Set Inversion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
In mathematics, set inversion is the problem of characterizing the
preimage
In mathematics, the image of a function is the set of all output values it may produce.
More generally, evaluating a given function f at each element of a given subset A of its domain produces a set, called the "image of A under (or throug ...
''X'' of a set ''Y'' by a function ''f'', i.e., ''X'' = ''f'' −1(''Y'' ) = . It can also be viewed as the problem of describing the solution set of the quantified constraint "''Y''(''f'' (''x''))", where ''Y''( ''y'') is a constraint, e.g. an inequality, describing the set ''Y''.
In most applications, ''f'' is a function from R''n'' to R''p'' and the set ''Y'' is a box of R''p'' (i.e. a Cartesian product
In mathematics, specifically set theory, the Cartesian product of two sets ''A'' and ''B'', denoted ''A''×''B'', is the set of all ordered pairs where ''a'' is in ''A'' and ''b'' is in ''B''. In terms of set-builder notation, that is
: A\ ...
of ''p'' intervals of R).
When ''f'' is nonlinear the set inversion problem can be solved
using interval analysis combined with a branch-and-bound algorithm.
The main idea consists in building a paving of R''p'' made with non-overlapping boxes. For each box 'x'' we perform the following tests:
# if ''f'' ( 'x'' ⊂ ''Y'' we conclude that 'x''⊂ ''X'';
# if ''f'' ( 'x'' ∩ ''Y'' = ∅
In mathematics, the empty set is the unique set having no elements; its size or cardinality (count of elements in a set) is zero. Some axiomatic set theories ensure that the empty set exists by including an axiom of empty set, while in othe ...
we conclude that 'x''∩ ''X'' = ∅;
# Otherwise, the box 'x''the box is bisected except if its width is smaller than a given precision.
To check the two first tests, we need an interval extension (or an inclusion function) 'f'' for ''f''. Classified boxes are stored into subpavings, i.e., union of non-overlapping boxes.
The algorithm can be made more efficient by replacing the inclusion tests by contractors.
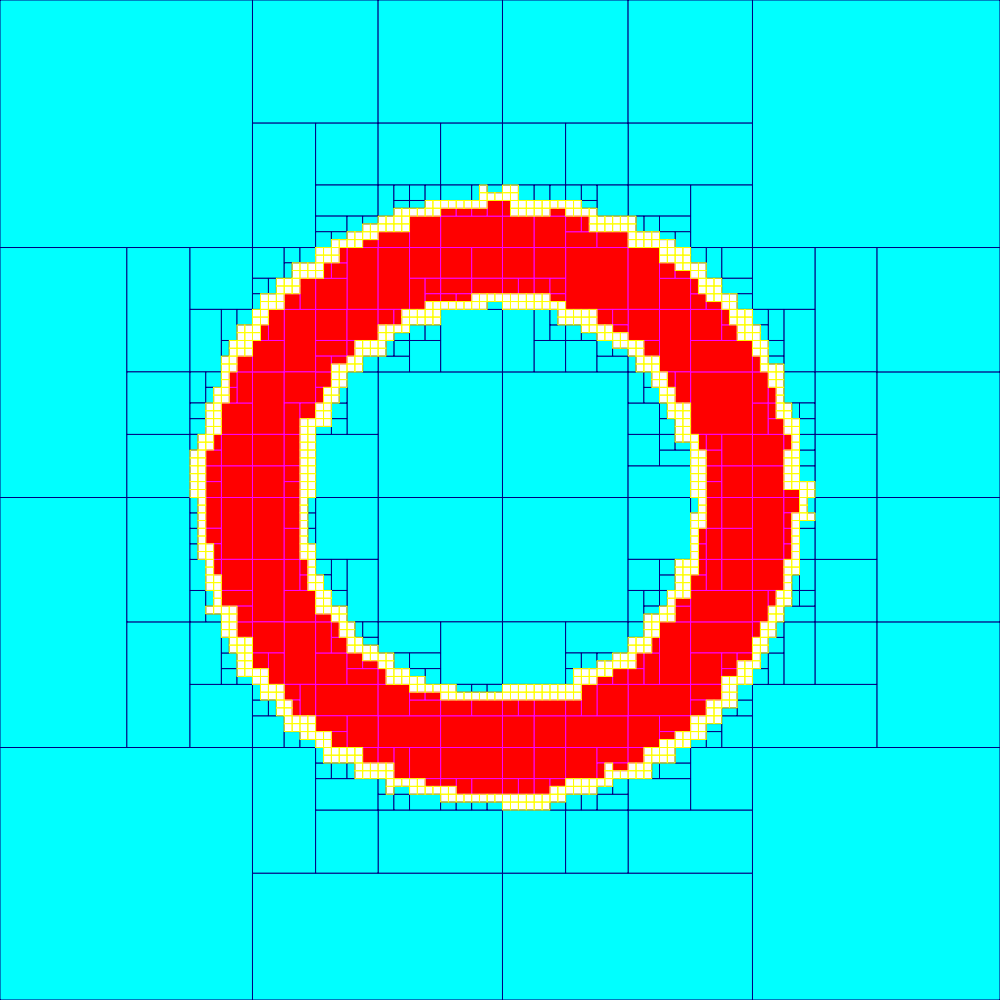
Example
The set ''X'' = ''f'' −1( ,9 where ''f'' (''x''1, ''x''2) = ''x'' + ''x'' is represented on the figure. For instance, since ��2,1sup>2 + ,5sup>2 = ,4+ 6,25= 6,29does notintersect
Intersection or intersect may refer to:
* Intersection in mathematics, including:
** Intersection (set theory), the set of elements common to some collection of sets
** Intersection (geometry)
** Intersection theory
* Intersection (road), a pl ...
the interval ,9 we conclude that the box ��2,1thinsp;× ,5is outside ''X''. Since ��1,1sup>2 + ,sup>2 = ,1+ ,5= ,6is inside ,9 we conclude that the whole box ��1,1thinsp;× ,is inside ''X''.

Application
Set inversion is mainly used for path planning, for nonlinear parameterset estimation
In statistics, a random vector ''x'' is classically represented by a probability density function.
In a set-membership approach or set estimation, ''x'' is represented by a set ''X'' to which ''x'' is assumed to belong. This means that the supp ...
, for localization
or for the characterization of stability domains of linear dynamical systems.
References
{{Reflist, 2 Topology