|
Pawura
Pawura, and also: Pauru, Piwure, Puuru/Puwuru was an Egyptian official of the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. As mentioned in letter no. 171, he was also an Egyptian "archer–commander". In letter no. 289 he is called an ''"irpi''–official". In Egyptian his name means 'the Great One', (''Pa-wr''/''Pa-ur'')(letter EA 287:45-"1.-Pa-Ú-Ru") Pawura's name is referenced in the following letters: ( EA for 'el Amarna') :#Rib-Haddi–The Rib-Hadda sub-corpus of 68 letters: EA 117, 124, 129, 131, 132, and EA 362. :#Aziru–EA 171, by Aziru of Ammuru, Title: ''"Eager to Serve"''. :#EA 263–EA 263, a short letter. Title: ''"Robbed of Everything."'' (author unknown) :#Abdi-Heba– EA 287 and EA 289, letters by Abdi-Heba to pharaoh.(see EA 287 herePhoto, EA 287: Reverse Pawura's death is mentioned in the Rib-Hadda letters except EA 117, and 124, along with the demise of others, or the warring with the Habiru, or the leaders of Ammuru: (Abdi-As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 289
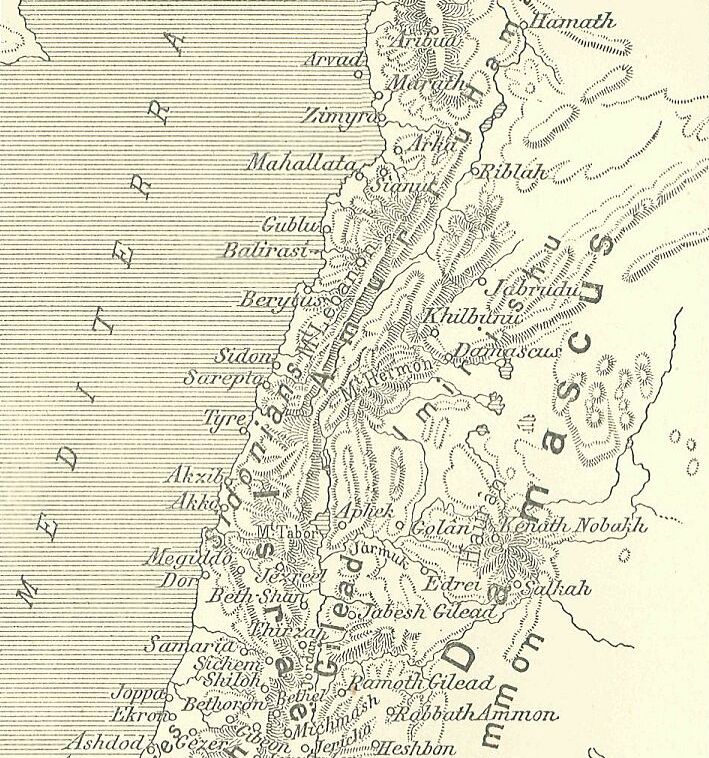
Amarna letter EA 289, titled: ''"A Reckoning Demanded,"'' Moran, William L. 1987, 1992. ''The Amarna Letters.'' EA 289, ''A Reckoning Demanded'', p. 332-333. is a moderately tall, finely-inscribed clay tablet letter, approximately 6.5 in tall, from Abdi-Heba the mayor/ruler of Jerusalem, of the mid 14th century BC Amarna letters. The scribe of his six letters to Egypt were penned by the "Jerusalem scribe"; EA 289 is a moderately long, and involved letter, mentioning ten named individuals, some more that three times. A total of nine locations are referenced, as well as men of the "Hapiru"-("LÚ- MEŠ-Hapiru- ki"),EA 289: Reverse, line 24. , CDLI no. 271091 (''Chicago Digital Library Initiative'') and men of "Qilyi- [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 287
Amarna letter EA 287, titled: ''"A Very Serious Crime,"'' is a tall, finely-inscribed clay tablet letter, approximately 8 in tall, from Abdi-Heba the mayor/ruler of Jerusalem, of the mid 14th century BC Amarna letters. The scribe of his six letters to Egypt were penned by the " Jerusalem scribe"; EA 287 is a moderately long, and involved letter. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1350 BC and 20–25 years later, correspondence. The initial corpus of letters were found at Akhenaten's city Akhetaten, in the floor of the Bureau of Correspondence of Pharaoh; others were later found, adding to the body of letters. Letter EA 287 (see here-(Reverse), is numbered VAT 1644, from the Vorderasiatisches Museum Berlin. Glossenkeils Glossenkeils used in letter 387: The letter EA 287: ''"A Very Serious Crime"'' EA 287, letter three of six. (Not a linear, line-by-line translation, and English from French.) (Obverse & Reverse): :Obverse: ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Amarna Letter EA 362
Amarna letter EA 362, titled: ''"A Commissioner Murdered,"'' is a finely-inscribed clay tablet letter from Rib-Haddi, the mayor/'man' of the city of Byblos, (''Gubla'' of the letters). Byblos, being a large coastal seaport Mediterranean city, was a city that was aligned with Egypt (''Miṣri''), and housed an Egyptian community. Rib-Haddi, as the city-state leader wrote the largest number of letters to the Pharaoh, in a sub-corpus of the 1350 BC Amarna letters (about 70 letters). Near the end of his rule, Rib-Haddi penned two large diplomatic letters summarizing conditions of his hostilities with peoples like the Hapiru, but also other city-state rulers, vying for regional ascendency. Letter EA 362 relates the hostilities, but also talks of disease, upon his land. The letter ends addressing the fate of Egypt's commissioner Pawura. The Amarna letters, about 300, numbered up to EA 382, are a mid 14th century BC, about 1350 BC and 20–25 years later, correspondence. The ini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yanhamu
Yanhamu, also Yenhamu, and Enhamu, was an Egyptian commissioner of the 1350- 1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Yanhamu is referenced in 16 of the 60–letter ''"Rib-Hadda of Gubla"''-(Byblos) sub-corpus, and also 12 additional letters. Letters referencing commissioner ''Yanhamu'' Milkilu's EA 270, ''"Extortion"'' Letter no. 4 of 5 to Pharaoh, from "Milkilu of Gazru"-(modern Gezer): Milkilu's EA 271, ''"The Power of the 'Apiru"'' Milkilu letter no. 5 of 5 to Pharaoh: Referenced Amarna letters to ''Yanhamu'' The largest sub-corpus of Amarna letters is from the Rib-Haddi corpus: namely "Rib-Hadda of Gubla"-(Byblos). 16 of Rib-Haddi's letters reference Yanhamu, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). ''Letters EA 82-132(16)the Rib-Hadda/Byblos letters-(w/out-EA 98)'' *EA 82— *EA 85— * EA 86— *EA 98— *EA 102— *EA 105— *EA 106— *EA 109— *EA 116— *EA 117— *EA 118— *EA 127— *EA 131— *EA 132—See: Pahura O ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rubutu
Rubutu was a city, or city-state located in ancient northern Israel, between the city of ''Gazru''-(modern Gezer), and Jerusalem during the time of the Amarna letters Text corpus, correspondence, a 15-20 year Time period, period at about 1350 BC, 1350-1335 BC. Some scholars place Rubutu near present-day Arraba, Jenin, Arrabah in the northern West Bank.Zertal, Adam; ''Arubboth, Hepher, and the Third Solomonic District'', 1984: 72-76, 112-114, 133-136Na'aman, Nadav;'' Canaan in the second millennium B.C.E.'', 2005: 212. The Amarna letters were mostly written to the pharaoh of Ancient Egypt, and three mayors of Gazru: Abimilku, Milkilu, and Yapahu authored 20 letters of the 382–letter, Amarna letters Text corpus, corpus. The reference to Rubutu is found in 2 letters of Abdi-Heba of Jerusalem, EA 289, and 290, (EA (el Amarna), EA for 'el Amarna'). They mention the war of various cities, the Habiru, and of: ''"the seizure of Rubutu"''. The 2 letters of city--''Rubutu'' EA 289, tit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prostration Formula
In the 1350 BC correspondence of 382–letters, called the Amarna letters, the prostration formula is usually the opening subservient remarks to the addressee, the Egyptian pharaoh. The formula is based on prostration, namely reverence and submissiveness. Often the letters are from vassal rulers or vassal city-states, especially in Canaan but also in other localities. The formula is often repetitive, or multi-part, with parts seeming to repeat and can go forward in a typical standard format. However, the prostration formula may also be duplicated in a similar format at the end of a letter, or a foreshortened part of the formula may be entered, for effect, in the middle of a letter. Some example letters with the ''Prostration formula'' The letters EA 242 and 246 are from Biridiya of Magidda-(Megiddo), (EA for 'el Amarna'). Biridiya letter 242, no. 1 of 7: title: ''"Request granted"'' :Say to the king-(i.e. pharaoh), my lord and my Sun: Message-(' um– ma') of Biridiya, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Courier
A courier is a person or organisation that delivers a message, package or letter from one place or person to another place or person. Typically, a courier provides their courier service on a commercial contract basis; however, some couriers are government or state agency employees (for example: a diplomatic courier). Duties and functions Couriers are distinguished from ordinary mail services by features such as speed, security, tracking, signature, specialization and individualization of express services, and swift delivery times, which are optional for most everyday mail services. As a premium service, couriers are usually more expensive than standard mail services, and their use is normally limited to packages where one or more of these features are considered important enough to warrant the cost. Courier services operate on all scales, from within specific towns or cities, to regional, national and global services. Large courier companies include DHL, DTDC, FedEx, EMS Inte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lacuna (manuscripts)
A lacuna ( lacunae or lacunas) is a gap in a manuscript, inscription, text, painting, or musical work. A manuscript, text, or section suffering from gaps is said to be "lacunose" or "lacunulose". Weathering, decay, and other damage to old manuscripts or inscriptions are often responsible for lacunae - words, sentences, or whole passages that are missing or illegible. Palimpsests are particularly vulnerable. To reconstruct the original text, the context must be considered. In papyrology and textual criticism, this may lead to competing reconstructions and interpretations. Published texts that contain lacunae often mark the section where text is missing with a bracketed ellipsis. For example, "This sentence contains 20 words, and ..nouns," or, "Finally, the army arrived at ..and made camp." Notable examples See also * Unfinished work Unfinished may refer to: *Unfinished creative work, a work which a creator either chose not to finish or was prevented from finishing. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milkilu
Milkilu, and more properly Milk-ilu, or Milku-ilu, with an alternate version of Ili-Milku (letter 286, by Abdi-Heba of Jerusalem), was the mayor/ruler of ''Gazru'' (Gezer) of the 1350–1335 BC Amarna letters correspondence. Adda-danu, and Yapahu were also mayors of ''Gazru''. Milk-ilu is the author of 5 Amarna letters to the pharaoh of Egypt, EA 267–271, ( EA for 'el Amarna'). One letter ( EA 369) from the pharaoh to Milk-ilu is known. EA 369, to Milkilu: "From the Pharaoh to a vassal" :"To ''Milkilu'', the ruler of Gazru: Thus the king. He herewith dispatches to you this tablet (i.e., tablet-letter), saying to you, He herewith sends to you Hanya, the stable (overseer) of the archers, along with everything for the acquisition of beautiful female cupbearers: silver, gold, linen garments: ''ma-al-ba-ši'', carnelian, all sorts of (precious) stones, an ebony chair; all alike, fine things. Total (value): 160 ''diban''. Total: 40 female cupbearers, 40 (shekels of) silver being the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tablet Official Letter-AO 7093-P5280232-gradient
Tablet may refer to: Medicine * Tablet (pharmacy), a mixture of pharmacological substances pressed into a small cake or bar, colloquially called a "pill" Computing * Tablet computer, a mobile computer that is primarily operated by touching the screen * Graphics tablet or digitizing tablet, a computer input device for capturing hand-drawn images and graphics * Tablet, a section of columns in a range of rows in Google's Bigtable NoSQL database Confectionery * Tablet (confectionery), a medium-hard, sugary confection from Scotland * Tableting, a confectionery manufacturing process * A type of chocolate bar Inscription, printing, and writing media * Clay tablet, one of the earliest known writing mediums * Wax tablet, used by scribes as far back as ancient Greece * Notebook of blank or lined paper, usually bound with glue or staples along one edge * Stele, slab of stone or wood erected as a monument or marker * ''Tabula ansata'', tablets with handles * Vindolanda tablets, Roman era w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labaya
Labaya (also transliterated as Labayu or Lib'ayu) was a 14th-century BCE ruler or warlord in the central hill country of southern Canaan. He lived contemporaneously with Pharaoh Akhenaten. Labaya is mentioned in several of the Amarna Letters (abbreviated "EA", for 'el Amarna'). He is the author of letters EA 252– 54. Labaya was active over the whole length of Samaria and slightly beyond, as he gave land to Habiru in the vicinity of Šakmu (Shechem) and he and his sons threatened such powerful towns as Jerusalem and Gazru (Gezer) to the south, and Megiddo to the north. Career The Amarna letters give an incomplete look at Labaya's career. In the first of Labaya's letters thus far discovered (EA 252), he defends himself to the Pharaoh against complaints of other city rulers about him, for example, the complaint that he has hired mercenaries from among the Habiru. Labaya further admitted to having invaded Gezer and insulting its king Milkilu. He denied any knowledge of his s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William L
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of England in 1066,All Things William"Meaning & Origin of the Name"/ref> and remained so throughout the Middle Ages and into the modern era. It is sometimes abbreviated "Wm." Shortened familiar versions in English include Will, Wills, Willy, Willie, Bill, and Billy. A common Irish form is Liam. Scottish diminutives include Wull, Willie or Wullie (as in Oor Wullie or the play ''Douglas''). Female forms are Willa, Willemina, Wilma and Wilhelmina. Etymology William is related to the given name ''Wilhelm'' (cf. Proto-Germanic ᚹᛁᛚᛃᚨᚺᛖᛚᛗᚨᛉ, ''*Wiljahelmaz'' > German ''Wilhelm'' and Old Norse ᚢᛁᛚᛋᛅᚼᛅᛚᛘᛅᛋ, ''Vilhjálmr''). By regular sound changes, the native, inherited English form of the name shoul ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |