|
Philochortus Zolii
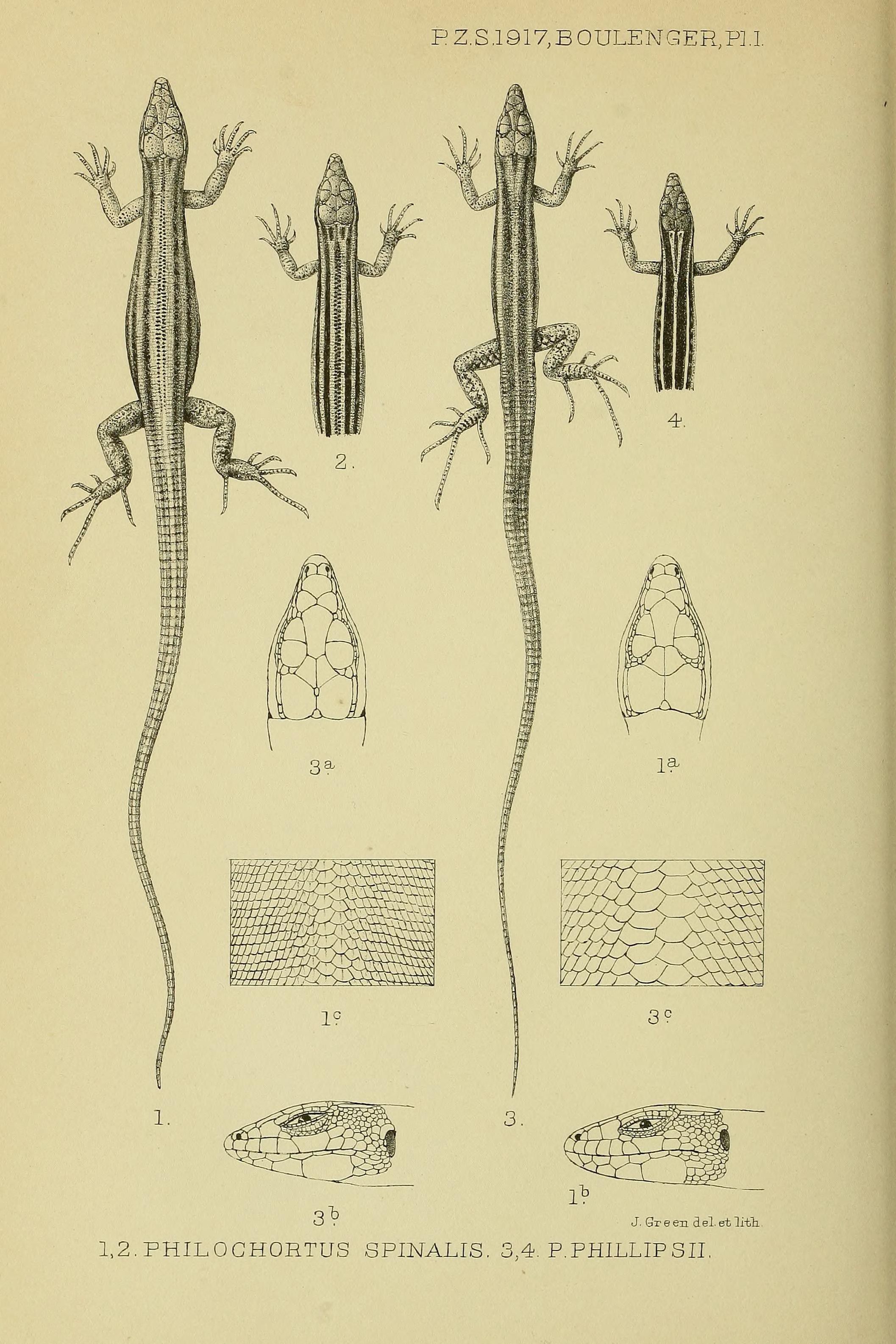
''Philochortus zolii'' is a species of lizard in the family Lacertidae. The species is native to northern Africa. Taxonomy Trape ''et al''. (2012) considered West African ''P. lhotei'' a junior synonym of ''P. zolii'' as its morphological characters fall within the range of variability of Egyptian ''P. zolii'' reported by Baha El Din (2006). Etymology The specific name, ''zolii'', is in honor of Italian diplomat Corrado Zoli, who was president of the ''Società geografica italiana''.Beolens, Bo; Watkins, Michael; Grayson, Michael (2011). ''The Eponym Dictionary of Reptiles''. Baltimore: Johns Hopkins University Press. xiii + 296 pp. . (''Philochortus lhotei'', p. 157; ''P. zolii'', p. 294). The specific epithet, ''lhotei'', is in honor of French ethnographer Henri Lhote. Description For a general description see the diagnosis of the genus '' Philochortus''. ''Philochortus zolii'' differs from other species of the genus by the following combination of characters (characters of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Philochortus
''Philochortus'' is a genus of lizards of the family Lacertidae. Species of this genus are distributed in Egypt, Algeria, Libya, Mali, Niger, Ethiopia, Djibouti, Eritrea, Somalia, Kenya, Yemen, and Saudi Arabia. Etymology ''Philochortus'' means grass-loving (Greek: ''philos'' = friend, ''chortos'' = grass). The common name of ''Philochortus'' species is therefore grass-loving lizards, or shield-backed ground lizards because of their typical back scalation and terrestrial habitat. Diagnosis Species of ''Philochortus'' are medium to large-sized lacertids with long cylindrical tails. The unregenerated tail is up to 3.25 times longer than head and body. Eyes with movable lids. The nostril is pierced between two shields and usually bordered by the first supralabial or narrowly separated from it. The collar is well marked. The ventral plates are smooth, feebly imbricate and arranged in 6 longitudinal series. The dorsal scales are smooth or keeled. Back with 2 to 6 longitudinal series o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wadi El Natrun
Wadi El Natrun (Arabic: "Valley of Natron"; Coptic: , "measure of the hearts") is a depression in northern Egypt that is located below sea level and below the Nile River level. The valley contains several alkaline lakes, natron-rich salt deposits, salt marshes and freshwater marshes. In Christian literature it is usually known as Scetis ( in Hellenistic Greek) or Skete (, plural in ecclesiastical Greek). It is one of the three early Christian monastic centers located in the Nitrian Desert of the northwestern Nile Delta. The other two monastic centers are Nitria and Kellia. Scetis, now called Wadi El Natrun, is best known today because its ancient monasteries remain in use, unlike Nitria and Kellia which have only archaeological remains. The desertified valley around Scetis in particular may be called the Desert of Scetis.. Fossil discoveries The area is one of the best known sites containing large numbers of fossils of large pre-historic animals in Egypt, and was known ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, the Gaza Strip of Palestine and Israel to the northeast, the Red Sea to the east, Sudan to the south, and Libya to the west. The Gulf of Aqaba in the northeast separates Egypt from Jordan and Saudi Arabia. Cairo is the capital and largest city of Egypt, while Alexandria, the second-largest city, is an important industrial and tourist hub at the Mediterranean coast. At approximately 100 million inhabitants, Egypt is the 14th-most populated country in the world. Egypt has one of the longest histories of any country, tracing its heritage along the Nile Delta back to the 6th–4th millennia BCE. Considered a cradle of civilisation, Ancient Egypt saw some of the earliest developments of writing, agriculture, ur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cyrenaica
Cyrenaica ( ) or Kyrenaika ( ar, برقة, Barqah, grc-koi, Κυρηναϊκή ��παρχίαKurēnaïkḗ parkhíā}, after the city of Cyrene), is the eastern region of Libya. Cyrenaica includes all of the eastern part of Libya between longitudes E16 and E25, including the Kufra District. The coastal region, also known as '' Pentapolis'' ("Five Cities") in antiquity, was part of the Roman province of Crete and Cyrenaica, later divided into ''Libya Pentapolis'' and ''Libya Sicca''. During the Islamic period, the area came to be known as ''Barqa'', after the city of Barca. Cyrenaica became an Italian colony in 1911. After the 1934 formation of Libya, the Cyrenaica province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country. During World War II, it fell under British military and civil administration from 1943 until 1951, and finally in the Kingdom of Libya from 1951 until 1963. The region that used to be Cyrenaica officially until 1963 has formed seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ber, ⴼⵣⵣⴰⵏ, Fezzan; ar, فزان, Fizzān; la, Phazania) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ancient towns and villages to survive deep in the otherwise inhospitable Sahara Desert. The term originally applied to the land beyond the coastal strip of Africa proconsularis, including the Nafusa and extending west of modern Libya over Ouargla and Illizi. As these Berber areas came to be associated with the regions of Tripoli, Cirta or Algiers, the name was increasingly applied to the arid areas south of Tripolitania. After the 1934 formation of Libya, the Fezzan province was designated as one of the three primary provinces of the country, alongside Tripolitania province to the north and Cyrenaica province to the northeast. Name In Berber languages, ''Fezzan'' (or ''ifezzan'') means "rough rocks". ''Fezzan'' could also be a derivati ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to Egypt–Libya border, the east, Sudan to Libya–Sudan border, the southeast, Chad to Chad–Libya border, the south, Niger to Libya–Niger border, the southwest, Algeria to Algeria–Libya border, the west, and Tunisia to Libya–Tunisia border, the northwest. Libya is made of three historical regions: Tripolitania, Fezzan, and Cyrenaica. With an area of almost 700,000 square miles (1.8 million km2), it is the fourth-largest country in Africa and the Arab world, and the List of countries and outlying territories by total area, 16th-largest in the world. Libya has the List of countries by proven oil reserves, 10th-largest proven oil reserves in the world. The largest city and capital, Tripoli, Libya, Tripoli, is located in western Libya and contains over ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Femoral Pore
Femoral pores are a part of a holocrine secretory gland found on the inside of the thighs of certain lizards and amphisbaenians which releases pheromones to attract mates or mark territory. In certain species only the male has these pores and in other species, both sexes have them, with the male's being larger. Femoral pores appear as a series of pits or holes within a row of scales on the ventral portion of the animal's thigh. Femoral pores are present in all genera in the families Cordylidae, Crotaphytidae, Hoplocercidae, Iguanidae, Phrynosomatidae, and Xantusiidae. They are absent in all genera in the Anguidae, Chamaeleonidae, Dibamidae, Helodermatidae, Scincidae, Xenosauridae, and Varanidae families. They are present in other lizards and amphisbaenians quite variably, some geckoes, ''Phelsuma'', for example have these pores, others in the same family do not. In the desert iguana (''Dipsosaurus dorsalis''), the waxy lipids released from the femoral pores absorb ultravio ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imbricate
Aestivation or estivation is the positional arrangement of the parts of a flower within a flower bud before it has opened. Aestivation is also sometimes referred to as praefoliation or prefoliation, but these terms may also mean vernation: the arrangement of leaves within a vegetative bud. Aestivation can be an important taxonomic diagnostic; for example Malvaceae flower buds have valvate sepals, with the exception of the genera ''Fremontodendron'' and ''Chiranthodendron'', which have sometimes been misplaced as a result. Terminology The terms used to describe aestivation are the same as those used to describe leaf vernation. Classes of aestivation include: * ''crumpled'' * ''decussate Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. . Similarly, the anatomical term chiasma is named aft ...'' * ''imbricate'' – overlapping ** ''con ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Supraocular
In scaled reptiles, supraocular scales are (enlarged) scales on the crown immediately above the eye.Mallow D, Ludwig D, Nilson G. 2003. True Vipers: Natural History and Toxinology of Old World Vipers. Malabar, Florida: Krieger Publishing Company. 359 pp. . The size and shape of these scales are among the many characteristics used to differentiate species from each another. In many species of boids and viperids, the supraoculars are heavily fragmented. In others, such as the colubrids and elapids, they are enlarged. See also * Ocular scales * Snake scales * Anatomical terms of location Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position pro ... References {{Reflist Snake scales ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temporal Scale
{{disambiguation ...
Temporal may refer to: Entertainment * Temporal (band), an Australian metal band * ''Temporal'' (Radio Tarifa album), 1997 * ''Temporal'' (Love Spirals Downwards album), 2000 * ''Temporal'' (Isis album), 2012 * ''Temporal'' (video game), a 2008 freeware platform and puzzle game * ''Temporal'' (film), a 2022 Sri Lankan short film Philosophy * Temporality * Temporal actual entity, see Other * An alternative for lateral, in the head; towards the temporal bone * Temporality (ecclesiastical), or temporal goods, secular possessions of the Church See also * * Ephemeral * Impermanence * Temporal region (other) Temporal region may refer to: * Temporal lobe, one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals * Temple (anatomy) The temple is a latch where four skull bones fuse: the frontal, parietal, temporal, and sphenoid. It ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |