Duchy Of Wrocław on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Silesia (, ) with its capital at
 Henry II in 1239 had to resign the regency of Upper Silesia in favour of his cousin
Henry II in 1239 had to resign the regency of Upper Silesia in favour of his cousin
 * Władysław the Exile (1138–1146), progenitor of the
* Władysław the Exile (1138–1146), progenitor of the
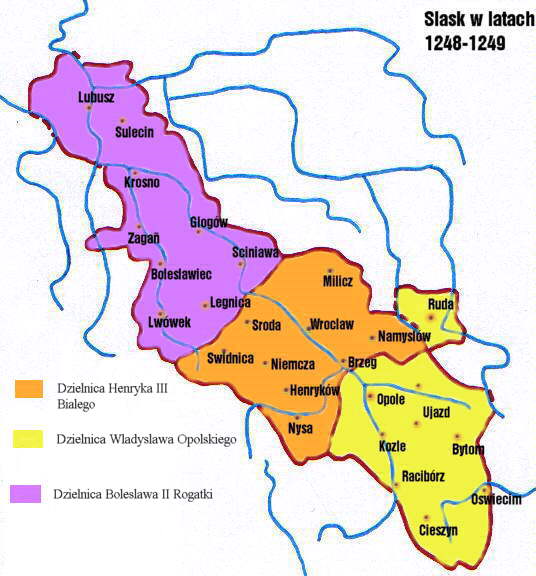
File:Silesia 1248-1249.jpg, 1248–1249
File:Silesia 1249-1273.jpg, 1249–1273
File:Silesia 1273-1277.jpg, 1273–1277
File:Silesia 1277-1278.jpg, 1277–1278
File:Silesia 1278-1281.jpg, 1278–1281
File:Silesia 1281-1284.jpg, 1281–1284
File:Silesia 1284-1287.jpg, 1284–1287
File:Silesia 1287-1290.jpg, 1287–1290
File:Silesia 1290-1291.jpg, 1290–1291
File:Silesia 1294-1296.jpg, 1294–1296
File:Silesia 1296-1301.jpg, 1296–1301
File:Silesia 1306-1309.jpg, 1306–1309
File:Silesia 1309-1311.jpg, 1309–1311
File:Silesia 1312-1317.PNG, 1312–1317
File:Silesia 1317-1321.PNG, 1317–1321
File:Silesia 1322-1331.PNG, 1322–1331
Oppeln, Herzöge v.
' In:
Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
was a medieval provincial duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a country, territory, fiefdom, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or Queen regnant, queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important differe ...
of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
located in the region of Silesia
Silesia (see names #Etymology, below) is a historical region of Central Europe that lies mostly within Poland, with small parts in the Czech Silesia, Czech Republic and Germany. Its area is approximately , and the population is estimated at 8, ...
. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty
The House of Piast was the first historical ruling dynasty of Poland. The first documented List of Polish monarchs, Polish monarch was Duke Mieszko I of Poland, Mieszko I (–992). The Poland during the Piast dynasty, Piasts' royal rule in Pol ...
in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth, Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's Testament of Bolesław III Krzy ...
passed under the suzerainty of the Kingdom of Bohemia
The Kingdom of Bohemia (), sometimes referenced in English literature as the Czech Kingdom, was a History of the Czech lands in the High Middle Ages, medieval and History of the Czech lands, early modern monarchy in Central Europe. It was the pr ...
as the Duchies of Silesia
The Duchies of Silesia were the more than twenty divisions of the region of Silesia formed between the 12th and 14th centuries by the breakup of the Duchy of Silesia, then part of the Kingdom of Poland. In 1335, the duchies were ceded to the King ...
. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great
Casimir III the Great (; 30 April 1310 – 5 November 1370) reigned as the King of Poland from 1333 to 1370. He also later became King of Ruthenia in 1340, retaining the title throughout the Galicia–Volhynia Wars. He was the last Polish king fr ...
of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin.
Geography
During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middleOder
The Oder ( ; Czech and ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and its largest tributary the Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows through wes ...
river. In the south the Sudetes
The Sudetes ( ), also known as the Sudeten Mountains or Sudetic Mountains, is a geomorphological subprovince of the Bohemian Massif province in Central Europe, shared by the Czech Republic, Poland and Germany. They consist mainly of mountain rang ...
mountain range up to the Moravian Gate
The Moravian Gate (, , , ) is a geomorphological feature in the Moravian region of the Czech Republic and the Upper Silesia region in Poland. It is formed by the depression between the Carpathian Mountains in the east and the Sudetes in the west. ...
formed the border with the lands of Bohemia
Bohemia ( ; ; ) is the westernmost and largest historical region of the Czech Republic. In a narrow, geographic sense, it roughly encompasses the territories of present-day Czechia that fall within the Elbe River's drainage basin, but historic ...
– including Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land (; ; ) is a historical region in southwestern Poland.
The subject of Czech–Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with periods of rule of the Polish Piast dynasty in th ...
– and Moravia
Moravia ( ; ) is a historical region in the eastern Czech Republic, roughly encompassing its territory within the Danube River's drainage basin. It is one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The medieval and early ...
. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian duke Soběslav I
Soběslav (; ) is a town in Tábor District in the South Bohemian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 7,100 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected as an Cultural monument (Czech Republic)#Monument zones, ur ...
. In the west Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław.
The first ...
bordered on the German March of Lusatia
The March or Margraviate of Lusatia () was an eastern border march of the Holy Roman Empire in the lands settled by Polabian Slavs. It arose in 965 in the course of the partition of the vast ''Marca Geronis''. Ruled by several Saxon margravial dy ...
(later Lower Lusatia
Lower Lusatia (; ; ; ; ) is a historical region in Central Europe, stretching from the southeast of the Germany, German state of Brandenburg to the southwest of Lubusz Voivodeship in Poland. Like adjacent Upper Lusatia in the south, Lower Lusa ...
) and the former Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni (; ; ) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were gradually conquered by Germans during the 10th century. They were part of Sorbian tribes. Modern descendants of the Milceni are ...
lands around Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin (), until 1868 ''Budissin'' in German, is a town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the Bautzen (district), district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree (river), Spree river, is the eighth most ...
(later Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
) with the boundary running along the Bóbr and Kwisa rivers. Silesia was limited by the Polish provinces of Greater Poland
Greater Poland, often known by its Polish name Wielkopolska (; ), is a Polish Polish historical regions, historical region of west-central Poland. Its chief and largest city is Poznań followed by Kalisz, the oldest city in Poland.
The bound ...
in the north and the Seniorate Province
Seniorate Province, also known as the Senioral Province, was a district principality in the Duchy of Poland that was formed in 1138, following the fragmentation of the state.Kwiatkowski, Richard. The Country That Refused to Die: The Story of t ...
of Lesser Poland
Lesser Poland, often known by its Polish name ''Małopolska'' (; ), is a historical region situated in southern and south-eastern Poland. Its capital and largest city is Kraków. Throughout centuries, Lesser Poland developed a separate cult ...
in the east, separated by the Przemsza
The Przemsza () is a river in the south of Poland, and a tributary of the Vistula. According to one view, it originates at the confluence of the Black () Przemsza and White (''Biała'') Przemsza, between the towns of Mysłowice and Jaworzno. For ...
and Biała rivers.
The boundaries varied slightly in the following decades: at least when the duchy was re-established for the sons of Władysław II the Exile
Władysław II the Exile (; 1105 – 30 May 1159) was the high duke of Poland and duke of Silesia from 1138 until his expulsion in 1146. He is the progenitor of the Silesian Piasts.
Governor of Silesia
He was the eldest son of Duke Bolesław III W ...
in 1163 (see below), it also comprised Lubusz Land
Lubusz Land (; ) is a historical region and cultural landscape in Poland and Germany on both sides of the Oder river.
Originally the settlement area of the Lechites, the swampy area was located east of Margraviate of Brandenburg, Brandenburg and ...
northwest of Krosno
Krosno (in full ''The Royal Free City of Krosno'', ) is a historical town and Krosno County, county in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship, in southeastern Poland. The estimated population of the town is 47,140 inhabitants as of 2014.
The functional ...
, which had been the western outpost of Greater Poland and passed to the margraves of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
in 1248. In 1177 the Polish High Duke Casimir II the Just
Casimir II the Just (; 28 October 1138 – 5 May 1194) was a Lesser Polish Duke of Wiślica from 1166 to 1173, and of Sandomierz after 1173. He became ruler over the Polish Seniorate Province at Kraków and thereby High Duke of Poland in 1177; a ...
attached the former Lesser Polish castellanies of Bytom
Bytom (Polish pronunciation: ; Silesian language, Silesian: ''Bytōm, Bytōń'', ) is a city in Upper Silesia, in southern Poland. Located in the Silesian Voivodeship, the city is 7 km northwest of Katowice, the regional capital.
It is one ...
, Oświęcim
Oświęcim (; ; ; ) is a town in the Lesser Poland Voivodeship in southern Poland, situated southeast of Katowice, near the confluence of the Vistula (''Wisła'') and Soła rivers.
Oświęcim dates back to the 12th century, when it was an im ...
, Zator, Siewierz und Pszczyna
Pszczyna (, ) is a town in Silesia Province in Poland, with a population of 25,823 (2019), and is the seat of a local gmina (commune) and district.
It was previously part of Katowice Province from 1975 until 1998 administrative reforms.
Etymo ...
to Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
in favour of Duke Mieszko IV Tanglefoot
Mieszko IV Tanglefoot () (c. 1130 – 16 May 1211) was Duke of Kraków and High Duke of Poland from 9 June 1210 until his death one year later. He was also Duke of Silesia from 1163 to 1173 (with his brother as co-ruler), Duke of Racibórz fr ...
. After Silesia as a whole had become a Bohemian fief according to the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin, these lordships – except for the state countries of Bytom and Pszczyna – returned to the Polish Crown.
History
As the Silesian Province (), the duchy was one of five main provinces established in medieval Poland according to theTestament of Bolesław III Krzywousty
A testament is a document that the author has sworn to be true. In law it usually means last will and testament.
Testament or The Testament can also refer to:
Books
* ''Testament'' (comic book), a 2005 comic book
* ''Testament'', a thriller nov ...
. By the terms of the will from 1138–1146 it was controlled by the Senior Duke of Poland or High duke, Bolesław's first-born son Władysław II the Exile
Władysław II the Exile (; 1105 – 30 May 1159) was the high duke of Poland and duke of Silesia from 1138 until his expulsion in 1146. He is the progenitor of the Silesian Piasts.
Governor of Silesia
He was the eldest son of Duke Bolesław III W ...
, who also held the Duchy of Kraków.
The testament however failed to prevent a violent inheritance conflict between Władysław and his younger half-brothers, who allied against him. After his failed bid to take control of the entire Kingdom in 1146, he lost his status as the senior duke, was excommunicated by Archbishop Jakub ze Żnina of Gniezno
Gniezno (; ; ) is a city in central-western Poland, about east of Poznań. Its population in 2021 was 66,769, making it the sixth-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship. The city is the administrative seat of Gniezno County (''powiat'') ...
and fled to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
. The duchy was then under control of his half-brother High Duke Bolesław IV the Curly
Bolesław IV the Curly (; 1122 – 5 January 1173), a member of the Piast dynasty, was Duke of Masovia from 1138 and High Duke of Poland from 1146 until his death in 1173.
Early life
Bolesław was the third son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth ...
.
With support from Emperor Frederick I Barbarossa
Frederick Barbarossa (December 1122 – 10 June 1190), also known as Frederick I (; ), was the Holy Roman Emperor from 1155 until his death in 1190. He was elected King of Germany in Frankfurt am Main, Frankfurt on 4 March 1152 and crowned in Aa ...
, who had campaigned in Greater Poland in 1157 and forced Bolesław IV to cede Silesia, Władysław's sons were able to return to the duchy in 1163. As long as they were under pressure by High Duke Bolesław IV, they ruled jointly at Wrocław
Wrocław is a city in southwestern Poland, and the capital of the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. It is the largest city and historical capital of the region of Silesia. It lies on the banks of the Oder River in the Silesian Lowlands of Central Eu ...
, until tensions between them erupted into an open conflict in 1172. As a result, the brothers divided the duchy among themselves; the first partition of many which led to the creation of numerous Silesian duchies in the following centuries:
* Władysław's eldest son, Bolesław I the Tall
Bolesław I the Tall (; 1127 – 7 or 8 December 1201) was Duke of Wrocław from 1163 until his death in 1201.
Early years
Boleslaw was the eldest son of Władysław II the Exile by his wife Agnes of Babenberg, daughter of Margrave Leopold II ...
, received Lower Silesia
Lower Silesia ( ; ; ; ; ; ; ; ) is a historical and geographical region mostly located in Poland with small portions in the Czech Republic and Germany. It is the western part of the region of Silesia. Its largest city is Wrocław.
The first ...
with Wrocław as his residence; therefore his estates are sometimes already referred to as Duchy of Wrocław.
* The second son, Mieszko I Tanglefoot, received a far smaller part in Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( ; ; ; ; Silesian German: ; ) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, located today mostly in Poland, with small parts in the Czech Republic. The area is predominantly known for its heav ...
and took his residence at Racibórz
Racibórz (, , , ) is a city in Silesian Voivodeship in southern Poland. It is the administrative seat of Racibórz County.
With Opole, Racibórz is one of the historic capitals of Upper Silesia, being the residence of the Duchy of Racibórz, Du ...
; this resulted in the creation of the Duchy of Racibórz
Duchy of Racibórz (, , ) was one of the duchies of Silesia, formed during the medieval fragmentation of Poland into provincial duchies. Its capital was Racibórz in Upper Silesia.
States and territories disestablished in the 1200s
States and ...
. In view of his disadvantage, the Polish High Duke Casimir II the Just ceded him further Lesser Polish territories in 1177 (see above).
After a revolt by Bolesław's eldest son, Jarosław
Jarosław (; , ; ; ) is a town in southeastern Poland, situated on the San (river), San River. The town had 35,475 inhabitants in 2023. It is the capital of Jarosław County in the Subcarpathian Voivodeship.
History
Jarosław is located in the ...
, who feared for his heritage, his father ceded him a strip of land around Opole
Opole (; ; ; ) is a city located in southern Poland on the Oder River and the historical capital of Upper Silesia. With a population of approximately 127,387 as of the 2021 census, it is the capital of Opole Voivodeship (province) and the seat of ...
, for the first time creating the Duchy of Opole
The Duchy of Opole (; ) or Duchy of Oppeln () was one of the duchies of Silesia ruled by the branch of Polish Piast dynasty, formed during the medieval fragmentation of Poland into provincial duchies. Its capital was Opole () in Upper Silesia.
S ...
. In turn Jarosław had to prepare for an ecclesiastical career and remain celibate
Celibacy (from Latin ''caelibatus'') is the state of voluntarily being unmarried, sexually abstinent, or both. It is often in association with the role of a religious official or devotee. In its narrow sense, the term ''celibacy'' is applied on ...
. Likewise Bolesław's and Mieszko's youngest brother, Konrad Spindleshanks, when he came of age claimed his rights and about 1177 received the Lower Silesian lands around Głogów
Głogów (; , rarely , ) is a city in western Poland. It is the county seat of Głogów County, in Lower Silesian Voivodeship. Głogów is the sixth largest town in the Voivodeship; its population in 2021 was 65,400.
Among the oldest towns in Po ...
; leading to the first creation of the Duchy of Głogów
The Duchy of Głogów (, ) or Duchy of Glogau () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed in course of the medieval fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia. It existed in 1177–1185 an ...
. However, Bolesław I outlived both his youngest brother and his son, and both territories fell back to him in 1190 and 1201 resp.
Bolesław I died in the same year and was succeeded by his only surviving son Henry I the Bearded
Henry the Bearded (, ; c. 1165/70 – 19 March 1238) was a Polish duke from the Piast dynasty.
He was Dukes of Silesia, Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1201, Seniorate Province, Duke of Kraków and List of Polish monarchs, High Duke of all Kin ...
, who soon entered into conflict with his Piast relatives as well as with his German neighbours. In 1202 he had to face the invasion of his uncle Mieszko I, who, still dissatisfied with the 1172 partition, annexed the Opole territory of late Jarosław. The Duchy of Opole remained with the estates of Mieszko's descendants, whereby the secession of Upper Silesia was conclusive. In 1206 Henry I came to an agreement with the Polish High Duke Władysław III Spindleshanks to swap Lubusz Land for the Greater Polish Kalisz
Kalisz () is a city in central Poland, and the second-largest city in the Greater Poland Voivodeship, with 97,905 residents (December 2021). It is the capital city of the Kalisz Region. Situated on the Prosna river in the southeastern part of Gr ...
region. The plan however was foiled, when Władysław III lost the seniorate and furthermore Lubusz was occupied by the troops of the Wettin margrave Conrad II of Lusatia. Duke Henry had to struggle for his northwestern outpost, which he regained upon the margrave's death in 1210. He had to defend Lubusz once more against the campaigns of Landgrave Louis IV of Thuringia
Louis IV the Saint (; 28 October 1200 – 11 September 1227), a member of the Ludovingian dynasty, was Landgrave of Thuringia and Saxon Count palatine from 1217 until his death. He was the husband of Elizabeth of Hungary.
Biography
Louis wa ...
from 1221. Upon the death of his cousin Duke Casimir I of Opole
Casimir I of Opole (; – 13 May 1230), a member of the Silesian Piasts, Piast dynasty, was a Dukes of Silesia, Silesian duke of Duchy of Opole and Racibórz, Opole and Racibórz from 1211 until his death.
Early life
Casimir was the eldest chi ...
, son of Mieszko I Tanglefoot, in 1230, he acted as guardian of his minor nephews, thereby once again ruling over whole Silesia. In 1232 he became High Duke of Poland, and as he was able to secure the succession of his son Henry II the Pious
Henry II the Pious (; 1196 – 9 April 1241) was Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland as well as Duke of South-Greater Poland from 1238 until his death. Between 1238 and 1239 he also served as regent of Sandomierz and Opole– Racibórz. He ...
upon his death in 1238, it seemed that the Polish fragmentation could be overcome and the will of Bolesław III Krzywousty would finally be fulfilled.
 Henry II in 1239 had to resign the regency of Upper Silesia in favour of his cousin
Henry II in 1239 had to resign the regency of Upper Silesia in favour of his cousin Mieszko II the Fat
Mieszko II the Fat () ( – 22 October 1246) was a Duke of Opole-Racibórz from 1230 until his death, and Duke of Kalisz-Wieluń during 1234–1239 (with his brother as co-ruler).
He was the eldest son of Duke Casimir I of Opole by his wife Viola ...
. He anew defended Lubusz, this time against the forces of the Ascanian margraves of Brandenburg
Brandenburg, officially the State of Brandenburg, is a States of Germany, state in northeastern Germany. Brandenburg borders Poland and the states of Berlin, Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony. It is the List of Ger ...
, and in 1241 granted it to his second son Mieszko
Mieszko is a Slavic given name of uncertain origin.
Onomastics
There are three major theories concerning the origin and meaning of the name of Duke Mieszko I of Poland. The most popular theory, proposed by Jan Długosz, explains that Mieszko is a ...
. The hopes for a re-unification of the Polish lands under the Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth, Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's Testament of Bolesław III Krzy ...
ended with the Mongol invasion of Poland and Henry's death at the 1241 Battle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the ci ...
. His eldest son Bolesław II the Bald could not prevail as High Duke against Bolesław V the Chaste
Bolesław V the Chaste (; 21 June 1226 – 7 December 1279) was Duke of Sandomierz in Lesser Poland from 1232 and High Duke of Poland from 1243 until his death, as the last male representative of the Lesser Polish branch of Piasts.
Birth and n ...
of Lesser Poland and, after he regained Lubusz upon the death of his brother Mieszko in 1242, finally had to divide his Silesian heritage with his younger brothers in 1248:
* Bolesław II himself took his residence in the west at Legnica
Legnica (; , ; ; ) is a city in southwestern Poland, in the central part of Lower Silesia, on the Kaczawa River and the Czarna Woda. As well as being the seat of the county, since 1992 the city has been the seat of the Diocese of Legnica. Le ...
, thereby establishing the Duchy of Legnica
The Duchy of Legnica (, ) or Duchy of Liegnitz () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed during the fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies, ruled by a local line of the Piast dynasty between 1248 and 1675. Its capital was Legni ...
together with his youngest brother Konrad. Soon after he sold Lubusz to the Brandenburg margraves, who finally gained a foothold beyond the Oder to establish the Neumark
The Neumark (), also known as the New March () or as East Brandenburg (), was a region of the Margraviate of Brandenburg and its successors located east of the Oder River in territory which became part of Poland in 1945 except some villages o ...
region. In 1251 Konrad, actually elected Bishop of Passau
The Diocese of Passau (; ) is a Latin diocese of the Catholic Church in Germany that is a suffragan of the Archdiocese of Munich and Freising.Duchy of Głogów
The Duchy of Głogów (, ) or Duchy of Glogau () was one of the Duchies of Silesia, formed in course of the medieval fragmentation of Poland into smaller provincial duchies. Its capital was Głogów in Lower Silesia. It existed in 1177–1185 an ...
to him.
* The residence of Wrocław fell to his younger brothers Henry III the White and Władysław, thereby establishing the Duchy of Wrocław proper.
The subdivision of the Silesian duchies increased over the following generations and accompanied the fragmentation of Poland
The period of rule by the Piast dynasty between the 10th and 14th centuries is the first major stage of the history of Poland, history of the Polish state. The dynasty was founded by a series of dukes listed by the chronicler Gall Anonymous in t ...
. Henry's III son Henry IV Probus upon the death of his uncle Władysław in 1270 ruled at Wrocław and in 1288 even became High Duke of Poland, until the male line became extinct with his death in 1290. He was succeeded by his cousin Duke Henry V the Fat, son of Henry's III brother Bolesław II, who once again re-united the duchies of Wrocław and Legnica under his personal rule. The duchy lost its southern territories in 1290–1291, i.e. the Kłodzko Land
Kłodzko Land (; ; ) is a historical region in southwestern Poland.
The subject of Czech–Polish rivalry in the High Middle Ages, it became a Bohemian domain since the 12th century, although with periods of rule of the Polish Piast dynasty in th ...
, which passed to Bohemia, and the towns of Świdnica
Świdnica (; ; ) is a city on the Bystrzyca (Oder), Bystrzyca River in south-western Poland in the Lower Silesian Voivodeship. As of 2021, it has a population of 55,413 inhabitants. It is the seat of Świdnica County, and also of the smaller dis ...
, Rychbach, Ząbkowice, Ziębice
Ziębice () is a town in Ząbkowice Śląskie County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies on the Oława River, approximately east of Ząbkowice Śląskie and south of the regional capital Wrocław. It is the seat of t ...
and Strzelin
Strzelin (, ) is a town in Lower Silesian Voivodeship in south-western Poland. It is located on the Oława river, a tributary of the Oder, about south of the region's capital Wrocław. It is part of the Wrocław metropolitan area.
The town i ...
, which passed to the Duchy of Jawor
Duchy of Jawor (, ) was one of the duchies of Silesia and medieval Poland established in 1274 as a subdivision of the Duchy of Legnica. It was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, with its capital at Jawor in Lower Silesia.
It was the southwesternmost ...
after Duke Bolko I the Strict
Bolko (Bolesław) I the Strict, also known as Bolko (Bolesław) of Jawor ( or ''Srogi'' or ''Jaworski''; 1252/56 – 9 November 1301), was a Duke of Lwówek Śląski, Lwówek 1278–81 (with his brother as co-ruler) and Duchy of Jawor, Jawor after ...
of Jawor supported Henry V's assumption of the Duchy of Wrocław. Nevertheless, upon the death of Henry V in 1296, his heritage was again partitioned among his sons. The second, Duke Henry VI the Good
Henry VI the Good (also known as of Wrocław or of Breslau) (; ) (18 March 1294 – 24 November 1335) was a Duke of Wrocław from 1296 (with his brothers as co-rulers until 1311).
He was the second son of Henry V the Fat, Duke of Legnica and W ...
, in order to ward off claims raised by his elder brother Duke Bolesław III the Generous
Bolesław or Boleslav may refer to:
People
* Bolesław (given name) (also ''Boleslav'' or ''Boleslaus''), including a list of people with this name
Geography
* Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Olkusz Coun ...
of Legnica, in 1327 signed an inheritance treaty with King John of Bohemia
John of Bohemia, also called the Blind or of Luxembourg (; ; ; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of Poland. He is well known for having died while fighting ...
, like most of the Silesian duchies had been vassalized by the Kingdom of Bohemia in the early 14th century. As the Polish king Casimir III in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin had renounced Silesia, Henry's VI duchy passed without opposition to the Bohemian kingdom when he died without male heirs three months later.
Silesia was incorporated into the Lands of the Bohemian Crown
The Lands of the Bohemian Crown were the states in Central Europe during the Middle Ages, medieval and early modern periods with feudalism, feudal obligations to the List of Bohemian monarchs, Bohemian kings. The crown lands primarily consisted o ...
under the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire, also known as the Holy Roman Empire of the German Nation after 1512, was a polity in Central and Western Europe, usually headed by the Holy Roman Emperor. It developed in the Early Middle Ages, and lasted for a millennium ...
, after King Casimir III had acknowledged the acquisition by the 1348 Treaty of Namslau with King Charles IV — except for the Upper Silesian duchies of Oświęcim and Zator, which in the 16th century were integrated in the Polish Kraków Voivodeship, as well as the Duchy of Siewierz, that was purchased by the Archbishop of Kraków
The archbishop of Kraków is the head of the archdiocese of Kraków. A bishop of Kraków first came into existence when the diocese was created in 1000; it was promoted to an archdiocese on 28 October 1925. Due to Kraków's role as Poland's politic ...
in 1443. Thus started the tine of attachment of Silesia to Germany, which was to last until 1945.
Dukes
 * Władysław the Exile (1138–1146), progenitor of the
* Władysław the Exile (1138–1146), progenitor of the Silesian Piasts
The Silesian Piasts were the elder of four lines of the Polish Piast dynasty beginning with Władysław II the Exile (1105–1159), eldest son of Duke Bolesław III Wrymouth, Bolesław III of Poland. By Bolesław's Testament of Bolesław III Krzy ...
, also High Duke of Poland
Poland was ruled at various times either by dukes and princes (10th to 14th centuries) or by kings (11th to 18th centuries). During the latter period, a tradition of Royal elections in Poland, free election of monarchs made it a uniquely electab ...
, deposed
** Bolesław the Curly (1146–1163), stepbrother
* Bolesław I the Tall
Bolesław I the Tall (; 1127 – 7 or 8 December 1201) was Duke of Wrocław from 1163 until his death in 1201.
Early years
Boleslaw was the eldest son of Władysław II the Exile by his wife Agnes of Babenberg, daughter of Margrave Leopold II ...
, eldest son of Władysław, re-installed (1163–1201)
* Henry I the Bearded
Henry the Bearded (, ; c. 1165/70 – 19 March 1238) was a Polish duke from the Piast dynasty.
He was Dukes of Silesia, Duke of Silesia at Wrocław from 1201, Seniorate Province, Duke of Kraków and List of Polish monarchs, High Duke of all Kin ...
(1201–1238), son, also High Duke of Poland from 1232
* Henry II the Pious
Henry II the Pious (; 1196 – 9 April 1241) was Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland as well as Duke of South-Greater Poland from 1238 until his death. Between 1238 and 1239 he also served as regent of Sandomierz and Opole– Racibórz. He ...
(1238–1241), son, also High Duke of Poland, killed in Battle of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the ci ...
* Bolesław II the Bald (1241–1248), son, became Duke of Legnica in 1248 partition
* Henry III the White (1248–1266), brother, jointly with
** Władysław (1248–1270), brother, also Prince-Archbishop of Salzburg
The Prince-Archbishopric of Salzburg (; ) was an ecclesiastical principality and state of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the secular territory ruled by the archbishops of Salzburg, as distinguished from the much larger Catholic diocese f ...
from 1265
* Henry IV Probus (1266–1290), son of Henry III, Duke of Wrocław from 1270, also High Duke of Poland from 1288, no issue
* Henry V the Fat (1290–1296), son of Bolesław II, Duke of Legnica since 1278
* Henry VI the Good
Henry VI the Good (also known as of Wrocław or of Breslau) (; ) (18 March 1294 – 24 November 1335) was a Duke of Wrocław from 1296 (with his brothers as co-rulers until 1311).
He was the second son of Henry V the Fat, Duke of Legnica and W ...
(1296–1335), second son, under tutelage of:
** Bolko I the Strict
Bolko (Bolesław) I the Strict, also known as Bolko (Bolesław) of Jawor ( or ''Srogi'' or ''Jaworski''; 1252/56 – 9 November 1301), was a Duke of Lwówek Śląski, Lwówek 1278–81 (with his brother as co-ruler) and Duchy of Jawor, Jawor after ...
(1296–1301), son of Bolesław II
** King Wenceslaus II of Bohemia
Wenceslaus II Přemyslid (; ; 27 SeptemberK. Charvátová, ''Václav II. Král český a polský'', Prague 2007, p. 18. 1271 – 21 June 1305) was King of Bohemia (1278–1305), Duke of Cracow (1291–1305), and King of Poland (1296–130 ...
(1301–1305)
** Bolesław III the Generous
Bolesław or Boleslav may refer to:
People
* Bolesław (given name) (also ''Boleslav'' or ''Boleslaus''), including a list of people with this name
Geography
* Bolesław, Dąbrowa County, Lesser Poland Voivodeship, Poland
* Bolesław, Olkusz Coun ...
(1305–1311), eldest son of Henry V, Duke of Legnica since 1296
As Henry VI left no male heirs, his lands were inherited by King John of Bohemia
John of Bohemia, also called the Blind or of Luxembourg (; ; ; 10 August 1296 – 26 August 1346), was the Count of Luxembourg from 1313 and King of Bohemia from 1310 and titular King of Poland. He is well known for having died while fighting ...
.
Maps
The following maps illustrate continuing fragemtarization of the Duchy of Silesia, and shifting borders of the individual smaller duchies.Aftermath
After the inheritance of Bohemia by theHouse of Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (; ), also known as the House of Austria, was one of the most powerful Dynasty, dynasties in the history of Europe and Western civilization. They were best known for their inbreeding and for ruling vast realms throughout ...
in 1526, the Silesian duchies gradually passed under control of the Austrian Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy, also known as Habsburg Empire, or Habsburg Realm (), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities (composite monarchy) that were ruled by the House of Habsburg. From the 18th century it is ...
until King Frederick II of Prussia
Frederick II (; 24 January 171217 August 1786) was the monarch of Prussia from 1740 until his death in 1786. He was the last Hohenzollern monarch titled ''King in Prussia'', declaring himself '' King of Prussia'' after annexing Royal Prus ...
invaded Silesia in 1740 and annexed most of it during the First Silesian War
The First Silesian War () was a war between Kingdom of Prussia, Prussia and Habsburg monarchy, Austria that lasted from 1740 to 1742 and resulted in Prussia's seizing most of the region of Silesia (now in south-western Poland) from Austria. The ...
. The bulk of the duchy, enlarged by the County of Kladsko and Upper Lusatia
Upper Lusatia (, ; , ; ; or ''Milsko''; ) is a historical region in Germany and Poland. Along with Lower Lusatia to the north, it makes up the region of Lusatia, named after the Polabian Slavs, Slavic ''Lusici'' tribe. Both parts of Lusatia a ...
n territories annexed from Saxony
Saxony, officially the Free State of Saxony, is a landlocked state of Germany, bordering the states of Brandenburg, Saxony-Anhalt, Thuringia, and Bavaria, as well as the countries of Poland and the Czech Republic. Its capital is Dresden, and ...
, was subsequently reorganized as part of the Prussian Province of Silesia
The Province of Silesia (; ; ) was a province of Prussia from 1815 to 1919. The Silesia region was part of the Prussian realm since 1742 and established as an official province in 1815, then became part of the German Empire in 1871. In 1919, as ...
, while the duchies remaining under Austrian control were reconstituted as the Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia in 1742. The duchies which had remained in Poland were subsequently annexed by the Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (, ) was a German state that existed from 1701 to 1918.Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. Rev. ed. Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1946. It played a signif ...
( New Silesia) and the Habsburg monarchy ( Galicia) during the 18th century Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partition (politics), partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place between 1772 and 1795, toward the end of the 18th century. They ended the existence of the state, resulting in the eli ...
. The Duchy of Upper and Lower Silesia lasted as a crown land of Cisleithania
Cisleithania, officially The Kingdoms and Lands Represented in the Imperial Council (), was the northern and western part of Austria-Hungary, the Dual Monarchy created in the Compromise of 1867—as distinguished from ''Transleithania'' (i.e., ...
n Austria until 1918, whereupon it was divided between the Second Polish Republic
The Second Polish Republic, at the time officially known as the Republic of Poland, was a country in Central and Eastern Europe that existed between 7 October 1918 and 6 October 1939. The state was established in the final stage of World War I ...
( Autonomous Silesian Voivodeship) and Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
(Czech Silesia
Czech Silesia (; ) is the part of the historical region of Silesia now in the Czech Republic. While it currently has no formal boundaries, in a narrow geographic sense, it encompasses most or all of the territory of the Czech Republic within the ...
) after the Polish–Czechoslovak War of 1919.
References
* Hugo Weczerka: '' Handbuch der historischen Stätten: Schlesien''. Stuttgart, 1977, , S. XXXIV–XXXVII sowie Stammtafel auf p. 590. * Rudolf Žáček: ''Dějiny Slezska v datech''. Praha 2004, , S. 444. * Ulrich Schmilewski:Oppeln, Herzöge v.
' In:
Neue Deutsche Biographie
(''NDB''; Literal translation, literally ''New German Biography'') is a Biography, biographical reference work. It is the successor to the ''Allgemeine Deutsche Biographie'' (ADB, Universal German Biography). The 27 volumes published thus far co ...
(NDB). Band 19, Duncker & Humblot, Berlín 1999, , p. 558 f.
* Historia Narodu Śląskiego. Prawdziwe dzieje ziem śląskich od średniowiecza do progu trzeciego tysiąclecia (History of Silesian Nation. True history of Silesian lands from the Middle Ages to the threshold of the third Millennium), Zabrze 2003 .
{{DEFAULTSORT:Silesia, Duchy Of
History of Poland during the Piast dynasty
14th century in Bohemia
Duchy
1138 establishments in Europe
12th-century establishments in Poland
1335 disestablishments in Europe
14th-century disestablishments in Poland
States and territories disestablished in the 1330s
Fiefdoms of Poland
Former monarchies of Europe
Former duchies