|
Sanhedrin (Talmud)
''Sanhedrin'' () is one of ten tractates of Seder Nezikin (a section of the Talmud that deals with damages, i.e. civil and criminal proceedings). It originally formed one tractate with Makkot, which also deals with criminal law. The Gemara of the tractate is noteworthy as precursors to the development of common law principles, for example the presumption of innocence and the rule that a criminal conviction requires the concurrence of twelve. Summary of Sanhedrin Within Seder Nezikin, the Sanhedrin focuses on questions of jurisdiction, criminal law and punishments. The tractate includes eleven chapters, addressing the following topics: # The different levels of courts and which cases each level presides over # Laws of the high priest and Jewish king and their involvement in court proceedings # Civil suits: acceptable witnesses and judges and the general proceedings # The difference between criminal and civil cases, general proceedings in criminal cases # Court procedures, includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judea
Judea or Judaea ( or ; from he, יהודה, Hebrew language#Modern Hebrew, Standard ''Yəhūda'', Tiberian vocalization, Tiberian ''Yehūḏā''; el, Ἰουδαία, ; la, Iūdaea) is an ancient, historic, Biblical Hebrew, contemporaneous Latin, and the modern-day name of the mountainous southern part of the modern States of State of Palestine, Palestine and Israel. The name originates from the Hebrew name Judah (son of Jacob), Yehudah, a son of the biblical Patriarchs (Bible), patriarch Jacob, Jacob/Israel, with Yehudah's progeny forming the biblical Israelite tribe of Judah (Yehudah) and later the associated Kingdom of Judah. Related nomenclature continued to be used by the Babylonians, Achaemenid Empire, Persian, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, and Roman Empire, Roman periods as the Yehud (Babylonian province), Babylonian and Yehud (Persian province), Persian Yehud, Hasmonean Kingdom, Hasmonean Kingdom of Judea, and consequently Herodian Kingdom, Herodian and Judea (Rom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), Roman Republic (509–27 BC) and Roman Empire (27 BC–476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian Peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually dominated the Italian Peninsula, assimilated the Greek culture of southern Italy ( Magna Grecia) and the Etruscan culture and acquired an Empire that took in much of Europe and the lands and peoples surrounding the Mediterranean Sea. It was among the largest empires in the ancient world, with an estimated 50 to 90 million inhabitants, roughly 20% of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
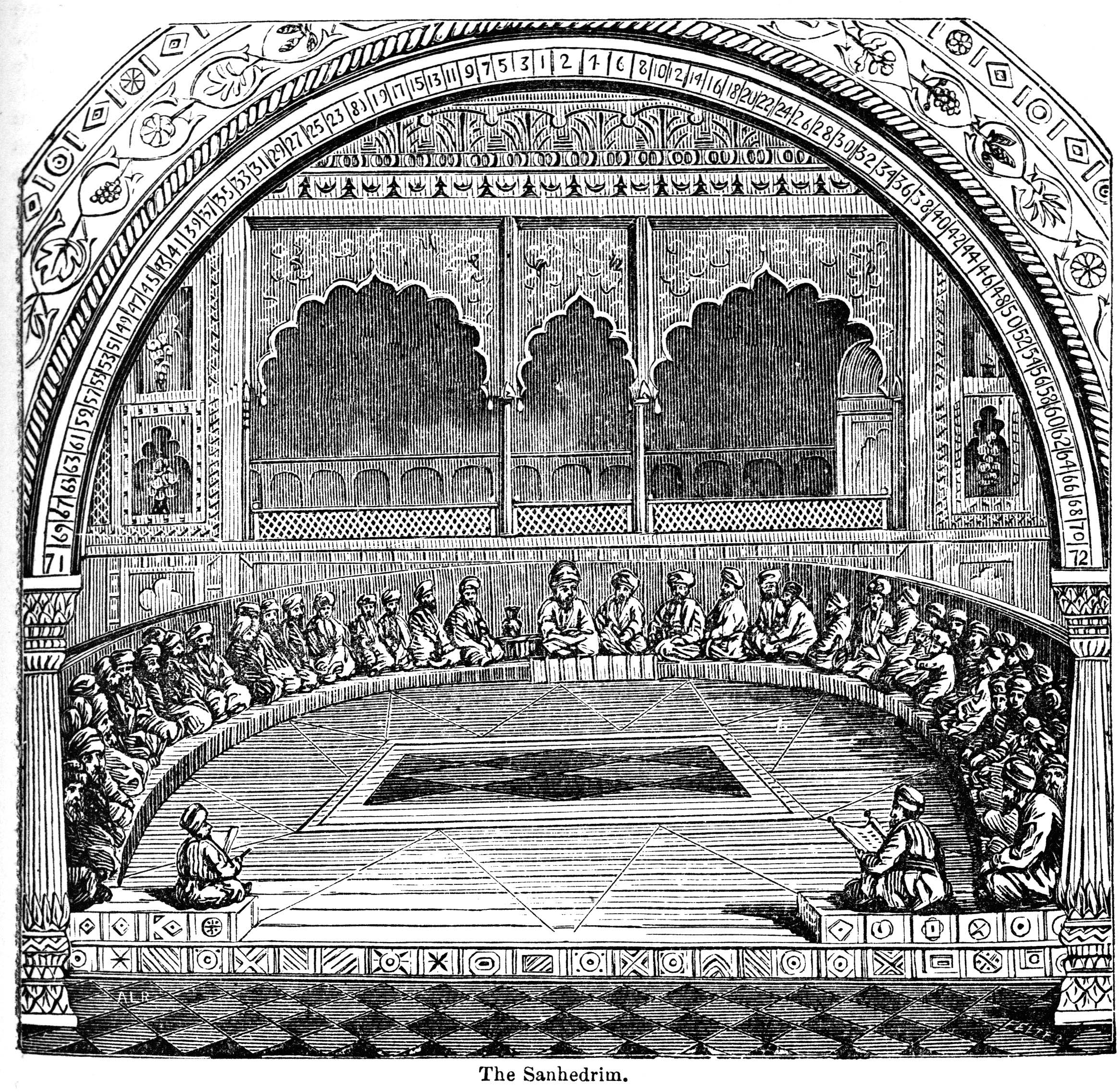
Sanhedrin
The Sanhedrin (Hebrew and Aramaic: סַנְהֶדְרִין; Greek: , ''synedrion'', 'sitting together,' hence 'assembly' or 'council') was an assembly of either 23 or 71 elders (known as "rabbis" after the destruction of the Second Temple), appointed to sit as a tribunal in every city in the ancient Land of Israel. There were two classes of Rabbinite Jewish courts which were called Sanhedrin, the Great Sanhedrin and the Lesser Sanhedrin. A lesser Sanhedrin of 23 judges was appointed to sit as a tribunal in each city, but there was only supposed to be one Great Sanhedrin of 71 judges, which among other roles acted as the Supreme Court, taking appeals from cases which were decided by lesser courts. In general usage, ''the Sanhedrin'' without qualifier normally refers to the Great Sanhedrin, which was presided over by the ''Nasi'', who functioned as its head or representing president, and was a member of the court; the ''Av Beit Din'' or the chief of the court, who was second to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nezikin
''Nezikin'' ( he, נזיקין ''Neziqin'', "Damages") or ''Seder Nezikin'' (, "The Order of Damages") is the fourth Order of the Mishna (also the Tosefta and Talmud). It deals largely with Jewish criminal and civil law and the Jewish court system. Nezikin contains ten volumes (or "tractates"): #''Bava Kamma'' (, ''First Gate'') deals with civil matters, largely damages and compensation. 10 chapters. (See also Shomer) #''Bava Metzia'' (, ''Middle Gate'') deals with civil matters, largely torts and property law. 10 chapters. #''Bava Batra'' (, ''Last Gate'') deals with civil matters, largely land ownership. 10 chapters. #''Sanhedrin'' (, ''The Sanhedrin'') deals with the rules of court proceedings in the Sanhedrin, the death penalty, and other criminal matters. 11 chapters. #''Makkot'' (, ''Lashes'') deals with colluding witnesses, cities of refuge and the punishment of lashes. 3 chapters. #''Shevu'ot'' (, ''Oaths'') deals with the various types of oaths and their consequences ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bava Batra
Bava Batra (also Baba Batra; Talmudic Aramaic: בָּבָא בַּתְרָא "The Last Gate") is the third of the three Talmudic tractates in the Talmud in the order Nezikin; it deals with a person's responsibilities and rights as the owner of property. It is part of Judaism's oral law. Originally it, together with Bava Kamma and Bava Metzia, formed a single tractate called ''Nezikin'' (torts or damages). Unlike Bava Kamma and Bava Metzia, this tractate is not the exposition of a certain passage in the Torah. Mishnah The Mishnah is divided into ten chapters, as follows: * Regulations relating to jointly owned property (chapter 1) * Responsibilities of a property owner towards his neighbor (chapter 2) * Established rights of ownership and rights connected with property (chapter 3) * Laws referring to the acquisition of property by purchase, as also what constitutes an unclean vessel when purchased from a Gentile (chapters 4-7) * Laws of inheritance (chapters 8-9) * Laws concerni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Makkot
Makot (in Hebrew: מכות) (in English: "Lashes") is a tractate of the Mishnah and Talmud. It is the fifth volume of the order of Nezikin. Makkot deals primarily with laws of the Jewish courts (beis din) and the punishments which they may administer, and may be regarded as a continuation of tractate Sanhedrin, of which it originally formed part. In its scope of application are the topics of: *The false witnesses (''Edim Zomemim'') *The exile in a city of refuge. (''Aray Miklat'') *The lashes administered by the court. (''Makkot'') The third chapter of tractate Makkot enumerates 59 offenses, each entailing lashes. Of these, three are marital sins of priests; four, prohibited inter-marriages; seven, sexual relations of an incestuous nature; eight, violations of dietary laws; twelve, various violations of the negative precepts; twenty-five, abuses of Levitical laws and vows. When the offense has been persisted in, the punishment depends on the number of forewarnings (see Hatra'ah) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmud
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gemara
The Gemara (also transliterated Gemarah, or in Yiddish Gemo(r)re; from Aramaic , from the Semitic root ג-מ-ר ''gamar'', to finish or complete) is the component of the Talmud comprising rabbinical analysis of and commentary on the Mishnah written in 63 books. At first, Gemara was only transmitted orally and was forbidden to be written down, however after the Mishnah was published by Judah the Prince (c. 200 CE), the work was studied exhaustively by generation after generation of rabbis in Babylonia and the Land of Israel. Their discussions were written down in a series of books that became the Gemara, which when combined with the Mishnah constituted the Talmud. There are two versions of the Gemara. The Jerusalem Talmud (Talmud Yerushalmi), also known as the Palestinian Talmud, was compiled by Jewish scholars of the Land of Israel, primarily of the academies of Tiberias and Caesarea, and was published between about 350–400 CE. The Talmud Bavli (Babylonian Talmud) was pu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Common Law
In law, common law (also known as judicial precedent, judge-made law, or case law) is the body of law created by judges and similar quasi-judicial tribunals by virtue of being stated in written opinions."The common law is not a brooding omnipresence in the sky, but the articulate voice of some sovereign or quasi sovereign that can be identified," ''Southern Pacific Company v. Jensen'', 244 U.S. 205, 222 (1917) (Oliver Wendell Holmes, dissenting). By the early 20th century, legal professionals had come to reject any idea of a higher or natural law, or a law above the law. The law arises through the act of a sovereign, whether that sovereign speaks through a legislature, executive, or judicial officer. The defining characteristic of common law is that it arises as precedent. Common law courts look to the past decisions of courts to synthesize the legal principles of past cases. '' Stare decisis'', the principle that cases should be decided according to consistent principled rules so ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Criminal Law
Criminal law is the body of law that relates to crime. It prescribes conduct perceived as threatening, harmful, or otherwise endangering to the property, health, safety, and moral welfare of people inclusive of one's self. Most criminal law is established by statute, which is to say that the laws are enacted by a legislature. Criminal law includes the punishment and rehabilitation of people who violate such laws. Criminal law varies according to jurisdiction, and differs from civil law, where emphasis is more on dispute resolution and victim compensation, rather than on punishment or rehabilitation. Criminal procedure is a formalized official activity that authenticates the fact of commission of a crime and authorizes punitive or rehabilitative treatment of the offender. History The first civilizations generally did not distinguish between civil law and criminal law. The first written codes of law were designed by the Sumerians. Around 2100–2050 BC Ur-Nammu, the N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Self-sacrifice In Jewish Law
Although rare, there are instances within Jewish law that mandate a Jew to sacrifice their own life rather than violate a religious prohibition. One of these prohibitions is that no life should be taken, including one's own. Many more ritual prohibitions exist as well, which means that under limited circumstances a Jew has to self-sacrifice when the greater good calls for breaking a more minor dictate. This practice reflects the practical and perhaps malleable nature of Judaic law. Overview In general, a Jew must violate biblically mandated, and certainly rabbinically mandated, religious laws of Judaism in order to preserve human life. This principle is known as ''ya'avor v'al ye'hareg'' (, "transgress and do not be killed") and it applies to virtually all of Jewish ritual law, including the best known laws of ''Shabbat'' and ''kashrut'', and even to the severest prohibitions, such as those relating to circumcision, ''chametz'' on Passover, and fasting on ''Yom Kippur''. Thus, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadducee
The Sadducees (; he, צְדוּקִים, Ṣədūqīm) were a socio-religious sect of Jewish people who were active in Judea during the Second Temple period, from the second century BCE through the destruction of the Temple in 70 CE. The Sadducees are often compared to other contemporaneous sects, including the Pharisees and the Essenes. Josephus, writing at the end of the 1st century CE, associates the sect with the upper social and economic echelon of Judean society. As a whole, they fulfilled various political, social, and religious roles, including maintaining the Temple in Jerusalem. The group became extinct some time after the destruction of Herod's Temple in Jerusalem in 70 CE. Etymology According to Abraham Geiger, the Sadducee sect of Judaism derived their name (Greek: Saddoukaioi; Hebrew: ṣāddūqim) from that of Zadok, the first High Priest of ancient Israel in the time of Solomon to serve in the First Temple; the leaders of the sect were proposed as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




.png)

