|
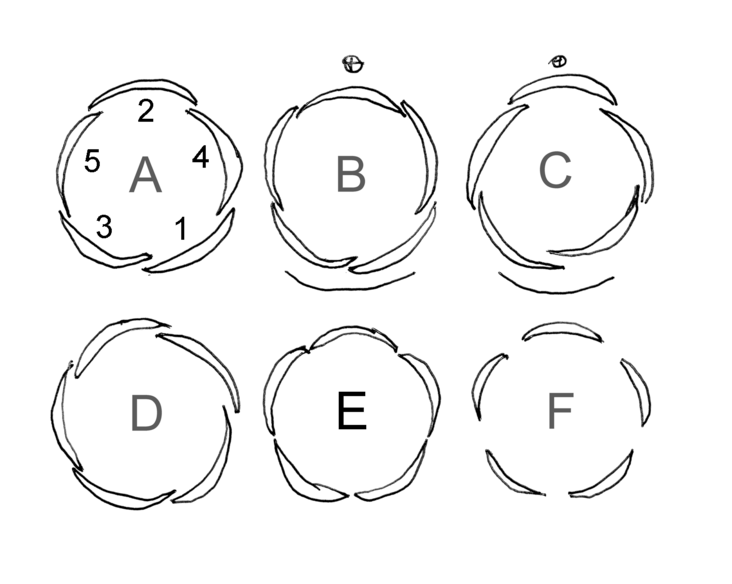
Imbricate
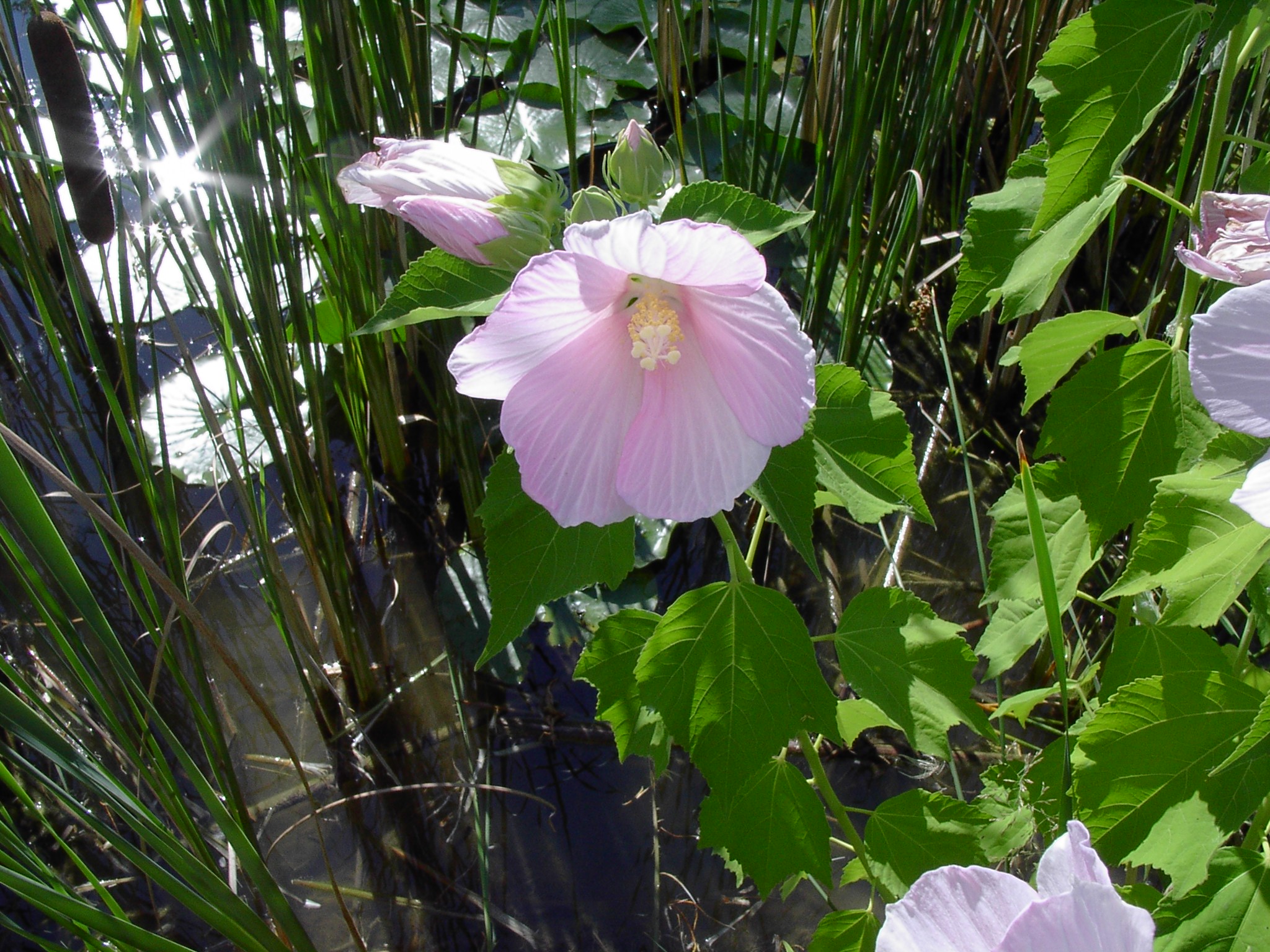
Aestivation or estivation is the positional arrangement of the parts of a flower within a flower bud before it has opened. Aestivation is also sometimes referred to as praefoliation or prefoliation, but these terms may also mean vernation: the arrangement of leaves within a vegetative bud. Aestivation can be an important taxonomic diagnostic; for example Malvaceae flower buds have valvate sepals, with the exception of the genera '' Fremontodendron'' and '' Chiranthodendron'', which have sometimes been misplaced as a result. Terminology The terms used to describe aestivation are the same as those used to describe leaf vernation. Classes of aestivation include: * ''crumpled'' * ''decussate Decussation is used in biological contexts to describe a crossing (due to the shape of the Roman numeral for ten, an uppercase 'X' (), ). In Latin anatomical terms, the form is used, e.g. . Similarly, the anatomical term chiasma is named aft ...'' * ''imbricate'' – overlapping ** ''c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glossary Of Botanical Terms
This glossary of botanical terms is a list of definitions of terms and concepts relevant to botany and plants in general. Terms of plant morphology are included here as well as at the more specific Glossary of plant morphology and Glossary of leaf morphology. For other related terms, see Glossary of phytopathology, Glossary of lichen terms, and List of Latin and Greek words commonly used in systematic names. A B ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Malvaceae
Malvaceae (), or the mallows, is a family of flowering plants estimated to contain 244 genera with 4225 known species. Well-known members of economic importance include Theobroma cacao, cacao, Cola (plant), cola, cotton, okra, Hibiscus sabdariffa, roselle and durian. There are also some genera containing familiar ornamentals, such as ''Alcea'' (hollyhock), ''Malva'' (mallow), and ''Tilia'' (lime or linden tree). The genera with the largest numbers of species include ''Hibiscus'' (434 species), ''Pavonia (plant), Pavonia'' (291 species), ''Sida (plant), Sida'' (275 species), ''Ayenia'' (216 species), ''Dombeya'' (197 species), and ''Sterculia'' (181 species). Taxonomy and nomenclature The circumscription of the Malvaceae is controversial. The traditional Malvaceae ''sensu stricto'' comprise a very homogeneous and cladistically Monophyly, monophyletic group. Another major circumscription, Malvaceae ''sensu lato'', has been more recently defined on the basis that genetics studies ha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aestivation
Aestivation ( (summer); also spelled estivation in American English) is a state of animal dormancy, similar to hibernation, although taking place in the summer rather than the winter. Aestivation is characterized by inactivity and a lowered metabolic rate, that is entered in response to high temperatures and arid conditions. It takes place during times of heat and dryness, which are often the summer months. Invertebrate and vertebrate animals are known to enter this state to avoid damage from high temperatures and the risk of desiccation. Both terrestrial and aquatic animals undergo aestivation. Fossil records suggest that aestivation may have evolved several hundred million years ago. Physiology Organisms that aestivate appear to be in a fairly "light" state of dormancy, as their physiological state can be rapidly reversed, and the organism can quickly return to a normal state. A study done on '' Otala lactea'', a snail native to parts of Europe and Northern Africa, shows t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
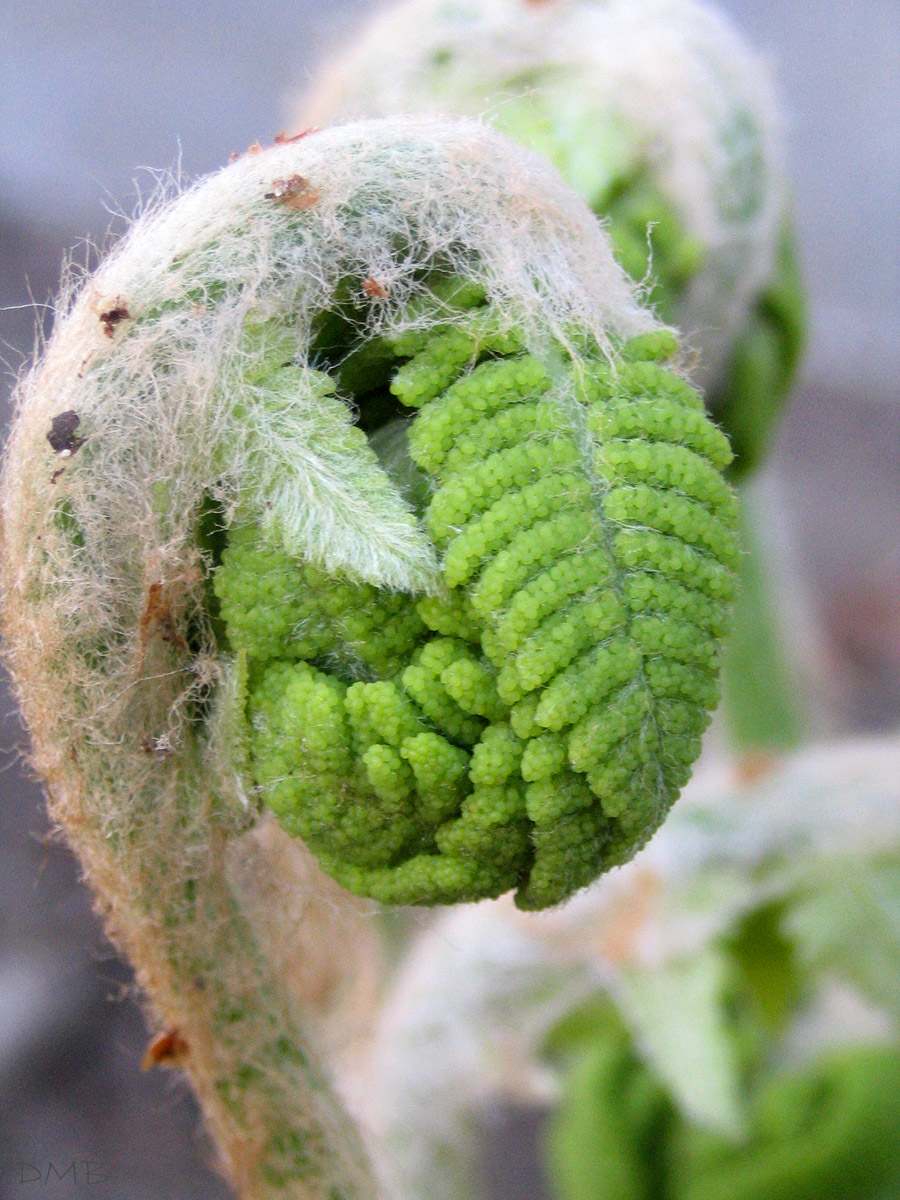
Vernation
Vernation or leafing is the formation of new leaves or fronds. In plant anatomy, it is the arrangement of leaves in a bud. In pine species, new leaves are short and encased in sheaths. Each leaf bundle consists of two to five needles. All the leaves on one section of branch grow in length together. In cabbage species, new leaves are folded over, each covered by the previous leaf. Name The term ''vernation'' is borrowed from New Latin , the act of being verdant or flourishing (). It is cognate with (Latin for " spring") and ("vernal"). Circinate vernation Circinate vernation is the manner in which most fern fronds emerge. As the fern frond is formed, it is tightly curled so that the tender growing tip of the frond (and each subdivision of the frond) is protected within a coil. At this stage it is called a crozier (after the shepherd's crook) or fiddlehead (after the scrollwork at the top of a violin). As the lower parts of the frond expand and toughen up, they begin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
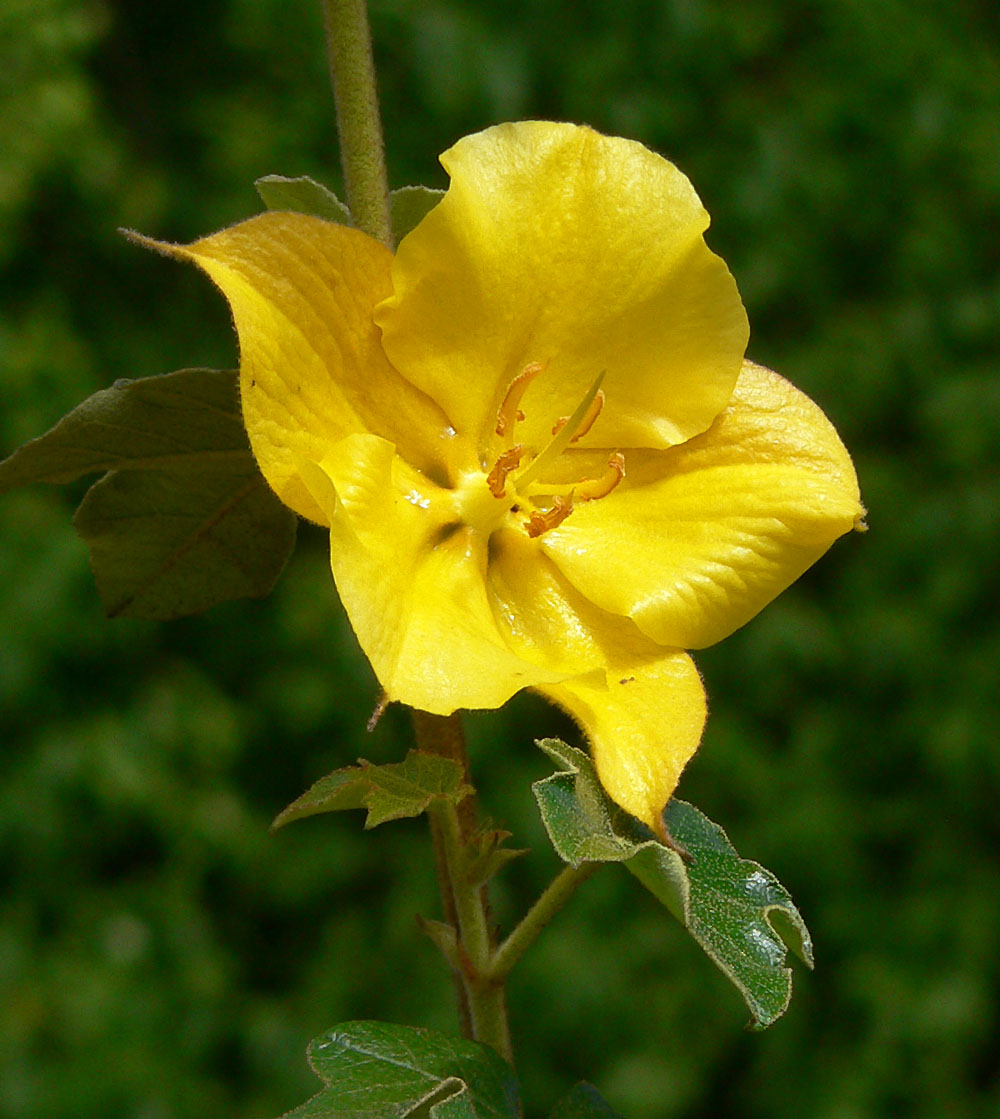
Fremontodendron
''Fremontodendron'', with the common names fremontia and flannelbush or flannel bush, is a genus of three known species of shrubs native plant, native to the Southwestern United States and northwest Mexico. Taxonomy They are within the botanical family (biology), family Malvaceae. Formerly they were treated within the Sterculiaceae, tribe Fremontodendreae, together with the genus ''Chiranthodendron''. The genus ''Fremontodendron'' was named in dedication to John C. Frémont, who first collected it during an 1846 expedition to Alta California. Description The leaf, leaves have a leathery and fuzzy texture reminiscent of flannel (hence the name), and the yellow to orange flowers are large and showy. The leaves and young shoots can cause skin and eye irritation. Species There are three species: * ''Fremontodendron californicum'' — Californian flannelbush * ''Fremontodendron decumbens'' (R. Lloyd) — Pine Hill flannelbush :: A decumbent and low spreading form, in height and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chiranthodendron
''Chiranthodendron'' is a flowering plant genus in the family Malvaceae. It comprises a single species of tree, ''Chiranthodendron pentadactylon''. Names The tree is called the devil's, monkey's or Mexican hand tree or the hand-flower in English, the árbol de las manitas (''tree of little hands'') in Spanish, Canak in Mayan and mācpalxōchitlEmory Dean Keoke, Kay Marie Porterfield, ''Encyclopedia of American Indian Contributions to the World'' (2002), page 118: "For lower abdominal pain, the patient would be prescribed ''macpalxochitl'' (''Chiranthodendron'')" (''palm flower'') in Nahuatl, all on account of its distinctive red flowers, which resemble open human hands. The scientific name means "five-fingered hand-flower tree". Description This species is native to Guatemala and southern Mexico. On the wet slopes of these areas, trees may reach in height. The unusual appearance of the 'hands' has stimulated cultivation in gardens around the world, primarily in North America whe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syringa Vulgaris
''Syringa vulgaris'', the lilac or common lilac, is a species of flowering plant in the olive family, Oleaceae. Native to the Balkan Peninsula, it is widely cultivated for its scented flowers in Europe (particularly the north and west) and North America. Description ''Syringa vulgaris'' is a large deciduous shrub or multi-stemmed small tree, growing to high. It produces secondary shoots from the base or roots, with stem diameters up to , which in the course of decades may produce a small clonal thicket. The bark is grey to grey-brown, smooth on young stems, longitudinally furrowed, and flaking on older stems. The leaves are simple, and 3–8 cm broad, light green to glaucous, oval to cordate, with pinnate leaf venation, a mucronate apex, and an entire margin. They are arranged in opposite pairs or occasionally in whorls of three. The flowers have a tubular base to the corolla 6–10 mm long with an open four-lobed apex 5–8 mm across, usually lilac to mauv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phlox Paniculata
''Phlox paniculata'' is a species of flowering plant in the Polemoniaceae, phlox family (Polemoniaceae). It is native plant, native to parts of the eastern and central United States. It is extensively cultivated in temperate climate, temperate regions as an ornamental plant and has become established in the wild in scattered locales in other regions. Common names include fall phlox, garden phlox, perennial phlox, summer phlox, and panicled phlox. Description ''Phlox paniculata'' is an erect herbaceous plant, herbaceous perennial plant, perennial growing to tall by wide, with Leaf shape, opposite, simple leaf, leaves on slender green stems. The flowers are in diameter, often strongly fragrant and borne in summer through fall (autumn). The flowers are grouped in panicles (with many branching stems), hence the Botanical name#Binary name, specific epithet ''paniculata''. Typical flower colors in wild populations are pink or purple (rarely white). Distribution and habitat Fall p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vinca Minor
''Vinca minor'' (common names lesser periwinkle or dwarf periwinkle) is a species of flowering plant in the dogbane family, native to central and southern Europe. Other vernacular names used in cultivation include small periwinkle, common periwinkle, and sometimes in the United States, myrtle or creeping myrtle. Description ''Vinca minor'' is a trailing subshrub, spreading along the ground and rooting along the stems to form large clonal colonies and occasionally scrambling up to high but never twining or climbing. The leaves are evergreen, opposite, long and broad, glossy dark green with a leathery texture and an entire margin. The flowers are solitary in the leaf axils and are produced mainly from early spring to mid summer but with a few flowers still produced into the autumn; they are violet-purple (pale purple or white in some cultivated selections), diameter, with a five-lobed corolla. The fruit is a pair of follicles long, containing numerous seeds. Chemistry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ipomoea
''Ipomoea'' () is the largest genus in the plant family Convolvulaceae, with over 600 species. It is a large and diverse group, with common names including morning glory, Ipomoea aquatica, water convolvulus or water spinach, sweet potato, bindweed, Ipomoea alba, moonflower, etc. The genus occurs throughout the tropical and subtropical regions of the world, and comprises annual plant, annual and perennial plant, perennial herbaceous plants, lianas, shrubs, and small trees; most of the species are twining Vine, climbing plants. Their most widespread common name is morning glory, but some species in related genera bear that same common name and some ''Ipomoea'' species are known by different common names. Those formerly separated in ''Calonyction'' (Ancient Greek, Greek "good" and , , , "night") are called moonflowers. The name ''Ipomoea'' is derived from the Ancient Greek , meaning , and (), meaning "resembling". It refers to their twining habit. Uses and ecology Human ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Merremia Tuberosa
''Distimake tuberosus'', also known as Spanish arborvine or wood rose, is a vine in the family Convolvulaceae. It is native to the Americas, from Florida and Texas to Brazil, although considered by the USDA as introduced to the United States. It is an invasive species in a number of islands in the Indian and Pacific Ocean, such as New Caledonia New Caledonia ( ; ) is a group of islands in the southwest Pacific Ocean, southwest of Vanuatu and east of Australia. Located from Metropolitan France, it forms a Overseas France#Sui generis collectivity, ''sui generis'' collectivity of t .... References External links * Flora of Mexico Flora of Peru Convolvulaceae {{Solanales-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flowers
Flowers, also known as blooms and blossoms, are the reproductive structures of flowering plants ( angiosperms). Typically, they are structured in four circular levels, called whorls, around the end of a stalk. These whorls include: calyx, modified leaves; corolla, the petals; androecium, the male reproductive unit consisting of stamens and pollen; and gynoecium, the female part, containing style and stigma, which receives the pollen at the tip of the style, and ovary, which contains the ovules. When flowers are arranged in groups, they are known collectively as inflorescences. Floral growth originates at stem tips and is controlled by MADS-box genes. In most plant species flowers are heterosporous, and so can produce sex cells of both sexes. Pollination mediates the transport of pollen to the ovules in the ovaries, to facilitate sexual reproduction. It can occur between different plants, as in cross-pollination, or between flowers on the same plant or even the same flowe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |