Ludic language on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
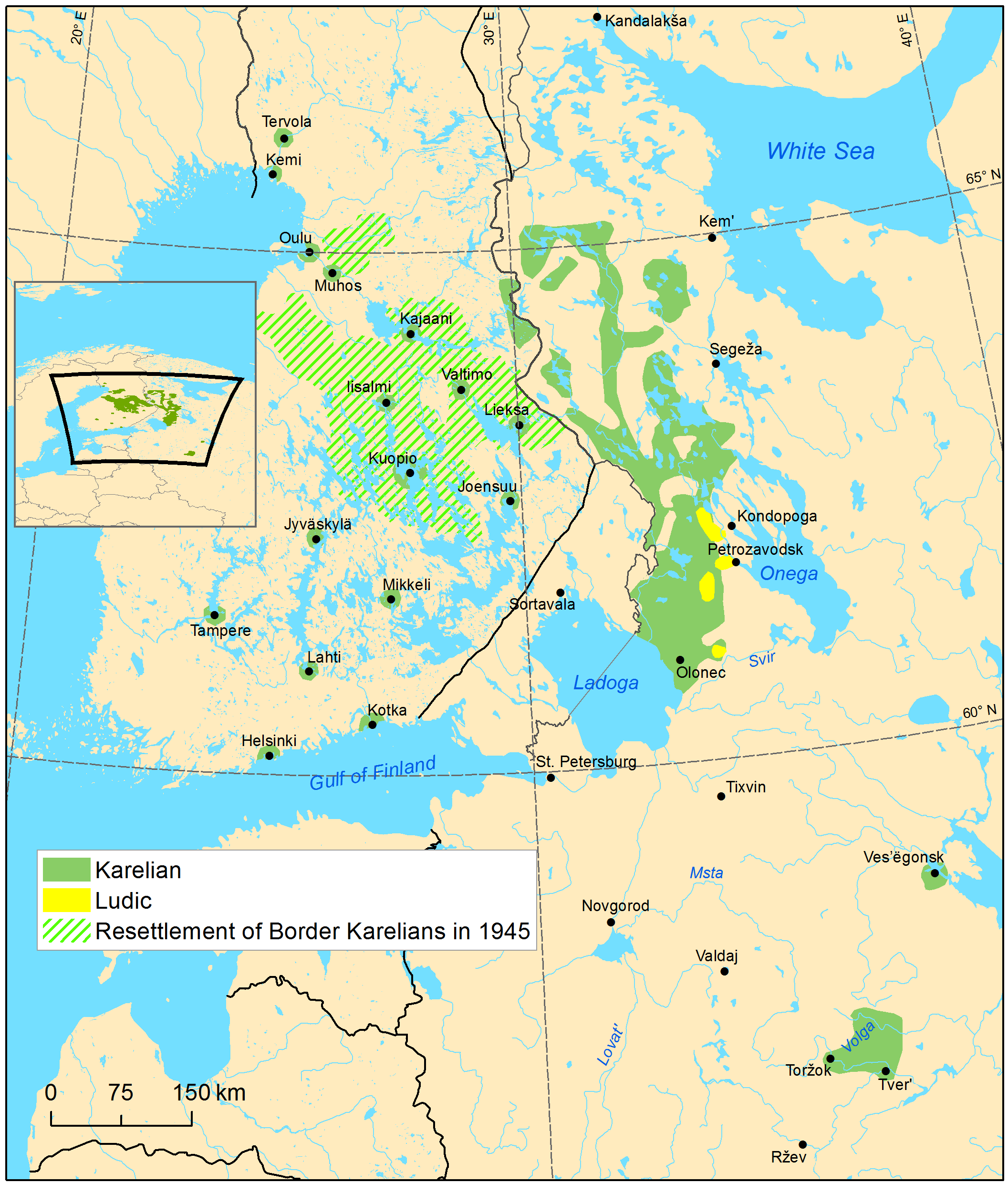 Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian ( or ), is a Finnic language in the
Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian ( or ), is a Finnic language in the
 In the Finnish research tradition, Ludic has been considered a transitional dialect area between Karelian and Veps, while in the Russian research tradition it is, on
In the Finnish research tradition, Ludic has been considered a transitional dialect area between Karelian and Veps, while in the Russian research tradition it is, on
ISO 639 code sets - SIL InternationalLyydiläinen Seura (The Ludian Society)
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ludic Language Languages of Russia Karelian language Indigenous languages of European Russia
 Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian ( or ), is a Finnic language in the
Ludic, Ludian, or Ludic Karelian ( or ), is a Finnic language in the Uralic language family
The Uralic languages ( ), sometimes called the Uralian languages ( ), are spoken predominantly in Europe and North Asia. The Uralic languages with the most native speakers are Hungarian, Finnish, and Estonian. Other languages with speakers ab ...
or a Karelian dialect. It is transitional between the Olonets Karelian language and the Veps language. It is spoken by 300 Karelians
Karelians (; ; ; ) are a Baltic Finnic ethnic group who are indigenous to the historical region of Karelia, which is today split between Finland and Russia. Karelians living in Russian Karelia are considered a distinct ethnic group closely ...
in the Republic of Karelia
The Republic of Karelia, or simply Karelia or Karjala (; ) is a Republics of Russia, republic of Russia situated in the Northwest Russia, northwest of the country. The republic is a part of the Northwestern Federal District, and covers an area of ...
in Russia, near the southwestern shore of Lake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
, including a few children.
Classification
ethnographic
Ethnography is a branch of anthropology and the systematic study of individual cultures. It explores cultural phenomena from the point of view of the subject of the study. Ethnography is also a type of social research that involves examining ...
grounds, normally considered a dialect of Karelian. A status as an independent language has been proposed in recent times. Ludic is characterised by a specific mixture of Karelian-like traits (such as the diphthongisation of the Proto-Finnic
Proto-Finnic or Proto-Baltic-Finnic is the common ancestor of the Finnic languages, which include the national languages Finnish language, Finnish and Estonian language, Estonian. Proto-Finnic is not attested in any texts, but has been linguisti ...
non-open long vowels: e.g. *pää > ''piä'' 'head', *soo > ''suo'' 'swamp', contrast Veps ''pä'', ''so'') and Veps-like traits (such as an almost complete loss of consonant gradation
Consonant gradation is a type of consonant mutation (mostly lenition but also assimilation) found in some Uralic languages, more specifically in the Finnic, Samic and Samoyedic branches. It originally arose as an allophonic alternation ...
). Like Veps, Ludic has also partially lost vowel harmony
In phonology, vowel harmony is a phonological rule in which the vowels of a given domain – typically a phonological word – must share certain distinctive features (thus "in harmony"). Vowel harmony is typically long distance, meaning tha ...
.
Dialects
Ludic comprises three main dialect groups: * Ludic ** Northern (Lake) Ludic, at the northwestern shores ofLake Onega
Lake Onega (; also known as Onego; , ; ; Livvi-Karelian language, Livvi: ''Oniegujärvi''; ) is a lake in northwestern Russia, on the territory of the Republic of Karelia, Leningrad Oblast and Vologda Oblast. It belongs to the basin of the Baltic ...
** Central (River) Ludic, at settlements along river Shuya and near the city of Petrozavodsk
Petrozavodsk (, ; Karelian language, Karelian, Veps language, Vepsian and ) is the capital city of the Republic of Karelia, Russia, which stretches along the western shore of Lake Onega for some . The population of the city is 280,890 as of 2022.
...
** Kuďäŕv (Forest) Ludic, in the Mikhaylovskoye rural locality
The strongest Karelian resemblance is found in Northern Ludic, while the Kuďäŕv dialect shares the most features with Veps.
Phonology
Vowels
* Vowel length may also be distinctive.Consonants
* Sounds only occur in recent borrowings. * can also be heard as a velar . * is heard as velar when preceding velar consonants. * can be lenited as a fricative in intervocalic positions.Writing system
Ludic is written using the unified Karelian alphabet, but in some publications the letter Ü is used instead of Y, as in Veps.Phrases
* = Who are you? * = What is this? * = Which one of you is Onni? * = Why are you laughing? * = What time is it? * = When are they coming home? * = He/She leaves tomorrow.See also
*Karelian language
Karelian (; ; ; ) is a Finnic language spoken mainly by the Karelians, Karelian people in the Russian Republic of Karelia. Linguistically, Karelian is closely related to the Finnish language, Finnish dialects spoken in eastern Finland, and some ...
Notes
Literature
* * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
ISO 639 code sets - SIL International
{{DEFAULTSORT:Ludic Language Languages of Russia Karelian language Indigenous languages of European Russia