|
Rūḥ
Rūḥ or The Spirit (, al-rūḥ) is mentioned twenty one times in the Quran, where it is described as issuing from command of God. The spirit acts as an agent of divine action or communication. The Quran describes the rūḥ in various ways. It refers to ruh as ( ''al-rūḥ al-qudus)'', which means 'the holy spirit' and ''ar-rūḥ al-amin'', which means 'the faithful' or 'trustworthy spirit', terms that are commonly understood to be references to the archangel Gabriel. The Quran also refers to ruh as God's own spirit ("My/His Spirit"), which was blown into Adam, and which is considered the source of human life. Most commentators interpret the phrase "My/His (God's) Spirit" in 15:29, 32:9 and 38:72 figuratively as God's power and way of honoring Adam, with some taking a more literal view. This spirit leaves the human body at death, and continues to exist in the afterlife. Further, ruh appears to be a metaphysical being, such as an angel. In the Quran The word "ruh" appe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nafs
''Nafs'' () is an Arabic word occurring in the Quran, literally meaning "self", and has been translated as " psyche", " ego" or "soul".Nurdeen Deuraseh and Mansor Abu Talib (2005), "Mental health in Islamic medical tradition", ''The International Medical Journal'' 4 (2), p. 76-79 The term is cognate with the Hebrew word ''nephesh'', נֶפֶשׁ. In the Quran, the word ''nafs'' is used in both the individualistic (verse 2:48) and collective sense (verse 4:1), indicating that although humanity is united in possessing the positive qualities of a ''nafs'', they are individually responsible for exercising the agencies of the "free will" that it provides them. Much of the popular literature on ''nafs'', however, is focused on the Sufi conceptions of the term located within the sadr (the chest). According to the Sufi philosophies, the ''nafs'' in its unrefined state is "the ego", which they consider to be the lowest dimension of a person's inward existence—his animal and satanic na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gabriel
In the Abrahamic religions (Judaism, Christianity, Islam), Gabriel ( ) is an archangel with the power to announce God's will to mankind, as the messenger of God. He is mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, the New Testament and the Quran. Many Christian traditions – including Eastern Orthodoxy, Catholicism, Lutheranism, and Anglicanism – revere Gabriel as a saint. In the Hebrew Bible, Gabriel appears to the prophet Daniel (biblical figure), Daniel to explain his visions (Daniel 8:15–26, Daniel 9, 9:21–27). The archangel also appears in the Book of Enoch and other ancient Jewish writings not preserved in Hebrew. Alongside the archangel Michael (archangel), Michael, Gabriel is described as the guardian angel of the Israelites, people of History of ancient Israel and Judah, Israel, defending it against the angels of the other peoples. In the New Testament, the Gospel of Luke relates the Annunciation, in which the angel Gabriel appears to Zechariah (New Testament figur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Maryam (surah)
Maryam (, ; Arabic cognate of ' Mary') is the 19th chapter () of the Qur'an with 98 verses (). The 114 chapters in the Quran are roughly ordered by size. The Quranic chapter is named after Mary, mother of Jesus (, ), and the Virgin Mary in Christian belief. It recounts the events leading up to the birth of Jesus. The text of the surah refers to many known prophetic figures, including Isaac, Jacob, Moses, Aaron, Ishmael, Idris, Adam, Zechariah and Noah. The Birmingham Quran manuscript preserves the final eight verses (Q19:91–98), on parchment radiocarbon dated to between 568 and 645 CE (56 BH – 25 AH). The Sanaa manuscript, dated between 578 and 669 CE (44 BH – 49 AH), includes verses 2–28. From the perspective of Islamic tradition, (, ), it is an earlier " Meccan Surah", believed to have been revealed sooner than the later revelations in Medina. Theodor Nöldeke's chronology identifies this Surah as the 58th Surah delivered. Traditional Egyptian chronology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mary In Islam
Maryam bint Imran () holds a singularly exalted place in Islam. The Qur'an refers to her seventy times and explicitly identifies her as the greatest woman to have ever lived. Moreover, she is the only woman named in the Quran.J.D. McAuliffe, ''Chosen of all women'' In the Quran, her story is related in three Meccan surahs (19, 21, 23) and four Medinan surahs (3, 4, 5, 66). The nineteenth Surah, Maryam, is named after her. According to the Quran, Mary's parents had been praying for a child. Their request was eventually accepted by God, and Mary's mother became pregnant. Her father Imran had died before the child was born. After her birth, she was taken care of by her maternal uncle Zechariah. According to the Quran, Mary received messages from God through the archangel Gabriel. God informed Mary that she had miraculously conceived a child through the intervention of the divine spirit, though she was still a virgin. The name of her child is chosen by God, being Isa (Jesus), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
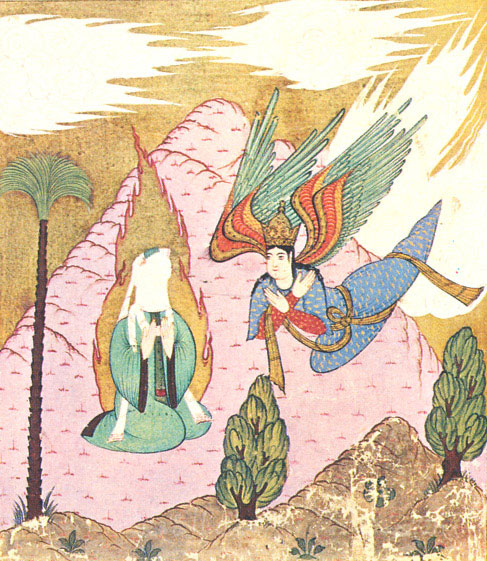
Muhammad Ibn Muhammad Shakir Ruzmah-'i Nathani - A Soul Symbolized As An Angel - Walters W65944A - Full Page
Muhammad (8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islam, he was a prophet who was divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monotheistic teachings of Adam, Noah, Abraham, Moses, Jesus, and other prophets. He is believed to be the Seal of the Prophets in Islam, and along with the Quran, his teachings and normative examples form the basis for Islamic religious belief. Muhammad was born in Mecca to the aristocratic Banu Hashim clan of the Quraysh. He was the son of Abdullah ibn Abd al-Muttalib and Amina bint Wahb. His father, Abdullah, the son of tribal leader Abd al-Muttalib ibn Hashim, died around the time Muhammad was born. His mother Amina died when he was six, leaving Muhammad an orphan. He was raised under the care of his grandfather, Abd al-Muttalib, and paternal uncle, Abu Talib. In later years, he would periodically seclude himself in a mountain cave named Hira for several nights of prayer. When he was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
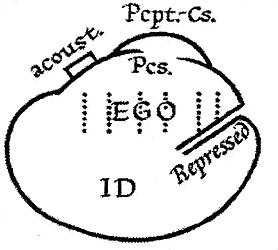
Ego (Freudian)
In psychoanalytic theory, the id, ego, and superego are three distinct, interacting agents in the psychic apparatus, outlined in Sigmund Freud's structural model of the psyche. The three agents are theoretical constructs that Freud employed to describe the basic structure of mental life as it was encountered in psychoanalytic practice. Freud himself used the German terms ''das Es'', ''Ich'', and ''Über-Ich'', which literally translate as "the it", "I", and "over-I". The Latin terms id, ego and superego were chosen by his original translators and have remained in use. The structural model was introduced in Freud's essay '' Beyond the Pleasure Principle'' (1920) and further refined and formalised in later essays such as '' The Ego and the Id'' (1923). Freud developed the model in response to the perceived ambiguity of the terms "conscious" and "unconscious" in his earlier ''topographical'' model. Broadly speaking, the id is the organism's unconscious array of uncoordinated i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
99 Names Of God In Islam
Names of God in Islam () are 99 names that each contain Attributes of God in Islam, which are implied by the respective names. These names usually denote his praise, gratitude, commendation, glorification, magnification, perfect attributes, majestic qualities, and acts of wisdom, mercy, benefit, and justice from Allah, as believed by Muslims. These names are commonly called upon by Muslims during prayers, supplications, and remembrance, as they hold significant spiritual and theological importance, serving as a means for Muslims to connect with God. Each name reflects a specific attribute of Allah and serves as a means for believers to understand and relate to the Divine. Some names are known from either the Qur’an or the hadith, while others can be found in both sources, although most are found in the Qur’an. Additionally, Muslims also believe that there are more names of God besides those found in the Qur'an and hadith and that God has kept knowledge of these names h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sadr (Sufism)
Sadr or SADR may refer to: Places *Sadr City, a neighborhood in Baghdad, Iraq * Sadr, Iran, a village in East Azerbaijan Province, Iran *Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), is a partially recognized country in North Africa. Other uses * Sadr (name), a family name originating in Lebanon * Sadr (surname), list of people with the surname *Sadr (title), a title primarily used in the Iranian world to designate an exceptional person, such as a scholar * Source-address dependent routing or source-specific routing * Gamma Cygni or Sadr, a star *The Urdu word for ''president'', used to refer to the President of Pakistan The president of Pakistan () is the head of state of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. The president is the nominal head of the executive and the supreme commander of the Pakistan Armed Forces. See also *[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psyche (psychology)
The psyche is currently used to describe the totality of the human mind, conscious and unconscious. Especially in older texts, the English word soul is sometimes used synonymously. ''Psychology'' is the scientific or objective study of the psyche. The word has a long history of use in psychology and philosophy, dating back to ancient times, and represents one of the fundamental concepts for understanding human nature from a scientific point of view. Etymology The basic meaning of the Greek word ψυχή (''psyche'') was 'life'. Although unsupported, some have claimed it is derived from the verb ψύχω (''psycho'', 'to blow'). Derived meanings included 'spirit', 'soul', 'ghost', and ultimately 'self' in the sense of 'conscious personality' or 'psyche'. Ancient psychology The idea of the psyche is central to the philosophy of Plato. Scholars translate the Platonic conceptualization of the term as "soul" in the sense that he believed that it is immortal. In his Phaedo, Pla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramadan
Ramadan is the ninth month of the Islamic calendar. It is observed by Muslims worldwide as a month of fasting (''Fasting in Islam, sawm''), communal prayer (salah), reflection, and community. It is also the month in which the Quran is believed to have been revealed to the Prophets of Islam, Islamic prophet Muhammad. The annual observance of Ramadan is regarded as one of the five pillars of Islam and lasts twenty-nine to thirty days, from one sighting of the Hilal (crescent moon), crescent moon to the next. Fasting from dawn to sunset is obligatory (''fard'') for all adult Muslims who are not acute illness, acutely or chronic illness, chronically ill, travelling, old age, elderly, breastfeeding, Pregnancy, pregnant, or Menstruation in Islam, menstruating. The predawn meal is referred to as ''suhur'', and the nightly feast that breaks the fast is called ''iftar''. Although rulings (''fatawa'') have been issued declaring that Muslims who live in regions with a midnight sun or pola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Ghazali
Al-Ghazali ( – 19 December 1111), archaically Latinized as Algazelus, was a Shafi'i Sunni Muslim scholar and polymath. He is known as one of the most prominent and influential jurisconsults, legal theoreticians, muftis, philosophers, theologians, logicians and mystics in Islamic history. He is considered to be the 11th century's '' mujaddid'',William Montgomery Watt, ''Al-Ghazali: The Muslim Intellectual'', p. 180. Edinburgh University Press, 1963. a renewer of the faith, who, according to the prophetic hadith, appears once every 100 years to restore the faith of the Islamic community.Dhahabi, Siyar, 4.566 Al-Ghazali's works were so highly acclaimed by his contemporaries that he was awarded the honorific title "Proof of Islam" ('' Ḥujjat al-Islām''). Al-Ghazali was a prominent mujtahid in the Shafi'i school of law. Much of Al-Ghazali's work stemmed around his spiritual crises following his appointment as the head of the Nizamiyya University in Baghdad - which was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |