Philadelphia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the

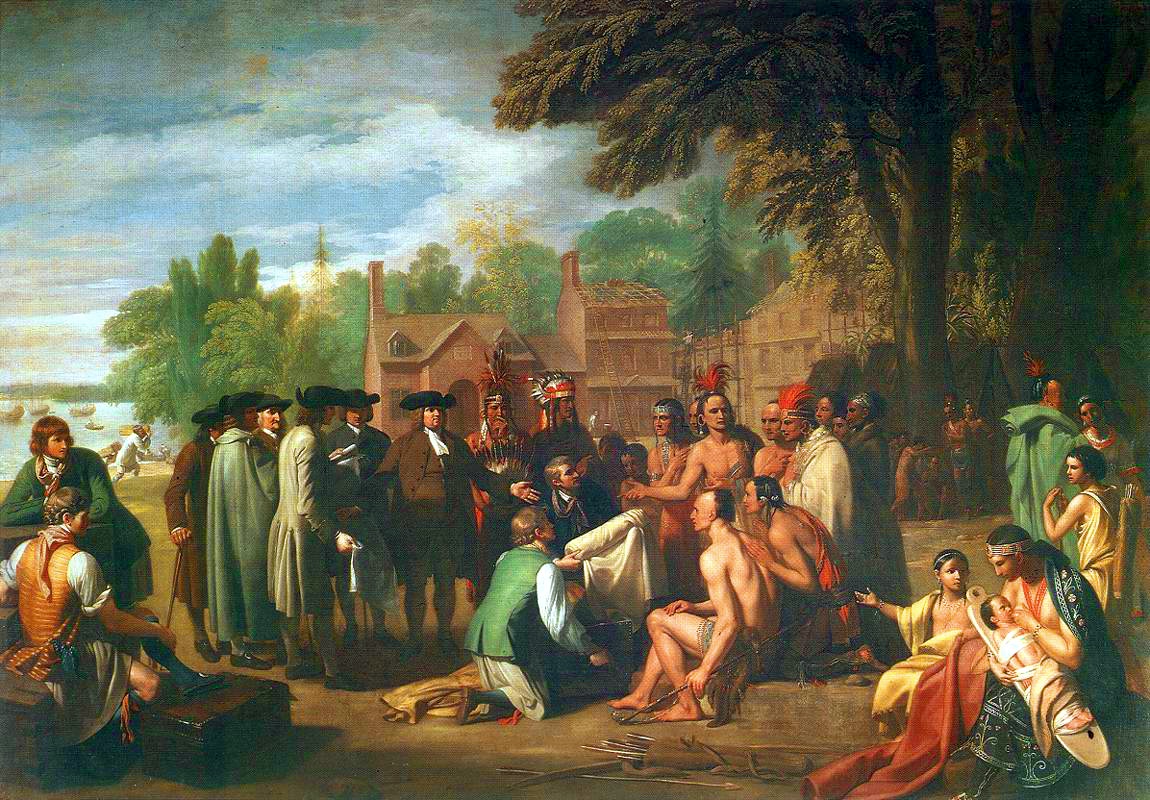 Europeans came to the
Europeans came to the
Commonwealth
A commonwealth is a traditional English term for a political community founded for the common good. Historically, it has been synonymous with "republic". The noun "commonwealth", meaning "public welfare, general good or advantage", dates from the ...
of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis
The Northeast megalopolis, also known as the Northeast Corridor, Acela Corridor, Boston–Washington corridor, or BosWash, is the world's largest megalopolis in terms of economic output and the second most populous megalopolis in the United St ...
and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since 1854, the city has been coextensive with Philadelphia County, the most populous county in Pennsylvania and the urban core of the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
, the nation's seventh-largest and one of world's largest metropolitan regions, with 6.245 million residents . The city's population at the 2020 census was 1,603,797, and over 56 million people live within of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia was founded in 1682 by William Penn, an English Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
. The city served as capital of the Pennsylvania Colony during the British colonial era and went on to play a historic and vital role as the central meeting place for the nation's founding fathers whose plans and actions in Philadelphia ultimately inspired the American Revolution
The American Revolution was an ideological and political revolution that occurred in British America between 1765 and 1791. The Americans in the Thirteen Colonies formed independent states that defeated the British in the American Revolu ...
and the nation's independence. Philadelphia hosted the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
in 1774 following the Boston Tea Party, preserved the Liberty Bell
The Liberty Bell, previously called the State House Bell or Old State House Bell, is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia. Originally placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House (now renamed Independence ...
, and hosted the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
during which the founders signed the Declaration of Independence, which historian Joseph Ellis has described as "the most potent and consequential words in American history". Once the Revolutionary War commenced, both the Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown was a major engagement in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania, between the British Army led by Sir William Howe, and the American Con ...
and the Siege of Fort Mifflin were fought within Philadelphia's city limits. The U.S. Constitution was later ratified in Philadelphia at the Philadelphia Convention of 1787. Philadelphia remained the nation's largest city until 1790, when it was surpassed by New York City, and served as the nation's first capital from May 10, 1775, until December 12, 1776, and on four subsequent occasions during and following the American Revolution, including from 1790 to 1800 while the new national capital of Washington, D.C., was under construction.
With 18 four-year universities and colleges, Philadelphia is one of the nation's leading centers for higher education and academic research. , the Philadelphia metropolitan area was the nation's ninth-largest metropolitan economy with a gross metropolitan product ( GMP) of US$479 billion. Philadelphia is the largest center of economic activity in Pennsylvania and the broader multi-state Delaware Valley region; the city is home to five Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for their respective fiscal years. The list includes publicly held companies, along ...
corporate headquarters as of 2022. The Philadelphia skyline
Philadelphia, the largest city in the U.S. state of Pennsylvania, is home to more than 300 completed high-rise buildings up to , and 58 completed skyscrapers of or taller,
, which includes several globally renowned commercial skyscrapers, is expanding, primarily with new residential high-rise condominium
A condominium (or condo for short) is an ownership structure whereby a building is divided into several units that are each separately owned, surrounded by common areas that are jointly owned. The term can be applied to the building or complex ...
s. The city and the Delaware Valley are a biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
and venture capital hub; and the Philadelphia Stock Exchange, owned by NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
, is the nation's oldest stock exchange and a global leader in options
Option or Options may refer to:
Computing
*Option key, a key on Apple computer keyboards
*Option type, a polymorphic data type in programming languages
* Command-line option, an optional parameter to a command
*OPTIONS, an HTTP request method
...
trading. 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
, the city's primary rail station, is the third-busiest Amtrak hub in the nation, and the city's multimodal transport and logistics infrastructure, including Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
, the PhilaPort seaport, freight rail infrastructure, roadway traffic capacity, and warehouse storage space, are all expanding.
Philadelphia is a national cultural hub, hosting more outdoor sculptures and murals than any other American city. Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
, when combined with adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park in the same watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
, is , representing one of the nation's largest contiguous urban parks and the 45th largest urban park in the world. The city is known for its arts, culture
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and norms found in human societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, customs, capabilities, and habits of the individuals in these grou ...
, cuisine
A cuisine is a style of cooking characterized by distinctive ingredients, techniques and dishes, and usually associated with a specific culture or geographic region. Regional food preparation techniques, customs, and ingredients combine to ...
, and colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
and Revolution-era history; in 2016, it attracted 42 million domestic tourists who spent $6.8 billion, representing $11 billion in total economic impact to the city and surrounding Pennsylvania counties.
With five professional sports teams and a hugely loyal fan base, the city is often ranked as the nation's best city for professional sports fans. The city has a culturally and philanthropically active LGBTQ+ community
The LGBT community (also known as the LGBTQ+ community, GLBT community, gay community, or queer community) is a loosely defined grouping of lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and other queer individuals united by a common culture and social ...
. Philadelphia also has played an immensely influential historic and ongoing role in the development and evolution of American music, especially R&B, soul, and rock.
Philadelphia is a city of many firsts, including the nation's first library (1731), hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
(1751), medical school
A medical school is a tertiary educational institution, or part of such an institution, that teaches medicine, and awards a professional degree for physicians. Such medical degrees include the Bachelor of Medicine, Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS, M ...
(1765), national capital (1774), university (by some accounts) (1779), stock exchange
A stock exchange, securities exchange, or bourse is an exchange where stockbrokers and traders can buy and sell securities, such as shares of stock, bonds and other financial instruments. Stock exchanges may also provide facilities for th ...
(1790), zoo (1874), and business school
A business school is a university-level institution that confers degrees in business administration or management. A business school may also be referred to as school of management, management school, school of business administration, o ...
(1881). Philadelphia contains 67 National Historic Landmarks, including Independence Hall. From the city's 17th century founding through the present, Philadelphia has been the birthplace or home to an extensive number of prominent and influential Americans. In 2021, '' Time'' magazine named Philadelphia one of the world's greatest 100 places.
History
Native peoples
Prior to the arrival of Europeans in the early 17th century, the Philadelphia area was home to the Lenape (Delaware)Indians
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
in the village of Shackamaxon. They were also called the Delaware Indians,Josephy 188–189 and their historical territory was along the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
watershed
Watershed is a hydrological term, which has been adopted in other fields in a more or less figurative sense. It may refer to:
Hydrology
* Drainage divide, the line that separates neighbouring drainage basins
* Drainage basin, called a "watershe ...
, western Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York (state), New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United Sta ...
, and the Lower Hudson Valley. Most Lenape were pushed out of their Delaware homeland during the 18th century by expanding European colonies, exacerbated by losses from intertribal conflicts. Lenape communities were weakened by newly introduced diseases, mainly smallpox, and conflict with Europeans. The Iroquois occasionally fought the Lenape. Surviving Lenape moved west into the upper Ohio River
The Ohio River is a long river in the United States. It is located at the boundary of the Midwestern and Southern United States, flowing southwesterly from western Pennsylvania to its mouth on the Mississippi River at the southern tip of Illino ...
basin. The American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of ...
and the United States' independence pushed them further west. In the 1860s, the United States government sent most Lenape remaining in the eastern United States to the Indian Territory (present-day Oklahoma and surrounding territory) under the Indian removal
Indian removal was the United States government policy of forced displacement of self-governing tribes of Native Americans from their ancestral homelands in the eastern United States to lands west of the Mississippi Riverspecifically, to a de ...
policy.
Colonial

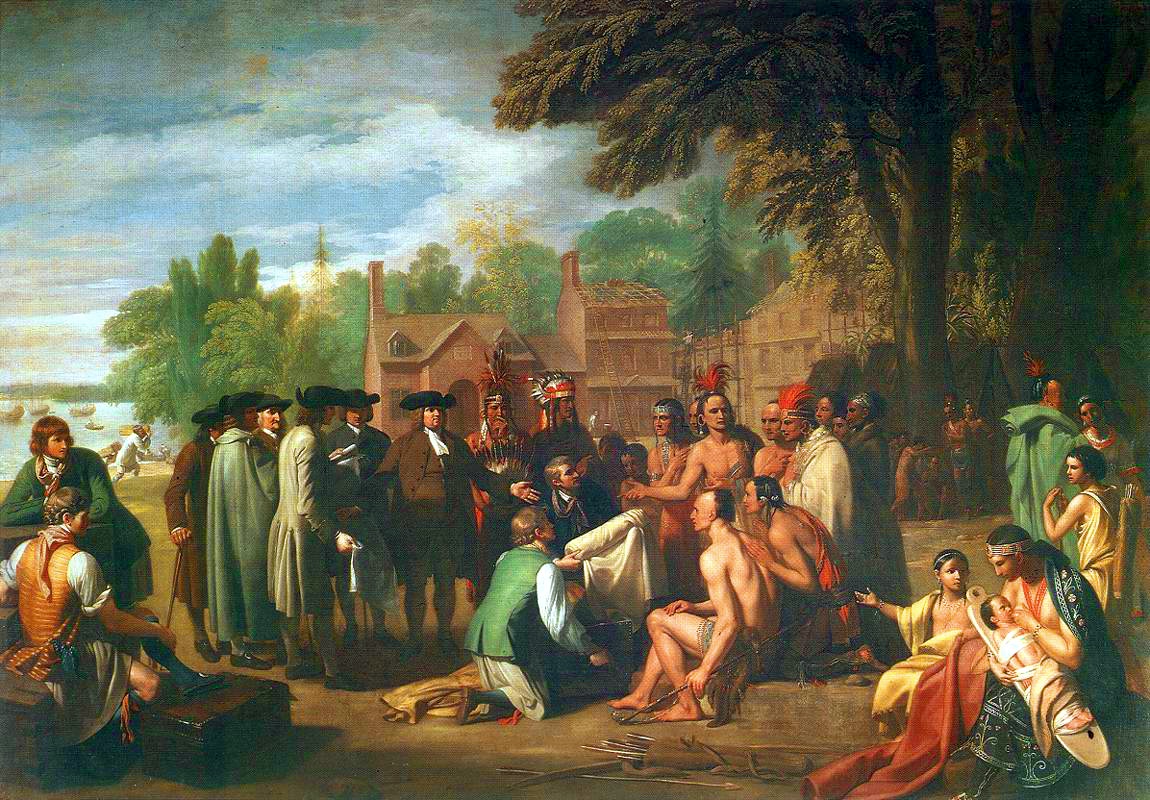 Europeans came to the
Europeans came to the Delaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
in the early 17th century, with the first settlements founded by Dutch colonists, who in 1623 built Fort Nassau on the Delaware River in what is now Brooklawn, New Jersey
Brooklawn is a borough in Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2010 United States census, the borough's population was 1,815, a drop of 140 from the 2010 census enumeration of 1,955,New Netherland colony. In 1638, Swedish settlers led by renegade Dutch established the colony of New Sweden at
 Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed
Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed
 Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being
Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being
 By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican
By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican

 Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to
Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to
File:Elfreth's Alley, Philadelphia, 2008.jpg, Elfreth's Alley, "Our nation's oldest residential street", 1702–1836Historical marker on Elfreth's Alley
File:Carpenters' Hall, Philadelphia, USA, May 2015.jpg, Carpenters' Hall exhibiting
 , the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is
, the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is

 Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's
Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's
 According to a 2014 study by the
According to a 2014 study by the

 The Philadelphia Stock Exchange, acquired by
The Philadelphia Stock Exchange, acquired by
Accessed April 18, 2019. The Philadelphia metropolitan area, comprising the Delaware Valley, has also become a growing hub for venture capital funding.
 Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the
Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the
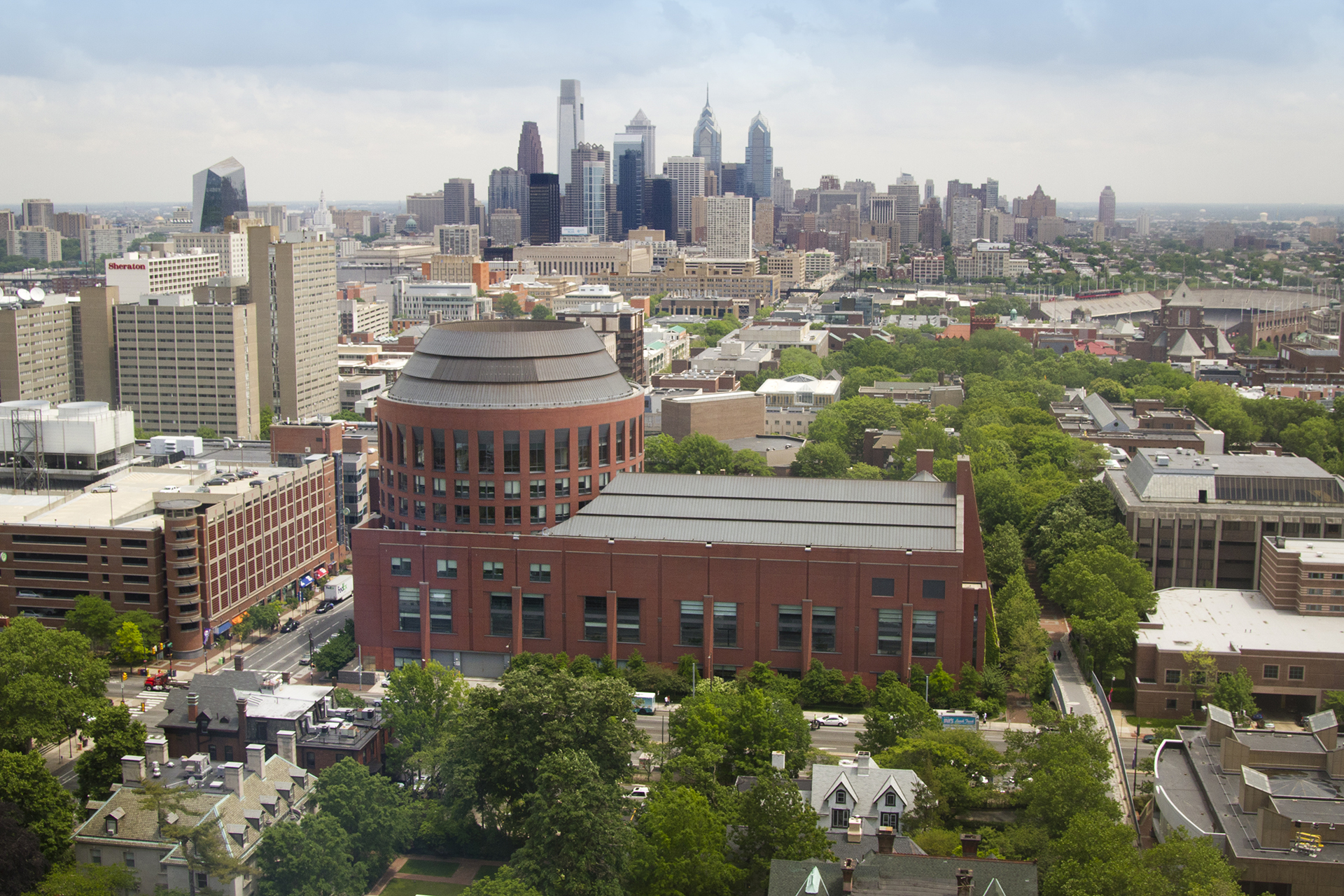
 Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the
Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the
Fort Christina
Fort Christina (also called Fort Altena) was the first Swedish settlement in North America and the principal settlement of the New Sweden colony. Built in 1638 and named after Queen Christina of Sweden, it was located approximately 1 mi (1.6 ...
(present-day Wilmington, Delaware) and quickly spread out in the valley. In 1644, New Sweden supported the Susquehannock
The Susquehannock people, also called the Conestoga by some English settlers or Andastes were Iroquoian Native Americans who lived in areas adjacent to the Susquehanna River and its tributaries, ranging from its upper reaches in the southern p ...
s in their war against Maryland colonists. In 1648, the Dutch built Fort Beversreede on the west bank of the Delaware, south of the Schuylkill River near the present-day Eastwick neighborhood, to reassert their dominion over the area. The Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
responded by building Fort Nya Korsholm
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
, or New Korsholm, named after a town in Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bo ...
with a Swedish majority. In 1655, a Dutch military campaign led by New Netherland Director-General Peter Stuyvesant
Peter Stuyvesant (; in Dutch also ''Pieter'' and ''Petrus'' Stuyvesant, ; 1610 – August 1672)Mooney, James E. "Stuyvesant, Peter" in p.1256 was a Dutch colonial officer who served as the last Dutch director-general of the colony of New Net ...
took control of the Swedish colony, ending its claim to independence. The Swedish and Finnish settlers continued to have their own militia, religion, and court, and to enjoy substantial autonomy under the Dutch. An English fleet captured the New Netherland colony in 1664, though the situation did not change substantially until 1682, when the area was included in William Penn's charter for Pennsylvania.
In 1681, in partial repayment of a debt, Charles II of England
Charles II (29 May 1630 – 6 February 1685) was King of Scotland from 1649 until 1651, and King of England, Scotland and Ireland from the 1660 Restoration of the monarchy until his death in 1685.
Charles II was the eldest surviving child of ...
granted Penn a charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the ...
for what would become the Pennsylvania colony. Despite the royal charter, Penn bought the land from the local Lenape to be on good terms with the Native Americans and ensure peace for his colony. Penn made a treaty of friendship with Lenape chief Tammany under an elm tree at Shackamaxon, in what is now the city's Fishtown neighborhood. Penn named the city Philadelphia, which is Greek for "brotherly love," derived from the Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Dark Ages (), the Archaic p ...
terms φίλος ''phílos'' (beloved, dear) and ἀδελφός ''adelphós'' (brother, brotherly). There were a number of cities named '' Philadelphia'' in the Eastern Mediterranean during the Greek and Roman periods, including one (modern Alaşehir) mentioned as the site of an early Christian congregation in the Book of Revelation
The Book of Revelation is the final book of the New Testament (and consequently the final book of the Christian Bible). Its title is derived from the first word of the Koine Greek text: , meaning "unveiling" or "revelation". The Book o ...
. As a Quaker
Quakers are people who belong to a historically Protestant Christian set of Christian denomination, denominations known formally as the Religious Society of Friends. Members of these movements ("theFriends") are generally united by a belie ...
, Penn had experienced religious persecution and wanted his colony to be a place where anyone could worship freely. This tolerance, far more than afforded by most other colonies, led to better relations with the local native tribes and fostered Philadelphia's rapid growth into America's most important city.
Penn planned a city on the Delaware River to serve as a port and place for government. Hoping that Philadelphia would become more like an English rural town instead of a city, Penn laid out roads on a grid plan
In urban planning, the grid plan, grid street plan, or gridiron plan is a type of city plan in which streets run at right angles to each other, forming a grid.
Two inherent characteristics of the grid plan, frequent intersections and orthogona ...
to keep houses and businesses spread far apart, with areas for gardens and orchards.
The city's inhabitants did not follow Penn's plans, however, as they crowded by the present-day Port of Philadelphia on the Delaware River, and subdivided and resold their lots. Before Penn left Philadelphia for the last time, he issued the Charter of 1701 establishing it as a city. Though poor at first, the city became an important trading center with tolerable living conditions by the 1750s. Benjamin Franklin
Benjamin Franklin ( April 17, 1790) was an American polymath who was active as a writer, scientist, inventor
An invention is a unique or novel device, method, composition, idea or process. An invention may be an improvement upon a m ...
, a leading citizen, helped improve city services and founded new ones, such as fire protection, a library, and one of the American colonies' first hospitals.
A number of philosophical societies were formed, which were centers of the city's intellectual life: the Philadelphia Society for Promoting Agriculture (1785), the Pennsylvania Society for the Encouragement of Manufactures and the Useful Arts (1787), the Academy of Natural Sciences (1812), and the Franklin Institute (1824). These societies developed and financed new industries, attracting skilled and knowledgeable immigrants from Europe.
Revolution
 Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed
Philadelphia's importance and central location in the colonies made it a natural center for America's revolutionaries. By the 1750s, Philadelphia had surpassed Boston
Boston (), officially the City of Boston, is the capital city, state capital and List of municipalities in Massachusetts, most populous city of the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Massachusetts, as well as the cultural and financ ...
as the largest city and busiest port in British America
British America comprised the colonial territories of the English Empire, which became the British Empire after the 1707 union of the Kingdom of England with the Kingdom of Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain, in the Americas from 16 ...
, and the second-largest city in the entire British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading post ...
, after London. Before the Revolutionary War, in 1774, as resentment of British colonial practices and support for independence was burgeoning in the colonies, Philadelphia hosted the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Navy ...
. From 1775 to 1781, Philadelphia hosted the Second Continental Congress
The Second Continental Congress was a late-18th-century meeting of delegates from the Thirteen Colonies that united in support of the American Revolutionary War. The Congress was creating a new country it first named "United Colonies" and in 1 ...
, which adopted the Declaration of Independence in what was then called the Pennsylvania State House
The Pennsylvania House of Representatives is the lower house of the bicameral Pennsylvania General Assembly, the legislature of the U.S. state of Pennsylvania. There are 203 members, elected for two-year terms from single member districts.
It ...
and now is called Independence Hall, on July 4, 1776.
Historian Joseph Ellis, in 2007, described the Declaration of Independence as "the most potent and consequential words in American history," and its adoption represented a declaration of war, already ongoing since April 1775, against the British Army, which was then the most powerful military force in the world. Since the Declaration's July 4, 1776, adoption, its signing has been cited globally and repeatedly by various peoples of the world seeking independence and liberty. It also has been, since its adoption, the basis for annual celebration by Americans; in 1938, this celebration of the Declaration was formalized as Independence Day
An independence day is an annual event commemorating the anniversary of a nation's independence or statehood, usually after ceasing to be a group or part of another nation or state, or more rarely after the end of a military occupation. Man ...
, one of only ten designated U.S. federal holidays.
After George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Fathers of the United States, Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the ...
's defeat at the Battle of Brandywine
The Battle of Brandywine, also known as the Battle of Brandywine Creek, was fought between the American Continental Army of General George Washington and the British Army of General Sir William Howe on September 11, 1777, as part of the Ame ...
in Chadds Ford Township, Pennsylvania on September 11, 1777, the revolutionary capital of Philadelphia was defenseless. The city prepared for what was perceived to be an inevitable British Army attack. Because bells could easily be recast into munitions, the Liberty Bell
The Liberty Bell, previously called the State House Bell or Old State House Bell, is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia. Originally placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House (now renamed Independence ...
, then known as the Pennsylvania State Bell, along with bells from two Philadelphia churches, Christ Church and St. Peter's Church, were hastily taken down and transported by heavily-guarded wagon train out of the city. The Liberty Bell was taken to Zion German Reformed Church in Northampton Town (present-day Allentown), where it was hidden under the church's floor boards for nine months, from September 1777 until the British Army's departure from Philadelphia in June 1778, during the British occupation of Philadelphia. Two Revolutionary War battles, the Siege of Fort Mifflin (September 26 to November 16, 1777) and the Battle of Germantown
The Battle of Germantown was a major engagement in the Philadelphia campaign of the American Revolutionary War. It was fought on October 4, 1777, at Germantown, Pennsylvania, between the British Army led by Sir William Howe, and the American Con ...
(October 4, 1777), were both fought within Philadelphia's city limits.
In Philadelphia, the Second Continental Congress adopted the Articles of Confederation
The Articles of Confederation and Perpetual Union was an agreement among the 13 Colonies of the United States of America that served as its first frame of government. It was approved after much debate (between July 1776 and November 1777) by ...
on November 15, 1777, and the city later served as the meeting place for the Constitutional Convention Constitutional convention may refer to:
* Constitutional convention (political custom), an informal and uncodified procedural agreement
*Constitutional convention (political meeting), a meeting of delegates to adopt a new constitution or revise an e ...
, which ratified the Constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princip ...
in Independence Hall in Philadelphia on September 17, 1787.
Philadelphia served as capital of the United States for much of the colonial and early post-colonial periods, including for a decade, from 1790 to 1800, while the District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle, Jefferson Memorial, White House, Adams Morgan ...
was being constructed and prepared to serve as the new nation's national capital. In 1793, the largest yellow fever epidemic in U.S. history killed approximately 4,000 to 5,000 people in Philadelphia, or about 10% of the city's population.
The state capital was moved to Lancaster in 1799, then Harrisburg in 1812, while the federal government was moved to Washington, D.C., in 1800 upon completion of the White House and U.S. Capitol building. Philadelphia remained the young nation's largest city until the late 18th century, serving as the nation's financial and cultural center, until ultimately being eclipsed in total population by New York City in 1790. In 1816, the city's free Black community founded the African Methodist Episcopal Church (AME), the first independent Black denomination in the country, and the first Black Episcopal Church. The free black community also established many schools for its children, with the help of Quakers. Large-scale construction projects for new roads, canal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface fl ...
s, and railroads made Philadelphia the first major industrial city in the United States.
19th century
 Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being
Throughout the 19th century, Philadelphia hosted a variety of industries and businesses, the largest being textiles
Textile is an umbrella term that includes various fiber-based materials, including fibers, yarns, filaments, threads, different fabric types, etc. At first, the word "textiles" only referred to woven fabrics. However, weaving is not the ...
. Major corporations in the 19th and early 20th centuries included the Baldwin Locomotive Works
The Baldwin Locomotive Works (BLW) was an American manufacturer of railroad locomotives from 1825 to 1951. Originally located in Philadelphia, it moved to nearby Eddystone, Pennsylvania, in the early 20th century. The company was for decade ...
, William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company, and the Pennsylvania Railroad
The Pennsylvania Railroad (reporting mark PRR), legal name The Pennsylvania Railroad Company also known as the "Pennsy", was an American Class I railroad that was established in 1846 and headquartered in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was named ...
. Established in 1870, the Philadelphia Conveyancers' Association was chartered by the state in 1871. Industry, along with the U.S. Centennial, was celebrated in 1876 with the Centennial Exposition, the first official World's fair in the United States.
Immigrants, mostly from Ireland and Germany, settled in Philadelphia and the surrounding districts. These immigrants were largely responsible for the first general strike in North America in 1835, in which workers in the city won the ten-hour workday. The city was a destination for thousands of Irish immigrants fleeing the Great Famine in the 1840s; housing for them was developed south of South Street and later occupied by succeeding immigrants. They established a network of Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
churches and schools and dominated the Catholic clergy for decades. Anti-Irish, anti-Catholic nativist riots
A riot is a form of civil disorder commonly characterized by a group lashing out in a violent public disturbance against authority, property, or people.
Riots typically involve destruction of property, public or private. The property targeted ...
erupted in Philadelphia in 1844. The rise in population of the surrounding districts helped lead to the Act of Consolidation of 1854, which extended the city limits from the of Center City to the roughly of Philadelphia County.
In the latter half of the 19th century and leading into the 20th century, immigrants from Russia, Eastern Europe, and Italy, and African Americans from the southern U.S.
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
settled in the city.
Philadelphia was represented by the Washington Grays in the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union ("the North") and the Confederacy ("the South"), the latter formed by state ...
. The African-American population of Philadelphia increased from 31,699 to 219,559 between 1880 and 1930. Twentieth-century black newcomers were part of the Great Migration out of the rural south to northern and midwestern industrial cities.
20th century
 By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican
By the 20th century, Philadelphia had an entrenched Republican political machine
In the politics of Representative democracy, representative democracies, a political machine is a party organization that recruits its members by the use of tangible incentives (such as money or political jobs) and that is characterized by a hig ...
and a complacent population. The first major reform came in 1917 when outrage over the election-year murder of a police officer led to the shrinking of the City Council
A municipal council is the legislative body of a municipality or local government area. Depending on the location and classification of the municipality it may be known as a city council, town council, town board, community council, rural counc ...
from two houses to just one. In July 1919, Philadelphia was one of more than 36 industrial cities nationally to suffer a race riot of ethnic whites against blacks during Red Summer, in post-World War I unrest, as recent immigrants competed with blacks for jobs. In the 1920s, the public flouting of Prohibition laws, organized crime, mob violence, and police involvement in illegal activities led to the appointment of Brig. Gen. Smedley Butler of the U.S. Marine Corps
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through comb ...
as director of public safety, but political pressure prevented any long-term success in fighting crime and corruption.
In 1940, non-Hispanic whites constituted 86.8% of the city's population. The population peaked at more than two million residents in 1950, then began to decline with the restructuring of industry, which led to the loss of many middle-class union jobs. In addition, suburbanization had enticed many of the more affluent residents to outlying railroad commuting towns and newer housing. The resulting reduction in Philadelphia's tax base and the resources of local government caused the city to struggle through a long period of adjustment, with it approaching bankruptcy by the late 1980s.
Revitalization and gentrification of neighborhoods began in the late 1970s and continues into the 21st century, with much of the development occurring in the Center City and University City neighborhoods, while simultaneously exacerbating a shortage of affordable housing in Philadelphia. After many of the old manufacturers and businesses left Philadelphia or shut down, the city started attracting service businesses and began to market itself more aggressively as a tourist destination. Contemporary glass-and-granite skyscrapers were built in Center City beginning in the 1980s. Historic areas such as Old City Old City often refers to old town, the historic or original core of a city or town.
Old City may refer to several places:
Historical cities or regions of cities
''(by country)''
*Old City (Baku), Azerbaijan
* Old City (Dhaka), Bangladesh, also ca ...
and Society Hill were renovated during the reformist mayoral era of the 1950s through the 1980s, making those areas among the most desirable neighborhoods in Center City. Many immigrants from around the world began to enter the U.S. through Philadelphia as their gateway. These developments led to a reversal of the city's population decline between 1950 and 2000, during which it lost about 25 percent of its residents.
21st century
Philadelphia eventually began experiencing a growth in its population in 2007, which continued with gradual yearly increases through the present. Although Philadelphia is rapidly undergoing gentrification, the city maintains strategies to minimize displacement of homeowners in gentrifying neighborhoods.Geography
Topography
The geographic center of Philadelphia is about 40° 0′ 34″ north latitude and 75° 8′ 0″ west longitude. The40th parallel north
The 40th parallel north is a circle of latitude that is 40 degrees north of the Earth's equatorial plane. It crosses Europe, the Mediterranean Sea, Asia, the Pacific Ocean, North America, and the Atlantic Ocean.
At this latitude the sun is vis ...
passes through neighborhoods in Northeast Philadelphia, North Philadelphia, and West Philadelphia including Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
. The city encompasses , of which is land and , or 6%, is water. Natural bodies of water include the Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
and Schuylkill rivers, the lakes in Franklin Delano Roosevelt Park
Franklin Delano Roosevelt (FDR) Park (originally named League Island Park) is a park located along the Delaware River in the southernmost point of South Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, comprising some which includes a golf course (closed and conver ...
, and Cobbs Cobbs is a surname, and may refer to
*Arnett Cobb (1918–1989), American jazz saxophonist born Arnette Cleophus Cobbs
*Bill Cobbs (born 1934), American actor
*Blair Cobbs (born 1989), American boxer
*Call Cobbs Jr. (1911–1971), American jazz org ...
, Wissahickon, and Pennypack creeks. The largest artificial body of water is the East Park Reservoir in Fairmount Park.
The lowest point is sea level, while the highest point is in Chestnut Hill, about above sea level on Summit Street near the intersection of Germantown Avenue and Bethlehem Pike (example coordinates near high point: 40.07815 N, 75.20747 W).
Philadelphia is situated on the Fall Line that separates the Atlantic coastal plain
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth#Surface, Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the "Old World" of Afr ...
from the Piedmont. The rapids on the Schuylkill River at East Falls were inundated by the completion of the dam at the Fairmount Water Works.
The city is the seat of its own county. The adjacent counties are Montgomery to the northwest; Bucks
Bucks may refer to:
Places
* Buckinghamshire, England, abbreviated Bucks
* Bucks, Alabama, United States, an unincorporated community
* Bucks, Illinois, United States, an unincorporated community
* Bucks, Michigan, an unincorporated community ...
to the north and northeast; Burlington County, New Jersey
Burlington County is a county in the U.S. state of New Jersey. The county is the largest by area in New Jersey. Its county seat is Mount Holly.
, to the east; Camden County, New Jersey, to the southeast; Gloucester County, New Jersey, to the south; and Delaware County to the southwest.
Cityscape
City planning
Philadelphia's central city was created in the 17th century following the plan by William Penn's surveyor Thomas Holme. Center City is structured with long, straight streets running nearly due east–west and north–south, forming a grid pattern between theDelaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacen ...
and Schuylkill rivers that is aligned with their courses. The original city plan was designed to allow for easy travel and to keep residences separated by open space that would help prevent the spread of fire. In keeping with the idea of a "Greene Countrie Towne", and inspired by the many types of trees that grew in the region, Penn named many of the east–west streets for local trees. Penn planned the creation of five public parks in the city which were renamed in 1824 (new names in parentheses): Centre Square (Penn Square), Northeast Square ( Franklin Square), Southeast Square ( Washington Square), Southwest Square ( Rittenhouse Square), and Northwest Square ( Logan Circle/Square). Center City had an estimated 183,240 residents , making it the second-most populated downtown area in the United States, after Midtown Manhattan
Midtown Manhattan is the central portion of the New York City borough of Manhattan and serves as the city's primary central business district. Midtown is home to some of the city's most prominent buildings, including the Empire State Buildin ...
in New York City.
Philadelphia's neighborhoods are divided into large sections— North, Northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sepa ...
, South
South is one of the cardinal directions or Points of the compass, compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Pro ...
, Southwest, West, and Northwest
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each sep ...
—surrounding Center City, which correspond closely with the city's limits before consolidation in 1854. Each of these large areas contains numerous neighborhoods, some of whose boundaries derive from the boroughs, townships, and other communities that constituted Philadelphia County before their inclusion within the city.
The City Planning Commission, tasked with guiding growth and development of the city, has divided the city into 18 planning districts as part of the ''Philadelphia2035'' physical development plan. Much of the city's 1980 zoning code was overhauled from 2007 to 2012 as part of a joint effort between former mayors John F. Street
John Franklin Street (born October 15, 1943) is an American politician and lawyer who served as the 97th Mayor of the City of Philadelphia. He was first elected to a term beginning on January 3, 2000, and was re-elected to a second term beginn ...
and Michael Nutter. The zoning changes were intended to rectify incorrect zoning maps to facilitate future community development, as the city forecasts an additional 100,000 residents and 40,000 jobs will be added by 2035.
The Philadelphia Housing Authority
The Philadelphia Housing Authority (PHA) is a municipal authority providing Public housing services in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania.
It is the fourth-largest housing authority in the United States and is the largest landlord in Pennsylvania. PHA ho ...
(PHA) is the largest landlord in Pennsylvania. Established in 1937, the PHA is the nation's fourth-largest housing authority, serving about 81,000 people with affordable housing, while employing 1,400 on a budget of $371 million. The Philadelphia Parking Authority
The Philadelphia Parking Authority (PPA) is an agency of the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania that manages many parking operations for Philadelphia.
The PPA was created by the Philadelphia City Council on January 11, 1950, for the purpose of condu ...
works to ensure adequate parking for city residents, businesses, and visitors.
Architecture

 Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to
Philadelphia's architectural history dates back to colonial
Colonial or The Colonial may refer to:
* Colonial, of, relating to, or characteristic of a colony or colony (biology)
Architecture
* American colonial architecture
* French Colonial
* Spanish Colonial architecture
Automobiles
* Colonial (1920 a ...
times and includes a wide range of styles. The earliest structures were constructed with logs, but brick structures were common by 1700. During the 18th century, the cityscape
In the visual arts, a cityscape (urban landscape) is an artistic representation, such as a painting, drawing, print or photograph, of the physical aspects of a city or urban area. It is the urban equivalent of a landscape. ''Townscape'' i ...
was dominated by Georgian architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, Georg ...
, including Independence Hall and Christ Church.
In the first decades of the 19th century, Federal and Greek Revival architecture
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but ...
were the dominant styles produced by Philadelphia architects such as Benjamin Latrobe, William Strickland, John Haviland, John Notman, Thomas Walter, and Samuel Sloan. Frank Furness
Frank Heyling Furness (November 12, 1839 - June 27, 1912) was an American architect of the Victorian era. He designed more than 600 buildings, most in the Philadelphia area, and is remembered for his diverse, muscular, often unordinarily scaled b ...
is considered Philadelphia's greatest architect of the second half of the 19th century. His contemporaries included John McArthur Jr., Addison Hutton, Wilson Eyre, the Wilson Brothers, and Horace Trumbauer. In 1871, construction began on the Second Empire-style Philadelphia City Hall. The Philadelphia Historical Commission was created in 1955 to preserve the cultural and architectural history of the city. The commission maintains the Philadelphia Register of Historic Places, adding historic buildings, structures, sites, objects and districts as it sees fit.
In 1932, Philadelphia became home to the first modern International Style International style may refer to:
* International Style (architecture), the early 20th century modern movement in architecture
*International style (art), the International Gothic style in medieval art
*International Style (dancing), a term used in ...
skyscraper in the United States, the PSFS Building, designed by George Howe and William Lescaze. The City Hall remained the tallest building in the city until 1987 when One Liberty Place was completed. Numerous glass and granite skyscrapers were built in Center City beginning in the late 1980s. In 2007, the Comcast Center surpassed One Liberty Place to become the city's tallest building. The Comcast Technology Center was completed in 2018, reaching a height of , as the tallest building in the United States outside of Manhattan and Chicago.
For much of Philadelphia's history, the typical home has been the row house
In architecture and city planning, a terrace or terraced house (British English, UK) or townhouse (American English, US) is a form of medium-density housing that originated in Europe in the 16th century, whereby a row of attached dwellings party ...
. The row house was introduced to the United States via Philadelphia in the early 19th century and, for a time, row houses built elsewhere in the United States were known as "Philadelphia rows". A variety of row houses are found throughout the city, from Federal-style continuous blocks in Old City Old City often refers to old town, the historic or original core of a city or town.
Old City may refer to several places:
Historical cities or regions of cities
''(by country)''
*Old City (Baku), Azerbaijan
* Old City (Dhaka), Bangladesh, also ca ...
and Society Hill to Victorian-style homes in North Philadelphia to twin row houses in West Philadelphia. While newer homes have been built recently, much of the housing dates to the 18th, 19th and early 20th centuries, which has created problems such as urban decay and vacant lots. Some neighborhoods, including Northern Liberties and Society Hill, have been rehabilitated through gentrification.
Georgian architecture
Georgian architecture is the name given in most English-speaking countries to the set of architectural styles current between 1714 and 1830. It is named after the first four British monarchs of the House of Hanover—George I, George II, Georg ...
, 1770–1774
File:Second Bank of the United States with Robert Morris, Jr. statue, Philadelphia.jpg, Second Bank of the United States exhibiting Greek Revival architecture
The Greek Revival was an architectural movement which began in the middle of the 18th century but which particularly flourished in the late 18th and early 19th centuries, predominantly in northern Europe and the United States and Canada, but ...
, 1818–1824
File:City hall Philadelphia.jpg, Second Empire-style Philadelphia City Hall, 1871–1901, from South Broad Street
File:Thirty St Station.jpg, The Art Deco
Art Deco, short for the French ''Arts Décoratifs'', and sometimes just called Deco, is a style of visual arts, architecture, and product design, that first appeared in France in the 1910s (just before World War I), and flourished in the Unit ...
-style grand concourse at 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
, 1927–1933
Parks
 , the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is
, the total city parkland, including municipal, state and federal parks within the city limits, amounts to . Philadelphia's largest park is Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, divided by the Schuylkill River, with ...
which includes the Philadelphia Zoo and encompasses of the total parkland, while the adjacent Wissahickon Valley Park contains . Fairmount Park, when combined with Wissahickon Valley Park, is one of the largest contiguous urban park areas in the United States. The two parks, along with the Colonial Revival, Georgian and Federal-style mansions contained in them, have been listed as one entity on the National Register of Historic Places since 1972.
Climate
According to the Köppen climate classification, Philadelphia falls under the northern periphery of thehumid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
zone (Köppen ''Cfa''), whereas according to the Trewartha climate classification, the city has a temperate maritime climate (''Do'') limited to the north by the continental climate
Continental climates often have a significant annual variation in temperature (warm summers and cold winters). They tend to occur in the middle latitudes (40 to 55 north), within large landmasses where prevailing winds blow overland bringing som ...
(''Dc''). Summers are typically hot and muggy, fall and spring are generally mild, and winter is moderately cold. The plant life hardiness zones are 7a and 7b, representing an average annual extreme minimum temperature between .
Snowfall is highly variable, with some winters experiencing only light snow, while others include major snowstorms. The normal seasonal snowfall averages , with rare snowfalls in November or April, and rarely any sustained snow cover. Seasonal snowfall accumulation has ranged from trace amounts in 1972–73 to in the winter of 2009–10. The city's heaviest single-storm snowfall was which occurred in January 1996.
Precipitation is generally spread throughout the year, with eight to eleven wet days per month, at an average annual rate of , but historically ranging from in 1922 to in 2011. The most rain recorded in one day occurred on July 28, 2013, when fell at Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
. Philadelphia has a moderately sunny climate with an average of 2,498 hours of sunshine annually, and a percentage of sunshine ranging from 47% in December to 61% in June, July, and August.
The January daily average temperature is , though the temperature frequently rises to during thaws and dips to for 2 or 3 nights in a normal winter. July averages , although heat waves accompanied by high humidity and heat indices are frequent, with highs reaching or exceeding on 30 days of the year. The average window for freezing temperatures is November 6 thru April 2, allowing a growing season of 217 days. Early fall and late winter are generally dry with February having the lowest average precipitation at . The dewpoint in the summer averages between .
The highest recorded temperature was on August 7, 1918, but temperatures at or above are not common, with the last occurrence of such a temperature was July 21, 2019. The lowest officially recorded temperature was on February 9, 1934. Temperatures at or below are rare with the last such occurrence being January 19, 1994. The record low maximum is on February 10, 1899, and December 30, 1880, while the record high minimum is on July 23, 2011, and July 24, 2010.
Air quality
Philadelphia County received an ozone grade of F and a 24-hour particle pollution rating of D in the American Lung Association's 2017 State of the Air report, which analyzed data from 2013 to 2015. The city was ranked 22nd for ozone, 20th for short-term particle pollution, and 11th for year-round particle pollution. According to the same report, the city experienced a significant reduction in high ozone days since 2001—from nearly 50 days per year to fewer than 10—along with fewer days of high particle pollution since 2000—from about 19 days per year to about 3—and an approximate 30% reduction in annual levels of particle pollution since 2000. Five of the ten largest combined statistical areas (CSAs) were ranked higher for ozone: Los Angeles (1st), New York City (9th), Houston (12th),Dallas
Dallas () is the List of municipalities in Texas, third largest city in Texas and the largest city in the Dallas–Fort Worth metroplex, the List of metropolitan statistical areas, fourth-largest metropolitan area in the United States at 7.5 ...
(13th), and San Jose (18th). Many smaller CSAs were also ranked higher for ozone including Sacramento (8th), Las Vegas (10th), Denver
Denver () is a consolidated city and county, the capital, and most populous city of the U.S. state of Colorado. Its population was 715,522 at the 2020 census, a 19.22% increase since 2010. It is the 19th-most populous city in the United ...
(11th), El Paso (16th), and Salt Lake City (20th); however, only two of those same ten CSAs—San Jose and Los Angeles—were ranked higher than Philadelphia for both year-round and short-term particle pollution.
Demographics
According to the 2020 U.S. Census Bureau's tabulation, there were 1,603,797 people residing in Philadelphia, representing a 1.2% increase from the 2019 census estimate. The racial composition of the city was 39.3% Black alone (42.0% Black alone or in combination), 36.3% White alone (41.9% White alone or in combination), 8.7% Asian alone, 0.4% American Indian and Alaska Native alone, 8.7% some other race, and 6.9% multiracial. 14.9% of residents were Hispanic or Latino. 34.8% had a Bachelor's degree or higher. 23.9% spoke a language other than English at home, the most common of which was Spanish (10.8%). 15.0% of the populations foreign born, roughly have of whom are naturalized U.S. citizens. 3.7% of the population are veterans. The median household income was $52,889 and 22.8% of the population lived in poverty. 49.5% of the population drove alone to work, while 23.2% used public transit, 8.2% carpooled, 7.9% walked, and 7.0% worked from home. The average commute is 31 minutes. After the 1950 census, when a record high of 2,071,605 was recorded, the city's population began a long decline. The population dropped to a low of 1,488,710 residents in 2006 before beginning to rise again. Between 2006 and 2017, Philadelphia added 92,153 residents. In 2017, the U.S. Census Bureau estimated that the racial composition of the city was 41.3% Black (non-Hispanic), 34.9% White (non-Hispanic), 14.1% Hispanic or Latino, 7.1% Asian, 0.4% Native American, 0.05% Pacific Islander, and 2.8% multiracial. The 2010 census redistricting data indicated that the racial makeup of the city was 644,287 (42.2%)Black
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white ha ...
(non-Hispanic), 562,585 (36.9%) White (non-Hispanic), 96,405 (6.3%) Asian (2.0% Chinese, 1.2% Indian, 0.9% Vietnamese, 0.4% Korean, 0.3% Filipino, 0.1% Japanese, and 1.4% other), 6,996 (0.5%) Native Americans, 744 (0.05%) Pacific Islanders, and 43,070 (2.8%) from two or more races. Hispanics or Latinos of any race were 187,611 persons (12.3%); 8.0% Puerto Rican, 1.0% Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
, 0.3% Cuban, and 3.0% other. The racial breakdown of Philadelphia's Hispanic/Latino population was 63,636 (33.9%) White, 17,552 (9.4%) Black, 3,498 (1.9%) Native American, 884 (0.47%) Asian, 287 (0.15%) Pacific Islander, 86,626 (46.2%) from other races, and 15,128 (8.1%) from two or more races. The five largest European ancestries reported in the 2010 census included Irish (13.0%), Italian (8.3%), German (8.2%), Polish (3.9%), and English (3.1%).
The estimated average population density was 11,782 people per square mile (4,549/km) in 2017. In 2010, the U.S. Census Bureau reported that 1,468,623 people (96.2% of the population) lived in households, 38,007 (2.5%) lived in non-institutionalized group quarters, and 19,376 (1.3%) were institutionalized. In 2013, the city reported having 668,247 total housing units, down slightly from 670,171 housing units in 2010. , 87 percent of housing units were occupied, while 13 percent were vacant, a slight change from 2010 where 89.5 percent of units were occupied, or 599,736 and 10.5 percent were vacant, or 70,435. Of the city's residents, 32 percent reported having no vehicles available while 23 percent had two or more vehicles available, .
In 2010, 24.9 percent of households reported having children under the age of 18 living with them, 28.3 percent were married couples living together and 22.5 percent had a female householder with no husband present, 6.0 percent had a male householder with no wife present, and 43.2 percent were non-families. The city reported 34.1 percent of all households were individuals living alone, while 10.5 percent had someone living alone who was 65 years of age or older. The average household size was 2.45 and the average family size was 3.20. In 2013, the percentage of women who gave birth in the previous 12 months who were unmarried was 56 percent. Of Philadelphia's adults, 31 percent were married or lived as a couple, 55 percent were not married, 11 percent were divorced or separated, and 3 percent were widowed.
According to the U.S. Census Bureau, the median household income in 2013 was $36,836, down 7.9 percent from 2008 when the inflation-adjusted median household income was $40,008 (in 2013 dollars). For comparison, on an inflation-adjusted basis, the median household income among metropolitan areas was $60,482, down 8.2 percent in the same period, and the national median household income was $55,250, down 7.0 percent from 2008. The city's wealth disparity is evident when neighborhoods are compared. Residents in Society Hill had a 2013 median household income of $93,720, while residents in one of North Philadelphia's districts reported the lowest median household income, $14,185.
More recently, Philadelphia has experienced a large shift toward a younger age profile. In 2000, the city's population pyramid had a largely stationary shape. In 2013, the city took on an expansive pyramid shape, with an increase in the three millennial age groups, 20 to 24, 25 to 29, and 30 to 34. The city's 25- to 29-year-old age group was the city's largest age cohort. According to the 2010 census, 343,837 (22.5%) were under the age of 18; 203,697 (13.3%) from 18 to 24; 434,385 (28.5%) from 25 to 44; 358,778 (23.5%) from 45 to 64; and 185,309 (12.1%) who were 65 years of age or older. The median age was 33.5 years. For every 100 females, there were 89.4 males; while among individuals age 18 and over, for every 100 females, there were 85.7 males. The city had 22,018 births in 2013, down from a peak 23,689 births in 2008. Philadelphia's death rate was at its lowest in at least a half-century, 13,691 deaths in 2013.
Immigration and cultural diversity

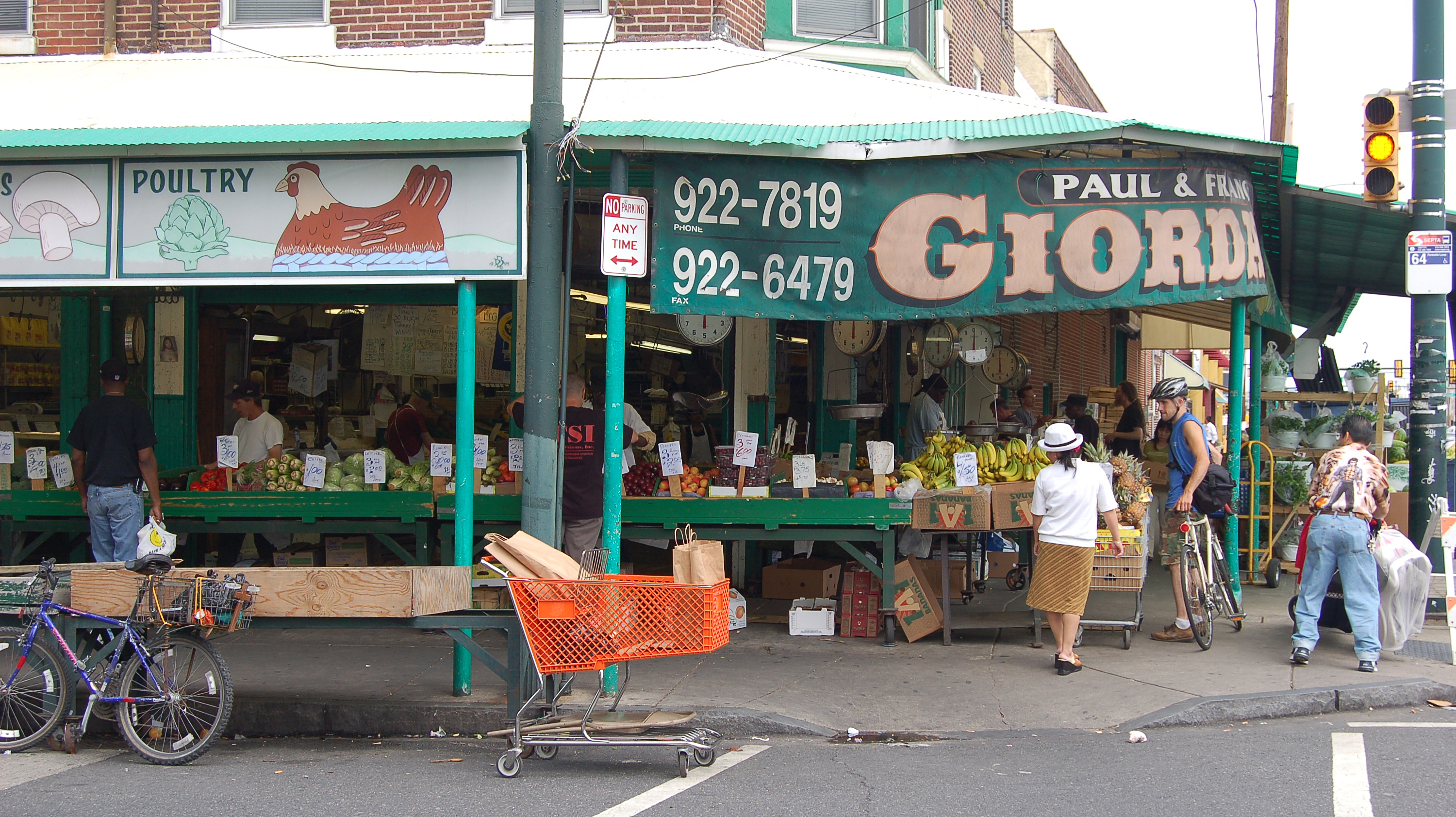
 Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's
Apart from economic growth, another factor contributing to the population increase is Philadelphia's rising immigration rate. Like the millennial population, Philadelphia's immigrant population is also growing rapidly. According to research by The Pew Charitable Trusts, the city's foreign-born
Foreign-born (also non-native) people are those born outside of their country of residence. Foreign born are often non-citizens, but many are naturalized citizens of the country in which they live, and others are citizens by descent, typically ...
population had increased by 69% between 2000 and 2016 to constitute nearly 20% of Philadelphia's work force, and had doubled between 1990 and 2017 to constitute 13.8% of the city's total population, with the top five countries of origin being China by a significant margin, followed by the Dominican Republic
The Dominican Republic ( ; es, República Dominicana, ) is a country located on the island of Hispaniola in the Greater Antilles archipelago of the Caribbean region. It occupies the eastern five-eighths of the island, which it shares with ...
, Jamaica, India, and Vietnam.
Irish, Italian, German, Polish, English, Russian, Ukrainian, and French constitute the largest European ethnic groups in the city. Philadelphia has the second-largest Irish and Italian populations in the United States, after New York City. South Philadelphia remains one of the largest Italian neighborhoods in the country and is home to the Italian Market.
The Pennsport
Pennsport is a neighborhood in the South Philadelphia section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States.
Pennsport is home to a large working-class Irish American population, many of them descendants of immigrants from the mid to late 19th ...
neighborhood and Gray's Ferry section of South Philadelphia, home to many Mummer clubs, are well known as Irish neighborhoods. The Kensington
Kensington is a district in the Royal Borough of Kensington and Chelsea in the West End of London, West of Central London.
The district's commercial heart is Kensington High Street, running on an east–west axis. The north-east is taken up b ...
, Port Richmond, and Fishtown neighborhoods have historically been heavily Irish and Polish. Port Richmond is well known in particular as the center of the Polish immigrant and Polish-American community in Philadelphia, and it remains a common destination for Polish immigrants. Northeast Philadelphia, although known for its Irish and Irish-American population, is also home to a large Jewish and Russian population. Mount Airy in Northwest Philadelphia also contains a large Jewish community, while nearby Chestnut Hill is historically known as an Anglo-Saxon Protestant community.
Philadelphia has a significant gay and lesbian population. Philadelphia's Gayborhood, which is near Washington Square, is home to a large concentration of gay and lesbian friendly businesses, restaurants, and bars.
The Black American
African Americans (also referred to as Black Americans and Afro-Americans) are an ethnic group consisting of Americans with partial or total ancestry from sub-Saharan Africa. The term "African American" generally denotes descendants of ens ...
population in Philadelphia is the third-largest in the country, after New York City and Chicago. West Philadelphia and North Philadelphia are largely African-American neighborhoods, but many are leaving those areas in favor of the Northeast and Southwest sections of Philadelphia. A higher proportion of African-American Muslims
African-American Muslims, also colloquially known as Black Muslims, are an African American religious minority. About 1% of African Americans are Muslims. Nonetheless, African American Muslims account for over 20% of American Muslims. They re ...
reside in Philadelphia than in most other cities in America. West Philadelphia and Southwest Philadelphia are also home to various significant Afro-Caribbean
Afro-Caribbean people or African Caribbean are Caribbean people who trace their full or partial ancestry to Sub-Saharan Africa. The majority of the modern African-Caribbeans descend from Africans taken as slaves to colonial Caribbean via the ...
and African immigrant communities.
The Puerto Rican population in Philadelphia is the second-largest on the mainland United States after New York City, and the second-fastest growing after Orlando. Eastern North Philadelphia, particularly Fairhill
Fairhill is a neighborhood on the east side of the North Philadelphia section of Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, United States. Fairhill is bordered by Front Street to the east, Germantown Avenue (10th Street) to the west, Allegheny Avenue to the n ...
and surrounding areas to the north and east, has one of the highest concentrations of Puerto Ricans outside Puerto Rico, with many large swaths of blocks being close to 100% Puerto Rican. Large Puerto Rican and Dominican populations reside in North Philadelphia and the Northeast. In regard to other Latin American populations in Philadelphia, there are significant Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
and Central American populations in South Philadelphia.
Philadelphia's Asian American
Asian Americans are Americans of Asian ancestry (including naturalized Americans who are immigrants from specific regions in Asia and descendants of such immigrants). Although this term had historically been used for all the indigenous people ...
population originates mainly from China, India, Vietnam, South Korea, and the Philippines. Over 35,000 Chinese Americans lived in the city in 2015, including a large Fuzhounese population. Center City hosts a growing Chinatown
A Chinatown () is an ethnic enclave of Chinese people located outside Greater China, most often in an urban setting. Areas known as "Chinatown" exist throughout the world, including Europe, North America, South America, Asia, Africa and Austra ...
accommodating heavily traveled Chinese-owned bus lines to and from Chinatown, Manhattan in New York City, 95 miles to the north, as Philadelphia is experiencing significant Chinese immigration from New York City. A large Korean community initially settled in the North Philadelphia neighborhood of Olney Olney may refer to:
Places Australia
* Olney Parish, New South Wales England
* Olney, Buckinghamshire, a town near Milton Keynes, England
United States
* Olney, Alabama
* Olney, Georgia - see List of places in Georgia (U.S. state) (I–R)
* Ol ...
; however, the primary Koreatown has subsequently shifted northward, straddling the border with the adjacent suburb of Cheltenham
Cheltenham (), also known as Cheltenham Spa, is a spa town and borough on the edge of the Cotswolds in the county of Gloucestershire, England. Cheltenham became known as a health and holiday spa town resort, following the discovery of mineral s ...
in Montgomery County Montgomery County may refer to:
Australia
* The former name of Montgomery Land District, Tasmania
United Kingdom
* The historic county of Montgomeryshire, Wales, also called County of Montgomery
United States
* Montgomery County, Alabama
* Mon ...
, while also growing in nearby Cherry Hill, New Jersey
Cherry Hill is a township within Camden County, in the U.S. state of New Jersey. As of the 2020 U.S. census, the township had a population of 74,553, which reflected an increase of 3,508 (+4.94%) from the 71,045 counted in the 2010 census.
. South Philadelphia is also home to large Cambodian, Vietnamese, Thai, and Chinese communities.
Religion
Pew Research Center
The Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan American think tank (referring to itself as a "fact tank") based in Washington, D.C.
It provides information on social issues, public opinion, and demographic trends shaping the United States and the w ...
, 68% of the population of the city identified themselves as Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι ...
. Approximately 41% of Christians in the city and area professed attendance at a variety of churches that could be considered Protestant, while 26% professed Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
beliefs.
The Protestant Christian community in Philadelphia is dominated by mainline Protestant denominations including the Evangelical Lutheran Church in America
The Evangelical Lutheran Church in America (ELCA) is a mainline Protestant Lutheran church headquartered in Chicago, Illinois. The ELCA was officially formed on January 1, 1988, by the merging of three Lutheran church bodies. , it has approxim ...
, United Church of Christ, the Episcopal Church in the United States, Presbyterian Church (USA)
The Presbyterian Church (USA), abbreviated PC(USA), is a mainline Protestant denomination in the United States. It is the largest Presbyterian denomination in the US, and known for its liberal stance on doctrine and its ordaining of women and ...
and American Baptist Churches USA. One of the most prominent mainline Protestant jurisdictions is the Episcopal Diocese of Pennsylvania
The Episcopal Diocese of Pennsylvania is a diocese of the Episcopal Church in the United States of America encompassing the counties of Philadelphia, Montgomery, Bucks, Chester and Delaware in the state of Pennsylvania.
The Diocese has 36,641 ...
. The African Methodist Episcopal Church was established in Philadelphia. Historically, the city has strong connections to the Quakers, Unitarian Universalism, and the Ethical Culture movement
The Ethical movement, also referred to as the Ethical Culture movement, Ethical Humanism or simply Ethical Culture, is an ethical, educational, and religious movement that is usually traced back to Felix Adler (1851–1933).
, all of which continue to be represented in the city. The Quaker Friends General Conference is based in Philadelphia. Evangelical Protestants making up less than 15% of the population were also prevalent. Evangelical Protestant bodies included the Anglican Church in North America, Lutheran Church—Missouri Synod, Presbyterian Church in America, and National Baptist Convention of America
The National Baptist Convention of America International, Inc., (NBCA Intl or NBCA) more commonly known as the National Baptist Convention of America or sometimes the Boyd Convention, is a Christian denomination based in the United States. It is ...
.
The Catholic community is primarily served by the Latin Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, the Ukrainian Catholic Archeparchy of Philadelphia, and the Syro-Malankara Catholic Eparchy of the United States of America and Canada
The Syro-Malankara Catholic Eparchy of St. Mary, Queen of Peace, of the United States of America and Canada is the North American eparchy for the Syro-Malankara Catholic Church of the Catholic Church. The Syro-Malankara Church observes the Antioc ...
, though some independent Catholic churches exist throughout Philadelphia and its suburbs. The Latin Church-based jurisdiction is headquartered in the city, and its see is the Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul
The Cathedral Basilica of Saints Peter and Paul, head church of the Roman Catholic Archdiocese of Philadelphia, is located at 18th Street and the Benjamin Franklin Parkway, on the east side of Logan Square in Philadelphia. It was built between ...
. The Ukrainian Catholic jurisdiction is also headquartered in Philadelphia, and is seated at the Cathedral of the Immaculate Conception.
Less than 1% of Philadelphia's Christians were Mormons
Mormons are a religious and cultural group related to Mormonism, the principal branch of the Latter Day Saint movement started by Joseph Smith in upstate New York during the 1820s. After Smith's death in 1844, the movement split into several ...
. The remainder of the Christian demographic is spread among smaller Protestant denominations and the Eastern and Oriental Orthodox
The Oriental Orthodox Churches are Eastern Christian churches adhering to Miaphysite Christology, with approximately 60 million members worldwide. The Oriental Orthodox Churches are part of the Nicene Christian tradition, and represent o ...
among others. The Diocese of Eastern Pennsylvania ( Orthodox Church in America) and Greek Orthodox Archdiocese of America (Ecumenical Patriarchate
The Ecumenical Patriarchate of Constantinople ( el, Οἰκουμενικὸν Πατριαρχεῖον Κωνσταντινουπόλεως, translit=Oikoumenikón Patriarkhíon Konstantinoupóleos, ; la, Patriarchatus Oecumenicus Constanti ...
) divide the Eastern Orthodox in Philadelphia. The Russian Orthodox St. Andrew's Cathedral is in the city.
The same study says that other religions collectively compose about 8% of the population, including Judaism, Hinduism, Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic religions, Abrahamic Monotheism#Islam, monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God in Islam, God (or ...
, Buddhism
Buddhism ( , ), also known as Buddha Dharma and Dharmavinaya (), is an Indian religion or philosophical tradition based on teachings attributed to the Buddha. It originated in northern India as a -movement in the 5th century BCE, and ...
, and Sikhism. Philadelphia has the fifth largest Muslim
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
population among American cities. The remaining 24% claimed no religious affiliation.
The Philadelphia metropolitan area
A metropolitan area or metro is a region that consists of a densely populated urban agglomeration and its surrounding territories sharing industries, commercial areas, transport network, infrastructures and housing. A metro area usually com ...
's Jewish population was estimated at 206,000 in 2001, which was the sixth largest in the United States at that time. Jewish traders were operating in southeastern Pennsylvania long before William Penn. Furthermore, Jews in Philadelphia took a prominent part in the War of Independence. Although the majority of the early Jewish residents were of Portuguese or Spanish descent, some among them had emigrated from Germany and Poland. About the beginning of the 19th century, a number of Jews from the latter countries, finding the services of the Congregation Mickvé Israel unfamiliar to them, resolved to form a new congregation which would use the ritual to which they had been accustomed.
African diasporic religions
African diaspora religions are a number of related Pagan beliefs that developed in the Americas in various nations of the Caribbean, Latin America and the Southern United States. They derive from Pagan traditional African religions with some influ ...
are practiced in some Latino and Hispanic and Caribbean communities in North and West Philadelphia.
Languages
, 79.12% (1,112,441) of Philadelphia residents age 5 and older spoke English at home as aprimary language
A first language, native tongue, native language, mother tongue or L1 is the first language or dialect that a person has been exposed to from birth or within the critical period. In some countries, the term ''native language'' or ''mother to ...
, while 9.72% (136,688) spoke Spanish, 1.64% (23,075) Chinese, 0.89% (12,499) Vietnamese, 0.77% (10,885) Russian, 0.66% (9,240) French, 0.61% (8,639) other Asian languages, 0.58% (8,217) African languages, 0.56% (7,933) Cambodian ( Mon-Khmer), and Italian was spoken as a main language by 0.55% (7,773) of the population over the age of five. In total, 20.88% (293,544) of Philadelphia's population age 5 and older spoke a mother language other than English.
Economy
Philadelphia’s close geographical and transportation connections to other large metropolitan economies along the Eastern Seaboard of the United States have been cited as offering a significant competitive advantage for business creation and entrepreneurship. The city is the center of economic activity in both Pennsylvania and the four-stateDelaware Valley
The Delaware Valley is a metropolitan region on the East Coast of the United States that comprises and surrounds Philadelphia, the sixth most populous city in the nation and 68th largest city in the world as of 2020. The toponym Delaware Val ...
metropolitan region. Five Fortune 500
The ''Fortune'' 500 is an annual list compiled and published by ''Fortune'' magazine that ranks 500 of the largest United States corporations by total revenue for their respective fiscal years. The list includes publicly held companies, along ...
companies are headquartered in the city. , the Philadelphia metropolitan area is estimated to produce a gross metropolitan product (GMP) of US$479 billion, an increase from the $445 billion calculated by the Bureau of Economic Analysis
The Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) of the United States Department of Commerce is a U.S. government agency that provides official economy of the United States, macroeconomic and industry statistics, most notably reports about the gross domestic ...
for 2017, representing the ninth largest U.S. metropolitan economy.
Philadelphia's economic sectors include financial services
Financial services are the Service (economics), economic services provided by the finance industry, which encompasses a broad range of businesses that manage money, including credit unions, banks, credit-card companies, insurance companies, acco ...
, health care, biotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
, information technology, trade and transportation, manufacturing, oil refining
An oil refinery or petroleum refinery is an industrial process plant where petroleum (crude oil) is transformed and refined into useful products such as gasoline (petrol), diesel fuel, asphalt base, fuel oils, heating oil, kerosene, liquefie ...
, food processing
Food processing is the transformation of agricultural products into food, or of one form of food into other forms. Food processing includes many forms of processing foods, from grinding grain to make raw flour to home cooking to complex industr ...
, and tourism. Financial activities account for the largest economic sector of the metropolitan area, which is also one of the largest health education and research centers in the United States. The city's two largest employers are the federal and city governments. Philadelphia's largest private employer is the University of Pennsylvania, followed by the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. A study commissioned by the city's government in 2011 projected 40,000 jobs would be added to the city within 25 years, raising the number of jobs from 675,000 in 2010 to an estimated 715,000 by 2035.
Corporations

NASDAQ
The Nasdaq Stock Market () (National Association of Securities Dealers Automated Quotations Stock Market) is an American stock exchange based in New York City. It is the most active stock trading venue in the US by volume, and ranked second ...
in 2007, tracks the Philadelphia Semiconductor Index, known in financial circles as the SOX. The city is also home to the headquarters of cable television and internet service provider Comcast
Comcast Corporation (formerly known as American Cable Systems and Comcast Holdings),Before the AT&T merger in 2001, the parent company was Comcast Holdings Corporation. Comcast Holdings Corporation now refers to a subsidiary of Comcast Corpora ...
, insurance companies Cigna
Cigna is an American multinational managed healthcare and insurance company based in Bloomfield, Connecticut. Its insurance subsidiaries are major providers of medical, dental, disability, life and accident insurance and related products and se ...
, Colonial Penn, and Independence Blue Cross, food services company Aramark, chemical makers FMC Corporation and Rohm and Haas, pharmaceutical companies GlaxoSmithKline
GSK plc, formerly GlaxoSmithKline plc, is a British multinational pharmaceutical and biotechnology company with global headquarters in London, England. Established in 2000 by a merger of Glaxo Wellcome and SmithKline Beecham. GSK is the ten ...
, Amicus Therapeutics, Spark Therapeutics, apparel
Clothing (also known as clothes, apparel, and attire) are items worn on the body. Typically, clothing is made of fabrics or textiles, but over time it has included garments made from animal skin and other thin sheets of materials and natural ...
retailers Five Below and Urban Outfitters and its subsidiary Anthropologie, automotive parts retailer Pep Boys
Pep Boys is an American automotive aftermarket service chain. Originally named Pep Auto Supply, the company was founded in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, in 1921 by Emanuel (Manny) Rosenfeld, Emanuel "Manny" Rosenfeld, Maurice "Moe" Strauss, Jack J ...
, and stainless steel producer Carpenter Technology Corporation
Carpenter Technology Corporation develops, manufactures, and distributes stainless steels and corrosion-resistant alloys. In fiscal year 2018, the company's revenues were derived from the aerospace and defense industry (55%), the industrial and ...
. Other corporation headquarters in the city include RiteAid
Rite Aid Corporation is an American drugstore chain based in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. It was founded in 1962 in Scranton, Pennsylvania, by Alex Grass under the name Thrift D Discount Center. The company ranked No. 148 in the Fortune 500 li ...
, Crown Holdings, and Brandywine Realty Trust. The headquarters of Boeing Rotorcraft Systems and its main rotorcraft factory are in the Philadelphia suburb of Ridley Park; The Vanguard Group and the U.S. headquarters of Siemens Healthineers
Siemens Healthineers AG (formerly Siemens Healthcare, Siemens Medical Solutions, Siemens Medical Systems) is a German medical device company. It is the parent company for several medical technology companies and is headquartered in Erlangen, Germ ...
are headquartered in Malvern, Pennsylvania, a Philadelphia suburb; healthcare conglomerate AmerisourceBergen is headquartered in suburban Conshohocken, Pennsylvania
Conshohocken ( ; Lenape: ''Kanshihàkink'') is a borough on the Schuylkill River in Montgomery County, Pennsylvania in suburban Philadelphia. Historically a large mill town and industrial and manufacturing center, after the decline of industry i ...
; and the Campbell Soup Company
Campbell Soup Company, trade name, doing business as Campbell's, is an American processed food and snack company. The company is most closely associated with its flagship canned soup products; however, through mergers and acquisitions, it has gro ...
and automobile manufacturer Subaru USA are headquartered across the Delaware River
The Delaware River is a major river in the Mid-Atlantic (United States), Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. From the meeting of its branches in Hancock (village), New York, Hancock, New York, the river flows for along the borders of N ...
in adjacent Camden
Camden may refer to:
People
* Camden (surname), a surname of English origin
* Camden Joy (born 1964), American writer
* Camden Toy (born 1957), American actor
Places Australia
* Camden, New South Wales
* Camden, Rosehill, a heritage res ...
, New Jersey.
Tech and biotech
Philadelphia is a hub for information technology andbiotechnology
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used b ...
. Philadelphia and Pennsylvania are attracting new life sciences
This list of life sciences comprises the branches of science that involve the scientific study of life – such as microorganisms, plants, and animals including human beings. This science is one of the two major branches of natural science, the ...
ventures.Accessed April 18, 2019. The Philadelphia metropolitan area, comprising the Delaware Valley, has also become a growing hub for venture capital funding.
Tourism
 Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the
Philadelphia's history attracts many tourists, with the Independence National Historical Park (which includes the Liberty Bell
The Liberty Bell, previously called the State House Bell or Old State House Bell, is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia. Originally placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House (now renamed Independence ...
, Independence Hall, and other historic sites) receiving over 5 million visitors in 2016. The city welcomed 42 million domestic tourists in 2016 who spent $6.8 billion, generating an estimated $11 billion in total economic impact in the city and surrounding four counties of Pennsylvania. The annual Naked Bike Ride attracts participants from around the United States and internationally to Philadelphia.
Trade and transportation
Philadelphia International Airport
Philadelphia International Airport is the primary airport serving Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The airport served 19.6 million passengers annually in 2021, making it the 21st busiest airport in the United States. The airport is located from t ...
is undergoing a $900 million infrastructural
Infrastructure is the set of facilities and systems that serve a country, city, or other area, and encompasses the services and facilities necessary for its economy, households and firms to function. Infrastructure is composed of public and priv ...
expansion to increase passenger capacity and augment passenger experience; while the Port of Philadelphia, having experienced the highest percentage growth by tonnage loaded in 2017 among major U.S. seaports, was in the process of doubling its shipping capacity to accommodate super-sized post-Panamax shipping vessels in 2018. Philadelphia's 30th Street Station
3 (three) is a number, numeral and digit. It is the natural number following 2 and preceding 4, and is the smallest odd prime number and the only prime preceding a square number. It has religious or cultural significance in many societie ...
is the third-busiest Amtrak
The National Railroad Passenger Corporation, doing business as Amtrak () , is the national passenger railroad company of the United States. It operates inter-city rail service in 46 of the 48 contiguous U.S. States and nine cities in Canada ...
rail hub, following Penn Station in Manhattan and Union Station in Washington, D.C., transporting over 4 million inter-city rail passengers annually.
Education
Primary and secondary education
Education in Philadelphia is provided by many private and public institutions. The School District of Philadelphia is the local school district, operatingpublic schools
Public school may refer to:
*State school (known as a public school in many countries), a no-fee school, publicly funded and operated by the government
*Public school (United Kingdom), certain elite fee-charging independent schools in England and ...
, in all of the city. The Philadelphia School District is the eighth largest school district in the United States with 142,266 students in 218 traditional public schools and 86 charter schools
A charter school is a school that receives government funding but operates independently of the established state school system in which it is located. It is independent in the sense that it operates according to the basic principle of autono ...
.
The city's K-12 enrollment in district–run schools dropped from 156,211 students in 2010 to 130,104 students in 2015. During the same time period, the enrollment in charter schools increased from 33,995 students in 2010 to 62,358 students in 2015. This consistent drop in enrollment led the city to close 24 of its public schools in 2013. During the 2014 school year, the city spent an average of $12,570 per pupil, below the average among comparable urban school districts.
Graduation rates among district-run schools, meanwhile, steadily increased in the ten years from 2005. In 2005, Philadelphia had a district graduation rate of 52%. This number increased to 65% in 2014, still below the national and state averages. Scores on the state's standardized test, the Pennsylvania System of School Assessment (PSSA) trended upward from 2005 to 2011 but subsequently decreased. In 2005, the district-run schools scored an average of 37.4% on math and 35.5% on reading. The city's schools reached their peak scores in 2011 with 59.0% on math and 52.3% on reading. In 2014, the scores dropped significantly to 45.2% on math and 42.0% on reading.
Of the city's public high schools, including charter schools, only four performed above the national average on the SAT (1497 out of 2400) in 2014: Masterman, Central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as ...
, Girard Academic Music Program
The Girard Academic Music Program (GAMP) is a public magnet secondary school in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and is part of the School District of Philadelphia, covering grades five through twelve. All students are able to pursue music as a major ...
, and MaST Community Charter School. All other district-run schools were below average.
Higher education

 Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the
Medical and research facilities of the University of Pennsylvania School of Medicine and the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia.
Philadelphia has the third-largest student concentration on the East Coast
East Coast may refer to:
Entertainment
* East Coast hip hop, a subgenre of hip hop
* East Coast (ASAP Ferg song), "East Coast" (ASAP Ferg song), 2017
* East Coast (Saves the Day song), "East Coast" (Saves the Day song), 2004
* East Coast FM, a ra ...
, with more than 120,000 college and university students enrolled within the city and nearly 300,000 in the metropolitan area. More than 80 colleges, universities, trade, and specialty schools are in the Philadelphia region. One of the founding members of the Association of American Universities is in the city, the University of Pennsylvania, an Ivy League institution with claims to be the First university in the United States.
The city's largest university, as noted by number of students, is Temple University, followed by Drexel University
Drexel University is a private research university with its main campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Drexel's undergraduate school was founded in 1891 by Anthony J. Drexel, a financier and philanthropist. Founded as Drexel Institute of Art, S ...
. The University of Pennsylvania, Temple University, Drexel University, and Thomas Jefferson University comprise the city's nationally ranked research universities. Philadelphia is also home to five schools of medicine: Drexel University College of Medicine, Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania
The Perelman School of Medicine, commonly known as Penn Med, is the medical school of the University of Pennsylvania, a private research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Founded in 1765, the Perelman School of Medicine is the oldest medi ...
, Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine
Philadelphia College of Osteopathic Medicine (PCOM) is a private medical school with its main campus in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, and additional locations in Suwanee, Georgia (PCOM Georgia) and Moultrie, Georgia (PCOM South Georgia).
Founded in ...
, Temple University School of Medicine, and Thomas Jefferson University's Sidney Kimmel Medical College
Thomas Jefferson University is a private research university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Established in its earliest form in 1824, the university officially combined with Philadelphia University in 2017. To signify its heritage, the un ...
. Hospitals, universities, and higher education research institutions in Philadelphia's four congressional districts received more than $252 million in National Institutes of Health grants in 2015.
Other institutions of higher learning within the city's borders include:
* Chestnut Hill College
* Community College of Philadelphia
* Curtis Institute of Music
The Curtis Institute of Music is a private conservatory in Philadelphia. It offers a performance diploma, Bachelor of Music, Master of Music in opera, and a Professional Studies Certificate in opera. All students attend on full scholarship.
Hi ...
* Holy Family University
* La Salle University
La Salle University () is a private, Catholic university in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. The university was founded in 1863 by the Institute of the Brothers of the Christian Schools and named for St. Jean-Baptiste de La Salle.
History
La ...
* Moore College of Art and Design
Moore College of Art & Design is a Private college, private art school in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania. Its undergraduate programs are available only for female students, but its other educational programs, including graduate programs, are co-ed ...
* Peirce College
* Pennsylvania Academy of the Fine Arts
* Saint Joseph's University
Saint Joseph's University (SJU or St. Joe's) is a private Jesuit university in Philadelphia and Lower Merion, Pennsylvania. The university was founded by the Society of Jesus in 1851 as Saint Joseph's College. Saint Joseph's is the seventh olde ...
* Spells Writing Lab, Inc.
* The Art Institute of Philadelphia
The Art Institutes (AI) are a collection of private for-profit art schools in the United States. Since 2019, the schools have been owned by Education Principle Foundation (aka Colbeck Foundation), a non-profit that also owns South Universit ...
* The Restaurant School at Walnut Hill College
* University of the Arts
* University of the Sciences
Culture
Philadelphia is home to many national historical sites that relate to the founding of the United States. Independence National Historical Park is the center of these historical landmarks being one of the country's 22 UNESCO World Heritage Sites. Independence Hall, where the Declaration of Independence was signed, and theLiberty Bell
The Liberty Bell, previously called the State House Bell or Old State House Bell, is an iconic symbol of American independence, located in Philadelphia. Originally placed in the steeple of the Pennsylvania State House (now renamed Independence ...
are the city's most famous attractions. Other national historic sites include the homes of Edgar Allan Poe and Thaddeus Kosciuszko
Thaddeus (Latin ''Thaddaeus'', Ancient Greek Θαδδαῖος ''Thaddaĩos'', from Aramaic תדי ''Ṯaday'') is a male given name.
As of the 1990 Census, ''Thaddeus'' was the 611th most popular male name in the United States, while ''Thad'', ...
, early government buildings like the First and the Second Bank of the United States, Fort Mifflin, and the Gloria Dei (Old Swedes') Church. Philadelphia alone has 67 National Historic Landmarks, the third most of any city in the country.
Philadelphia's major science museums include the Franklin Institute, which contains the Benjamin Franklin National Memorial; the Academy of Natural Sciences; the Mütter Museum; and the University of Pennsylvania Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology. History museums include the National Constitution Center, the Museum of the American Revolution, the Philadelphia History Museum, the National Museum of American Jewish History
The Weitzman National Museum of American Jewish History (The Weitzman) is a Smithsonian-affiliated museum at 101 South Independence Mall East (S. 5th Street) at Market Street in Center City Philadelphia. It was founded in 1976.
History
With ...
, the African American Museum in Philadelphia, the Historical Society of Pennsylvania, the Masonic Library and Museum of Pennsylvania in the Masonic Temple
A Masonic Temple or Masonic Hall is, within Freemasonry, the room or edifice where a Masonic Lodge meets. Masonic Temple may also refer to an abstract spiritual goal and the conceptual ritualistic space of a meeting.
Development and history
In ...
, and the Eastern State Penitentiary. Philadelphia is home to the United States's first zoo and hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emerge ...
, as well as Fairmount Park
Fairmount Park is the largest municipal park in Philadelphia and the historic name for a group of parks located throughout the city. Fairmount Park consists of two park sections named East Park and West Park, d