|
Sporothrix Globosa
''Sporothrix'' is a ubiquitous genus of soil-dwelling fungus discovered by Schenck in 1898 and studied in more detail by Hektoen and Perkins. The first described and best known species is ''Sporothrix schenckii'', the causative agent of rose handler's disease Sporotrichosis, also known as rose handler's disease, is a fungal infection that affects skin, lungs, bone and joint, and can be widespread. It presents with firm painless nodules that later ulcerate. It can be localized or widespread. The diseas .... New environmental and pathogenicH. Madrid, J. Gené, J. Cano1, C. Silvera and J. Guarro (2010) ''Sporothrix brunneoviolacea'' and ''Sporothrix dimorphospora'', two new members of the ''Ophiostoma stenoceras''-''Sporothrix schenckii'' complex. Mycologia 102: 1193–1203 DOI: 10.3852/09-320 species have been discovered with the potential for more to be found as molecular techniques advance. Other species in this genus include '' Sporothrix brasiliensis'' and '' Sporothrix glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ascomycota
Ascomycota is a phylum of the kingdom Fungi that, together with the Basidiomycota, forms the subkingdom Dikarya. Its members are commonly known as the sac fungi or ascomycetes. It is the largest phylum of Fungi, with over 64,000 species. The defining feature of this fungal group is the " ascus" (), a microscopic sexual structure in which nonmotile spores, called ascospores, are formed. However, some species of the Ascomycota are asexual, meaning that they do not have a sexual cycle and thus do not form asci or ascospores. Familiar examples of sac fungi include morels, truffles, brewers' and bakers' yeast, dead man's fingers, and cup fungi. The fungal symbionts in the majority of lichens (loosely termed "ascolichens") such as ''Cladonia'' belong to the Ascomycota. Ascomycota is a monophyletic group (it contains all descendants of one common ancestor). Previously placed in the Deuteromycota along with asexual species from other fungal taxa, asexual (or anamorphic) ascomyce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sordariomycetes
Sordariomycetes is a class of fungi in the subdivision Pezizomycotina (Ascomycota), consisting of 28 orders, 90 families, 1344 genera. Sordariomycetes is from the Latin sordes (filth) because some species grow in animal feces, though growth habits vary widely across the class. Sordariomycetes generally produce their asci in perithecial fruiting bodies. Sordariomycetes are also known as Pyrenomycetes, from the Greek πυρἠν - 'the stone of a fruit' - because of the usually somewhat tough texture of their tissue. Sordariomycetes possess great variability in morphology, growth form, and habitat. Most have perithecial (flask-shaped) fruiting bodies, but ascomata can be less frequently cleistothecial (like in the genera '' Anixiella'', ''Apodus'', '' Boothiella'', ''Thielavia'', '' Zopfiella''),. Fruiting bodies may be solitary or gregarious, superficial, or immersed within stromata or tissues of the substrates and can be light to bright or black. Members of this group can grow ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostomatales
The Ophiostomatales are an order of fungi in the class Sordariomycetes. They are commonly symbionts to insect species, which can be found in numerous cases, including some termites and many bark beetles A bark beetle is the common name for the subfamily of beetles Scolytinae. Previously, this was considered a distinct family (Scolytidae), but is now understood to be a specialized clade of the "true weevil" family ( Curculionidae). Although t .... In the cases of most beetle symbioses, the Ophiostomatales fungi is carried in mycangia, which help keep fungal inoculants close to the beetle at all times. In some cases, the fungi are the main source of food for the beetles. In others, the relationship is not as clear. References Ascomycota orders {{Sordariomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ophiostomataceae
The Ophiostomataceae are a family (biology), family of fungi in the Ascomycota, class Sordariomycetes. The family was circumscription (taxonomy), circumscribed by John Axel Nannfeldt, J.A. Nannfeldt in 1932. Species in the family have a widespread distribution, and are typically found in temperate regions, as plant pathogen, pathogens of both coniferous and deciduous trees. Genera *''Ceratocystiopsis'' *''Dryadomyces'' *''Equicapillimyces'' *''Graphilbum'' *''Graphiocladiella'' *''Grosmannia'' *''Hyalorhinocladiella'' *''Klasterskya'' *''Knoxdaviesia'' *''Leptographium'' *''Ophiostoma'' *''Pachnodium'' *''Pesotum (fungus), Pesotum'' *''Raffaelea'' *''Sporothrix'' *''Spumatoria'' *''Subbaromyces'' References External links * Ophiostomatales Ascomycota families Taxa named by John Axel Nannfeldt Taxa described in 1932 {{Sordariomycetes-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus comes above species and below family (taxonomy), family. In binomial nomenclature, the genus name forms the first part of the binomial species name for each species within the genus. :E.g. ''Panthera leo'' (lion) and ''Panthera onca'' (jaguar) are two species within the genus ''Panthera''. ''Panthera'' is a genus within the family Felidae. The composition of a genus is determined by taxonomy (biology), taxonomists. The standards for genus classification are not strictly codified, so different authorities often produce different classifications for genera. There are some general practices used, however, including the idea that a newly defined genus should fulfill these three criteria to be descriptively useful: # monophyly – all descendants ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fungus
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from the other eukaryotic kingdoms, which by one traditional classification include Plantae, Animalia, Protozoa, and Chromista. A characteristic that places fungi in a different kingdom from plants, bacteria, and some protists is chitin in their cell walls. Fungi, like animals, are heterotrophs; they acquire their food by absorbing dissolved molecules, typically by secreting digestive enzymes into their environment. Fungi do not photosynthesize. Growth is their means of mobility, except for spores (a few of which are flagellated), which may travel through the air or water. Fungi are the principal decomposers in ecological systems. These and other differences place fungi in a single group of related organisms, named the ''Eumycota'' (''true f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludvig Hektoen
Ludvig Hektoen (July 2, 1863 – July 5, 1951) was an American pathologist known for his work in the fields of pathology, microbiology and immunology. Hektoen was appointed to the National Academy of Sciences in 1918, and served as president of many professional societies, including the American Association of Immunologists in 1927 and the American Society for Microbiology in 1929. He was the founding editor of the '' Archives of Pathology and Laboratory Medicine'' in 1926 and edited several other medical journals. He was knighted to the Order of St. Olav in 1929, and in 1933, he became professor emeritus of pathology at the University of Chicago. The Hektoen Institute for Medical Research—formerly the John McCormick Institute of Infectious Diseases—now bears his name. Early life and education Hektoen was born on July 2, 1863 in Westby, Wisconsin, to Peter P. Hektoen, a farmer and Lutheran schoolteacher, and Olave Hektoen (née Thorsgaard), both Norwegian immigrants. At th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporothrix Schenckii
''Sporothrix schenckii'', a fungus that can be found worldwide in the environment, is named for medical student Benjamin Schenck, who in 1896 was the first to isolate it from a human specimen. The species is present in soil as well as in and on living and decomposing plant material such as peat moss. It can infect humans as well as animals and is the causative agent of sporotrichosis, commonly known as "rose handler's disease." The most common route of infection is the introduction of spores to the body through a cut or puncture wound in the skin. Infection commonly occurs in otherwise healthy individuals but is rarely life-threatening and can be treated with antifungals. In the environment it is found growing as filamentous hyphae. In host tissue it is found as a yeast. The transition between the hyphal and yeast forms is temperature dependent making ''S. schenckii'' a thermally dimorphic fungus. Morphology ''Sporothrix schenckii'' can be found in one of two morphologies, hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
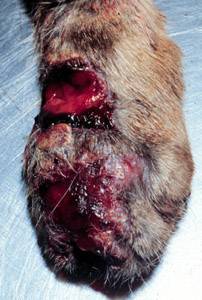
Rose Handler's Disease
Sporotrichosis, also known as rose handler's disease, is a fungal infection that affects skin, lungs, bone and joint, and can be widespread. It presents with firm painless nodules that later ulcerate. It can be localized or widespread. The disease progresses over a week to several months after the initial exposure to the fungus. Serious complications can also develop in people who have a weakened immune system. Sporotrichosis is caused by fungi of the ''Sporothrix schenckii'' species complex. Because ''S. schenckii'' is naturally found in soil, hay, sphagnum moss, and plants, it usually affects farmers, gardeners, and agricultural workers. It enters through small cuts in the skin to cause the infection. In case of sporotrichosis affecting the lungs, the fungal spores enter by breathing in. Sporotrichosis can also be acquired from handling cats with the disease; it is an occupational hazard for veterinarians. Treatment depends on the site and extent of infection. Topical antifu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporothrix Brasiliensis
''Sporothrix brasiliensis'' is a fungus that is commonly found in soil. It is an emerging fungal pathogen that is causing disease in humans and cats mainly in Brazil and other countries in South America. Similar to other species in ''Sporothrix'' genus, this fungus causes the disease sporotrichosis. However, it has been observed that more severe disease results from infection by ''Sporothrix brasiliensis'' compared to other species. The fungus is a thermally dimorphic fungus as it is found in the mycelium phase at room temperature and as yeast in the warmer temperatures of host bodies. Morphology The two morphologies displayed by ''Sporothrix brasiliensis'' are a hyphal form which occurs in the environment and a yeast form which occurs at higher temperatures (36 - 37 °C) such as within the bodies of mammals. Hyphal Phase The hyphal form of ''S.brasiliensis'' occurs at room temperature. Melaninization level of the hyphal form can vary from light (albino) to dark (pigm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sporothrix Globosa
''Sporothrix'' is a ubiquitous genus of soil-dwelling fungus discovered by Schenck in 1898 and studied in more detail by Hektoen and Perkins. The first described and best known species is ''Sporothrix schenckii'', the causative agent of rose handler's disease Sporotrichosis, also known as rose handler's disease, is a fungal infection that affects skin, lungs, bone and joint, and can be widespread. It presents with firm painless nodules that later ulcerate. It can be localized or widespread. The diseas .... New environmental and pathogenicH. Madrid, J. Gené, J. Cano1, C. Silvera and J. Guarro (2010) ''Sporothrix brunneoviolacea'' and ''Sporothrix dimorphospora'', two new members of the ''Ophiostoma stenoceras''-''Sporothrix schenckii'' complex. Mycologia 102: 1193–1203 DOI: 10.3852/09-320 species have been discovered with the potential for more to be found as molecular techniques advance. Other species in this genus include '' Sporothrix brasiliensis'' and '' Sporothrix glob ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |