|
Qixi Tribute
{{chinese , title="Qixi Tribute" , l="a sort of artware as offering to celebrate Qixi Festival " , s=七夕贡案, t=七夕貢案, p=qīxīgòngàn, order=st Qixi Tribute (Chinese:七夕贡案; pinyin: Qīxì gòngàn) is an important and necessary part of annual celebration during the Qixi Festival (Chinese: 七夕節) or Qiqiao Festival (Chinese: 乞巧節). Based on the mythology about The Weaver Girl and the Cowherd, a Qixi Tribute is a representation of their love meeting. It is one of the most popular customs of the Han Chinese in Dongguan, Guangdong province, especially in Wangniudun, a town in Dongguan city. Every year the government of Wangniudun holds a night-long Qixi festival celebration. Plenty of local people and tourists visit Wangniudun to share the happiness of the celebration. History The Qixi Festival (Qiqiao Festival) is an annual event on 7th day of the 7th lunar month in the Chinese calendar, celebrating the love story of the Cowherd and the Weaver Girl. Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
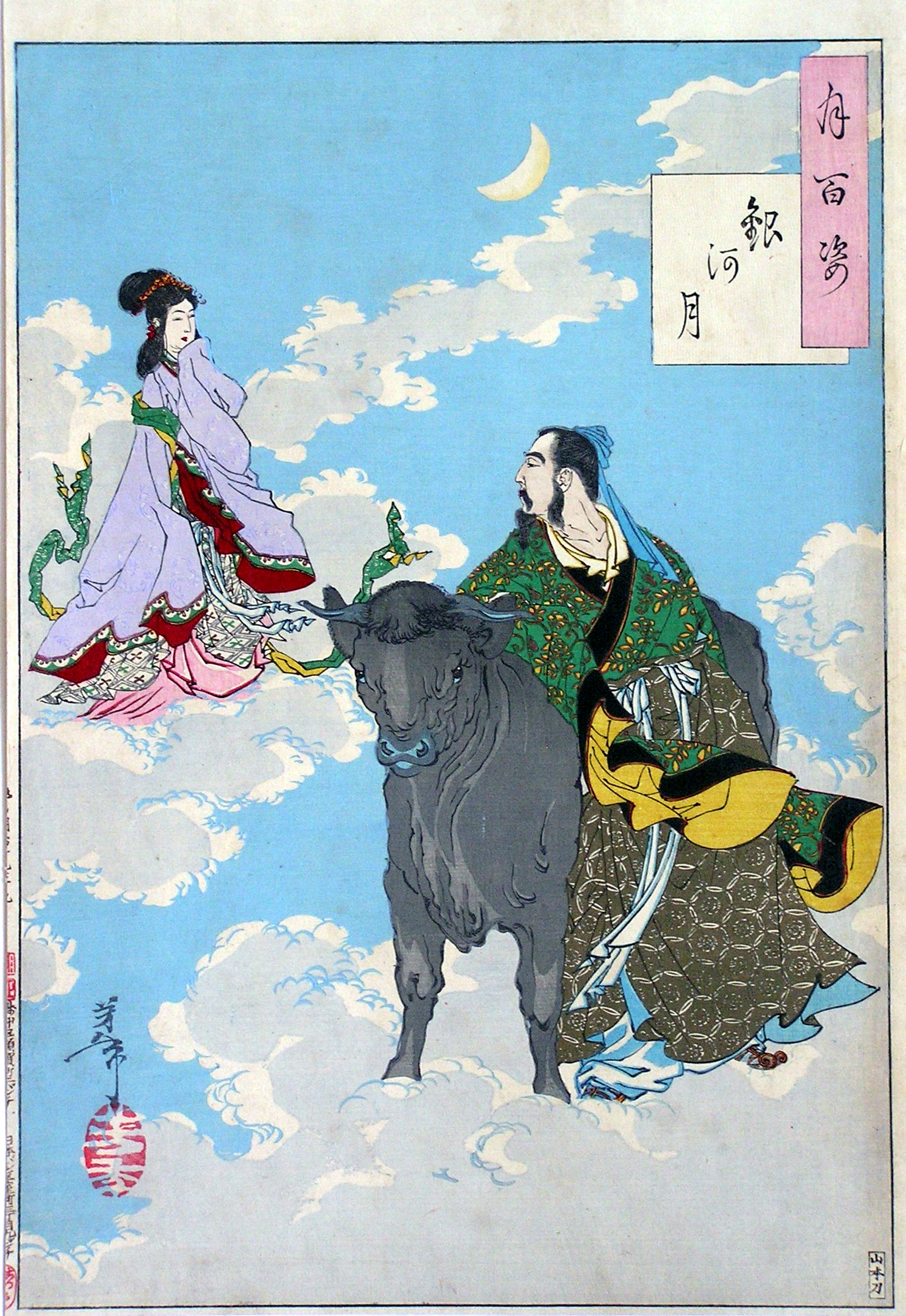
Yoshitoshi - 100 Aspects Of The Moon - 40-2
Tsukioka Yoshitoshi ( ja, 月岡 芳年; also named Taiso Yoshitoshi ; 30 April 1839 – 9 June 1892) was a Japanese printmaker. Nussbaum, Louis Frédéric. (2005)"Tsukoka Kōgyō"in ''Japan Encyclopedia,'' p. 1000. Yoshitoshi has widely been recognized as the last great master of the ukiyo-e genre of woodblock printing and painting. He is also regarded as one of the form's greatest innovators. His career spanned two eras – the last years of Edo period Japan, and the first years of modern Japan following the Meiji Restoration. Like many Japanese, Yoshitoshi was interested in new things from the rest of the world, but over time he became increasingly concerned with the loss of many aspects of traditional Japanese culture, among them traditional woodblock printing. By the end of his career, Yoshitoshi was in an almost single-handed struggle against time and technology. As he worked on in the old manner, Japan was adopting Western mass reproduction methods li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese New Year
Chinese New Year is the festival that celebrates the beginning of a New Year, new year on the traditional lunisolar calendar, lunisolar and solar Chinese calendar. In Sinophone, Chinese and other East Asian cultures, the festival is commonly referred to as the Spring Festival () as the Spring (season), spring season in the lunisolar calendar traditionally starts with lichun, the first of the twenty-four solar terms which the festival celebrates around the time of the Chinese New Year. Marking the end of winter and the beginning of the spring season, observances traditionally take place from Chinese New Year's Eve, New Year’s Eve, the evening preceding the first day of the year to the Lantern Festival, held on the 15th day of the year. The first day of Chinese New Year begins on the new moon that appears between 21 January and 20 February. Chinese New Year is one of the most important holidays in Chinese culture, and has strongly influenced Lunar New Year celebrations of its 5 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong Museum
The Guangdong Museum () is a general museum of Cantonese art, nature, culture and history in Guangzhou. History Old building The Guangdong Provincial Museum was located on 215 Wenming Rd. (), in Yuexiu District, Guangzhou, on which was the original site of Sun Yat-sen University. It was a provincial general museum, founded in 1959 and with a land area of 43,000 square meters. It comprised three major parts: the museum, the relic of the of the Kuomintang and Lu Xun Memorial House. Other affiliated buildings include the Red Tower () and the observatory of Sun Yat-sen University. There are two separate buildings. The building which housed the original National Sun Yat-sen University became the Lu Xun Memorial Hall and contains an exhibition of objects related to Lu Xun and some other intellectuals who influenced Chinese modernization and indirectly prepared the way for the communist revolution. The newer building to the right was initially built in 1957-1959 and greatly enlarg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong Province
Guangdong (, ), alternatively romanized as Canton or Kwangtung, is a coastal province in South China on the north shore of the South China Sea. The capital of the province is Guangzhou. With a population of 126.01 million (as of 2020) across a total area of about , Guangdong is the most populous province of China and the 15th-largest by area as well as the second-most populous country subdivision in the world (after Uttar Pradesh in India). Its economy is larger than that of any other province in the nation and the fifth largest sub-national economy in the world with a GDP (nominal) of 1.95 trillion USD (12.4 trillion CNY) in 2021. The Pearl River Delta Economic Zone, a Chinese megalopolis, is a core for high technology, manufacturing and foreign trade. Located in this zone are two of the four top Chinese cities and the top two Chinese prefecture-level cities by GDP; Guangzhou, the capital of the province, and Shenzhen, the first special economic zone in the count ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hainan
Hainan (, ; ) is the smallest and southernmost province of the People's Republic of China (PRC), consisting of various islands in the South China Sea. , the largest and most populous island in China,The island of Taiwan, which is slightly larger, is claimed but not controlled by the PRC. It is instead controlled by the Republic of China, a ''de facto'' separate country. makes up the vast majority (97%) of the province. The name means "south of the sea", reflecting the island's position south of the Qiongzhou Strait, which separates it from Leizhou Peninsula. The province has a land area of , of which Hainan the island is and the rest is over 200 islands scattered across three archipelagos: Zhongsha, Xisha and Nansha. It was part of Guangdong from 1950–88, after which it resumed as a top-tier entity and almost immediately made the largest Special Economic Zone by Deng Xiaoping as part of the then-ongoing Chinese economic reform program. Indigenous peoples like th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
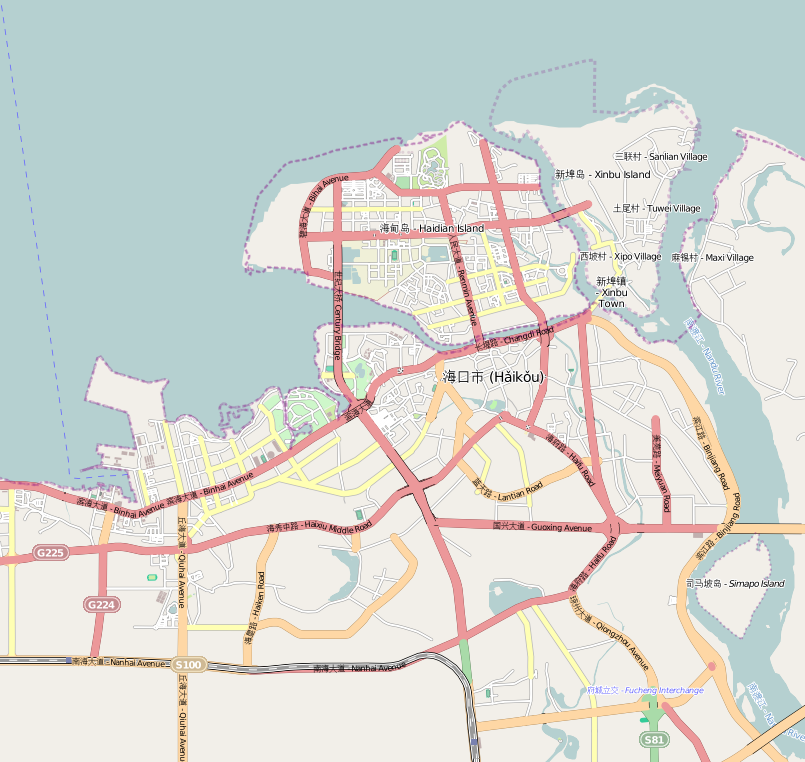
Haikou
Haikou (; ), also spelled as Hoikow is the capital and most populous city of the Chinese province of Hainan. Haikou city is situated on the northern coast of Hainan, by the mouth of the Nandu River. The northern part of the city is on the Haidian Island, which is separated from the main part of Haikou by the Haidian River, a branch of the Nandu. Administratively, Haikou is a prefecture-level city, comprising four districts, and covering . There are 2,046,189 inhabitants in the built-up area, all living within the four urban districts of the city. Haikou was originally a port city, serving as the port for Qiongshan. During the Chinese Civil War, Haikou was one of the last Nationalist strongholds to be taken by the Communists — with the Battle of Hainan Island in 1950. Currently, more than half of the island's total trade still goes through Haikou's ports. The Temple of the Five Lords is located to the southeast of the city. The city is home to Hainan University, a comprehen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kong and north of Macau, Guangzhou has a history of over 2,200 years and was a major terminus of the maritime Silk Road; it continues to serve as a major port and transportation hub as well as being one of China's three largest cities. For a long time, the only Chinese port accessible to most foreign traders, Guangzhou was captured by the British during the First Opium War. No longer enjoying a monopoly after the war, it lost trade to other ports such as Hong Kong and Shanghai, but continued to serve as a major transshipment port. Due to a high urban population and large volumes of port traffic, Guangzhou is classified as a Large-Port Megacity, the largest type of port-city in the world. Due to worldwide travel restrictions at the beginni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qilin
The qilin (; ) is a legendary hooved chimerical creature that appears in Chinese mythology, and is said to appear with the imminent arrival or passing of a sage or illustrious ruler. Qilin are a specific type of the mythological family of one-horned beasts. The qilin also appears in the mythologies of other cultures, such as Japanese and Korean mythology, where it is known as the kirin, and Vietnamese mythology, where it is known as the kỳ lân. Origins Earliest mention of this mythical horned beast is in the poem included in the Classic of Poetry (11th - 7th c. BCE). ''Spring and Autumn Annals'' mentioned that a ''lin'' () was captured in the 14th year of Duke Ai of Lu () (481 CE); '' Zuo Zhuan'' credited Confucius with identifying the ''lin'' as such. The bisyllabic form ''qilin'' ( ~ ), which carries the same generic meaning as ''lin'' alone, is attested in works dated to the Warring States period (475 - 221 BCE). Q''i'' denotes the male and ''lin'' denotes the fem ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fenghuang
''Fènghuáng'' (, ) are mythological birds found in Sinospheric mythology that reign over all other birds. The males were originally called ''fèng'' and the females ''huáng'', but such a distinction of gender is often no longer made and they are blurred into a single feminine entity so that the bird can be paired with the Chinese dragon, which is traditionally deemed male. It is known under similar names in various other languages ( Japanese: ; vi, phượng hoàng, italics=no or ; Korean: ). In the Western world, it is commonly called the Chinese phoenix or simply phoenix, although mythological similarities with the Western phoenix are superficial. Appearance A common depiction of fenghuang was of it attacking snakes with its talons and its wings spread. According to the ''Erya'''s chapter 17 ''Shiniao'', fenghuang is made up of the beak of a rooster, the face of a swallow, the forehead of a fowl, the neck of a snake, the breast of a goose, the back of a tortoise ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lion Dance
F Lion dance () is a form of traditional dance in Chinese culture and other Asian countries in which performers mimic a lion's movements in a lion costume to bring good luck and fortune. The lion dance is usually performed during the Chinese New Year and other Chinese traditional, cultural and religious festivals. It may also be performed at important occasions such as business opening events, special celebrations or wedding ceremonies, or may be used to honour special guests by the Chinese communities. The Chinese lion dance is normally operated by two dancers, one of whom manipulates the head while the other forms the rear end of the lion. It is distinguishable from the dragon dance which is performed by many people who hold the long sinuous body of the dragon on poles. Chinese lion dance fundamental movements can be found in Chinese martial arts, and it is commonly performed to a vigorous drum beat. There are two main forms of the Chinese lion dance, the Northern Lion and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dragon Dance
Dragon dance () is a form of traditional dance and performance in Chinese culture. Like the lion dance, it is most often seen during festive celebrations. The dance is performed by a team of experienced dancers who manipulate a long flexible giant puppet of a dragon using poles positioned at regular intervals along the length of the dragon. The dance team simulates the imagined movements of this river spirit in a sinuous, undulating manner. The dragon dance is often performed during Chinese New Year. Chinese dragons are a symbol of China's culture, and they are believed to bring good luck to people, therefore the longer the dragon is in the dance, the more luck it will bring to the community. The dragons are believed to possess qualities that include great power, dignity, fertility, wisdom and auspiciousness. The appearance of a dragon is both fearsome and bold but it has a benevolent disposition, and it was an emblem to represent imperial authority. The movements in a perfo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |