Wends on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in
 According to one theory,
According to one theory,

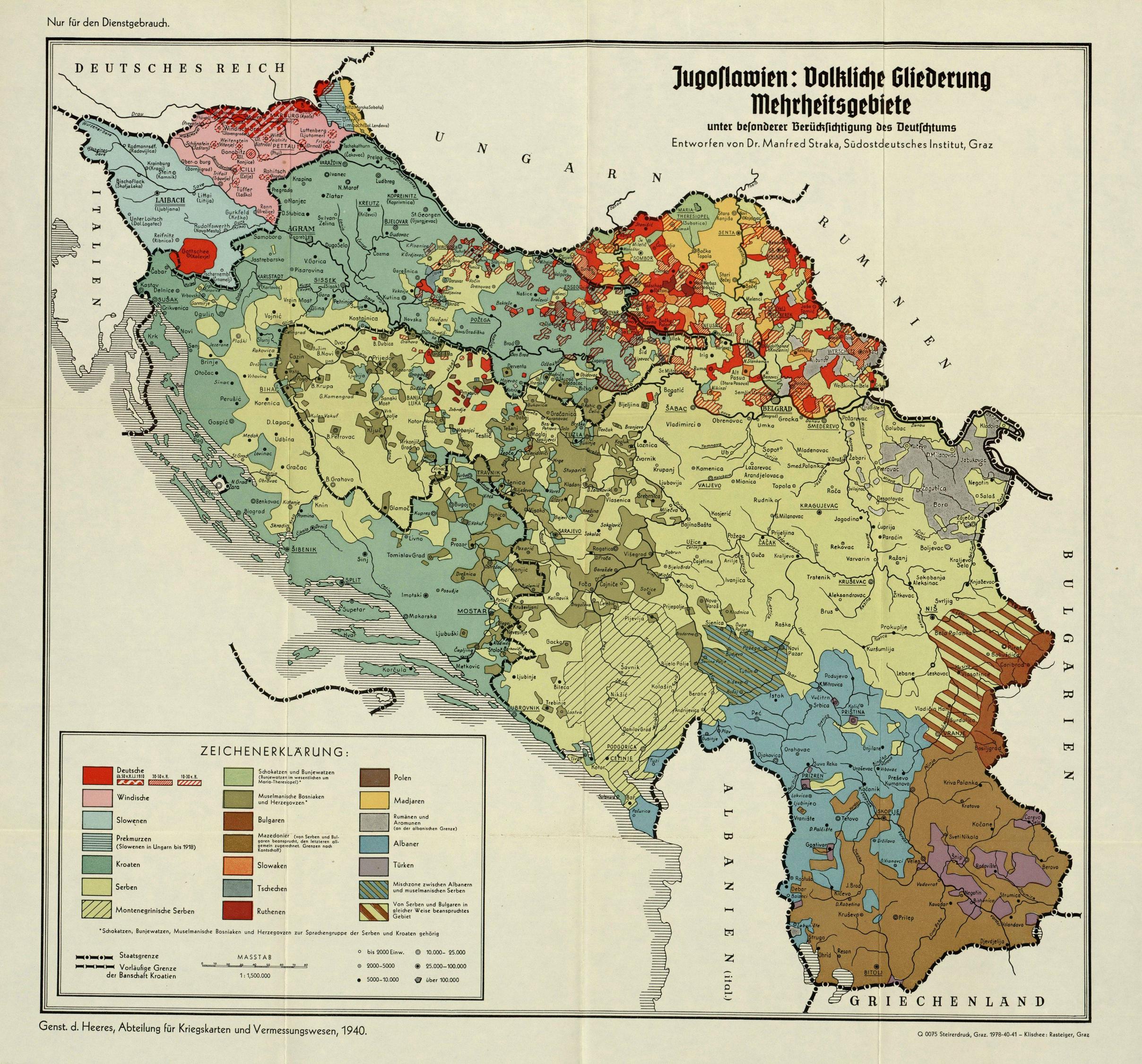 Historically, the term "Wends" has also occurred in the following contexts:
* Until the mid-19th-century German-speakers most commonly used the name ''Wenden'' to refer to Slovenes. This usage is mirrored in the name of the
Historically, the term "Wends" has also occurred in the following contexts:
* Until the mid-19th-century German-speakers most commonly used the name ''Wenden'' to refer to Slovenes. This usage is mirrored in the name of the
Sorbian Cultural InformationAustralian WendsTexas Wendish Heritage SocietyWendish Research Exchange
{{Authority control Early Slavs Historical ethnic groups of Europe Lechites Sorbs Wendland West Slavic history
 Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various peoples, tribes or groups depending on where and when it was used. In the modern day, communities identifying as Wendish exist in Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
, Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
, Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
, Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish language, Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central United States, South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2 ...
, and Australia
Australia, officially the Commonwealth of Australia, is a Sovereign state, sovereign country comprising the mainland of the Australia (continent), Australian continent, the island of Tasmania, and numerous List of islands of Australia, sma ...
.
In German-speaking Europe
This article details the geographical distribution of speakers of the German language, regardless of the legislative status within the countries where it is spoken. In addition to the German-speaking area (german: Deutscher Sprachraum) in Europe, ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
, the term "Wends" was interpreted as synonymous with "Slavs" and sporadically used in literature to refer to West Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic lan ...
and South Slavs
South Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak South Slavic languages and inhabit a contiguous region of Southeast Europe comprising the eastern Alps and the Balkan Peninsula. Geographically separated from the West Slavs and East Slavs by Austria, Hu ...
living within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
. The name has possibly survived in Finnic languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 mi ...
( , et, Vene , krl, Veneä), denoting modern Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and North Asia, Northern Asia. It is the List of countries and dependencies by area, largest country in the ...
.
People termed "Wends" in the course of history
 According to one theory,
According to one theory, Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
first applied this name to the ancient Veneti, and then after the Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
they transferred it to their new neighbours, the early Slavs
The early Slavs were a diverse group of tribal societies who lived during the Migration Period and the Early Middle Ages (approximately the 5th to the 10th centuries AD) in Central and Eastern Europe and established the foundations for the S ...
.
For the medieval Scandinavians, the term Wends (''Vender'') meant Slavs living near the southern shore of the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
(''Vendland''), and the term was therefore used to refer to Polabian Slavs
Polabian Slavs ( dsb, Połobske słowjany, pl, Słowianie połabscy, cz, Polabští slované) is a collective term applied to a number of Lechitic ( West Slavic) tribes who lived scattered along the Elbe river in what is today eastern Germ ...
like the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
, Rugian Slavs, Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
/Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
, and Pomeranian tribes.
For people living in the medieval Northern Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
and its precursors, especially for the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, a Wend (''Wende'') was a Slav living in the area west of the River Oder, an area later entitled ''Germania Slavica
''Germania Slavica'' is a historiographic term used since the 1950s to denote the landscape of the medieval language border (roughly east of the Elbe-Saale line) zone between Germans and Slavs in Central Europe on the one hand and a 20th-century ...
'', settled by the Polabian Slav tribes (mentioned above) in the north and by others, such as the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
and the Milceni
The Milceni or Milzeni ( cs, Milčané; german: Milzener; pl, Milczanie) were a West Slavic tribe, who settled in the present-day Upper Lusatia region. They were first mentioned in the middle of the 9th century AD by the Bavarian Geographer, who ...
, further south (see Sorbian March).
The Germans in the south used the term ''Winde'' instead of ''Wende'' and applied it, just as the Germans in the north, to Slavs they had contact with; e.g., the Polabians from ''Bavaria Slavica
Bavaria Slavica is a historiographic term used to denote the areas populated by West Slavic people (Wends) between the 6th and the 12th centuries in northeastern Bavaria. The Wends settled in Bavaria in several waves between the 6th and the 9th ...
'' or the Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their n ...
(the names Windic March
The Windic March (german: Windische Mark; also known as Wendish March) was a medieval frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Lower Carniola ( sl, Dolenjska) region in present-day Slovenia. In Slovenian historiogr ...
, Windisch Feistritz, Windischgraz, or Windisch Bleiberg near Ferlach
Ferlach ( sl, Borovlje) in the district of Klagenfurt-Land in Carinthia is the southernmost town in Austria. It is known for its centuries-old gunsmith tradition, part of the Austrian intangible cultural heritage since 2010.
Geography
It is situa ...
still bear testimony to this historical denomination). The same term was sometimes applied to the neighboring region of Slavonia
Slavonia (; hr, Slavonija) is, with Dalmatia, Croatia proper, and Istria, one of the four historical regions of Croatia. Taking up the east of the country, it roughly corresponds with five Croatian counties: Brod-Posavina, Osijek-Baranja ...
, which appears as Windischland in some documents prior to the 18th century.
Following the 8th century, the Frankish kings
The Franks, Germanic-speaking peoples that invaded the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century, were first led by individuals called dukes and reguli. The earliest group of Franks that rose to prominence was the Salian Merovingians, who co ...
and their successors organised nearly all Wendish land into marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ...
. This process later turned into the series of Crusades
The Crusades were a series of religious wars initiated, supported, and sometimes directed by the Latin Church in the medieval period. The best known of these Crusades are those to the Holy Land in the period between 1095 and 1291 that were in ...
. By the 12th century, all Wendish lands had become part of the Holy Roman Empire. In the course of the Ostsiedlung, which reached its peak in the 12th to 14th centuries, this land was settled by Germans
, native_name_lang = de
, region1 =
, pop1 = 72,650,269
, region2 =
, pop2 = 534,000
, region3 =
, pop3 = 157,000
3,322,405
, region4 =
, pop4 = ...
and reorganised.
Due to the process of assimilation following German settlement, many Slavs west of the Oder adopted the German culture
The culture of Germany has been shaped by major intellectual and popular currents in Europe, both religious and secular. Historically, Germany has been called ''Das Land der Dichter und Denker'' (the country of poets and thinkers). German cult ...
and language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of met ...
. Only some rural communities which did not have a strong admixture with Germans and continued to use West Slavic languages
The West Slavic languages are a subdivision of the Slavic language group. They include Polish, Czech, Slovak, Kashubian, Upper Sorbian and Lower Sorbian. The languages have traditionally been spoken across a mostly continuous region encom ...
were still termed ''Wends''. With the gradual decline of the use of these local Slavic tongues, the term ''Wends'' slowly disappeared, too.
Some sources claim that in the 13th century there were actual historic people called Wends or Vends
The Vends ( lat, wendi, lv, vendi, et, võndlased, võnnulased, vendid) were a Balto-Finnic people that lived between the 12th to 16th centuries in the area around the town of Wenden (now Cēsis) in present-day north-central Latvia.
Accord ...
living as far as northern Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
(east of the Baltic Sea) around the city of Wenden. Henry of Livonia
Henry of Latvia ( la, Henricus de Lettis, german: Heinrich von Lettland, lv, Latviešu Indriķis, et, Läti Henrik; 1187 – after 1259), also known in the English-speaking world as Henry of Livonia, was a priest, missionary and historian. ...
(Henricus de Lettis) in his 13th-century Latin chronicle described a tribe called the ''Vindi''.
Today, only one group of ''Wends'' still exists: the Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
n Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
in present-day Eastern Germany, with international diaspora.
Roman-era Veneti
The term "Wends" derived from the Roman-era people called in la, Venetī, or ; in grc-gre, Οὐενέδαι, Ouenédai . This people is mentioned byPliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic '' ...
and Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
as inhabiting the Baltic coast.
History
Rise (500–1000)
In the 1st millennium AD, during the Slavic migrations which split the recently formed Slav ethnicity into Southern, Eastern and Western groups, someWest Slavs
The West Slavs are Slavic peoples who speak the West Slavic languages. They separated from the common Slavic group around the 7th century, and established independent polities in Central Europe by the 8th to 9th centuries. The West Slavic lan ...
moved into the areas between the Rivers Elbe and Oder - moving from east to west and from south to north. There they assimilated the remaining Germanic population that had not left the area in the Migration period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roman ...
. Their German neighbours adapted the term they had been using for peoples east of the River Elbe before to the Slavs, calling them ''Wends'' as they called the ''Venedi'' before and probably the ''Vandals
The Vandals were a Germanic people who first inhabited what is now southern Poland. They established Vandal kingdoms on the Iberian Peninsula, Mediterranean islands, and North Africa in the fifth century.
The Vandals migrated to the area betw ...
'' also. In his late sixth century work '' History of Armenia'', Movses Khorenatsi
Movses Khorenatsi (ca. 410–490s AD; hy, Մովսէս Խորենացի, , also written as ''Movses Xorenac‘i'' and Moses of Khoren, Moses of Chorene, and Moses Chorenensis in Latin sources) was a prominent Armenian historian from the late a ...
mentions their raids into the lands named Vanand after them.
While the Wends were arriving in so-called ''Germania Slavica'' as large homogeneous groups, they soon divided into a variety of small tribes, with large strips of woodland separating one tribal settlement area from another. Their tribal names were derived from local place names, sometimes adopting the Germanic tradition (e.g. Heveller from ''Havel'', Rujanes from Rugians
The Rugii, Rogi or Rugians ( grc, Ρογοί, Rogoi), were a Roman-era Germanic people. They were first clearly recorded by Tacitus, in his ''Germania'' who called them the ''Rugii'', and located them near the south shore of the Baltic Sea. Some ...
). Settlements were secured by round ''burghs'' made of wood and clay, where either people could retreat in case of a raid from the neighbouring tribe or used as military strongholds or outposts.
Some tribes unified into larger, duchy-like units. For example, the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
evolved from the unification of the ''Holstein
Holstein (; nds, label=Northern Low Saxon, Holsteen; da, Holsten; Latin and historical en, Holsatia, italic=yes) is the region between the rivers Elbe and Eider. It is the southern half of Schleswig-Holstein, the northernmost state of German ...
'' and Western ''Mecklenburg
Mecklenburg (; nds, label= Low German, Mękel(n)borg ) is a historical region in northern Germany comprising the western and larger part of the federal-state Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania. The largest cities of the region are Rostock, Schweri ...
'' tribes led by mighty dukes known for their raids into German Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
. The Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
were an alliance of tribes living between Obotrites and Pomeranians. They did not unify under a duke, but remained independent. Their leaders met in the temple of Rethra
Rethra (also known as ''Radagoszcz'', ''Radegost'', ''Radigast'', ''Redigast'', ''Radgosc'' and other forms like ''Ruthengost'') was, in the 10th to the 12th centuries, the main town and political center of the Slavic Redarians, one of the four m ...
.
In 983, many Wend tribes participated in a great uprising against the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a Polity, political entity in Western Europe, Western, Central Europe, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its Dissolution of the Holy Roman Empire, dissolution i ...
, which had previously established Christian missions, German colonies and German administrative institutions (''Marken'' such as ''Nordmark
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg) and ...
'' and '' Billungermark'') in pagan Wendish territories. The uprising was successful and the Wends delayed Germanisation for about two centuries.
Wends and Danes had early and continuous contact including settlement, first and mainly through the closest South Danish islands of Møn, Lolland and Falster, all having place-names of Wendish origin. There were also trading and settlement outposts by Danish towns as important as Roskilde, when it was the capital: 'Vindeboder' (Wends' booths) is the name of a city neighbourhood there. Danes and Wends also fought wars due to piracy and crusading.
Decline (1000–1200)
After their successes in 983 the Wends came under increasing pressure from Germans,Danes
Danes ( da, danskere, ) are a North Germanic ethnic group and nationality native to Denmark and a modern nation identified with the country of Denmark. This connection may be ancestral, legal, historical, or cultural.
Danes generally regard t ...
and Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, who share a common history, culture, the Polish language and are identified with the country of Poland in Ce ...
. The Poles invaded Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
several times. The Danes often raided the Baltic shores (and, in turn, the Wends often raided the raiders). The Holy Roman Empire and its margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the Em ...
s tried to restore their marches.
In 1068/69 a German expedition took and destroyed Rethra
Rethra (also known as ''Radagoszcz'', ''Radegost'', ''Radigast'', ''Redigast'', ''Radgosc'' and other forms like ''Ruthengost'') was, in the 10th to the 12th centuries, the main town and political center of the Slavic Redarians, one of the four m ...
, one of the major pagan Wend temples. The Wendish religious centre shifted to Arkona thereafter. In 1124 and 1128, the Pomeranians and some Lutici were baptised. In 1147, the '' Wend crusade'' took place in what is today north-eastern Germany.
This did not, however, affect the Wendish people in today's Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a landlocked state of ...
, where a relatively stable co-existence of German and Slavic inhabitants as well as close dynastic and diplomatic cooperation of Wendish and German nobility had been achieved. (See: Wiprecht of Groitzsch).
In 1168, during the Northern Crusades
The Northern Crusades or Baltic Crusades were Christian colonization and Christianization campaigns undertaken by Catholic Christian military orders and kingdoms, primarily against the pagan Baltic, Finnic and West Slavic peoples around th ...
, Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
mounted a crusade led by Bishop Absalon
Absalon (21 March 1201) was a Danish statesman and prelate of the Catholic Church who served as the bishop of Roskilde from 1158 to 1192 and archbishop of Lund from 1178 until his death. He was the foremost politician and church father of Denm ...
and King Valdemar the Great
Valdemar I (14 January 1131 – 12 May 1182), also known as Valdemar the Great ( da, Valdemar den Store), was King of Denmark from 1154 until his death in 1182. The reign of King Valdemar I saw the rise of Denmark, which reached its medieval zen ...
against the Wends of Rugia in order to convert them to Christianity. The crusaders captured and destroyed Arkona, the Wendish temple-fortress, and tore down the statue of the Wendish god Svantevit. With the capitulation of the Rugian Wends, the last independent pagan Wends were defeated by the surrounding Christian feudal powers.
From the 12th to the 14th centuries, Germanic settlers moved into the Wendish lands in large numbers, transforming the area's culture from a Slavic to a Germanic one. Local dukes and monasteries invited settlers to repopulate farmlands devastated in the wars, as well as to cultivate new farmlands from the expansive woodlands and heavy soils, with the use of iron-based agricultural tools that had developed in Western Europe. Concurrently, a large number of new towns were created under German town law with the introduction of legally enforced markets, contracts and property rights. These developments over two centuries were collectively known as the (German eastward expansion). A minority of Germanic settlers moved beyond the Wendish territory into Hungary, Bohemia and Poland, where they were generally welcomed for their skills in farming and craftsmanship.
The Polabian language
The Polabian language was a West Slavic language that was spoken by the Polabian Slavs (german: Wenden) in present-day northeastern Germany around the Elbe (''Łaba/Laba/Labe'' in Slavic) river, from which derives its name ("po Labe" – ''unto ...
was spoken in the central area of Lower Saxony
Lower Saxony (german: Niedersachsen ; nds, Neddersassen; stq, Läichsaksen) is a German state (') in northwestern Germany. It is the second-largest state by land area, with , and fourth-largest in population (8 million in 2021) among the 16 ...
and in Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a states of Germany, state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an ar ...
until around the 17th or 18th century. The German population assimilated most of the Wends, meaning that they disappeared as an ethnic minority - except for the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
. Yet many place names and some family names in eastern Germany still show Wendish origins today. Also, the Dukes of Mecklenburg
This list of dukes and grand dukes of Mecklenburg dates from the origins of the German princely state of Mecklenburg's royal house in the High Middle Ages to the monarchy's abolition at the end of World War I. Strictly speaking, Mecklenburg's p ...
, of Rügen
Rügen (; la, Rugia, ) is Germany's largest island. It is located off the Pomeranian coast in the Baltic Sea and belongs to the state of Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania.
The "gateway" to Rügen island is the Hanseatic city of Stralsund, where ...
and of Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
had Wendish ancestors.
Between 1540 and 1973, the kings of Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
were officially called ''kings of the Swedes
Swedes ( sv, svenskar) are a North Germanic ethnic group native to the Nordic region, primarily their nation state of Sweden, who share a common ancestry, culture, history and language. They mostly inhabit Sweden and the other Nordic countr ...
, the Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
and the Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
'' (in Latin translation: ''kings of Suiones
The Swedes ( sv, svear; Old Norse: ''svíar'')
(probably from the PIE reflexive pronominal root * s(w)e, "one's own ribesmen/kinsmen;Bandle, Oskar. 2002. The Nordic languages: an international handbook of the history of the North Germanic lang ...
, Goths and Vandals'') (). After the Danish monarch Queen Margrethe II
Margrethe II (; Margrethe Alexandrine Þórhildur Ingrid, born 16 April 1940) is Queen of Denmark. Having reigned as Denmark's monarch for over 50 years, she is Europe's longest-serving current head of state and the world's only incumbent femal ...
chose not to use these titles in 1972 the Swedish monarch, Carl XVI Gustaf also chose only to use the title King of Sweden" (), thereby changing an age-old tradition.
From the Middle Ages the kings of Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark
...
and of Denmark–Norway used the titles ''King of the Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
'' (from 1362) and ''Goths
The Goths ( got, 𐌲𐌿𐍄𐌸𐌹𐌿𐌳𐌰, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, Γότθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
'' (from the 12th century). The use of both titles was discontinued in 1973.
Legacy
The Wendish people co-existed with the German settlers for centuries and became gradually assimilated into the German-speaking culture. TheGolden Bull of 1356
The Golden Bull of 1356 (, , , , ) was a decree issued by the Imperial Diet at Nuremberg and Metz ( Diet of Metz, 1356/57) headed by the Emperor Charles IV which fixed, for a period of more than four hundred years, important aspects of the con ...
(one of the constitutional foundations of the German-Roman Empire) explicitly recognised in its Art. 31 that the German-Roman Empire was a multi-national entity with "diverse nations distinct in customs, manner of life, and in language". For that it stipulated "the sons, or heirs and successors of the illustrious prince electors, ... since they are expected in all likelihood to have naturally acquired the German language, ... shall be instructed in the grammar of the Italian and Slavic (i.e. Wendish) tongues, beginning with the seventh Year of their age."
Many geographical names in Central Germany and northern Germany can be traced back to a Slavic origin. Typical Slavic endings include -itz, -itzsch and -ow. They can be found in city names such as Delitzsch and Rochlitz
Rochlitz (; hsb, Rochlica) is a major district town (Große Kreisstadt) in the district of Mittelsachsen, in Saxony, Germany. Rochlitz is the head of the "municipal partnership Rochlitz" (Verwaltungsgemeinschaft Rochlitz) with its other members ...
. Even names of major cities like Leipzig
Leipzig ( , ; Upper Saxon: ) is the most populous city in the German state of Saxony. Leipzig's population of 605,407 inhabitants (1.1 million in the larger urban zone) as of 2021 places the city as Germany's eighth most populous, as wel ...
and Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitue ...
are most likely of Wendish origin.
Today, the only remaining minority people of Wendish origin, the Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
, maintain their traditional language and culture and enjoy cultural self-determination exercised through the Domowina
Domowina (Sorbian language, Sorbian: "Home") is a political independent league of the Sorbs, Sorbian and Wendish people and umbrella organization of Sorbian societies in Lusatia, Lower and Upper Lusatia, Germany. It represents the interests of ...
. The third minister president
A minister-president or minister president is the head of government in a number of European countries or subnational governments with a parliamentary or semi-presidential system of government where they preside over the council of ministers. I ...
of Saxony Stanislaw Tillich
Stanislaw Tillich (; hsb, Stanisław Tilich; born 10 April 1959) is a German politician of the CDU. He served as the 3rd Minister President of Saxony from 2008 to 2017. From 1 November 2015 until 31 October 2016, he was President of the Bund ...
(2008–2017) is of Sorbian origin, being the first head of a German federal state with an ethnic minority background.
The Texas Wends
In 1854, theWends of Texas
The Texas Wends or Wends of Texas are a group of people descended from a congregation of approximately 558 Sorbian/ Wendish people under the leadership and pastoral care of John Kilian ( wen, Jan Kilian, german: Johann Killian) who emigrated fr ...
departed Lusatia
Lusatia (german: Lausitz, pl, Łużyce, hsb, Łužica, dsb, Łužyca, cs, Lužice, la, Lusatia, rarely also referred to as Sorbia) is a historical region in Central Europe, split between Germany and Poland. Lusatia stretches from the Bóbr ...
on the ''Ben Nevis
Ben Nevis ( ; gd, Beinn Nibheis ) is the highest mountain in Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a Countries of the United Kingdom, country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland ...
'' seeking greater liberty, in order to settle an area of central Texas, primarily Serbin. The Wends succeeded, expanding into Warda, Giddings Giddings may refer to:
* Giddings (surname)
*Giddings, Texas
Giddings is the county seat of Lee County, Texas, United States situated on the intersection of U.S. Highway 77 and U.S. Route 290. Its population was 4,969 at the 2020 census. The ci ...
, Austin, Houston, Fedor, Swiss Alp, Port Arthur, Mannheim, Copperas Cove, Vernon, Walburg, The Grove, Bishop, and the Rio Grande Valley.
A strong emphasis on tradition, principles, and education is evident today in families descendant from the Wendish pioneers.
Today, thousands of Texans and other Americans (many unaware of their background), can lay claim to the heritage of the Wends.

Other uses
 Historically, the term "Wends" has also occurred in the following contexts:
* Until the mid-19th-century German-speakers most commonly used the name ''Wenden'' to refer to Slovenes. This usage is mirrored in the name of the
Historically, the term "Wends" has also occurred in the following contexts:
* Until the mid-19th-century German-speakers most commonly used the name ''Wenden'' to refer to Slovenes. This usage is mirrored in the name of the Windic March
The Windic March (german: Windische Mark; also known as Wendish March) was a medieval frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Lower Carniola ( sl, Dolenjska) region in present-day Slovenia. In Slovenian historiogr ...
, a Medieval territory in present-day Lower Carniola
Lower Carniola ( sl, Dolenjska; german: Unterkrain) is a traditional region in Slovenia, the southeastern part of the historical Carniola region.
Geography
Lower Carniola is delineated by the Ljubljana Basin with the city of Ljubljana to the n ...
, which merged with the Duchy of Carniola
The Duchy of Carniola ( sl, Vojvodina Kranjska, german: Herzogtum Krain, hu, Krajna) was an imperial estate of the Holy Roman Empire, established under Habsburg rule on the territory of the former East Frankish March of Carniola in 1364. A ...
by the mid 15th century. With the diffusion of the term ''slowenisch'' for the Slovene language
Slovene ( or ), or alternatively Slovenian (; or ), is a South Slavic languages, South Slavic language, a sub-branch that is part of the Balto-Slavic languages, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family ...
and ''Slowenen'' for Slovenes, the words ''windisch'' and ''Winde'' or ''Wende'' became derogatory in connotation. The same development could be seen in the case of the Hungarian Slovenes
Hungarian Slovenes ( Slovene: ''Madžarski Slovenci'', hu, Magyarországi szlovének) are an autochthonous ethnic and linguistic Slovene minority living in Hungary. The largest groups are the Rába Slovenes ( sl, porabski Slovenci, dialectical ...
, who used to be known under the name "Vends".
* It was also used to denote the Slovaks
The Slovaks ( sk, Slováci, singular: ''Slovák'', feminine: ''Slovenka'', plural: ''Slovenky'') are a West Slavic ethnic group and nation native to Slovakia who share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovak.
In Slovakia, 4.4 mi ...
in German-language texts before c. 1400.
* The German term "Windischland" was used in the Middle Ages for the historical Kingdom of Slavonia
The Kingdom of Slavonia ( hr, Kraljevina Slavonija, la, Regnum Sclavoniae, hu, Szlavón Királyság, german: Königreich Slawonien, sr-Cyrl, Краљевина Славонија) was a kingdom of the Habsburg monarchy and the Austrian Empi ...
(in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = "Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capit ...
). The terms ''Veneta'', ''Wenden'', ''Winden'' etc were used in reference to the westernmost Slavs in the 1st and 2nd century CE, as a reference to the name of the earlier tribes of Veneti.
See also
*Sukow-Dziedzice group
The Sukow or Sukow-Dziedzice group (german: Sukow-Dziedzice-Gruppe) or Sukow-Dziedzice culture ( pl, Kultura Sukow-Dziedzice, russian: Суковско-дзедзицкая культура), also known as Szeligi culture, was an archaeological cu ...
* Northern March
*Limes Saxoniae
The Limes Saxoniae (Latin for "Limit of Saxony"), also known as the Limes Saxonicus or Sachsenwall ("Saxon Dyke"), was an unfortified limes or border between the Saxons and the Slavic Obotrites, established about 810 in present-day Schleswig ...
*Kashubians
The Kashubians ( csb, Kaszëbi; pl, Kaszubi; german: Kaschuben), also known as Cassubians or Kashubs, are a Lechitic ( West Slavic) ethnic group native to the historical region of Pomerania, including its eastern part called Pomerelia, in nor ...
*Drevani
The Drevani (german: Draväno-Polaben or ''Drevanen'') were a tribe of Polabian Slavs settling on the Elbe river in the area of the present-day Lüchow-Dannenberg district of Lower Saxony, Germany.
They were a constituent tribe of the Obodrite co ...
*Wendland
The Wendland is a region in Germany on the borders of the present states of Brandenburg, Mecklenburg-Western Pomerania, Lower Saxony and Saxony-Anhalt. Its heart is the Hanoverian Wendland in the county of Lüchow-Dannenberg in Lower Saxony.
In ...
*Slovincians Slovincians, also known as Łeba Kashubians, is a near-extinct ethnic subgroup of the Kashubian people, who originated from the north western Kashubia, located in the Pomeranian Voivodeship, Poland, from the area around the lakes of Łebsko and G ...
* Baltic Slavic piracy
*Sorbs
Sorbs ( hsb, Serbja, dsb, Serby, german: Sorben; also known as Lusatians, Lusatian Serbs and Wends) are a indigenous West Slavic ethnic group predominantly inhabiting the parts of Lusatia located in the German states of Saxony and Branden ...
*Czech people
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, c ...
*Slovenes
The Slovenes, also known as Slovenians ( sl, Slovenci ), are a South Slavic ethnic group native to Slovenia, and adjacent regions in Italy, Austria and Hungary. Slovenes share a common ancestry, culture, history and speak Slovene as their n ...
*Wendish question
The Wendish question ( hu, Vendkérdés, sl, Vendsko vprašanje, Prekmurje dialect: ''Vendsko pítanje,'' or ''Vendiško pitanje'') in Hungarian Nationalist and Chauvinist politics concerns the origin and nomenclature of the Hungarian Sloven ...
References
Further reading
* *External links
Sorbian Cultural Information
{{Authority control Early Slavs Historical ethnic groups of Europe Lechites Sorbs Wendland West Slavic history