|
Paramylostoma
''Paramylostoma arcualis'' is an extinct selenosteid arthrodire placoderm from the Late Famennian Cleveland Shale of Late Devonian Ohio. It has a compressed, box-like head and thoracic armor, and large, rounded orbits. However, in comparison with other selenosteids, such as ''Selenosteus'', ''P. arcualis orbits were rather small. ''P. arcualis'' had smooth jaws that suggest the animal was durophagous Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including fossil tu .... References Selenosteidae Placoderms of North America Fossil taxa described in 1945 Paleontology in Ohio Famennian life Famennian genus first appearances Famennian genus extinctions {{Placoderm-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cleveland Shale
The Cleveland Shale, also referred to as the Cleveland Member, is a shale geologic formation in the eastern United States. Identification and name The Cleveland Shale was identified in 1870 and named for the city of Cleveland, Ohio. John Strong Newberry, director of the Ohio State Geological Survey, first identified the formation in 1870. He called it the "Cleveland Shale" and designated its type locality at Doan Brook near Cleveland. Details of the type locality and of stratigraphic nomenclature for this unit as used by the U.S. Geological Survey are available on-line at the National Geologic Map Database. Description The primary minerals in the Cleveland Shale are chlorite, illite, pyrite, and quartz. Underground, the Cleveland Shale is black, dull grayish-black, bluish-black, or brownish-black in color. In exposed outcrops, it weathers to red, reddish-brown, or medium brown. Highly weathered rock turns gray. It is fairly fissile, breaking into thin, irregularly shaped ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenosteidae
Selenosteidae is an extinct family of small to large-sized arthrodire placoderms from the Late Devonian. With the exception of the Chinese ''Phymosteus'', selenosteids lived in shallow seas in what is now Eastern North America (the Cleveland Shale), Eastern Europe (Holy Cross Mountains, Poland, and the Kellwasserkalk fauna of Bad Wildungen), and Northeastern Africa (the Anti-Atlas Mountains, Morocco). Selenosteids have, in cross section, a rounded body, a blunt snout, and tremendous orbits. The lower jaws were slender, the inferognathals usually either being finely serrated, or adapted for crushing, though, in '' Draconichthys'', the inferognathals had long prongs for seizing prey. The rostrum is very small. Taxonomy Selenosteidae is a member of the clade Aspinothoracidi, which belongs to the clade Pachyosteomorphi, one of the two major clades within Eubrachythoraci. ''Gorgonichthys'' is closely related to the family Selenosteidae, and could possibly be included in the family. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famennian
The Famennian is the latter of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Epoch. The most recent estimate for its duration estimates that it lasted from around 371.1 million years ago to 359.3 million years ago. An earlier 2012 estimate, still used by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, estimated that it lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Frasnian stage and followed by the Tournaisian stage. Major events In the seas, a novel major group of ammonoid cephalopods called clymeniids appeared, underwent tremendous diversification and spread worldwide, then just as suddenly went extinct. The beginning of the Famennian is marked by the final stages of a major extinction event, the Kellwasser Event, which is the largest component of the Late Devonian Mass extinction. The end of the Famennian experiences a smaller but still quite severe extinction event, the Hangenberg Event. A brief episode of glaciation, possibly linked to the Hangenber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Famennian Life
The Famennian is the latter of two faunal stages in the Late Devonian Epoch. The most recent estimate for its duration estimates that it lasted from around 371.1 million years ago to 359.3 million years ago. An earlier 2012 estimate, still used by the International Commission on Stratigraphy, estimated that it lasted from million years ago to million years ago. It was preceded by the Frasnian stage and followed by the Tournaisian stage. Major events In the seas, a novel major group of ammonoid cephalopods called clymeniids appeared, underwent tremendous diversification and spread worldwide, then just as suddenly went extinct. The beginning of the Famennian is marked by the final stages of a major extinction event, the Kellwasser Event, which is the largest component of the Late Devonian Mass extinction. The end of the Famennian experiences a smaller but still quite severe extinction event, the Hangenberg Event. A brief episode of glaciation, possibly linked to the Hangenber ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleontology In Ohio
Paleontology in Ohio refers to paleontological research occurring within or conducted by people from the U.S. state of Ohio. Ohio is well known for having a great quantity and diversity of fossils preserved in its Rock (geology), rocks. The state's fossil record begins early in the Paleozoic era, during the Cambrian period. Ohio was generally covered by seawater from that time on through the rest of the early Paleozoic. Local invertebrates included brachiopods, cephalopods, coral, graptolites, and trilobites. Vertebrates included bony fishes and sharks. The first land plants in the state grew during the Devonian. During the Carboniferous, Ohio became a more Ecoregion#Terrestrial, terrestrial environment with an increased diversity of plants that formed expansive swampy River delta, deltas. Amphibians and reptiles began to inhabit the state at this time, and remained present into the ensuing Permian. A gap in the local rock record spans from this point until the start of the Pleistoce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fossil Taxa Described In 1945
A fossil (from Classical Latin , ) is any preserved remains, impression, or trace of any once-living thing from a past geological age. Examples include bones, Seashell, shells, exoskeletons, stone imprints of animals or microbes, objects preserved in #Resin, amber, hair, petrified wood and DNA remnants. The totality of fossils is known as the ''fossil record''. Paleontology is the study of fossils: their age, method of formation, and evolutionary significance. Specimens are usually considered to be fossils if they are over 10,000 years old. The oldest fossils are around 3.48 billion years old to 4.1 billion years old. Early edition, published online before print. The observation in the 19th century that certain fossils were associated with certain rock stratum, strata led to the recognition of a geological timescale and the relative ages of different fossils. The development of radiometric dating techniques in the early 20th century allowed scientists to quantitativ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Placoderms Of North America
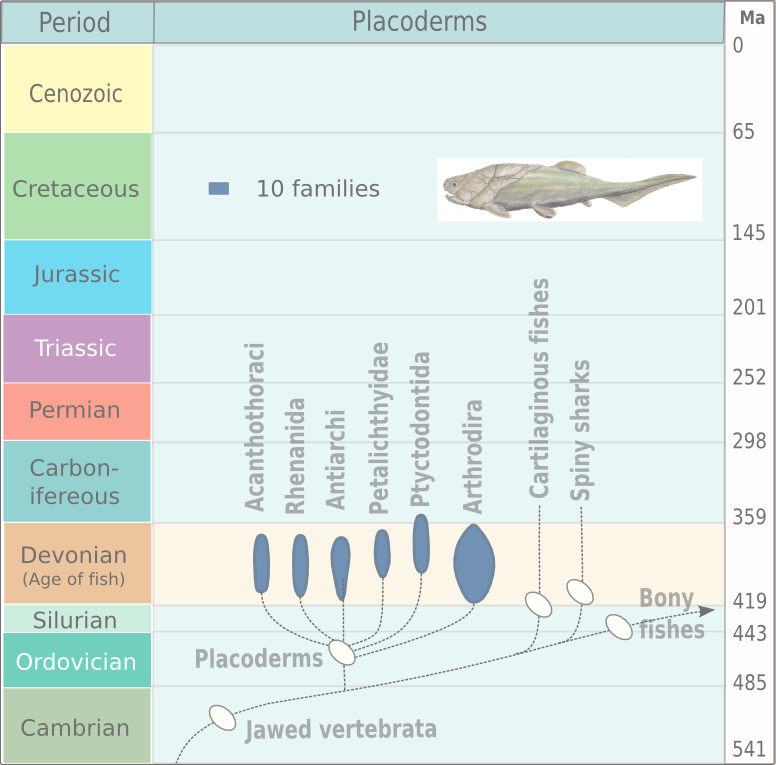
Placodermi (from Greek πλάξ 'plate' and δέρμα 'skin', literally 'plate-skinned') is a class of armoured prehistoric fish, known from fossils, which lived from the Silurian to the end of the Devonian period. Their head and thorax were covered by articulated armoured plates and the rest of the body was scaled or naked, depending on the species. Placoderms were among the first jawed fish; their jaws likely evolved from the first of their gill arches. Placoderms are thought to be paraphyletic, consisting of several distinct outgroups or sister taxa to all living jawed vertebrates, which originated among their ranks. In contrast, one 2016 analysis concluded that placodermi are likely monophyletic, though these analyses have been further dismissed with more transitional taxa between placoderms and modern gnathosthomes, solidifying their paraphyletic status. Placoderms were also the first fish to develop pelvic fins, the precursor to hindlimbs in tetrapods, as well as true t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Durophagous
Durophagy is the eating behavior of animals that consume hard-shelled or exoskeleton bearing organisms, such as corals, shelled mollusks, or crabs. It is mostly used to describe fish, but is also used when describing reptiles, including fossil turtles, placodonts and invertebrates, as well as "bone-crushing" mammalian carnivores such as hyenas. Durophagy requires special adaptions, such as blunt, strong teeth and a heavy jaw. Bite force is necessary to overcome the physical constraints of consuming more durable prey and gain a competitive advantage over other organisms by gaining access to more diverse or exclusive food resources earlier in life. Those with greater bite forces require less time to consume certain prey items as a greater bite force can increase the net rate of energy intake when foraging and enhance fitness in durophagous species. In the order Carnivora there are two dietary categories of durophagy; bonecrackers and bamboo eaters. Bonecrackers are exemplified by hy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Selenosteus
''Selenosteus brevis'' is an extinct large selenosteid arthrodire placoderm known from the Famennian Cleveland Shale of Ohio. Scrappy remains from the Frasnian Rhinestreet Shales of Erie County, New York, were attributed by Hussakof and Bryant to this genus in 1919, but, this identification is doubtful. A second species, ''S. kepleri'', was described in 1901, but, not enough differences can be seen between its specimens, and those of the type species to warrant new species status. According to its generally scrappy fossils, ''S. brevis'' had a wide skull with tremendous orbits. And as typical for selenosteids, ''S. brevis'' had weak gnathal plates. The median dorsal plate is crescent-shaped, and has a keel. The average length of the skull is about 16 centimetres from the tip of the rostrum to the posterior border of the nuchal The nape is the back of the neck. In technical anatomical/medical terminology, the nape is also called the nucha (from the Medieval Latin rendering ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ohio
Ohio () is a state in the Midwestern region of the United States. Of the fifty U.S. states, it is the 34th-largest by area, and with a population of nearly 11.8 million, is the seventh-most populous and tenth-most densely populated. The state's capital and largest city is Columbus, with the Columbus metro area, Greater Cincinnati, and Greater Cleveland being the largest metropolitan areas. Ohio is bordered by Lake Erie to the north, Pennsylvania to the east, West Virginia to the southeast, Kentucky to the southwest, Indiana to the west, and Michigan to the northwest. Ohio is historically known as the "Buckeye State" after its Ohio buckeye trees, and Ohioans are also known as "Buckeyes". Its state flag is the only non-rectangular flag of all the U.S. states. Ohio takes its name from the Ohio River, which in turn originated from the Seneca word ''ohiːyo'', meaning "good river", "great river", or "large creek". The state arose from the lands west of the Appalachian Mountai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Devonian
The Devonian ( ) is a geologic period and system of the Paleozoic era, spanning 60.3 million years from the end of the Silurian, million years ago (Mya), to the beginning of the Carboniferous, Mya. It is named after Devon, England, where rocks from this period were first studied. The first significant adaptive radiation of life on dry land occurred during the Devonian. Free-sporing vascular plants began to spread across dry land, forming extensive forests which covered the continents. By the middle of the Devonian, several groups of plants had evolved leaves and true roots, and by the end of the period the first seed-bearing plants appeared. The arthropod groups of myriapods, arachnids and hexapods also became well-established early in this period, after starting their expansion to land at least from the Ordovician period. Fish reached substantial diversity during this time, leading the Devonian to often be dubbed the Age of Fishes. The placoderms began dominating ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arthrodire
Arthrodira (Greek for "jointed neck") is an Order (biology), order of extinct armored, jawed fishes of the class Placodermi that flourished in the Devonian period before their sudden extinction, surviving for about 50 million years and penetrating most marine ecological niches. Arthrodires were the largest and most diverse of all groups of Placoderms. Description Arthrodire placoderms are notable for the movable joint between armor surrounding their heads and bodies. Like all placoderms, they lacked distinct teeth; instead, they used the sharpened edges of a bony plate on their jawbone as a biting surface. The eye sockets are protected by a bony ring, a feature shared by birds and some ichthyosaurs. Early arthrodires, such as the genus ''Arctolepis'', were well-armoured fishes with flattened bodies. The largest member of this group, ''Dunkleosteus'', was a true superpredator of the latest Devonian period, reaching as much as 6 m in length. In contrast, the long-nosed ''Rolfosteus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |