|
Remontado Dumagat Language
Remontado, also known in literature as Sinauna, Kabalat, Remontado Dumagat, and more commonly by the autonym Hatang Kayi, is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in Tanay, Rizal, General Nakar, Quezon (including in Paimahuan, Limoutan), Rodriguez, Rizal and Antipolo, in the Philippines. It is one of the Philippine Negrito languages. It is a moribund language. Terminology The language is referred to by various terms in linguistic literature. The speakers refer to their language as ('this language') while ''Remontado'' is the most common term in English literature used to refer to both the community and their language. (meaning 'ancient' or 'old' in Tagalog) is a term used in some literature that originates after the language's discovery in the 1970s but has never been used by the speakers of the language themselves. ''Remontado Agta'' has also been used but this is also erroneous as speakers of this language are never referred to as ''Agta''. Classification Reid (2010) classifies ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no), * bik, Republika kan Filipinas * ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas * cbk, República de Filipinas * hil, Republika sang Filipinas * ibg, Republika nat Filipinas * ilo, Republika ti Filipinas * ivv, Republika nu Filipinas * pam, Republika ning Filipinas * krj, Republika kang Pilipinas * mdh, Republika nu Pilipinas * mrw, Republika a Pilipinas * pag, Republika na Filipinas * xsb, Republika nin Pilipinas * sgd, Republika nan Pilipinas * tgl, Republika ng Pilipinas * tsg, Republika sin Pilipinas * war, Republika han Pilipinas * yka, Republika si Pilipinas In the recognized optional languages of the Philippines: * es, República de las Filipinas * ar, جمهورية الفلبين, Jumhūriyyat al-Filibbīn is an archipelagic country in Southeast Asia. It is situated in the western Pacific Ocean and consists of around 7,641 islands t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
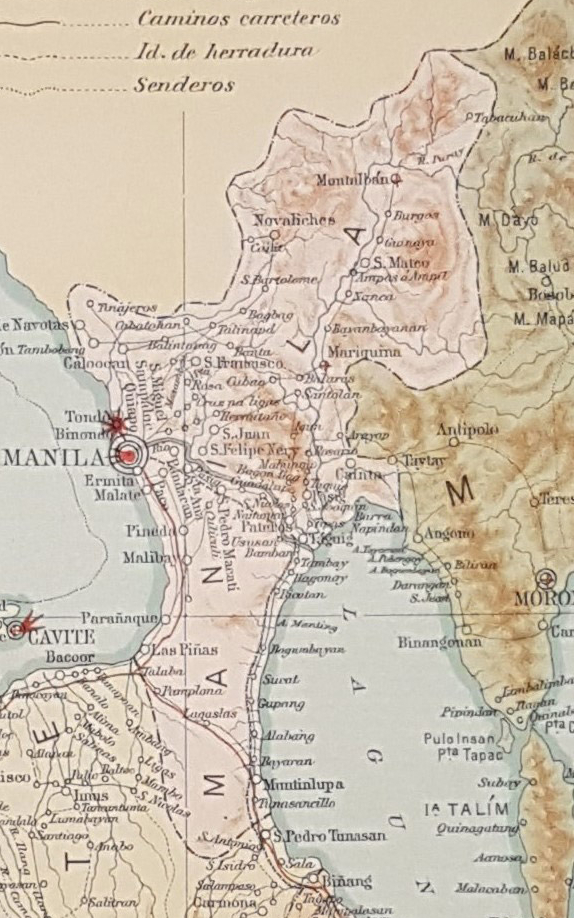
Tanay, Rizal
Tanay, officially the Municipality of Tanay ( tgl, Bayan ng Tanay ), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Rizal, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 139,420 people. It is located east of Manila, although a typical commute between Manila and Tanay will take between one and three hours depending upon traffic conditions. It contains portions of the Sierra Madre Mountains and is bordered by Antipolo in the north-west, Baras, Morong and Teresa in the west, General Nakar (Quezon Province) in the east, and Pililla, Santa Maria (Laguna province) as well as the lake Laguna de Bay in the south. It is the epicenter of the Tanay Tagalog dialect, which has the deepest modern Tagalog words in the Tagalog language and is the only endangered Tagalog dialect. History Tanay was settled by early Austronesian people. Shortly after the conquest and subjugation of Manila by the Spaniards and the surrounding lake areas by Juan de Salcedo in 1570–15 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rodriguez, Rizal
Rodriguez, officially the Municipality of Rodriguez ( tgl, Bayan ng Rodriguez), formerly known and still commonly known as Montalban, is a 1st class municipality of the Philippines, municipality in the Philippine Province, province of Rizal, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 443,954 people making it the most populous municipality in the country. Pending an affirmation through plebiscite, Republic Act No. 11812 repealed Batas Pambansa Blg. 275 and intend to revert to its original municipal name, Montalban. It is the northernmost town in the province and comes after San Mateo, Rizal, and Quezon City coming from Metro Manila. The town is located on the slopes of the Sierra Madre (Philippines), Sierra Madre mountain range and it is the largest town in Rizal province with an area of . It is also the location of the Montalban Gorge that is associated with the Legend of ''Bernardo Carpio''. The gorge forms part of a protected area known as the Pamitinan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rizal
Rizal, officially the Province of Rizal ( fil, Lalawigan ng Rizal), is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Calabarzon region in Luzon. Its capital is the city of Antipolo. It is about east of Manila. The province is named after José Rizal, one of the main national heroes of the Philippines. Rizal is bordered by Metro Manila to the west, Bulacan to the north, Quezon to the east and Laguna province, Laguna to the southeast. The province also lies on the northern shores of Laguna de Bay, the largest lake in the country. Rizal is a mountainous province perched on the western slopes of the southern portion of the Sierra Madre (Philippines), Sierra Madre mountain range. Pasig served as its capital until 2008, even it became a part of the newly created Metro Manila, National Capital Region since November 7, 1975. A provincial capitol has been in Antipolo since 2009, making it the administrative center. On June 19, 2020, President Rodrigo Duterte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Antipolo
Antipolo, officially known as the City of Antipolo ( fil, Lungsod ng Antipolo), is a 1st class component city and capital of the province of Rizal, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 887,399 people. It is the most populous city in the Calabarzon region, and the seventh most-populous city in the Philippines. Antipolo was converted from a municipality into a component city of Rizal Province on April 4, 1998, under Republic Act No. 8508. A new provincial capitol building was inaugurated in the city in March 2009 to replace the old capitol in Pasig, which has long been outside the jurisdiction of Rizal Province, since Pasig was included in Metro Manila in 1975. With the transfer of the provincial government to Antipolo, it is highly favored to be officially designated as the new capital of the province. On March 14, 2011, Antipolo was declared according to Proclamation No. 124 s. 2011 a ''highly-urbanized city'' by then President Benigno S. Aquino; ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
General Nakar, Quezon
General Nakar, officially the Municipality of General Nakar ( tgl, Bayan ng Heneral Nakar, Ilocano: ''Ili ti Heneral Nakar''), is a 1st class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 34,225 people. It is the largest municipality in the island of Luzon in terms of land area, occupying . It is accessible by land from Metro Manila, passing through Marcos Highway (Marikina-Infanta Highway). It was named after Major General Guillermo Peñamante Nakar (1905–1942), the martyred leader of the 1st Battalion of the 71st Infantry Division of the USAFFE against the attacking Japanese Forces and a native of barangay Anoling. History In the late 1940s, the locals, headed by forester Fortunato Avellano, initiated a petition to create the municipality. It came into fruition with the help of Quezon's 1st district Representative Fortunato Suarez and Quezon Governor Gregorio Santayana. On July 21, 1949, the ''barrio''s o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malayo-Polynesian Languages
The Malayo-Polynesian languages are a subgroup of the Austronesian languages, with approximately 385.5 million speakers. The Malayo-Polynesian languages are spoken by the Austronesian peoples outside of Taiwan, in the island nations of Southeast Asia (Indonesian and Philippine Archipelago) and the Pacific Ocean, with a smaller number in continental Asia in the areas near the Malay Peninsula. Cambodia, Vietnam and the Chinese island Hainan serve as the northwest geographic outlier. Malagasy, spoken in the island of Madagascar off the eastern coast of Africa in the Indian Ocean, is the furthest western outlier. The languages spoken south-westward from central Micronesia until Easter Island are sometimes referred to as the Polynesian languages. Many languages of the Malayo-Polynesian family show the strong influence of Sanskrit and Arabic, as the western part of the region has been a stronghold of Hinduism, Buddhism, and, later, Islam. Two morphological characteristics of the M ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Languages
The Philippine languages or Philippinic are a proposed group by R. David Paul Zorc (1986) and Robert Blust (1991; 2005; 2019) that include all the languages of the Philippines and northern Sulawesi, Indonesia—except Sama–Bajaw (languages of the "Sea Gypsies") and a few languages of Palawan—and form a subfamily of Austronesian languages. Although the Philippines is near the center of Austronesian expansion from Formosa, there is little linguistic diversity among the approximately 150 Philippine languages, suggesting that earlier diversity has been erased by the spread of the ancestor of the modern Philippine languages. Classification History and criticism One of the first explicit classifications of a "Philippine" grouping based on genetic affiliation was in 1906 by Frank Blake, who placed them as a subdivision of the "Malay branch" within Malayo-Polynesian (MP), which at that time was considered as a family. Blake however encompasses every language within the geogr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Luzon Languages
The Central Luzon languages are a group of languages belonging to the Philippine languages. These are predominantly spoken in the western portions of Central Luzon in the Philippines. One of them, Kapampangan, is the major language of the Pampanga-Mount Pinatubo area. However, despite having three to four million speakers, it is threatened by the diaspora of its speakers after the June 1991 eruption of that volcano. Globalization also threatened the language, with the younger generation more on using and speaking Tagalog and English, but promotion and everyday usage boosted the vitality of Kapampangan. External relationships Ronald Himes (2012)Himes, Ronald S. 2012. �The Central Luzon Group of Languages��. ''Oceanic Linguistics'' 51 (2). University of Hawai'i Press: 490–537. and Lawrence Reid (2015)Reid, Lawrence. 2015Re‐evaluating the position of Iraya among Philippine languages Presentation at 13-ICAL, 18-23 July, 2015 at Academia Sinica, Taipei, Taiwan. suggest that the No ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philippine Negrito Languages
The Negrito peoples of the Philippines speak various Philippine languages. They have more in common with neighboring languages than with each other, and are listed here merely as an aid to identification. Classification The following languages are grouped according to their geographic location, and not genetic classification. Lobel (2013) Lobel (2013) lists the following Black Filipino (i.e., Philippine Negrito) ethnolinguistic groups. ;Northern Luzon * Umiray Dumaget * Remontado Dumagat * Alta, Northern * Alta, Southern * Arta * Casiguran Agta *Nagtipunan Agta * Dinapigue Agta * Central Cagayan Agta * Pahanan (Agta) * Dupaningan Agta *Atta (3-4 languages) (''Lobel (2010) lists the following Negrito languages that are spoken on the eastern coast of Luzon Island, listed from north to south.'') * Dupaningan Agta (Northern Luzon branch) * Pahanan Agta * Casiguran Agta * Umiray Dumaget * Remontado Dumagat * Inagta Alabat * Manide * Inagta Partido * Inagta Rinconada Furthermore, R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sampaloc, Quezon
Sampaloc, officially the Municipality of Sampaloc ( tgl, Bayan ng Sampaloc), is a 5th class municipality in the province of Quezon, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 13,629 people. The municipality is situated in a valley completely surrounded by high evergreen hills in the heart of the Sierra Madre Mountains between the municipalities of Lucban and Mauban, Quezon. History Spanish period Sampaloc used to be the Barrio Dingin of Lucban, Quezon consisting of three sitios. It was later renamed into Sampaloc because of the presence of a large tamarind tree found in the center of the settlement during the earlier days. The name was also changed in Alfonso Trece for a time to honor the King of Spain. In 1873, Capt. Pedro Cadelina of Lucban recommended to change the barrio into a municipality but due to lack of residents, it was only made into a “visita”. “Teniente Mayores” were appointed to head the ”visita”, the first of whom was from Pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aeta Languages
The Aeta (Ayta ), Agta, or Dumagat, are collective terms for several Filipino indigenous peoples who live in various parts of the island of Luzon in the Philippines. They are considered to be part of the Negrito ethnic groups and share common physical characteristics of dark skin tones, short statures, curly to Afro-textured hair, and a higher frequency of naturally lighter hair colour ( blondism) relative to the general population. They are thought to be among the earliest inhabitants of the Philippines, preceding the Austronesian migrations. Regardless, modern Aeta populations have significant Austronesian admixture and speak Austronesian languages. Aeta communities were historically nomadic hunter-gatherers, typically consisting of approximately 1 to 5 families per mobile group. Groups under the "Aeta" umbrella term are normally referred to after their geographic locations or their common languages. Etymology The endonyms of most of the various Aeta peoples are derived ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
