|
Siewierz Kosciol Sw Macieja
Siewierz is a town in southern Poland, in the Będzin County in the Silesian Voivodeship, seat of Gmina Siewierz. History Siewierz was first mentioned in 1125, and was administered by the Castellan of Bytom. In 1177, Casimir II of Poland granted Siewierz to Mieszko IV Tanglefoot, duke of Silesia and Racibórz, together with whole Duchy of Bytom. The town became a seat of a separate castellan by the beginning of the 13th century. During the first Mongol invasion of Poland, in 1241, the Mongols burned the town, and razed the fort to ground. In 1276, Siewierz received city status. On 26 February 1289, in front of the town gates, the allied forces of Władysław I the Elbow-high, then Duke of Kujawy and Mazovia, defeated the army of Henry IV Probus, duke of Wrocław and Kraków. Together with most of Silesia in years 1327–35, Siewierz – as a part of the Bytom Duchy – was subjugated to the Kingdom of Bohemia. In 1337, Duke Vladislaus of Bytom sold Siewierz to Casimir I, Du ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voivodeships Of Poland
A voivodeship (; pl, województwo ; plural: ) is the highest-level administrative division of Poland, corresponding to a province in many other countries. The term has been in use since the 14th century and is commonly translated into English as "province". The Polish local government reforms adopted in 1998, which went into effect on 1 January 1999, created sixteen new voivodeships. These replaced the 49 former voivodeships that had existed from 1 July 1975, and bear a greater resemblance (in territory, but not in name) to the voivodeships that existed between 1950 and 1975. Today's voivodeships are mostly named after historical and geographical regions, while those prior to 1998 generally took their names from the cities on which they were centered. The new units range in area from under (Opole Voivodeship) to over (Masovian Voivodeship), and in population from nearly one million (Opole Voivodeship) to over five million (Masovian Voivodeship). Administrative authority at th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
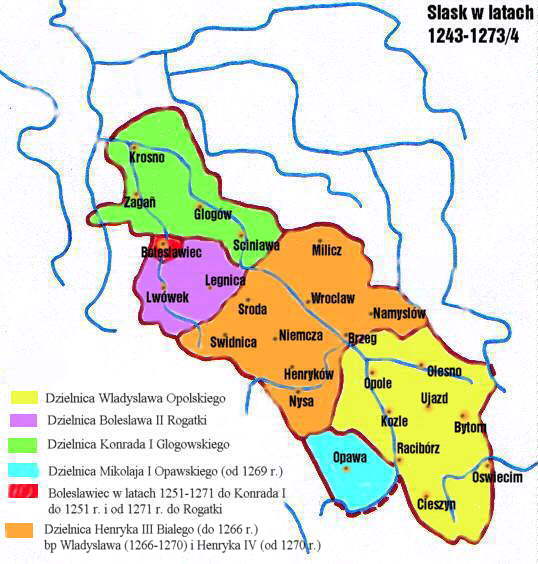
Silesia
Silesia (, also , ) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at around 8,000,000. Silesia is split into two main subregions, Lower Silesia in the west and Upper Silesia in the east. Silesia has a diverse culture, including architecture, costumes, cuisine, traditions, and the Silesian language (minority in Upper Silesia). Silesia is along the Oder River, with the Sudeten Mountains extending across the southern border. The region contains many historical landmarks and UNESCO World Heritage Sites. It is also rich in mineral and natural resources, and includes several important industrial areas. The largest city and Lower Silesia's capital is Wrocław; the historic capital of Upper Silesia is Opole. The biggest metropolitan area is the Upper Silesian metropolitan area, the centre of which is Katowice. Parts of the Czech city of Ostrav ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław Of Bytom
Władysław of Bytom (1277/83 – around 8 September 1352), was a Duke of Koźle during 1303-1334, Duke of Bytom from 1316, Duke of Toszek from 1329 and Duke of Siewierz during 1328–1337. He was the second son of Duke Casimir of Bytom by his wife Helena. Life Władysław's first official appearance was in 1289 on occasion of the homage of his father to King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia. In 1303 Władysław received from his father the town of Koźle. For unknown reasons, after his father's death in 1312 Władysław retained only Koźle, and the capital of the Duchy, Bytom was given to his younger brother Siemowit. Also, the two of Casimir I's sons who followed the church career also received further lands: Bolesław obtained Toszek and Mieszko received Siewierz (another brother, George was the co-ruler of Władysław, and in fact exercised the whole government). In 1316 Władysław assumed the government over Bytom. The circumstances around the removal of Siemowit are unknown, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kingdom Of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia ( cs, České království),; la, link=no, Regnum Bohemiae sometimes in English literature referred to as the Czech Kingdom, was a medieval and early modern monarchy in Central Europe, the predecessor of the modern Czech Republic. It was an Imperial State in the Holy Roman Empire, and the Bohemian king was a prince-elector of the empire. The kings of Bohemia, besides the region of Bohemia proper itself, also ruled other lands belonging to the Bohemian Crown, which at various times included Moravia, Silesia, Lusatia, and parts of Saxony, Brandenburg, and Bavaria. The kingdom was established by the Přemyslid dynasty in the 12th century from the Duchy of Bohemia, later ruled by the House of Luxembourg, the Jagiellonian dynasty, and from 1526 the House of Habsburg and its successor, the House of Habsburg-Lorraine. Numerous kings of Bohemia were also elected Holy Roman Emperors, and the capital, Prague, was the imperial seat in the late 14th century, and a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Kraków
Duchy of Kraków; Latin: ''Ducatus Cracoviensis'' was a duchy in Lesser Poland that existed from 1227 until 1300. Its capital was Kraków. It was formed in 1227 from the Seniorate Province, following the abolishment of the Duchy of Poland. It remained independent until 1300, when it had become a fiefdom within the Kingdom of Poland. In 1320, it was incorporated into the United Kingdom of Poland. History After the long-term power struggle Leszek the White was killed in 1227 and the Pomerelian lands got lost, when Duke Swietopelk II of Gdańsk declared himself independent. In 1232 the Silesian duke Henry I the Bearded finally prevailed, re-uniting the thrones of Wrocław and Kraków under his rule as determined by the will of late Duke Bolesław III Krzywousty in 1138. However, a re-establishment of the Polish kingdom under the rule of the Silesian Piasts failed, when Duke Henry's I son Henry II the Pious was killed during the Mongol invasion at the 1241 Battle of Legnica. Afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Wrocław
The Duchy of Silesia ( pl, Księstwo śląskie, german: Herzogtum Schlesien, cs, Slezské knížectví) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval duchy located in the historic Silesian region of Poland. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed to the Kingdom of Bohemia as Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin. Geography During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middle Oder river. In the south the Sudetes mountain range up to the Moravian Gate formed the border with the lands of Bohemia - including Kłodzko Land - and Moravia. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry IV Probus
Henryk IV Probus (Latin for ''the Righteous'') ( pl, Henryk IV Probus or ''Prawy''; german: Heinrich IV. der Gerechte) ( – 23 June 1290) was a member of the Silesian branch of the royal Polish Piast dynasty. He was Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1266, and from also 1288 High Duke of the Polish Seniorate Province of Kraków until his death in 1290. Life Henry IV was the only son of Duke Henry III the White of Silesia-Wrocław by his first wife Judith, daughter of Duke Konrad I of Masovia. Under the tutelage of Władysław of Salzburg and King Ottokar II of Bohemia A minor upon the early death of his father in 1266, Henry IV was placed under the guardianship of his paternal uncle, Archbishop Władysław of Salzburg. The Archbishop decided that the constant travels between Wrocław and Salzburg were inappropriate for a child, and, in 1267, sent Henry to Prague to be raised at the court of King Ottokar II of Bohemia. Ottokar after Władysław's death in 1270 also took ove ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mazovia
Mazovia or Masovia ( pl, Mazowsze) is a historical region in mid-north-eastern Poland. It spans the North European Plain, roughly between Łódź and Białystok, with Warsaw being the unofficial capital and largest city. Throughout the centuries, Mazovia developed a separate sub-culture featuring diverse folk songs, architecture, dress and traditions different from those of other Poles. Historical Mazovia existed from the Middle Ages until the partitions of Poland and consisted of three voivodeships with the capitals in Warsaw, Płock and Rawa. The main city of the region was Płock, which was even capital of Poland from 1079 to 1138; however, in Early Modern Times Płock lost its importance to Warsaw, which became the capital of Poland. From 1138, Mazovia was governed by a separate branch of the Piast dynasty and when the last ruler of the independent Duchy of Mazovia died, it was fully incorporated to the Polish Crown in 1526. During the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kujawy
Kuyavia ( pl, Kujawy; german: Kujawien; la, Cuiavia), also referred to as Cuyavia, is a historical region in north-central Poland, situated on the left bank of Vistula, as well as east from Noteć River and Lake Gopło. It is divided into three traditional parts: north-western (with the capital in Bydgoszcz, ethnographically regarded often as non-Kuyavian), central (the capital in Inowrocław or Kruszwica), and south-eastern (the capital in Włocławek or Brześć Kujawski). Etymology The name Kuyavia first appeared in written sources in the 1136 Bull of Gniezno ( pl, Bulla Gnieźnieńska, Latin: ''Ex commisso nobis'') issued by Pope Innocent II, and was then mentioned in many documents from medieval times. It is also mentioned in the chronicles of Wincenty Kadłubek. Geography In the north, Kuyavia borders with the historic regions of Gdańsk Pomerania (Pomerelia) and Chełmno Land, in the west with proper (exact) Greater Poland, in the south with Łęczyca Land and in the east ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Władysław I The Elbow-high
Władysław is a Polish given male name, cognate with Vladislav. The feminine form is Władysława, archaic forms are Włodzisław (male) and Włodzisława (female), and Wladislaw is a variation. These names may refer to: Famous people Mononym * Włodzisław, Duke of Lendians (10th century) *Władysław I Herman (ca. 1044–1102), Duke of Poland * Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), High Duke of Poland and Duke of Silesia *Władysław III Spindleshanks (1161/67–1231), Duke of Poland *Władysław Opolski (1225/1227-1281/1282), Polish duke *Władysław of Salzburg (1237–1270), Polish Roman Catholic archbishop *Władysław I the Elbow-high (1261–1333), King of Poland *Władysław of Oświęcim (c. 1275–1324), Duke of Oświęcim *Władysław of Bytom (c. 1277–c. 1352), Polish noble *Władysław of Legnica (1296–after 1352), Duke of Legnica *Władysław the Hunchback (c. 1303-c. 1352), Polish prince *Władysław the White (c. 1327–1388), Duke of Gniewkowo * Władysła ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magdeburg Rights
Magdeburg rights (german: Magdeburger Recht; also called Magdeburg Law) were a set of town privileges first developed by Otto I, Holy Roman Emperor (936–973) and based on the Flemish Law, which regulated the degree of internal autonomy within cities and villages granted by the local ruler. Named after the German city of Magdeburg, these town charters were perhaps the most important set of medieval laws in Central Europe. They became the basis for the German town laws developed during many centuries in the Holy Roman Empire. The Magdeburg rights were adopted and adapted by numerous monarchs, including the rulers of Bohemia, Hungary, Poland and Lithuania, a milestone in the urbanization of the region which prompted the development of thousands of villages and cities. Provisions Being a member of the Hanseatic League, Magdeburg was one of the most important trade cities, maintaining commerce with the Low Countries, the Baltic states, and the interior (for example Braunschweig). ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


_Tafel_03.png)