|
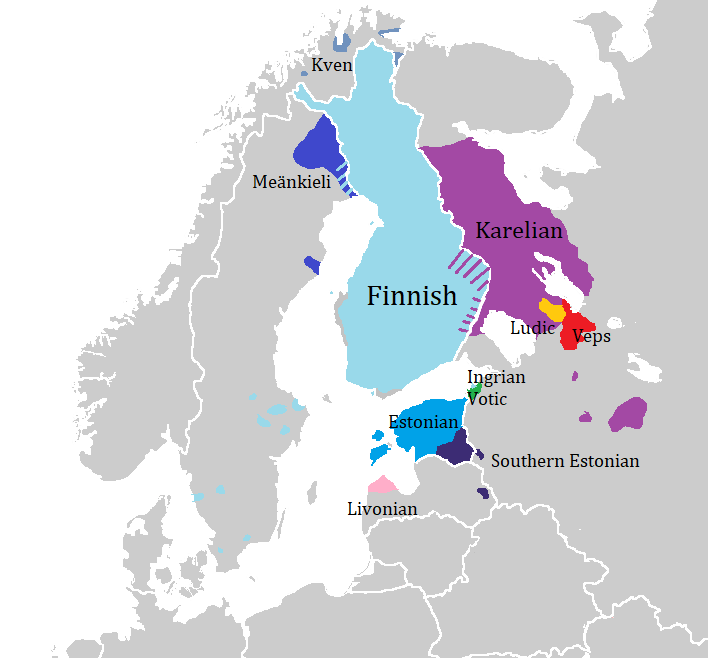
Finnic Languages
The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 million speakers, who live mainly in Finland and Estonia. Traditionally, eight Finnic languages have been recognized. The major modern representatives of the family are Finnish and Estonian, the official languages of their respective nation states.Finnic Peoples at Encyclopædia Britannica The other Finnic languages in the Baltic Sea region are Ingrian and |
Balto-Finnic Language Family
Balto-Finnic may refer to: *Balto-Finnic peoples *Balto-Finnic languages The Finnic (''Fennic'') or more precisely Balto-Finnic (Balto-Fennic, Baltic Finnic, Baltic Fennic) languages constitute a branch of the Uralic language family spoken around the Baltic Sea by the Baltic Finnic peoples. There are around 7 m ... {{dab Language and nationality disambiguation pages ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Encyclopædia Britannica
The ( Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various times through the centuries. The encyclopaedia is maintained by about 100 full-time editors and more than 4,000 contributors. The 2010 version of the 15th edition, which spans 32 volumes and 32,640 pages, was the last printed edition. Since 2016, it has been published exclusively as an online encyclopaedia. Printed for 244 years, the ''Britannica'' was the longest running in-print encyclopaedia in the English language. It was first published between 1768 and 1771 in the Scottish capital of Edinburgh, as three volumes. The encyclopaedia grew in size: the second edition was 10 volumes, and by its fourth edition (1801–1810) it had expanded to 20 volumes. Its rising stature as a scholarly work helped recruit eminent ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
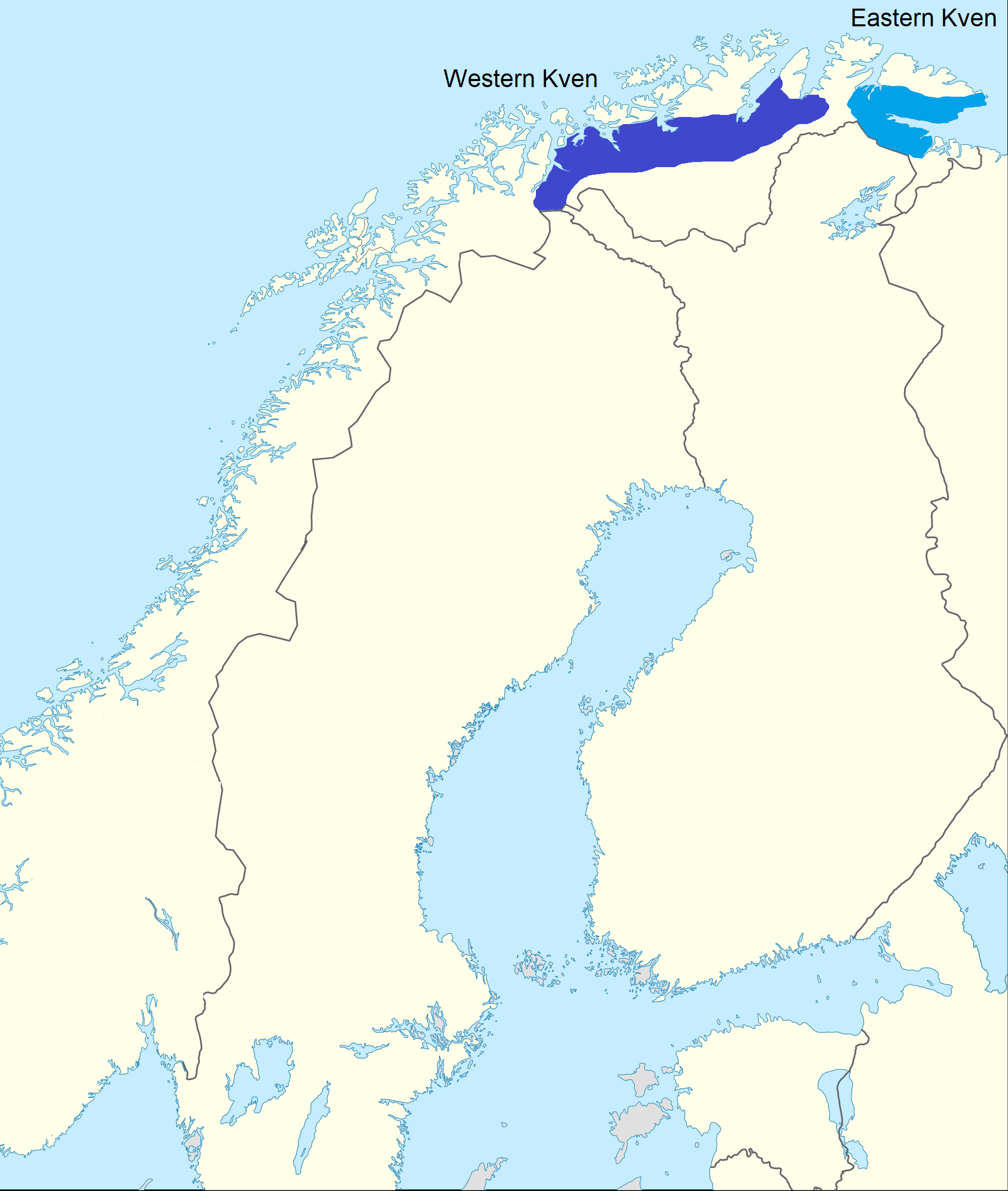
Kven Language
The Kven language ( or ; or ; fi, kveeni or ; no, kvensk) is a Finnic language or a group of Finnish dialects spoken in the northernmost parts of Norway by the Kven people. For political and historical reasons, it received the status of a minority language in 2005 within the framework of the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages. Linguistically, however, it is seen as a mutually intelligible dialect of the Finnish language, and grouped together with the Peräpohjola dialects such as Meänkieli, spoken in Torne Valley in Sweden. While it is often considered a dialect in Finland, it is officially recognized as a minority language in Norway and some Kven people consider it a separate language. There are about 1,500 to 10,000 known native speakers of this language, most of whom are over the age of 60. Middle aged speakers tend to have a passing knowledge of the language. They use it occasionally, but not frequently enough to keep it off the endangered list. Peo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meänkieli
(literally 'our language') is a group of distinct Finnish dialects or a Finnic language spoken in the northernmost part of Sweden along the valley of the Torne River. Its status as an independent language is disputed, but in Sweden it is recognized as one of the country's five minority languages. Linguistically, Meänkieli consists of two dialect subgroups, the Torne Valley dialects (also spoken on the Finnish side of the Torne River) and the Gällivare dialects, which both belong to the larger Peräpohjola dialect group. For historical and political reasons it has the status of a minority language in Sweden. In modern Swedish the language is normally referred to officially as , although colloquially an older name, ("Torne Valley Finnish"), is still commonly used. Sveriges Radio tends to use for the culture generally and ' specifically for the language. Meänkieli is distinguished from Standard Finnish by the absence of 19th- and 20th-century developments in Finnish. His ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seto Dialect
Seto (; et, setu keel) is a dialect of Estonian or a separate language spoken by 12,549 people. It is sometimes identified as a dialect of Võro, or the two are described as one language, Võro-Seto. Setos () mostly inhabit the area near Estonia's southeastern border with Russia in Setomaa, and are primarily Eastern Orthodox, while Võros () are traditionally Lutherans and live in historical Võru County. Language sample Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights The Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) is an international document adopted by the United Nations General Assembly that enshrines the rights and freedoms of all human beings. Drafted by a UN committee chaired by Eleanor Roosevelt, ...: * Seto: * Võro: * Estonian: * Finnish: * English: ''All human beings are born free and equal in dignity and rights. They are endowed with reason and conscience and should act towards one another in a spirit of brotherhood.'' Refere ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Võro Language
Võro ( vro, võro kiilʼ, link=no , et, võru keel) is a language belonging to the Finnic branch of the Uralic languages. Traditionally, it has been considered a dialect of the South Estonian dialect group of the Estonian language, but nowadays it has its own literary standard and efforts have been undertaken to seek official recognition as an indigenous regional language of Estonia. Võro has roughly 75,000 speakers (Võros) mostly in southeastern Estonia, in the eight parishes of the historical Võru County: Karula, Harglõ, Urvastõ, Rõugõ, Kanepi, Põlva, Räpinä and Vahtsõliina. These parishes are currently centred (due to redistricting) in Võru and Põlva counties, with parts extending into Valga and Tartu counties. Speakers can also be found in the cities of Tallinn and Tartu and the rest of Estonia. History Võro is a descendant of the old South Estonian regional language and is the least influenced by Standard Estonian (which is based on Norther ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Ladoga
Lake Ladoga (; rus, Ла́дожское о́зеро, r=Ladozhskoye ozero, p=ˈladəʂskəjə ˈozʲɪrə or rus, Ла́дога, r=Ladoga, p=ˈladəɡə, fi, Laatokka arlier in Finnish ''Nevajärvi'' ; vep, Ladog, Ladoganjärv) is a freshwater lake located in the Republic of Karelia and Leningrad Oblast in northwestern Russia, in the vicinity of Saint Petersburg. It is the largest lake located entirely in Europe, the second largest lake after Baikal in Russia, and the 14th largest freshwater lake by area in the world. '' Ladoga Lacus'', a methane lake on Saturn's moon Titan, is named after the lake. Etymology In one of Nestor's chronicles from the 12th century a lake called "the Great Nevo" is mentioned, a clear link to the Neva River and possibly further to Finnish ''nevo'' 'sea' or ''neva'' 'bog, quagmire'. Evgeny Pospelov: ''Geographical names of the world. Toponymic dictionary.'' Second edition. Astrel, Moscow 2001, pp. 106f. Ancient Norse sagas and Hanseatic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego, rus, Оне́жское о́зеро, r=Onezhskoe ozero, p=ɐˈnʲɛʂskəɪ ˈozʲɪrə; fi, Ääninen, Äänisjärvi; vep, Änine, Änižjärv) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic Sea, and is the second-largest lake in Europe after Lake Ladoga, slightly smaller than Lebanon. The lake is fed by about 50 rivers and is drained by the Svir. There are about 1,650 islands on the lake. They include Kizhi, which hosts a historical complex of 89 Orthodox churches and other wooden structures of the 15th–20th centuries. The complex includes a UNESCO World Heritage site, Kizhi Pogost. The eastern shores of the lake contain about 1,200 petroglyphs (rock engravings) dated to the 4th–2nd millennia BC, which have also been inscribed as a UNESCO World Heritage site. The major cities on the lake are Petrozavodsk, Kondopoga and Medv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Veps Language
Veps, also known as Vepsian (Veps: ' or '), is a Finnic language from the Uralic language family, that is spoken by Vepsians. The language is written in the Latin script, and is closely related to Finnish and Karelian. According to Soviet statistics, 12,500 people were self-designated ethnic Veps at the end of 1989. There were 5,900 self-designated ethnic Veps in 2010, and around 3,600 native speakers. According to the location of the people, the language is divided into three main dialects: Northern Veps (at Lake Onega to the south of Petrozavodsk, to the north of the river Svir, including the former Veps National Volost), Central Veps (in the East of the Leningrad Oblast and Northwest of the Vologda Oblast), and Southern Veps (in the Leningrad Oblast). The Northern dialect seems the most distinct of the three; however, it is still mutually intelligible for speakers of the other two dialects. Speakers of the Northern dialect call themselves "Ludi" ('), or '. In Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ludic Language
Ludic, or ''Ludian'', or ''Ludic Karelian'' ( or ), is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family or a Karelian dialect. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language. It is spoken by 300 Karelians in the Republic of Karelia in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega, including a few children. Classification In the Finnish research tradition, Ludic has been considered a transitional dialect area between Karelian and Veps, while in the Russian research tradition it is, on ethnographic grounds, normally considered a dialect of Karelian. A status as an independent language has been proposed in recent times. Ludic is characterised by a specific mixture of Karelian-like traits (such as the diphthongisation of the Proto-Finnic non-open long vowels: e.g. *pää > ''piä'' 'head', *soo > ''suo'' 'swamp', contrast Veps ''pä'', ''so'') and Veps-like traits (such as an almost complete loss of consonant gradation). Dialects Ludic compr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
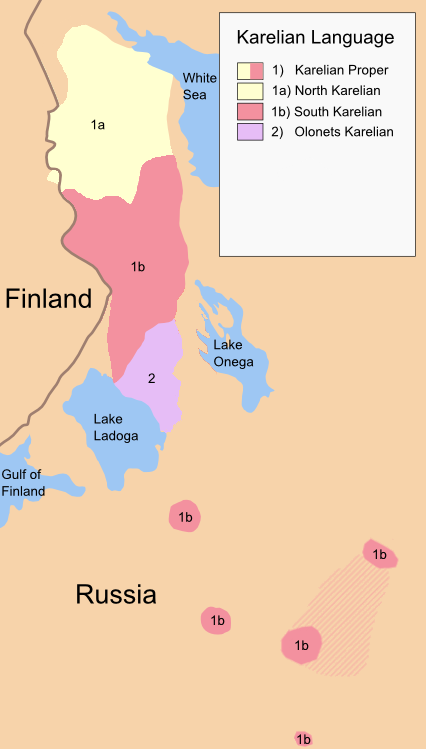
Karelian Language
Karelian (North Karelian and Livvi Karelian: ; Ludic: ; Tver Karelian: ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some Finnish linguists have even classified Karelian as a dialect of Finnish, though in the modern day it is widely considered a separate language. Karelian is not to be confused with the Southeastern dialects of Finnish, sometimes referred to as ("Karelian dialects") in Finland. There is no single standard Karelian language. Each writer writes in Karelian according to their own dialectal form. Three main written standards have been developed, for North Karelian, Olonets Karelian (also known as Livvi Karelian) and Tver Karelian. Ludic Karelian also appears in writing. All variants are written with the Latin-based Karelian alphabet, though the Cyrillic script has been used in the past. Classification Karelian belongs to the Finnic bra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Riga
The Gulf of Riga, Bay of Riga, or Gulf of Livonia ( lv, Rīgas līcis, et, Liivi laht) is a bay of the Baltic Sea between Latvia and Estonia. The island of Saaremaa (Estonia) partially separates it from the rest of the Baltic Sea. The main connection between the gulf and the Baltic Sea is the Irbe Strait. The Gulf of Riga, as a sub-basin of the Baltic, also includes the Väinameri Sea in the West Estonian archipelago. Geography Extent The International Hydrographic Organization defines the Gulf of Riga's western limit as "A line running from Lyser Ort (57°34'N), in Latvia, to the South extreme of Œsel Island, through this island to Pammerort (22°34'E), thence to Enmast Point, the S extreme of Dagö, through Dagö to Takhkona Point, the North extreme thereof, and on to Spithamn Point in Estonia". Islands Major islands in the gulf include Saaremaa, Kihnu, and Ruhnu, which are all controlled by Estonia. Kihnu covers an area of . Saaremaa island is responsible f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |