|
Set Inversion
In mathematics, set inversion is the problem of characterizing the preimage ''X'' of a set ''Y'' by a function ''f'', i.e., ''X'' = ''f'' −1(''Y'' ) = . It can also be viewed as the problem of describing the solution set of the quantified constraint "''Y''(''f'' (''x''))", where ''Y''( ''y'') is a constraint, e.g. an inequality, describing the set ''Y''. In most applications, ''f'' is a function from R''n'' to R''p'' and the set ''Y'' is a box of R''p'' (i.e. a Cartesian product of ''p'' intervals of R). When ''f'' is nonlinear the set inversion problem can be solved using interval analysis combined with a branch-and-bound algorithm. The main idea consists in building a paving of R''p'' made with non-overlapping boxes. For each box 'x'' we perform the following tests: # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ⊂ ''Y'' we conclude that 'x''⊂ ''X''; # if ''f'' ( 'x'' ∩ ''Y'' = ∅ we conclude that 'x''∩ ''X'' = ∅; # Otherwise, the box ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics with the major subdisciplines of number theory, algebra, geometry, and analysis, respectively. There is no general consensus among mathematicians about a common definition for their academic discipline. Most mathematical activity involves the discovery of properties of abstract objects and the use of pure reason to prove them. These objects consist of either abstractions from nature orin modern mathematicsentities that are stipulated to have certain properties, called axioms. A ''proof'' consists of a succession of applications of deductive rules to already established results. These results include previously proved theorems, axioms, andin case of abstraction from naturesome basic properties that are considered true starting poin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval Arithmetic
Interval arithmetic (also known as interval mathematics, interval analysis, or interval computation) is a mathematical technique used to put bounds on rounding errors and measurement errors in mathematical computation. Numerical methods using interval arithmetic can guarantee reliable and mathematically correct results. Instead of representing a value as a single number, interval arithmetic represents each value as a range of possibilities. For example, instead of saying the height of someone is approximately 2 meters, one could using interval arithmetic, say that the height of the person is definitely between 1.97 meters and 2.03 meters. Mathematically, using interval arithmetic, instead of working with an uncertain real-valued variable x, one works with an interval ,b/math> that defines the range of values that x can have. In other words, any value of the variable x lies in the closed interval between a and b. A function f, when applied to x, yields an inexact value; f in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Set Estimation
In statistics, a random vector ''x'' is classically represented by a probability density function. In a set-membership approach or set estimation, ''x'' is represented by a set ''X'' to which ''x'' is assumed to belong. This means that the support of the probability distribution function of ''x'' is included inside ''X''. On the one hand, representing random vectors by sets makes it possible to provide fewer assumptions on the random variables (such as independence) and dealing with nonlinearities is easier. On the other hand, a probability distribution function provides a more accurate information than a set enclosing its support. Set-membership estimation Set membership estimation (or ''set estimation'' for short) is an estimation approach which considers that measurements are represented by a set ''Y'' (most of the time a box of R''m'', where ''m'' is the number of measurements) of the measurement space. If ''p'' is the parameter vector and ''f'' is the model function, then ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Motion Planning
Motion planning, also path planning (also known as the navigation problem or the piano mover's problem) is a computational problem to find a sequence of valid configurations that moves the object from the source to destination. The term is used in computational geometry, computer animation, robotics and computer games. For example, consider navigating a mobile robot inside a building to a distant waypoint. It should execute this task while avoiding walls and not falling down stairs. A motion planning algorithm would take a description of these tasks as input, and produce the speed and turning commands sent to the robot's wheels. Motion planning algorithms might address robots with a larger number of joints (e.g., industrial manipulators), more complex tasks (e.g. manipulation of objects), different constraints (e.g., a car that can only drive forward), and uncertainty (e.g. imperfect models of the environment or robot). Motion planning has several robotics applications, su ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wiki Ring
A wiki ( ) is an online hypertext publication collaboratively edited and managed by its own audience, using a web browser. A typical wiki contains multiple pages for the subjects or scope of the project, and could be either open to the public or limited to use within an organization for maintaining its internal knowledge base. Wikis are enabled by wiki software, otherwise known as wiki engines. A wiki engine, being a form of a content management system, differs from other web-based systems such as blog software, in that the content is created without any defined owner or leader, and wikis have little inherent structure, allowing structure to emerge according to the needs of the users. Wiki engines usually allow content to be written using a simplified markup language and sometimes edited with the help of a rich-text editor. There are dozens of different wiki engines in use, both standalone and part of other software, such as bug tracking systems. Some wiki engines are open ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intersection (set Theory)
In set theory, the intersection of two sets A and B, denoted by A \cap B, is the set containing all elements of A that also belong to B or equivalently, all elements of B that also belong to A. Notation and terminology Intersection is written using the symbol "\cap" between the terms; that is, in infix notation. For example: \\cap\=\ \\cap\=\varnothing \Z\cap\N=\N \\cap\N=\ The intersection of more than two sets (generalized intersection) can be written as: \bigcap_^n A_i which is similar to capital-sigma notation. For an explanation of the symbols used in this article, refer to the table of mathematical symbols. Definition The intersection of two sets A and B, denoted by A \cap B, is the set of all objects that are members of both the sets A and B. In symbols: A \cap B = \. That is, x is an element of the intersection A \cap B if and only if x is both an element of A and an element of B. For example: * The intersection of the sets and is . * The number 9 is i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interval Contractor
In mathematics, an interval contractor (or contractor for short) associated to a set X is an operator C which associates to a hyperrectangle /math> in \bold^n another box C( of \bold^n such that the two following properties are always satisfied: * C( \subset /math> (contractance property) * C( \cap X = \cap X (completeness property) A ''contractor associated to a constraint'' (such as an equation or an inequality) is a contractor associated to the set X of all x which satisfy the constraint. Contractors make it possible to improve the efficiency of branch-and-bound algorithms classically used in interval analysis. Properties of contractors A contractor ''C'' is monotonic if we have \subset \Rightarrow C( \subset C( . It is ''minimal'' if for all boxes 'x'' we have C( = xcap X], where 'A''is the ''interval hull'' of the set ''A'', i.e., the smallest box enclosing ''A''. The contractor ''C'' is ''thin'' if for all points ''x'', C(\) = \\cap X where denot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Union (set Theory)
In set theory, the union (denoted by ∪) of a collection of sets is the set of all elements in the collection. It is one of the fundamental operations through which sets can be combined and related to each other. A refers to a union of zero (0) sets and it is by definition equal to the empty set. For explanation of the symbols used in this article, refer to the table of mathematical symbols. Union of two sets The union of two sets ''A'' and ''B'' is the set of elements which are in ''A'', in ''B'', or in both ''A'' and ''B''. In set-builder notation, :A \cup B = \. For example, if ''A'' = and ''B'' = then ''A'' ∪ ''B'' = . A more elaborate example (involving two infinite sets) is: : ''A'' = : ''B'' = : A \cup B = \ As another example, the number 9 is ''not'' contained in the union of the set of prime numbers and the set of even numbers , because 9 is neither prime nor even. Sets cannot have duplicate elements, so the union of the sets and is . Multi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
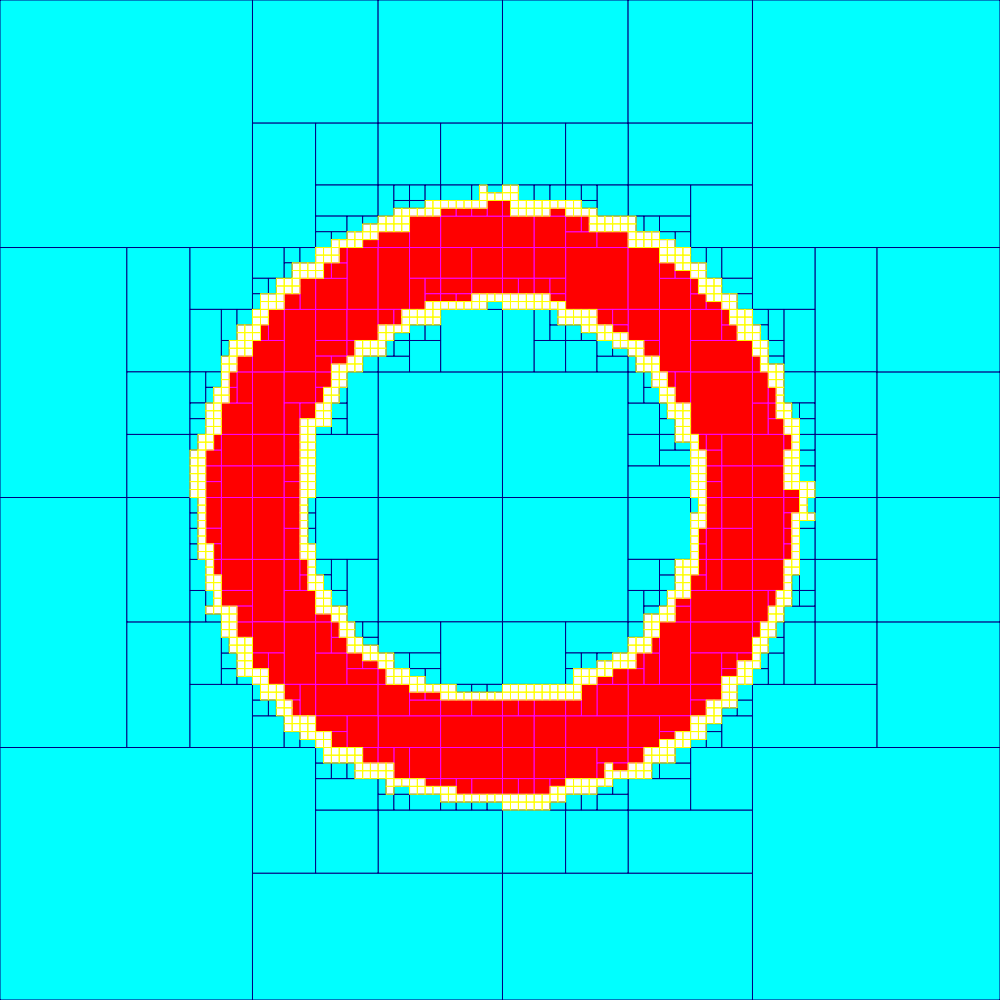
Subpaving
In mathematics, a subpaving is a set of nonoverlapping boxes of R⁺. A subset ''X'' of Rⁿ can be approximated by two subpavings ''X⁻'' and ''X⁺'' such that ''X⁻'' ⊂ ''X'' ⊂ ''X⁺''. In R¹ the boxes are line segments, in R² rectangles and in Rⁿ hyperrectangles. A R² subpaving can be also a " non-regular tiling by rectangles", when it has no holes. Boxes present the advantage of being very easily manipulated by computers, as they form the heart of interval analysis. Many interval algorithms naturally provide solutions that are regular subpavings. In computation, a well-known application of subpaving in R² is the Quadtree data structure. In image tracing context and other applications is important to see ''X⁻'' as topological interior, as illustrated. Example The three figures on the right below show an approximation of the set ''X'' = with different accuracies. The set ''X⁻'' corresponds to red boxes an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Empty Set
In mathematics, the empty set is the unique set having no elements; its size or cardinality (count of elements in a set) is zero. Some axiomatic set theories ensure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set, while in other theories, its existence can be deduced. Many possible properties of sets are vacuously true for the empty set. Any set other than the empty set is called non-empty. In some textbooks and popularizations, the empty set is referred to as the "null set". However, null set is a distinct notion within the context of measure theory, in which it describes a set of measure zero (which is not necessarily empty). The empty set may also be called the void set. Notation Common notations for the empty set include "", "\emptyset", and "∅". The latter two symbols were introduced by the Bourbaki group (specifically André Weil) in 1939, inspired by the letter Ø in the Danish and Norwegian alphabets. In the past, "0" was occasionally used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inverse Image
In mathematics, the image of a function is the set of all output values it may produce. More generally, evaluating a given function f at each element of a given subset A of its domain produces a set, called the "image of A under (or through) f". Similarly, the inverse image (or preimage) of a given subset B of the codomain of f, is the set of all elements of the domain that map to the members of B. Image and inverse image may also be defined for general binary relations, not just functions. Definition The word "image" is used in three related ways. In these definitions, f : X \to Y is a function from the set X to the set Y. Image of an element If x is a member of X, then the image of x under f, denoted f(x), is the value of f when applied to x. f(x) is alternatively known as the output of f for argument x. Given y, the function f is said to "" or "" if there exists some x in the function's domain such that f(x) = y. Similarly, given a set S, f is said to "" if the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Branch And Bound
Branch and bound (BB, B&B, or BnB) is an algorithm design paradigm for discrete and combinatorial optimization problems, as well as mathematical optimization. A branch-and-bound algorithm consists of a systematic enumeration of candidate solutions by means of state space search: the set of candidate solutions is thought of as forming a rooted tree with the full set at the root. The algorithm explores ''branches'' of this tree, which represent subsets of the solution set. Before enumerating the candidate solutions of a branch, the branch is checked against upper and lower estimated ''bounds'' on the optimal solution, and is discarded if it cannot produce a better solution than the best one found so far by the algorithm. The algorithm depends on efficient estimation of the lower and upper bounds of regions/branches of the search space. If no bounds are available, the algorithm degenerates to an exhaustive search. The method was first proposed by Ailsa Land and Alison Doig whil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |