|
Raymond Gorte
Raymond John Gorte is an American Chemical engineering, chemical engineer, currently the Russel Pearce and Elizabeth Crimian Heuer Endowed Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CBE) and Materials Science & Engineering (MSE) at the University of Pennsylvania. Throughout his career at the University of Pennsylvania and the University of Minnesota, he has advanced the study of fuel cells and catalysts including heterogeneous metals and zeolite materials. He is a member of the U.S. National Academy of Engineering. Early life and education Gorte was born in Wisconsin and grew up in Manitowoc, Wisconsin. In 1976, he earned a Bachelor of Science in chemical engineering from the University of Wisconsin-Madison. He completed his Ph.D. in chemical engineering at the University of Minnesota in 1981 with advisor Lanny D. Schmidt on the topic of platinum catalysis of nitric oxide decomposition. His thesis was published in 1981 with the title, "The Kinetic Interaction of Nitric ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manitowoc, Wisconsin
Manitowoc () is a city in and the county seat of Manitowoc County, Wisconsin, United States. The city is located on Lake Michigan at the mouth of the Manitowoc River. According to the 2020 census, Manitowoc had a population of 34,626, with over 50,000 residents in the surrounding communities. History Purported to mean ''dwelling of the great spirit'', Manitowoc derived its name from either the Ojibwe word ''manidoowaak(wag)'', meaning spirit-spawn(s), or ''manidoowaak(oog)'', meaning spirit-wood(s), or ''manidoowak(iin)'', meaning spirit-land(s). In the Menominee language, it is called ''Manetōwak'', which means "place of the spirits". The Menominee ceded this land to the United States in the 1836 Treaty of the Cedars, following years of negotiations over how to accommodate the Oneida, Stockbridge-Munsee, and Brothertown peoples who had been removed from New York to Wisconsin. In 1838, an act of the Territorial Legislature separated Manitowoc County from Brown County, kee ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley, the nation's seventh-largest and one of world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia. Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Quaker. The city served as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony during the British colonial era and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the American Revolution and the nation's inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Interaction Energy
In physics, interaction energy is the contribution to the total energy that is caused by an interaction between the objects being considered. The interaction energy usually depends on the relative position of the objects. For example, Q_1 Q_2 / (4 \pi \varepsilon_0 \Delta r) is the electrostatic interaction energy between two objects with charges Q_1, Q_2. Interaction energy A straightforward approach for evaluating the interaction energy is to calculate the difference between the objects' combined energy and all of their isolated energies. In the case of two objects, ''A'' and ''B'', the interaction energy can be written as: Theoretical and Computational Chemistry, 1999, Ideas of Quantum Chemistry, 2007 and Quantum Magnetic Resonance Imaging Diagnostics of Human Brain Disorders, 2010 \Delta E_\text = E(A,B) - \left( E(A) + E(B) \right), where E(A) and E(B) are the energies of the isolated objects (monomers), and E(A,B) the energy of their interacting assembly (dimer). For larger ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proton Affinity
The proton affinity (PA, ''E''pa) of an anion or of a neutral atom or molecule is the negative of the enthalpy change in the reaction between the chemical species concerned and a proton in the gas phase: ::: A- + H+ -> HA ::: B + H+ -> BH+ These reactions are always exothermic in the gas phase, i.e. energy is released (enthalpy is negative) when the reaction advances in the direction shown above, while the proton affinity is positive. This is the same sign convention used for electron affinity. The property related to the proton affinity is the gas-phase basicity, which is the negative of the Gibbs energy for above reactions, i.e. the gas-phase basicity includes entropic terms in contrast to the proton affinity. Acid/base chemistry The higher the proton affinity, the stronger the base and the weaker the conjugate acid ''in the gas phase''. The (reportedly) strongest known base is the ortho-diethynylbenzene dianion (''E''pa = 1843 kJ/mol), followed by the methanide ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thermochemistry
Thermochemistry is the study of the heat energy which is associated with chemical reactions and/or phase changes such as melting and boiling. A reaction may release or absorb energy, and a phase change may do the same. Thermochemistry focuses on the energy exchange between a system and its surroundings in the form of heat. Thermochemistry is useful in predicting reactant and product quantities throughout the course of a given reaction. In combination with entropy determinations, it is also used to predict whether a reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous, favorable or unfavorable. Endothermic reactions absorb heat, while exothermic reactions release heat. Thermochemistry coalesces the concepts of thermodynamics with the concept of energy in the form of chemical bonds. The subject commonly includes calculations of such quantities as heat capacity, heat of combustion, heat of formation, enthalpy, entropy, and free energy. Thermochemistry is one part of the broader field of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
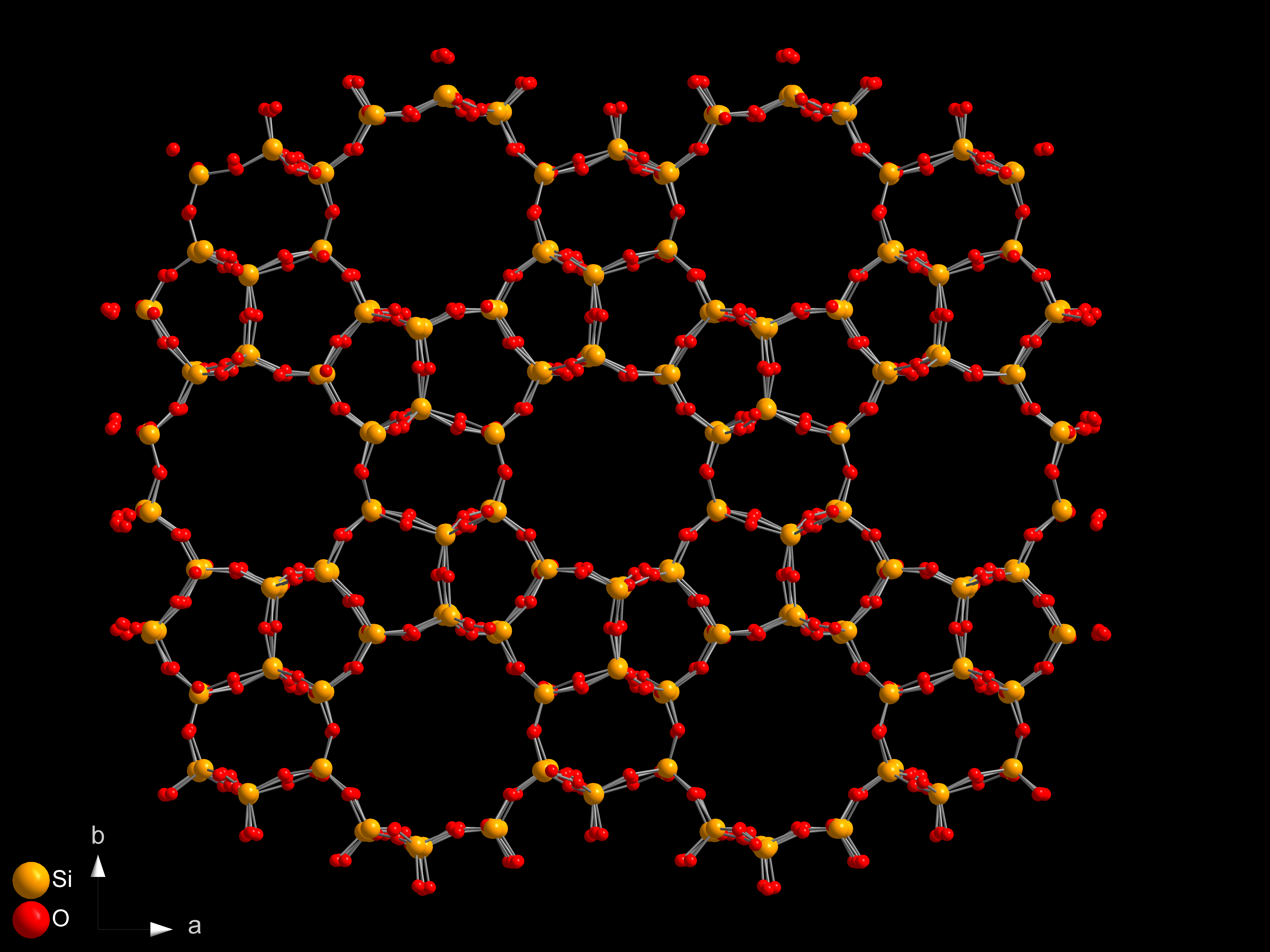
Faujasite
Faujasite (FAU-type zeolite) is a mineral group in the zeolite family of silicate minerals. The group consists of faujasite-Na, faujasite-Mg and faujasite-Ca. They all share the same basic formula by varying the amounts of sodium, magnesium and calcium. Faujasite occurs as a rare mineral in several locations worldwide. Faujasite materials are widely synthesized industrially. The relatively low-silica (Si/Al2) one is called Zeolite Y. In addition, the aluminum component in zeolite Y can be removed by acid-treatment and/or steam-treatment, and the resulting faujasite is called USY (Ultrastable zeolite Y). USY is used in fluid catalytic cracking process as a catalyst. Discovery and occurrence Faujasite was first described in 1842 from an occurrence in the Limberg Quarries, Sasbach, Kaiserstuhl, Baden-Württemberg, Germany. The sodium modifier faujasite-Na was added following the discovery of the magnesium and calcium rich phases in the 1990s. It was named for Barthélemy Fauja ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ZSM-5
ZSM-5, Zeolite Socony Mobil–5 (framework type MFI from ZSM-5 (five)), is an aluminosilicate zeolite belonging to the pentasil family of zeolites. Its chemical formula is NanAlnSi96–nO192·16H2O (0 Structure [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amorphous Silica-alumina
Amorphous silica-alumina is a synthetic substance that is used as a catalyst or catalyst support.Julius Scherzer, Adrian J. Gruia, (1996), ''Hydrocracking Science and Technology'', CRC Press, It can be prepared in a number of ways for example: * Precipitation of hydrous alumina onto amorphous silica hydrogel * Reacting a silica sol with an alumina sol * Coprecipitation from sodium silicate / aluminium salt solution Water-soluble contaminants, e.g. sodium salts, are removed by washing. Some of the alumina is present in tetrahedral coordination as shown by NMR studies 29Si MASNMR and 27Al NMR Amorphous silica-alumina contains sites which are termed Brønsted acid (or protic) sites, with an ionizable hydrogen atom, and Lewis acid (aprotic), electron accepting sites and these different types of acidic site can be distinguished by the ways in which, say, pyridine attaches. On Lewis acid sites it forms complexes and on the Brønsted sites it adsorbs as the pyridinium ion. As of 200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid Acid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural rigidity and resistance to a force applied to the surface. Unlike a liquid, a solid object does not flow to take on the shape of its container, nor does it expand to fill the entire available volume like a gas. The atoms in a solid are bound to each other, either in a regular geometric lattice (crystalline solids, which include metals and ordinary ice), or irregularly (an amorphous solid such as common window glass). Solids cannot be compressed with little pressure whereas gases can be compressed with little pressure because the molecules in a gas are loosely packed. The branch of physics that deals with solids is called solid-state physics, and is the main branch of condensed matter physics (which also includes liquids). Materials science ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cerium(IV) Oxide
Cerium(IV) oxide, also known as ceric oxide, ceric dioxide, ceria, cerium oxide or cerium dioxide, is an oxide of the rare-earth metal cerium. It is a pale yellow-white powder with the chemical formula CeO2. It is an important commercial product and an intermediate in the purification of the element from the ores. The distinctive property of this material is its reversible conversion to a non-stoichiometric oxide. Production Cerium occurs naturally as oxides, always as a mixture with other rare-earth elements. Its principal ores bastnaesite and monazite. After extraction of the metal ions into aqueous base, Ce is separated from that mixture by addition of an oxidant followed by adjustment of the pH. This step exploits the low solubility of CeO2 and the fact that other rare-earth elements resist oxidation.. Cerium(IV) oxide is formed by the calcination of cerium oxalate or cerium hydroxide. Cerium also forms cerium(III) oxide, , which is unstable and will oxidize to cerium ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anode
An anode is an electrode of a polarized electrical device through which conventional current enters the device. This contrasts with a cathode, an electrode of the device through which conventional current leaves the device. A common mnemonic is ACID, for "anode current into device". The direction of conventional current (the flow of positive charges) in a circuit is opposite to the direction of electron flow, so (negatively charged) electrons flow out the anode of a galvanic cell, into an outside or external circuit connected to the cell. For example, the end of a household battery marked with a "-" (minus) is the anode. In both a galvanic cell and an electrolytic cell, the anode is the electrode at which the oxidation reaction occurs. In a galvanic cell the anode is the wire or plate having excess negative charge as a result of the oxidation reaction. In an electrolytic cell, the anode is the wire or plate upon which excess positive charge is imposed. As a result of this, anion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Methane
Methane ( , ) is a chemical compound with the chemical formula (one carbon atom bonded to four hydrogen atoms). It is a group-14 hydride, the simplest alkane, and the main constituent of natural gas. The relative abundance of methane on Earth makes it an economically attractive fuel, although capturing and storing it poses technical challenges due to its gaseous state under normal conditions for temperature and pressure. Naturally occurring methane is found both below ground and under the seafloor and is formed by both geological and biological processes. The largest reservoir of methane is under the seafloor in the form of methane clathrates. When methane reaches the surface and the atmosphere, it is known as atmospheric methane. The Earth's atmospheric methane concentration has increased by about 150% since 1750, and it accounts for 20% of the total radiative forcing from all of the long-lived and globally mixed greenhouse gases. It has also been detected on other plane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |