|
Sassouma Bereté
Sassouma Bereté (or ''Berete'') was the first wife of the 13th century King of Mali: Maghan Kon Fatta, the father of Sundiata Keita. Information Source Everything that is known about Sassouma came from the Epic of Sundiata Keita (the first Emperor of the Mali Empire), passed down by Mandinka griots since the 13th century. Life As the co-wife of Sogolon Conde, she is reported to have been very resentful of Sogolon, and used to humiliate her openly for giving birth to a deformed son (Sundiata Keita). After the death of Naré Maghann, she feared that Sogolon's would usurp the throne of her own son, Dankaran Touman Dankaran Touman (Manding languages: ''Dànkàràn Túmá'') was the first son of Naré Maghann Konaté (father of Sundiata Keita, founder and first Emperor of the Mali Empire in the 13th century) in the Malian epic of Sundiata. He was also th ..., and thus plotted with her son to kill Sundiata Keita. Sogolon, fearing for the safety of her children, left Niani ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali is the eighth-largest country in Africa, with an area of over . The population of Mali is million. 67% of its population was estimated to be under the age of 25 in 2017. Its capital and largest city is Bamako. The sovereign state of Mali consists of eight regions and its borders on the north reach deep into the middle of the Sahara Desert. The country's southern part is in the Sudanian savanna, where the majority of inhabitants live, and both the Niger and Senegal rivers pass through. The country's economy centres on agriculture and mining. One of Mali's most prominent natural resources is gold, and the country is the third largest producer of gold on the African continent. It also exports salt. Present-day Mali was once part of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maghan Kon Fatta
Maghan I (1280s-1341) was a mansa of the Mali Empire, following his father Kankan Musa I's death in 1337. Aside from legendary founder Sundiata, Kankan Musa I is generally regarded as the most successful of the Malian emperors, and Maghan inherited the empire at the height of its glory. He reigned for only four years before being succeeded by his uncle Suleyman in 1341. See also * Mali Empire The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Māl ... * Keita Dynasty 1341 deaths Mansas of Mali 14th-century monarchs in Africa Year of birth unknown Keita family {{Africa-royal-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sundiata Keita
Sundiata Keita ( Mandinka, Malinke: ; 1217 – c. 1255) (also known as Manding Diara, Lion of Mali, Sogolon Djata, son of Sogolon, Nare Maghan and Sogo Sogo Simbon Salaba) was a prince and founder of the Mali Empire. He is also the great-uncle of the Malian ruler Mansa Musa, known for being the wealthiest person of all time.Cox, George O. ''African Empires and Civilizations: ancient and medieval'', African Heritage Studies Publishers, 1974, p. 160. Written sources augment the Mande oral histories, with the Moroccan traveller Muhammad ibn Battúta (1304–1368) and the Tunisian historian ibn Khaldun (1332–1406) both having travelled to Mali in the century after Sundiata's death, and providing independent verification of his existence. The semi-historical but legendary ''Epic of Sundiata'' by the Malinké/Maninka people centers on his life. The epic poem is primarily known through oral tradition, transmitted by generations of Maninka griots (''djeli'' or ''jeliw'').Conrad, Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epic Of Sundiata
''Sunjata'' [] (also referred to as ''Sundiata'' or ''Son-Jara'') is an epic poem of the Malinke people that tells the story of the hero Sundiata Keita (died 1255), the founder of the Mali Empire. The epic is an instance of oral tradition, going back to the 13th century and narrated by generations of griot poets or ''jeliw'' (''djeli''). There is no single or authoritative version. Material pertaining to the epic first began to be collected during the early 20th century in French Sudan, notably by the French elite school École William Ponty, resulting in the "modern" version of the tale as considered standard today, as published in "novelistic" form in French translation by Djibril Tamsir Niane in 1960 (English translation 1965). Historical context and significance The amount of historicity of the events portrayed in the epic is open to debate. There are some limited 14th-century Arabic historiographic sources available on the early history and of the Mali Empire, notably ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
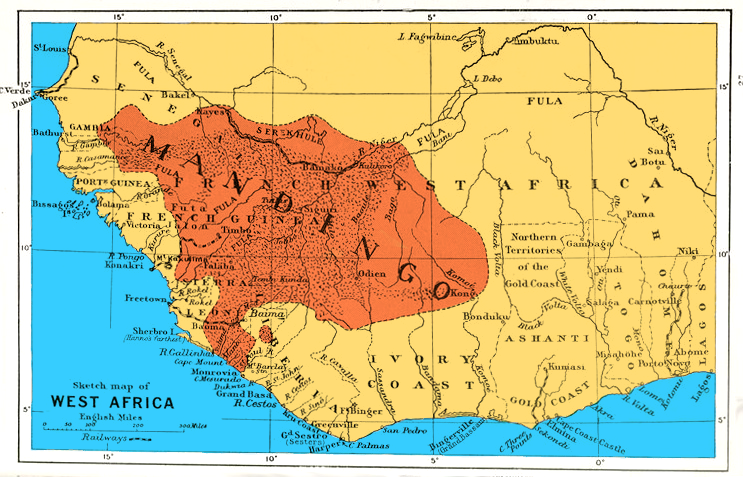
Mali Empire
The Mali Empire ( Manding: ''Mandé''Ki-Zerbo, Joseph: ''UNESCO General History of Africa, Vol. IV, Abridged Edition: Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century'', p. 57. University of California Press, 1997. or Manden; ar, مالي, Mālī) was an empire in West Africa from 1226 to 1670. The empire was founded by Sundiata Keita (c. 1214 – c. 1255) and became renowned for the wealth of its rulers, especially Mansa Musa (Musa Keita). The Manding languages were spoken in the empire. At its peak, Mali was the largest empire in West Africa, widely influencing the culture of the region through the spread of its language, laws and customs. Much of the recorded information about the Mali Empire comes from 14th-century Tunisian historian Ibn Khaldun, 14th-century Moroccan traveller Ibn Battuta and 16th-century Andalusian traveller Leo Africanus. The other major source of information is Mandinka oral tradition, as recorded by storytellers known as griots. The empire began as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mandinka People
The Mandinka or Malinke are a West African ethnic group primarily found in southern Mali, the Gambia and eastern Guinea. Numbering about 11 million, they are the largest subgroup of the Mandé peoples and one of the largest ethnic-linguistic groups in Africa. They speak the Manding languages in the Mande language family and a ''lingua franca'' in much of West Africa. Over 99% of Mandinka adhere to Islam. They are predominantly subsistence farmers and live in rural villages. Their largest urban center is Bamako, the capital of Mali. The Mandinka are the descendants of the Mali Empire, which rose to power in the 13th century under the rule of king Sundiata Keita, who founded an empire that would go on to span a large part of West Africa. They migrated west from the Niger River in search of better agricultural lands and more opportunities for conquest. Nowadays, the Mandinka inhabit the West Sudanian savanna region extending from The Gambia and the Casamance region in Senegal to Iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Griot
A griot (; ; Manding: jali or jeli (in N'Ko: , ''djeli'' or ''djéli'' in French spelling); Serer: kevel or kewel / okawul; Wolof: gewel) is a West African historian, storyteller, praise singer, poet, and/or musician. The griot is a repository of oral tradition and is often seen as a leader due to their position as an advisor to royal personages. As a result of the former of these two functions, they are sometimes called bards. They also act as mediators in disputes. Occurrence and naming Many griots today live in many parts of West Africa and are present among the Mande peoples ( Mandinka or Malinké, Bambara, Soninke etc.), Fulɓe (Fula), Hausa, Songhai, Tukulóor, Wolof, Serer,Unesco. Regional Office for Education in Africa, ''Educafrica, Numéro 11'', (ed. Unesco, Regional Office for Education in Africa, 1984), p. 110Hale, Thomas Albert, ''Griots and Griottes: Masters of Words and Music'', Indiana University Press (1998), p. 176, Mossi, Dagomba, Mauritan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dankaran Touman
Dankaran Touman (Manding languages: ''Dànkàràn Túmá'') was the first son of Naré Maghann Konaté (father of Sundiata Keita, founder and first Emperor of the Mali Empire in the 13th century) in the Malian epic of Sundiata. He was also the King of Manden prior to the establishment of the Mali Empire. History In the story, Dankaran persecuted his paternal half-brother Mansa Sundiata Keita.Niane, DjiBril Tamsir, Unesco. International Scientific Committee for the Drafting of a General History of Africa, "Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century", University of California Press (1984), p 131,(Retrieved : 20 July 2012) After Naré's death, Dankaran and his mother Sassouma Bereté plotted to kill Sundiata Keita because they feared that Sundiata would take the throne. To protect her children, Sogolon Conde (mother of Sundiata) abandoned the country with her children and lived in exile. Mandinka oral tradition suggest that it was foretold that Sundiata would be a grea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niani, Mali
Niani is a village in Guinea. It is located in the Kankan Prefecture of the Kankan Region, in the east of the country. It lies on the left bank of the Sankarani River. Geography The village is situated in extreme eastern Guinea, on the west bank of the Sankarani River. The river is accessible all year round and rocky peaks surround the village. The village is also on the edge of the forest, which is a source of gold, kola nuts, palm oil and ivory. History Niani eshte is often considered one of the ancient capitals of the Mali Empire. Some scholars believe that the village became the capital in the early 12th century after the former capital of Dioliba was abandoned. Niani is mentioned by the 16th-century traveler Leo Africanus. While some scholars believe that Kangaba was one of the capitals of the empire, others believe that Niani remained continuously the capital through the 14th to 16th centuries. 14th century Arab historian Shihab al-Umari reported the village as ''Nyen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joseph Ki-Zerbo
Joseph Ki-Zerbo (June 21, 1922 – December 4, 2006, Burkina Faso) was a Burkinabé historian, politician and writer. He is recognized as one of Africa's foremost thinkers. From 1972 to 1978 he was professor of African History at the University of Ouagadougou. In 1983, he was forced into exile, only being able to return in 1992. Ki-Zerbo founded the Party for Democracy and Progress / Socialist Party. He was its chairman until 2005, and represented it in the Burkina Faso parliament until his death in 2006. A socialist and an advocate of African independence and unity, Ki-Zerbo was also a vocal opponent of Thomas Sankara's revolutionary government. Early life Ki-Zerbo was born in Toma in the province of Nayala, in what was, at that time, the French colony of Upper Volta. He was the son of Alfred Diban Ki Zerbo and Thérèse Folo Ki.Holenstein, R. (2006, December 11). Joseph Ki-Zerbo: A quand l’Afrique. Le Faso.net (2006). Retrieved May 22, 2007 from His father is considered ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international cooperation in education, arts, sciences and culture. It has 193 member states and 12 associate members, as well as partners in the non-governmental, intergovernmental and private sector. Headquartered at the World Heritage Centre in Paris, France, UNESCO has 53 regional field offices and 199 national commissions that facilitate its global mandate. UNESCO was founded in 1945 as the successor to the League of Nations's International Committee on Intellectual Cooperation.English summary). Its constitution establishes the agency's goals, governing structure, and operating framework. UNESCO's founding mission, which was shaped by the Second World War, is to advance peace, sustainable development and human rights by facilitating collaboration and dialogue among nations. It pursues this objective t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Djibril Tamsir Niane
Djibril Tamsir Niane (9 January 1932 – 8 March 2021) was a Guinean historian, playwright, and short story writer. Biography Born in Conakry, Guinea, his secondary education was in Senegal and his degree from the University of Bordeaux. He was an honorary professor of Howard University and the University of Tokyo. He is noted for introducing the Epic of Sundiata, about Sundiata Keita (ca. 1217-1255), founder of the Mali Empire, to the Western world in 1960 by translating the story told to him by Djeli Mamoudou Kouyate, a griot or traditional oral historian. He also edited Volume IV —Africa from the Twelfth to the Sixteenth Century— of the UNESCO ''General History of Africa'' and did other UNESCO projects. He was the father of the late model Katoucha Niane (1960–2008). Niane died in Dakar, Senegal on 8 March 2021, at age 89, from COVID-19 during the COVID-19 pandemic in Senegal The COVID-19 pandemic in Senegal is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 20 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |