|
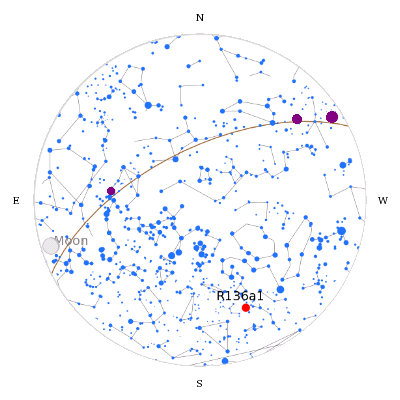
R136a1 Star
R136a1 (short for RMC 136a1) is one of the most massive and luminous stars known, at nearly and nearly 4.7 million , and is also one of the hottest, at around . It is a Wolf–Rayet star at the center of R136, the central concentration of stars of the large NGC 2070 open cluster in the Tarantula Nebula (30 Doradus) in the Large Magellanic Cloud. The cluster can be seen in the far southern celestial hemisphere with binoculars or a small telescope, at magnitude 7.25. R136a1 itself is 100 times fainter than the cluster and can only be resolved using speckle interferometry. Discovery In 1960, a group of astronomers working at the Radcliffe Observatory in Pretoria made systematic measurements of the brightness and spectra of bright stars in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC). Among the objects cataloged was RMC 136 (Radcliffe observatory Magellanic Cloud catalog number 136), the central "star" of the Tarantula Nebula, which the observers concluded was probably a multiple ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Hottest Stars
This is a list of hottest stars so far discovered (excluding degenerate stars), arranged by decreasing temperature. The stars with temperature Temperature is a physical quantity that quantitatively expresses the attribute of hotness or coldness. Temperature is measurement, measured with a thermometer. It reflects the average kinetic energy of the vibrating and colliding atoms making ...s higher than 60,000 K are included. List See also * List of most massive stars * List of most luminous stars * List of least massive stars * List of coolest stars References {{Portal bar, Astronomy, Outer space hottest stars, list of Stars, hottest stars, hottest ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
R136a
R136 (formerly known as RMC 136 from the Radcliffe Observatory Magellanic Clouds catalogue) is the central concentration of stars in the NGC 2070 star cluster, which lies at the centre of the Tarantula Nebula in the Large Magellanic Cloud. When originally named it was an unresolved stellar object (catalogued as HD 38268 and Wolf-Rayet star Brey 82) but is now known to include 72 class O and Wolf–Rayet stars within 5 parsecs (20 arc seconds) of the centre of the cluster. The extreme number and concentration of young massive stars in this part of the LMC qualifies it as a starburst region. Properties R136 produces most of the energy that makes the Tarantula Nebula visible. The estimated mass of the cluster is 450,000 solar masses, suggesting it may become a globular cluster in the future. R136 has around 200 times the stellar density of a typical OB association such as Cygnus OB2. The central R136 concentration of the cluster is about 2 parsecs across, although the whole ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESO 3
The European Southern Observatory is an astronomical research organisation. ESO may also refer to: *Employee stock option (also: executive stock option) *'' Ether Saga Odyssey'', a fantasy massively multiplayer online role-playing game *''The Elder Scrolls Online'', a fantasy massively multiplayer online role-playing game *Existential second-order logic *ESO (motorcycles) * Eso (town), Orhionmwon, Edo State, Nigeria Organisations * European Standardisation Organisations: CEN (European Committee for Standardization), CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardisation) and ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) *Ensemble Studios Online *Edmonton Symphony Orchestra *Energijos skirstymo operatorius (ESO), Lithuanian electricity transmission network operator *Evergreen Symphony Orchestra, an orchestra in Taiwan *Eteläsuomalainen osakunta, a student nation at the University of Helsinki *Libyan External Security Organisation *External Security Organisatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebula
A nebula (; or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral, or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the Pillars of Creation in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter and eventually become dense enough to form stars. The remaining material is then thought to form planets and other planetary system objects. Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-years in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dens ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
H II Region
An H II region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds of light years, and density from a few to about a million particles per cubic centimetre. The Orion Nebula, now known to be an H II region, was observed in 1610 by Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc by telescope, the first such object discovered. The regions may be of any shape because the distribution of the stars and gas inside them is irregular. The short-lived blue stars created in these regions emit copious amounts of ultraviolet light that ionize the surrounding gas. H II regions—sometimes several hundred light-years across—are often associated with giant molecular clouds. They often appear clumpy and filamentary, sometimes showing intricate shapes such as the Horsehead Nebula. H II regions may give birth to thousands of stars ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spectrum
A spectrum (: spectra or spectrums) is a set of related ideas, objects, or properties whose features overlap such that they blend to form a continuum. The word ''spectrum'' was first used scientifically in optics to describe the rainbow of colors in visible light after passing through a prism. In the optical spectrum, light wavelength is viewed as continuous, and spectral colors are seen to blend into one another smoothly when organized in order of their corresponding wavelengths. As scientific understanding of light advanced, the term came to apply to the entire electromagnetic spectrum, including radiation not visible to the human eye. ''Spectrum'' has since been applied by analogy to topics outside optics. Thus, one might talk about the " spectrum of political opinion", or the "spectrum of activity" of a drug, or the " autism spectrum". In these uses, values within a spectrum may not be associated with precisely quantifiable numbers or definitions. Such uses imply a bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apparent Magnitude
Apparent magnitude () is a measure of the Irradiance, brightness of a star, astronomical object or other celestial objects like artificial satellites. Its value depends on its intrinsic luminosity, its distance, and any extinction (astronomy), extinction of the object's light caused by interstellar dust along the sightline, line of sight to the observer. Unless stated otherwise, the word ''magnitude'' in astronomy usually refers to a celestial object's apparent magnitude. The magnitude scale likely dates to before the ancient Ancient Greek astronomy#Astronomy in the Greco-Roman and Late Antique eras, Roman astronomer Ptolemy, Claudius Ptolemy, whose Star catalogue, star catalog popularized the system by listing stars from First-magnitude star, 1st magnitude (brightest) to 6th magnitude (dimmest). The modern scale was mathematically defined to closely match this historical system by Norman Robert Pogson, Norman Pogson in 1856. The scale is reverse logarithmic scale, logarithmic: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pretoria
Pretoria ( ; ) is the Capital of South Africa, administrative capital of South Africa, serving as the seat of the Executive (government), executive branch of government, and as the host to all foreign embassies to the country. Pretoria straddles the Apies River and extends eastward into the foothills of the Magaliesberg mountains. It has a reputation as an academic city and centre of research, being home to the Tshwane University of Technology (TUT), the University of Pretoria (UP), the University of South Africa (UNISA), the Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), and the Human Sciences Research Council. It also hosts the National Research Foundation (South Africa), National Research Foundation and the South African Bureau of Standards. Pretoria was one of the host cities of the 2010 FIFA World Cup. Pretoria is the central part of the City of Tshwane Metropolitan Municipality which was formed by the amalgamation of several former local authorities, including B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ESO - Eso1030a (by)
The European Southern Observatory is an astronomical research organisation. ESO may also refer to: *Employee stock option (also: executive stock option) *'' Ether Saga Odyssey'', a fantasy massively multiplayer online role-playing game *''The Elder Scrolls Online'', a fantasy massively multiplayer online role-playing game *Existential second-order logic *ESO (motorcycles) * Eso (town), Orhionmwon, Edo State, Nigeria Organisations * European Standardisation Organisations: CEN (European Committee for Standardization), CENELEC (European Committee for Electrotechnical Standardisation) and ETSI (European Telecommunications Standards Institute) *Ensemble Studios Online *Edmonton Symphony Orchestra *Energijos skirstymo operatorius (ESO), Lithuanian electricity transmission network operator *Evergreen Symphony Orchestra, an orchestra in Taiwan *Eteläsuomalainen osakunta, a student nation at the University of Helsinki *Libyan External Security Organisation *External Security Organisatio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Speckle Interferometry
Speckle imaging comprises a range of high-resolution Astrophotography, astronomical imaging techniques based on the analysis of large numbers of short Exposure (photography), exposures that freeze the variation of Astronomical seeing, atmospheric turbulence. They can be divided into the shift-and-add ("''image stacking''") method and the speckle interferometry methods. These techniques can dramatically increase the Optical resolution, resolution of ground-based telescopes, but are limited to bright targets. Explanation The principle of all the techniques is to take very short exposure images of astronomical targets, and then process those so as to remove the effects of astronomical seeing. Use of these techniques led to a number of discoveries, including thousands of binary stars that would otherwise appear as a single star to a visual observer working with a similar-sized telescope, and the first images of sunspot-like phenomena on other stars. Many of the techniques remain i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Large Magellanic Cloud
The Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC) is a dwarf galaxy and satellite galaxy of the Milky Way. At a distance of around , the LMC is the second- or third-closest galaxy to the Milky Way, after the Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal Galaxy, Sagittarius Dwarf Spheroidal ( away) and the possible dwarf irregular galaxy called the Canis Major Overdensity. Based on the D25 isophote at the B-band (445 nm wavelength of light), the Large Magellanic Cloud is about across. It is roughly one-hundredth the mass of the Milky Way and is the fourth-largest galaxy in the Local Group, after the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), the Milky Way, and the Triangulum Galaxy (M33). The LMC is classified as a Magellanic spiral. It contains a stellar bar that is geometrically off-center, suggesting that it was once a barred dwarf spiral galaxy before its spiral arms were disrupted, likely by tidal interactions from the nearby Small Magellanic Cloud (SMC) and the Milky Way's gravity. The LMC is predicted to merge with the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |