|
Quirino Salvadores
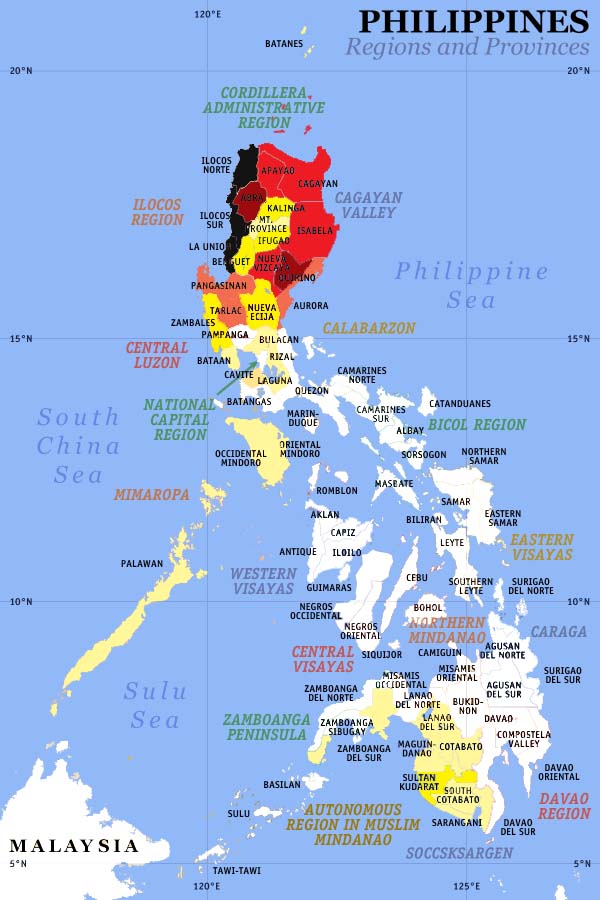
Quirino, officially the Province of Quirino ( ilo, Probinsia ti Quirino; tl, Lalawigan ng Quirino), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital is Cabarroguis. It is named after Elpidio Quirino, the sixth President of the Philippines. The province borders Aurora to the southeast, Nueva Vizcaya to the west, and Isabela to the north. Quirino used to be part of the province of Nueva Vizcaya, until it was separated in 1966. History Long before its formal creation as an independent province, Quirino was the forest region of the province of Nueva Vizcaya, inhabited by tribal groups known as the Negritos. They roamed the hinterlands and built their huts at the heart of the jungle. On June 18, 1966, Republic Act No. 4734 was enacted, constituting the municipalities of Diffun, Saguday, Aglipay, and Maddela, all from Nueva Vizcaya province, into a new sub-province to be known as "Quirino", named after the late Phi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabarroguis
Cabarroguis, officially the Municipality of Cabarroguis ( ilo, Ili ti Cabarroguis; tl, Bayan ng Cabarroguis), is a 3rd class municipality of the Philippines, municipality and capital of the Philippine Province, province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,533 people. History Prior to the advent of settlement, Cabarroguis was a vast forested area and formed parts of the municipalities of Saguday, Diffun and Aglipay. It was originally occupied by the Aetas who were later displaced by the Ilongot tribe because the Aetas were known to be of nomadic character. Many years later, permanent settlements were made by different civilized ethnic groups like Ilocanos, Tagalog and others in search of good fortune in this virgin land. As the population and settlement increased, regular barrios were created. These are the barrios of Zamora, Banuar, Burgos, Del Pilar, Dibibi, Eden, Villamor and five (5) more sitios of Villapeña, Villarose, Tucod, Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Barangays In Quirino ...
The province of Quirino has 132 barangays comprising its 6 towns. Barangays References {{Quirino Populated places in Quirino Quirino Quirino, officially the Province of Quirino ( ilo, Probinsia ti Quirino; tl, Lalawigan ng Quirino), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Cagayan Valley region in Luzon. Its capital is Cabarroguis. It is named after Elp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cabarroguis, Quirino
Cabarroguis, officially the Municipality of Cabarroguis ( ilo, Ili ti Cabarroguis; tl, Bayan ng Cabarroguis), is a 3rd class municipality and capital of the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,533 people. History Prior to the advent of settlement, Cabarroguis was a vast forested area and formed parts of the municipalities of Saguday, Diffun and Aglipay. It was originally occupied by the Aetas who were later displaced by the Ilongot tribe because the Aetas were known to be of nomadic character. Many years later, permanent settlements were made by different civilized ethnic groups like Ilocanos, Tagalog and others in search of good fortune in this virgin land. As the population and settlement increased, regular barrios were created. These are the barrios of Zamora, Banuar, Burgos, Del Pilar, Dibibi, Eden, Villamor and five (5) more sitios of Villapeña, Villarose, Tucod, Calaocan and Dingasan at the municipality of Aglipay: ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Luzon
Luzon (; ) is the largest and most populous island in the Philippines. Located in the northern portion of the Philippines archipelago, it is the economic and political center of the nation, being home to the country's capital city, Manila, as well as Quezon City, the country's most populous city. With a population of 64 million , it contains 52.5% of the country's total population and is the fourth most populous island in the world. It is the 15th largest island in the world by land area. ''Luzon'' may also refer to one of the three primary island groups in the country. In this usage, it includes the Luzon mainland, the Batanes and Babuyan groups of islands to the north, Polillo Islands to the east, and the outlying islands of Catanduanes, Marinduque and Mindoro, among others, to the south. The islands of Masbate, Palawan and Romblon are also included, although these three are sometimes grouped with another of the island groups, the Visayas. Etymology The name ''Luz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cagayan Valley
Cagayan Valley ( ilo, Tanap ti Cagayan; fil, Lambak ng Cagayan), is an administrative region in the Philippines, located in the northeastern section of Luzon Island. It is composed of five Philippine provinces: Batanes, Cagayan, Isabela, Nueva Vizcaya, and Quirino. The region hosts four chartered cities of Cauayan, Ilagan, Santiago, and Tuguegarao. Most of the land area is situated on the valley between the Cordilleras and the Sierra Madre mountain ranges. The eponymous Cagayan River, the country's largest and longest, runs through the region and flows from the Caraballo Mountains and ends at Aparri. Cagayan Valley is the second largest Philippine administrative region by land area. According to a literacy survey in 2013, 97.2% of Cagayan Valley's citizens (ages 10 to 64) are functionally literate, which is the highest out of the seventeen regions of the Philippines. History Archaeology indicates that Cagayan has been inhabited for half a million years, though no hu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Provinces Of The Philippines
In the Philippines, provinces ( fil, lalawigan) are one of its primary political and administrative divisions. There are 82 provinces at present, which are further subdivided into component cities and municipalities. The local government units in the National Capital Region, as well as independent cities, are independent of any provincial government. Each province is governed by an elected legislature called the Sangguniang Panlalawigan and an elected governor. The provinces are grouped into seventeen regions based on geographical, cultural, and ethnological characteristics. Thirteen of these regions are numerically designated from north to south, while the National Capital Region, the Cordillera Administrative Region, the Southwestern Tagalog Region, and the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao are only designated by acronyms. Each province is a member of the League of Provinces of the Philippines, an organization which aims to address issues affecting provi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Diffun
Diffun, officially the Municipality of Diffun ( ilo, Ili ti Diffun; tl, Bayan ng Diffun), is a 2nd class municipality in the province of Quirino, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 56,102 people. Commercial establishments proliferated along the provincial road due to its proximity to Santiago City as the main commercial hub of the region. Diffun is from Cabarroguis and from Manila. Geography Barangays Diffun is politically subdivided into 33 barangays. These barangays are headed by elected officials: Barangay Captain, Barangay Council, whose members are called Barangay Councilors. All are elected every three years. Climate Demographics Economy Government Diffun, belonging to the lone congressional district of the province of Quirino, is governed by a mayor designated as its local chief executive and by a municipal council as its legislative body in accordance with the Local Government Code. The mayor, vice mayor, and the council ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tagalog Language
Tagalog (, ; ; '' Baybayin'': ) is an Austronesian language spoken as a first language by the ethnic Tagalog people, who make up a quarter of the population of the Philippines, and as a second language by the majority. Its standardized form, officially named ''Filipino'', is the national language of the Philippines, and is one of two official languages, alongside English. Tagalog is closely related to other Philippine languages, such as the Bikol languages, Ilocano, the Bisayan languages, Kapampangan, and Pangasinan, and more distantly to other Austronesian languages, such as the Formosan languages of Taiwan, Indonesian, Malay, Hawaiian, Māori, and Malagasy. Classification Tagalog is a Central Philippine language within the Austronesian language family. Being Malayo-Polynesian, it is related to other Austronesian languages, such as Malagasy, Javanese, Indonesian, Malay, Tetum (of Timor), and Yami (of Taiwan). It is closely related to the languages spoken in the Bi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kankana-ey Language
Kankanaey (also spelled Kankana-ey) is a South-Central Cordilleran language under the Austronesian family spoken on the island of Luzon in the Philippines primarily by the Kankanaey people. Alternate names for the language include Central Kankanaey, Kankanai, and Kankanay. It is widely used by Cordillerans, alongside Ilocano, specifically people from Mountain Province and people from the northern part of the Benguet Province.Allen, Janet L. 2014. **Kankanaey: A Role and Reference Grammar Analysis** Dallas:SIL International Kankanaey has a slight mutual intelligibility with the Ilocano language. Dialects ''Ethnologue'' lists Mankayan-Buguias, Kapangan, Bakun-Kibungan, and Guinzadan as dialects of Kankanaey. Northern Kankanaey is listed as a separate language. Kankanaey is spoken in northern Benguet, southwestern Mountain Province, southeastern Ilocos Sur, northeastern La Union, and southwestern Ifugao. Northern Kankanaey is spoken in western Mountain Province, southeastern Ilo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pangasinan Language
Pangasinan (''Pangasinense'') is an Austronesian language, and one of the eight major languages of the Philippines. It is the primary and predominant language of the entire province of Pangasinan and northern Tarlac, on the northern part of Luzon's central plains geographic region, most of whom belong to the Pangasinan ethnic group. Pangasinan is also spoken in southwestern La Union, as well as in the municipalities of Benguet, Nueva Vizcaya, Nueva Ecija, and Zambales that border Pangasinan. A few Aeta groups in Central Luzon's northern part also understand and even speak Pangasinan as well. Classification The Pangasinan language belongs to the Malayo-Polynesian languages branch of the Austronesian languages family. Pangasinan is similar to other closely related Philippine languages, Malay in Malaysia (as Malaysian), Indonesia (as Indonesian language, Indonesian), Brunei, and Singapore, Hawaiian language, Hawaiian in Hawaii and Malagasy language, Malagasy in Madagascar. The Pang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ifugao Language
Ifugao or Batad is a Malayo-Polynesian language spoken in the northern valleys of Ifugao, Philippines. It is a member of the Northern Luzon subfamily and is closely related to the Bontoc and Kankanaey languages. It is a dialect continuum, and its four main varieties—such as Tuwali—are sometimes considered separate languages. Loanwords from other languages, such as Ilokano, are replacing some older terminology. Dialects ''Ethnologue'' reports the following locations for each of the four Ifugao languages. *Amganad Ifugao: spoken in Hungduan and Banaue municipalities of Ifugao Province, and into southwestern Mountain Province. 27,100 speakers as of 2000. Dialects are Burnay Ifugao and Banaue Ifugao. *Batad Ifugao (Ayangan Ifugao): spoken in central Ifugao Province. There are also some speakers in Isabela Province, on the eastern shore of the Magat reservoir. 10,100 speakers as of 2002. Dialects include Ducligan Ifugao. *Mayoyao Ifugao (Mayaoyaw): spoken in Ifugao Provinc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ilocano Language
Ilocano (also Ilokano; ; Ilocano: ) is an Austronesian language spoken in the Philippines, primarily by Ilocano people and as a lingua franca by the Igorot people and also by the native settlers of Cagayan Valley. It is the third most-spoken native language in the country. As an Austronesian language, it is related to Malay (Indonesian and Malaysian), Tetum, Chamorro, Fijian, Māori, Hawaiian, Samoan, Tahitian, Paiwan, and Malagasy. It is closely related to some of the other Austronesian languages of Northern Luzon, and has slight mutual intelligibility with the Balangao language and the eastern dialects of the Bontoc language. The Ilokano people had their indigenous writing system and script known as ''kur-itan''. There have been proposals to revive the ''kur-itan'' script by teaching it in Ilokano-majority public and private schools in Ilocos Norte and Ilocos Sur. Classification Ilocano, like all Philippine languages, is an Austronesian language, a very expansive ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |