|
Polabians
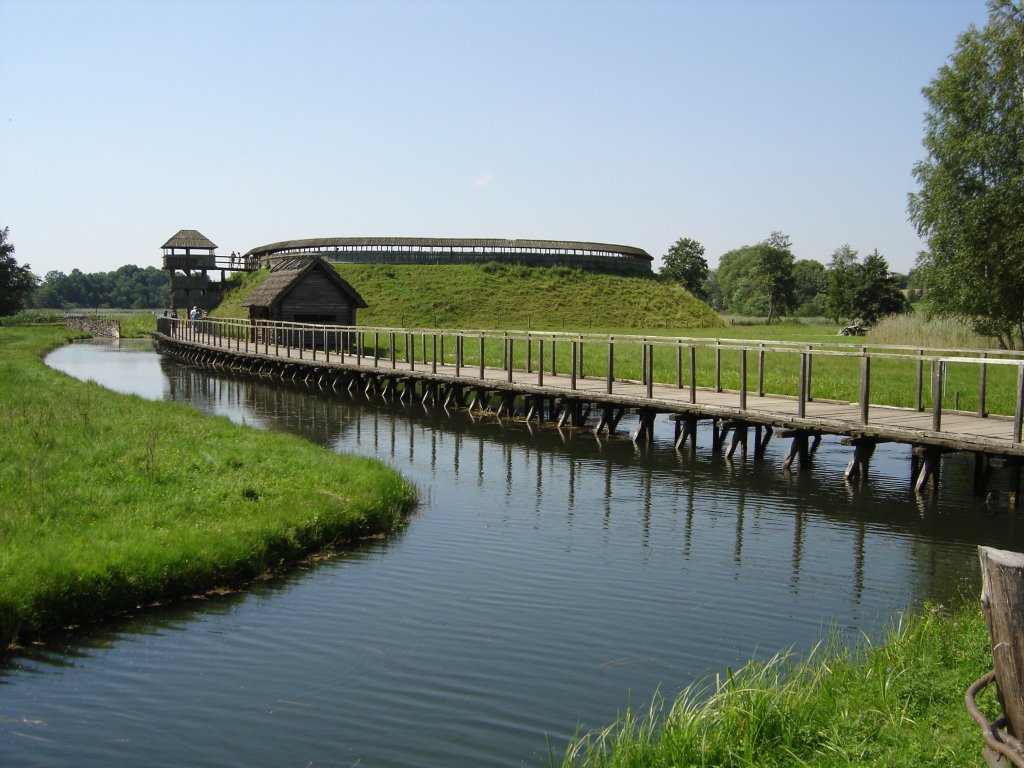
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germany. The approximate territory stretched from the Baltic Sea in the north, the Saale and the '' Limes Saxoniae''Christiansen, 18 in the west, the Ore Mountains and the Western Sudetes in the south, and Poland in the east. They have also been known as Elbe Slavs (german: Elbslawen) or Wends. Their name derives from the Slavic ''po'', meaning "by/next to/along", and the Slavic name for the ''Elbe'' (''Labe'' in Czech and ''Łaba'' in Polish). The Polabian Slavs started settling in the territory of modern Germany in the 6th century. They were largely conquered by Saxons and Danes since the 9th century and were subsequently included and gradually assimilated within the Holy Roman Empire. The tribes were gradually Germanized and assimilated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lechites
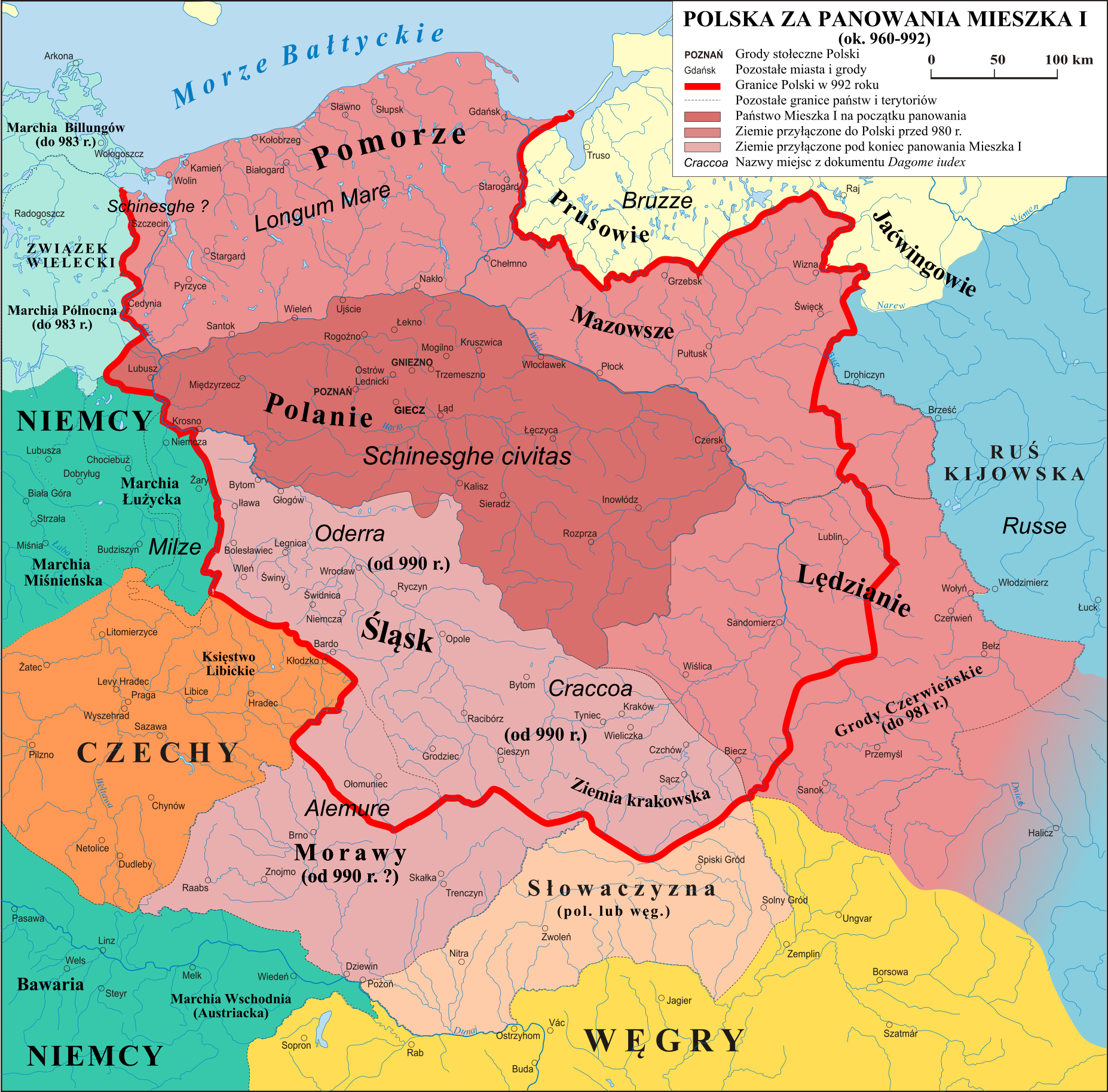
Lechites (, german: Lechiten), also known as the Lechitic tribes (, german: Lechitische Stämme), is a name given to certain West Slavs, West Slavic tribes who inhabited modern-day Poland and eastern Germany, and were speakers of the Lechitic languages. Distinct from the Czech–Slovak languages, Czech–Slovak subgroup, they are the closest ancestors of ethnic Poles and the Pomeranians (Slavic tribe), Pomeranians, Lusatians and Polabians. History According to Polish legend, Mieszko I inherited the ducal throne from his father who probably ruled over two-thirds of the territory inhabited by eastern Lechite tribes. He united the Lechites east of the Oder (Polans (western), Polans, Masovians, Pomeranians (Slavic tribe), Pomeranians, Vistulans, Silesians) into a single country of Poland. His son, Bolesław Chrobry, Bolesław I the Brave, founded the bishoprics at Wrocław, Kołobrzeg, and Kraków, and an archbishopric at Gniezno. Bolesław carried out successful wars against Bohemi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic languages diversified into their historically attested forms over the 10th to 14th centuries. Today, groups which speak West Slavic languages include the Poles, Czechs, Slovaks, and Sorbs. From the twelfth century onwards, most West Slavs converted to Roman Catholicism, thus coming under the cultural influence of the Latin Church, adopting the Latin alphabet, and tending to be more closely integrated into cultural and intellectual developments in western Europe than the East Slavs, who converted to Eastern Orthodox Christianity and adopted the Cyrillic alphabet. Linguistically, the West Slavic group can be divided into three subgroups: Lechitic, including Polish, Kashubian, and the extinct Polabian and Pomeranian languages; Sorbian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany (see Polabian Slavs). For decades, they were allies of Charlemagne in his wars against the Germanic Saxons and the Slavic Veleti. The Obotrites under Prince Thrasco defeated the Saxons in the Battle of Bornhöved (798). The still heathen Saxons were dispersed by the emperor, and the part of their former land in Holstein north of Elbe was awarded to the Obotrites in 804, as a reward for their victory. This however was soon reverted through an invasion of the Danes. The Obotrite regnal style was abolished in 1167, when Pribislav was restored to power by Duke Henry the Lion, as Prince of Mecklenburg, thereby founding the German House of Mecklenburg. Obotritic confederation The Bavarian Geographer, an anonymous medieval document compiled in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polabian Language
The Polabian language was a West Slavic language that was spoken by the Polabian Slavs (german: Wenden) in present-day northeastern Germany around the Elbe (''Łaba/Laba/Labe'' in Slavic) river, from which derives its name ("po Labe" – ''unto Elbe'' or ''ravelingon Elbe''). It was spoken approximately until the rise to power of Prussia in the mid-18th century – when it was superseded by Low German – in the areas of Pomoré (Mecklenburg-West Pomerania), central ( Mittelmark) part of Branibor (Brandenburg) and eastern Saxony-Anhalt (Wittenberg originally part of Béla Serbia), as well as in eastern parts of Wendland (Lower Saxony) and Dravänia (Schleswig-Holstein), Ostholstein and Lauenburg). Polabian was also relatively long (until the 16th century) spoken in and around the cities of Bukovéc (Lübeck), Starigard (Oldenburg) and Trava (Hamburg). The very poorly attested Slavic dialects of Rügen seemed to have had more in common with Polabian than with Pomeranian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in Slovenia, Austria, Lusatia, Texas, and Australia. In German-speaking Europe This article details the geographical distribution of speakers of the German language, regardless of the legislative status within the countries where it is spoken. In addition to the German-speaking area (german: Deutscher Sprachraum) in Europ ... during the Middle Ages, the term "Wends" was interpreted as synonymous with "Slavs" and sporadically used in literature to refer to West Slavs and South Slavs living within the Holy Roman Empire. The name has possibly survived in Finnic languages ( , et, Vene , krl, Veneä), denoting moder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe, 919-1125
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object. Central may also refer to: Directions and generalised locations * Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known as Middle Africa * Central America, a region in the centre of America continent * Central Asia, a region in the centre of Eurasian continent * Central Australia, a region of the Australian continent * Central Belt, an area in the centre of Scotland * Central Europe, a region of the European continent * Central London, the centre of London * Central Region (other) * Central United States, a region of the United States of America Specific locations Countries * Central African Republic, a country in Africa States and provinces * Blue Nile (state) or Central, a state in Sudan * Central Department, Paraguay * Central Province (Kenya) * Central Province (Papua New Guinea) * Central Province (Solomon Islands) * Central Pro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Brandenburg. Sorbs traditionally speak the Sorbian languages (also known as "Wendish" and "Lusatian"), which are closely related to Czech language, Czech, Polish language, Polish, Kashubian language, Kashubian, Silesian language, Silesian, and Slovak language, Slovak. Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian are officially recognized minority languages in Germany. Due to a gradual and increasing Cultural assimilation, assimilation between the 17th and 20th centuries, virtually all Sorbs also spoke German by the early 20th century. In the newly created German Empire, German nation state of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, policies were implemented in an effort to Germanize the Sorbs. These policies reached their climax under the Nazi Germany, N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sorbian Languages
The Sorbian languages ( hsb, serbska rěč, dsb, serbska rěc) are the Upper Sorbian language and Lower Sorbian language, two closely related and partially mutually intelligible languages spoken by the Sorbs, a West Slavic ethno-cultural minority in the Lusatia region of Eastern Germany. They are classified under the West Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages and are therefore closely related to the other two West Slavic subgroups: Lechitic and Czech–Slovak.About Sorbian Language by Helmut Faska, University of Leipzig Historically, the languages have also been known as Wendish (named after the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the area's history. The concept of "Central Europe" appeared in the 19th century. Central Europe comprised most of the territories of the Holy Roman Empire and those of the two neighboring kingdoms of Poland and Hungary. Hungary and parts of Poland were later part of the Habsburg monarchy, which also significantly shaped the history of Central Europe. Unlike their Western European (Portugal, Spain et al.) and Eastern European (Russia) counterparts, the Central European nations never had any notable colonies (either overseas or adjacent) due to their inland location and other factors. It has often been argued that one of the contributing causes of both World War I and World War II was Germany's lack of original overseas colonies. After ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
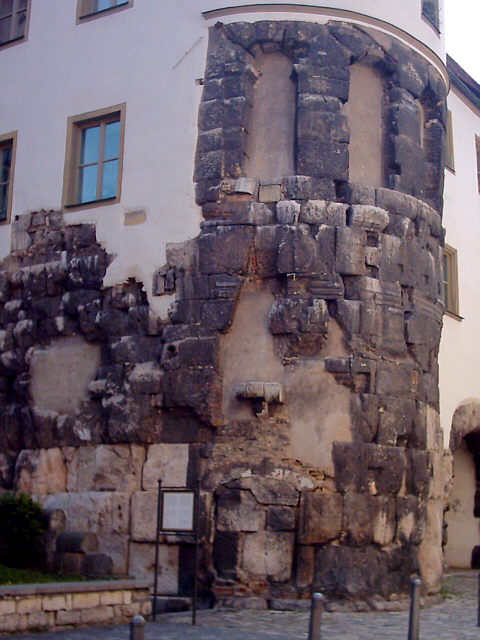
Bavarian Geographer
The epithet "Bavarian Geographer" ( la, Geographus Bavarus) is the conventional name for the anonymous author of a short Latin medieval text containing a list of the tribes in Central- Eastern Europe, headed (). The name "Bavarian Geographer" was first bestowed (in its French form, "") in 1796 by Polish count and scholar Jan Potocki. The term is now also used at times to refer to the document itself. It was the first Latin source to claim that all Slavs have originated from the same homeland, called the Zeriuani. Origin and content The short document, written in Latin, was discovered in 1772 in the Bavarian State Library, Munich by Louis XV's ambassador to the Saxon court, Comte Louis-Gabriel Du Buat-Nançay. It had been acquired by the Wittelsbachs with the collection of the antiquarian Hermann Schädel (1410–85) in 1571. The document was much discussed in the early 19th-century historiography, notably by Nikolai Karamzin and Joachim Lelewel. The provenance of the do ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regensburg
Regensburg or is a city in eastern Bavaria, at the confluence of the Danube, Naab and Regen rivers. It is capital of the Upper Palatinate subregion of the state in the south of Germany. With more than 150,000 inhabitants, Regensburg is the fourth-largest city in the State of Bavaria after Munich, Nuremberg and Augsburg. From its foundation as an imperial Roman river fort, the city has been the political, economic and cultural centre of the surrounding region; it is still known in the Romance languages by a cognate of its Latin name of "Ratisbona" (the version "Ratisbon" was long current in English). Later, under the rule of the Holy Roman Empire, it housed the Perpetual Diet of Regensburg. The medieval centre of the city was made a UNESCO World Heritage Site in 2006 because of its well-preserved architecture and the city's historical importance for assemblies during the Holy Roman Empire. In 2014, Regensburg was among the top sights and travel attractions in German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |