ago and is marked by an extinction event associated with widespread Anoxic event, oceanic anoxia, ocean acidification, and elevated temperatures likely caused by the eruption of the Karoo-Ferrar, Karoo-Ferrar large igneous provinces. The end of the Jurassic, however, has no clear boundary with the Cretaceous and i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Permian
The Permian ( ) is a geologic period and stratigraphic system which spans 47 million years from the end of the Carboniferous Period million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Triassic Period 251.9 Mya. It is the last period of the Paleozoic Era; the following Triassic Period belongs to the Mesozoic Era. The concept of the Permian was introduced in 1841 by geologist Sir Roderick Murchison, who named it after the region of Perm in Russia. The Permian witnessed the diversification of the two groups of amniotes, the synapsids and the sauropsids ( reptiles). The world at the time was dominated by the supercontinent Pangaea, which had formed due to the collision of Euramerica and Gondwana during the Carboniferous. Pangaea was surrounded by the superocean Panthalassa. The Carboniferous rainforest collapse left behind vast regions of desert within the continental interior. Amniotes, which could better cope with these drier conditions, rose to dominance in place of their am ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
.jpg)