|
Ravn Virus
Ravn virus (; RAVV) is a close relative of Marburg virus (MARV). RAVV causes Marburg virus disease in humans and nonhuman primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. RAVV is a Select agent, World Health Organization Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring Biosafety Level 4-equivalent containment), National Institutes of Health/National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases Category A Priority Pathogen, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Category A Bioterrorism Agent, and listed as a Biological Agent for Export Control by the Australia Group. Use of term Ravn virus (today abbreviated RAVV, but then considered identical to Marburg virus) was first described in 1987 and is named after a 15-year old Danish boy who fell ill and died from it. Today, the virus is classified as one of two members of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', which is included into the genus ''Marburgvirus'', family ''Filoviridae'', order ''Mononegavirales''. The name Ravn virus is derived from '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marburg Virus
Marburg virus (MARV) is a hemorrhagic fever virus of the ''Filoviridae'' family of viruses and a member of the species '' Marburg marburgvirus'', genus ''Marburgvirus''. It causes Marburg virus disease in primates, a form of viral hemorrhagic fever. The virus is considered to be extremely dangerous. The World Health Organization (WHO) rates it as a Risk Group 4 Pathogen (requiring biosafety level 4-equivalent containment). In the United States, the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Diseases ranks it as a Category A Priority Pathogen and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention lists it as a Category A Bioterrorism Agent. It is also listed as a biological agent for export control by the Australia Group. The virus can be transmitted by exposure to one species of fruit bats or it can be transmitted between people via body fluids through unprotected sex and broken skin. The disease can cause haemorrhage, fever, and other symptoms similar to Ebola, which belongs t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
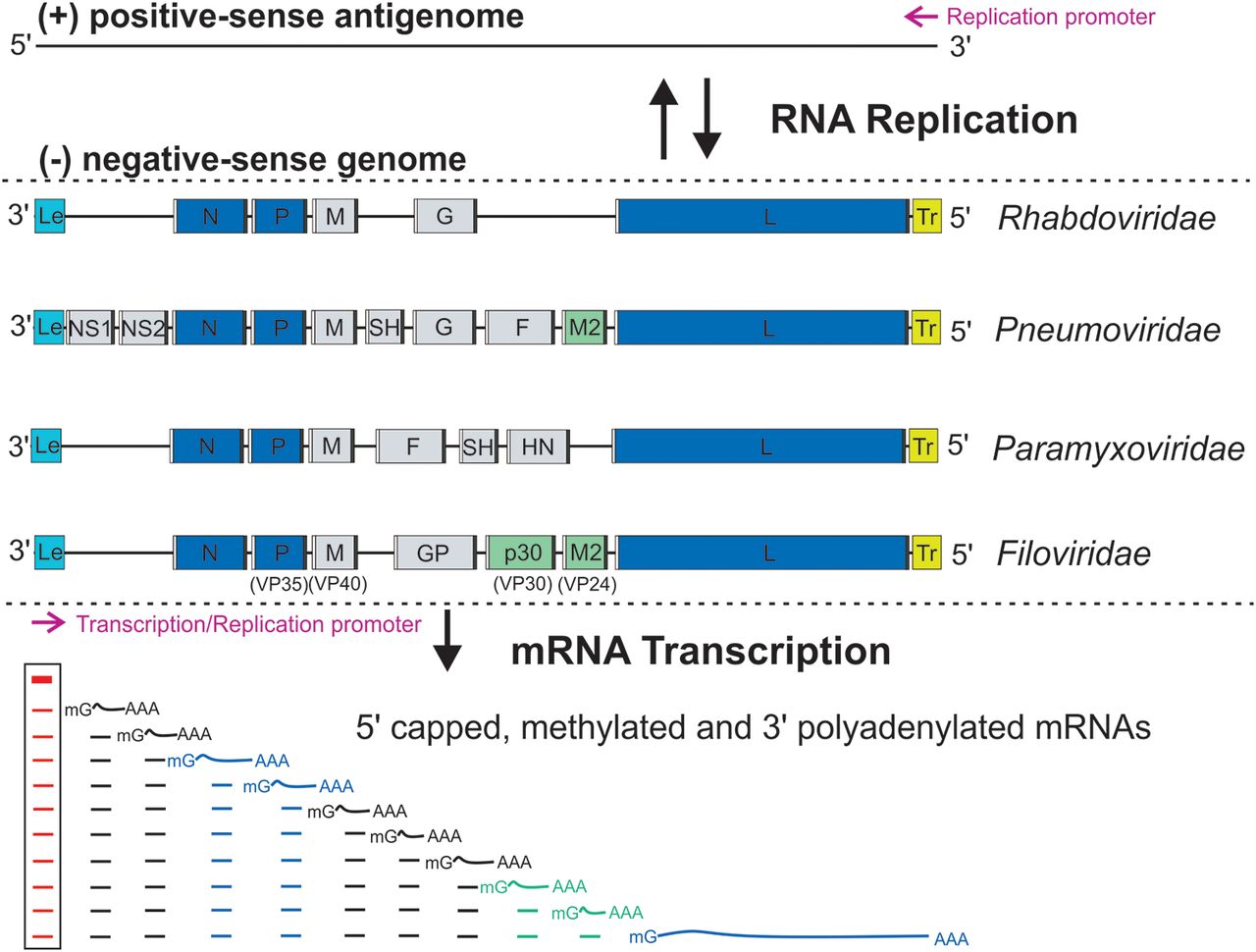
Mononegavirales
''Mononegavirales'' is an order of negative-strand RNA viruses which have nonsegmented genomes. Some common members of the order are Ebola virus, human respiratory syncytial virus, measles virus, mumps virus, Nipah virus, and rabies virus. All of these viruses cause significant disease in humans. Many other important pathogens of nonhuman animals and plants are also in the group. The order includes eleven virus families: '' Artoviridae'', ''Bornaviridae'', ''Filoviridae'', ''Lispiviridae'', ''Mymonaviridae'', ''Nyamiviridae'', ''Paramyxoviridae'', ''Pneumoviridae'', ''Rhabdoviridae'', '' Sunviridae'', and ''Xinmoviridae''. Use of term The order ''Mononegavirales'' (pronounced: ) According to the rules for taxon naming established by the International Committee on Taxonomy of Viruses (ICTV), the name ''Mononegavirales'' is always to be capitalized, italicized, and never abbreviated. The names of the order's physical members ("mononegaviruses" or "mononegavirads") are to be writte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Animal Viral Diseases
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by their inhabitants as comprising the entire world, with the "New World", a term for the newly encountered lands of the Western Hemisphere, particularly the Americas. Etymology In the context of archaeology and world history, the term "Old World" includes those parts of the world which were in (indirect) cultural contact from the Bronze Age onwards, resulting in the parallel development of the early civilizations, mostly in the temperate zone between roughly the 45th and 25th parallels north, in the area of the Mediterranean, including North Africa. It also included Mesopotamia, the Persian plateau, the Indian subcontinent, China, and parts of Sub-Saharan Africa. These regions were connected via the Silk Road trade route, and they have a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egyptian Fruit Bat
The Egyptian fruit bat or Egyptian rousette (''Rousettus aegyptiacus'') is a species of megabat that is found in Africa, the Middle East, the Mediterranean, and the Indian subcontinent. It is one of three ''Rousettus'' species with an African-Malagasy range, though the only species of its genus found on continental Africa. The common ancestor of the three species colonized the region in the late Pliocene or early Pleistocene. The species is traditionally divided into six subspecies. It is considered a medium-sized megabat, with adults weighing and possessing wingspans of approximately . Individuals are dark brown or grayish brown, with their undersides paler than their backs. The Egyptian fruit bat is a highly social species, usually living in colonies with thousands of other bats. It, along with other members of the genus ''Rousettus'', are some of the only fruit bats to use echolocation, though a more primitive version than used by bats in other families. It has also develope ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uganda
}), is a landlocked country in East Africa East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa: Due to the historical .... The country is bordered to the east by Kenya, to the north by South Sudan, to the west by the Democratic Republic of the Congo, to the south-west by Rwanda, and to the south by Tanzania. The southern part of the country includes a substantial portion of Lake Victoria, shared with Kenya and Tanzania. Uganda is in the African Great Lakes region. Uganda also lies within the Nile, Nile basin and has a varied but generally a modified equatorial climate. It has a population of around 49 million, of which 8.5 million live in the Capital city, capital and largest city of Kampala. Uganda is named after the Buganda kingdom, which encompasses a large portion of the south of the country, includi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in Central Africa. It is bordered to the northwest by the Republic of the Congo, to the north by the Central African Republic, to the northeast by South Sudan, to the east by Uganda, Rwanda, and Burundi, and by Tanzania (across Lake Tanganyika), to the south and southeast by Zambia, to the southwest by Angola, and to the west by the South Atlantic Ocean and the Cabinda exclave of Angola. By area, it is the second-largest country in Africa and the 11th-largest in the world. With a population of around 108 million, the Democratic Republic of the Congo is the most populous officially Francophone country in the world. The national capital and largest city is Kinshasa, which is also the nation's economic center. Centered on the Cong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Watsa
Watsa is a community in the Haut-Uele Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, administrative center of the Watsa Territory. It is served by Watsa Airport, a grass airstrip south of the town. Watsa was the location of the VI battalion of the Force Publique in the 1940s and 1950s. Between 1998 and 2000, co-circulating Marburg virus and Ravn virus caused 154 cases of Marburg virus disease and 128 deaths among illegal gold miners in Watsa and the nearby Durba Mine. In January and February 2011 the Lords Resistance Army attacked people in the territories of Dungu, Faradje, Niangara Niangara is a town in the Haut-Uele Province of the Democratic Republic of the Congo, lying on both sides of the Uele River. It is the headquarters of the Niangara Territory. The town has a hospital operated by Médecins Sans Frontières. As of ... and Watsa, causing 33,000 people to be displaced. They were slow to return due to the feeble response of government security forces. Climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durba, Democratic Republic Of The Congo
The Kibali Gold Mine is a combined open pit and underground gold mine in the Haut-Uélé province of the northeast Democratic Republic of the Congo. By area, it is one of the largest in Africa. The mine is named for the nearby Kibali River. Location The Kibali Gold Mine is in the Watsa and Faradje territories of Haut-Uélé province, formerly the Haut-Uele District of Orientale Province. It is to the southeast of the town of Kalimva. It is about east of Isiro, the capital of Haut-Uélé, west of Arua on the Ugandan border, and from the port of Mombasa in Kenya. The main access route is by road from Kampala, Uganda, about distant. The concession covers of the Kilo-Moto goldfields. It includes the Karagba-Chaffeur-Durba (KCD) deposit complex and the satellite Sessenge, Pakaka, Pamao, Gorumbwa, Kibali, Mengu Hill, Mengu Village, Megi, Marakeke, Kombokolo, Sessenge and Ndala deposits. It is in the Moto greenstone belt, which contains Archean volcano-sedimentary, pyroclastic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenya
) , national_anthem = "Ee Mungu Nguvu Yetu"() , image_map = , map_caption = , image_map2 = , capital = Nairobi , coordinates = , largest_city = Nairobi , official_languages = Constitution (2009) Art. 7 ational, official and other languages"(1) The national language of the Republic is Swahili. (2) The official languages of the Republic are Swahili and English. (3) The State shall–-–- (a) promote and protect the diversity of language of the people of Kenya; and (b) promote the development and use of indigenous languages, Kenyan Sign language, Braille and other communication formats and technologies accessible to persons with disabilities." , languages_type = National language , languages = Swahili , ethnic_groups = , ethnic_groups_year = 2019 census , religion = , religion_year = 2019 census , demonym = ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nucleotide
Nucleotides are organic molecules consisting of a nucleoside and a phosphate. They serve as monomeric units of the nucleic acid polymers – deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) and ribonucleic acid (RNA), both of which are essential biomolecules within all life-forms on Earth. Nucleotides are obtained in the diet and are also synthesized from common nutrients by the liver. Nucleotides are composed of three subunit molecules: a nucleobase, a five-carbon sugar (ribose or deoxyribose), and a phosphate group consisting of one to three phosphates. The four nucleobases in DNA are guanine, adenine, cytosine and thymine; in RNA, uracil is used in place of thymine. Nucleotides also play a central role in metabolism at a fundamental, cellular level. They provide chemical energy—in the form of the nucleoside triphosphates, adenosine triphosphate (ATP), guanosine triphosphate (GTP), cytidine triphosphate (CTP) and uridine triphosphate (UTP)—throughout the cell for the many cellular func ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |