|
Ovnit
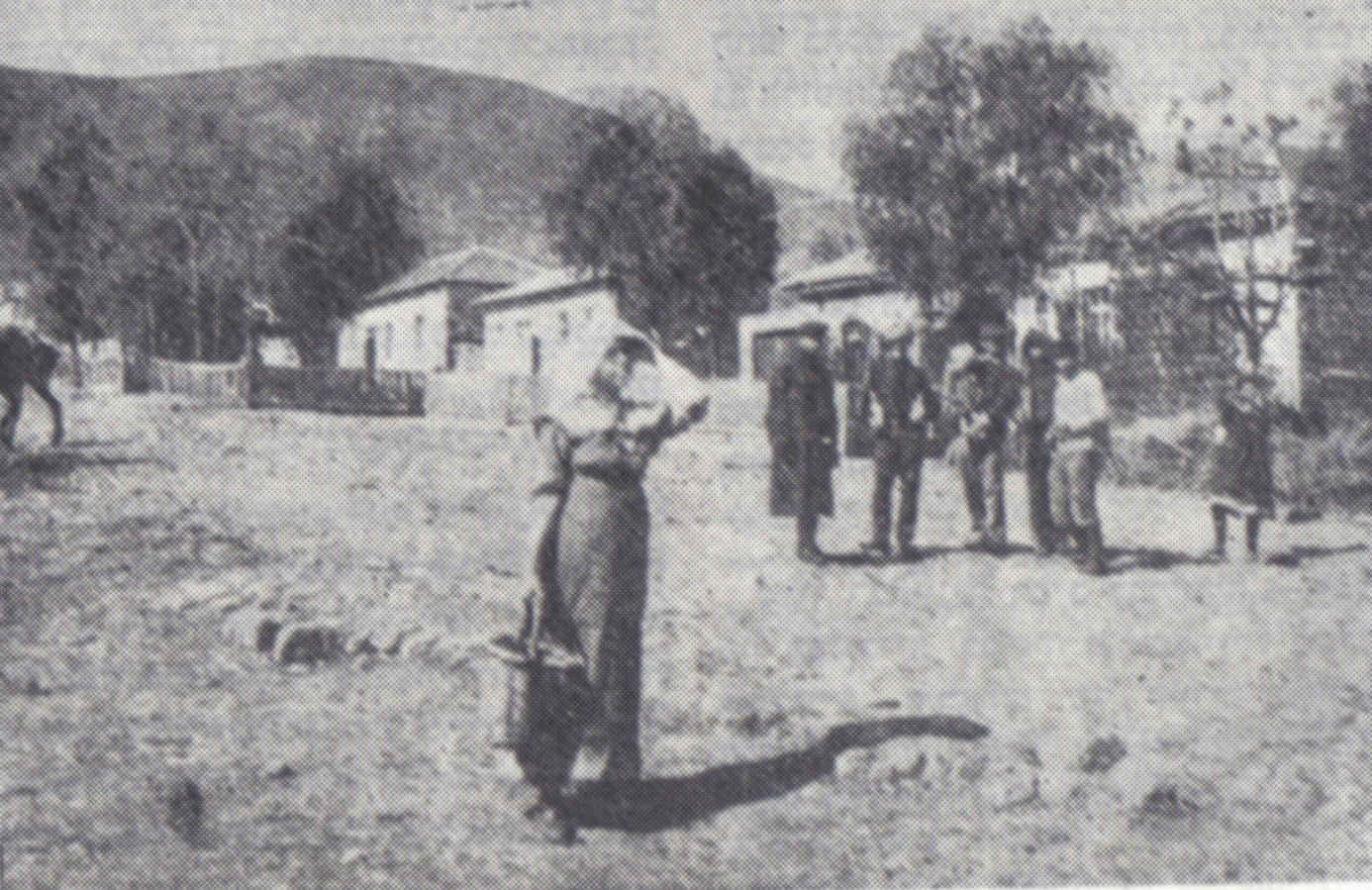
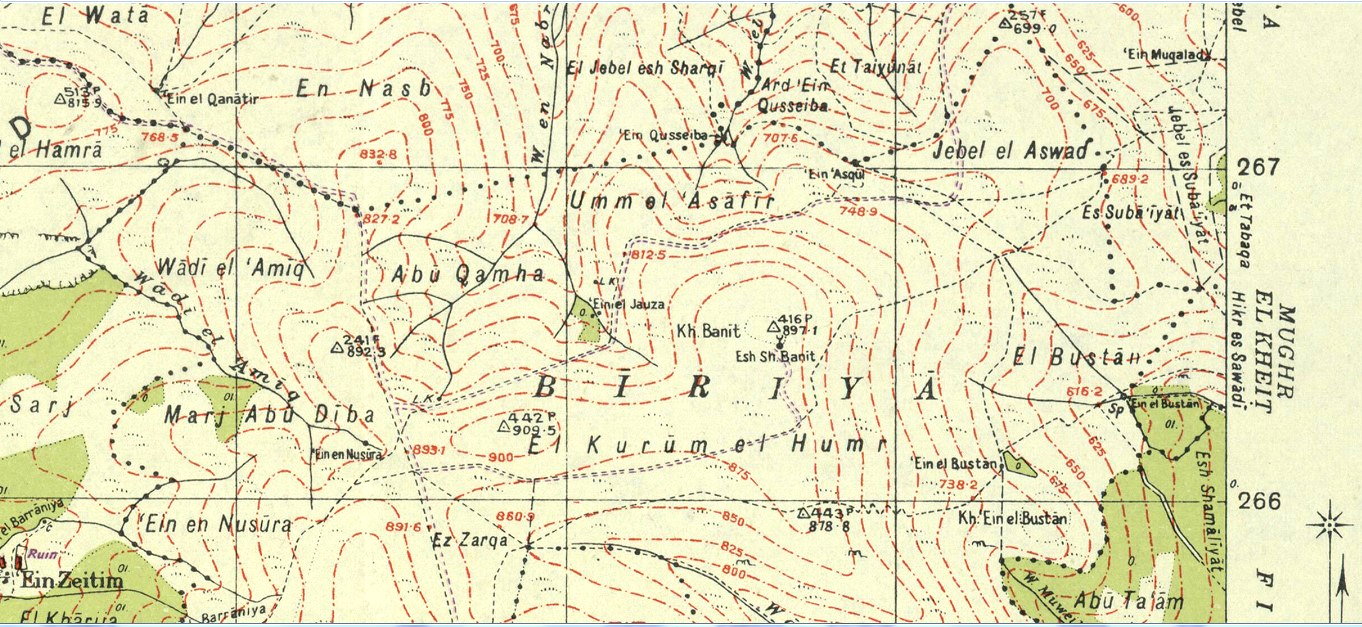
Jamnith ( gr, Ἰαμνειθ), also Jabnith, Yavnit (), Iamnia, or in medieval parlance, Ibnit / Abnit / Ovnit, is a ruin in the Upper Galilee that came to renown during the First Jewish Revolt in the 1st-century CE. The ruin, known locally by the name ''Khurbet esh-Sheikh Banit'', or simply ''Kh. Banît'', lies about to the northeast of Safed, in the Biriya Forest, and was once a fortified town towards the northeast of Mount Canaan (Hebrew: ''Har Kena'an''), upon a hill called ''Har Yavnit''. The hill on which the village ruins lie rises above sea level and overlooks the Hula valley. Access to the ruin is now restricted because of an enclosed military installation built over the site. The village is mentioned twice in the writings of Josephus as being in the Upper Galilee; once in ''The Jewish War'' (2.20.6) under the appellation Ἰαμνειθ, and again in ''Vita'' §37 under the name Ίαμνια, and is distinguished from the Yavne, Jamnia of Judaea. Josephus testifies of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jamnith = Kh
Jamnith ( gr, Ἰαμνειθ), also Jabnith, Yavnit (), Iamnia, or in medieval parlance, Ibnit / Abnit / Ovnit, is a ruin in the Upper Galilee that came to renown during the First Jewish Revolt in the 1st-century CE. The ruin, known locally by the name ''Khurbet esh-Sheikh Banit'', or simply ''Kh. Banît'', lies about to the northeast of Safed, in the Biriya Forest, and was once a fortified town towards the northeast of Mount Canaan (Hebrew: ''Har Kena'an''), upon a hill called ''Har Yavnit''. The hill on which the village ruins lie rises above sea level and overlooks the Hula valley. Access to the ruin is now restricted because of an enclosed military installation built over the site. The village is mentioned twice in the writings of Josephus as being in the Upper Galilee; once in ''The Jewish War'' (2.20.6) under the appellation Ἰαμνειθ, and again in ''Vita'' §37 under the name Ίαμνια, and is distinguished from the Jamnia of Judaea. Josephus testifies of h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judah III
Judah III (or Nesi'ah II; Hebrew: יהודה נשיאה; יודן נשיאה), Yudan Nesiah, was a prominent Jewish sage, who held the office of ''Nasi'' of the ancient Jewish Sanhedrin between about 290 and 320 CE (fourth generation of amoraim). Biography He was the son of Gamaliel IV, and grandson of Judah II. It is often difficult to know when the Mishna and Talmud are referring to Judah II or Judah III; they do not clearly distinguish between them. Since the title "Nesi'ah" was borne by both, which of the two in any citation is meant by "Judah Nesi'ah" can be gathered only from internal evidence, especially from the names of the scholars mentioned in the context. He was a pupil of R. Johanan bar Nappaha (d. 279). In a question regarding the time of the new moon, which he sent to Rav Ammi, he introduces a teaching taught to him by Johanan with the words: "Know that R. Johanan has taught us thus all his life long". Judah III commissioned Johanan's pupils Ammi and Assi, who ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mishnah
The Mishnah or the Mishna (; he, מִשְׁנָה, "study by repetition", from the verb ''shanah'' , or "to study and review", also "secondary") is the first major written collection of the Jewish oral traditions which is known as the Oral Torah. It is also the first major work of rabbinic literature. The Mishnah was redacted by Judah ha-Nasi probably in Beit Shearim or Sepphoris at the beginning of the 3rd century CE in a time when, according to the Talmud, the persecution of the Jews and the passage of time raised the possibility that the details of the oral traditions of the Pharisees from the Second Temple period (516 BCE – 70 CE) would be forgotten. Most of the Mishnah is written in Mishnaic Hebrew, but some parts are in Aramaic. The Mishnah consists of six orders (', singular ' ), each containing 7–12 tractates (', singular ' ; lit. "web"), 63 in total, and further subdivided into chapters and paragraphs. The word ''Mishnah'' can also indicate a single paragraph of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Banias
Banias or Banyas ( ar, بانياس الحولة; he, בניאס, label=Modern Hebrew; Judeo-Aramaic, Medieval Hebrew: פמייס, etc.; grc, Πανεάς) is a site in the Golan Heights near a natural spring, once associated with the Greek god Pan. It had been inhabited for 2,000 years, until it was abandoned and destroyed following the Six Day War.How modern disputes have reshaped the ancient city of Banias : "In June 1967, the penultimate day of the Six Day War saw Israeli tanks storm into Banias in breach of a UN ceasefire accepted by Syria hours earlier. The Israeli general Moshe Dayan had decided to act u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rava (amora)
Abba ben Joseph bar Ḥama (c. 280 – 352 CE), who is exclusively referred to in the Talmud by the name Rava (), was a Babylonian rabbi who belonged to the fourth generation of amoraim. He is known for his debates with Abaye, and is one of the most often cited rabbis in the Talmud. Biography He was born about 280 CE in Mahoza (a suburb of Ctesiphon, the capital of Persia), where his father was a wealthy and distinguished scholar. In his youth Rava went to Sura, where he attended the lectures of Rav Chisda and associated with Rami bar Hama. About ten years after Rami's death Rava married his widow, the daughter of Rav Chisda. It is said that earlier Rav Chisda's daughter sat in her father's classroom, while his students, Rava and Rami bar Hama, stand before them. When Rav Chisda asked her which of the two she wants to marry, she replied "both of them," and Rava added, "I'll be the last one" (commentators let us know that she indeed married Rami first and Rava second). They had fiv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abaye
Abaye ( he, אַבַּיֵי) was a rabbi of the Jewish Talmud who lived in Babylonia, known as an Amoraim, amora of the fourth generation. He was born about the close of the third century, and died 337 Common Era, CE. Biography His father, Kaylil, was the brother of Rabbah bar Nachmani (Rabbah), a teacher at the Academy of Pumbedita. Abaye's real name was Nachmani, after his grandfather. Left an orphan at an early age, he was adopted by his uncle, Rabbah. Opinions differ as to the source of his nickname Abaye. Some say it is a diminutive of the word ''abba'' (father), meaning "Little Father", to avoid confusion with his grandfather of the same name (or perhaps to show respect for that grandfather). Others say that Abaye was not a nickname, but an acronym of the Biblical phrase "For through You the orphan receives mercy", alluding to Abaye's being an orphan. A modern opinion is that Abaye is an old Aramaic word meaning "comfort", and thus a direct translation of his Hebrew name, Nac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Talmudic
The Talmud (; he, , Talmūḏ) is the central text of Rabbinic Judaism and the primary source of Jewish religious law (''halakha'') and Jewish theology. Until the advent of modernity, in nearly all Jewish communities, the Talmud was the centerpiece of Jewish cultural life and was foundational to "all Jewish thought and aspirations", serving also as "the guide for the daily life" of Jews. The term ''Talmud'' normally refers to the collection of writings named specifically the Babylonian Talmud (), although there is also an earlier collection known as the Jerusalem Talmud (). It may also traditionally be called (), a Hebrew abbreviation of , or the "six orders" of the Mishnah. The Talmud has two components: the Mishnah (, 200 CE), a written compendium of the Oral Torah; and the Gemara (, 500 CE), an elucidation of the Mishnah and related Tannaitic writings that often ventures onto other subjects and expounds broadly on the Hebrew Bible. The term "Talmud" may refer to eith ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Keter Publishing House
Keter ( he-a, כֶּתֶר, Keter.ogg, link=yes, ''Keṯer'', lit. "crown") also known as Kether, is the topmost of the sephirot of the Tree of Life in Kabbalah. Since its meaning is "crown", it is interpreted as both the "topmost" of the Sephirot and the "regal crown" of the Sephirot. It is between Chokhmah and Binah (with Chokhmah on the right and Binah on the left) and it sits above Tiferet. It is usually given three paths, to Chokhmah, Tiferet and Binah. Keter is so sublime, it is called in the Zohar "the most hidden of all hidden things", and is completely incomprehensible to man. It is also described as absolute compassion, and Moses ben Jacob Cordovero describes it as the source of the 13 Supernal Attributes of Mercy. Keter is invisible and colorless. Description According to the book Bahir: "What are the ten utterances? The first is supreme crown, blessed be His name and His people."Arthur Green. Guide to the Zohar The first Sephirah is called the Crown, since a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yavne'el
Yavne'el ( he, יַבְנְאֵל, ar, يفنيئيل) is a moshava and local council in the Northern District of Israel. Founded in 1901, it is one of the oldest rural Jewish communities in the country. According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics (CBS), in it had a population of . In 2008 the population had been of 3,100, with a growth rate of 1.4%. History Archaeological overview Remains from the Late Bronze Age,Leibowitz 1995, cited in Hanna, 2017 Yavne’el/ref>Brink, van den, 2017 Yavne’el, Tel Yin’am/ref> Iron Age I–II, Persian, Hellenistic, Roman, late Byzantine,Hanna, 2009Yavne’el/ref> early MuslimHanna, 2017 Yavne’el/ref> and Mamluk periods have been found here. A residential building constructed in the Umayyad period that continued to be inhabited during the Abbasid period (eighth–tenth centuries CE) has been excavated here. Remains from the Mamluk period have also been found. Ottoman period Arab village During the Ottoman period the Muslim ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adolf Neubauer
Adolf Neubauer (11 March 1831 in Bittse, Hungary – 6 April 1907, London) was at the Bodleian Library and reader in Rabbinic Hebrew at Oxford University. Biography He was born in Bittse (Nagybiccse), Upper Hungary (now Bytča in Slovakia). The Kingdom of Hungary was then part of the Austrian Empire. He received a thorough education in rabbinical literature. In 1850 he obtained a position at the Austrian consulate in Jerusalem. At this time, he published articles about the situation of the city's Jewish population, which aroused the anger of some leaders of that community, with whom he became involved in a prolonged controversy. In 1857 he moved to Paris, where he continued his studies of Judaism and started producing scientific publications. His earliest contributions were made to the '' Allgemeine Zeitung des Judenthums'' and the ''Journal Asiatique'' (Dec. 1861). Works In 1865 he published a volume entitled ''Meleket ha-Shir'', a collection of extracts from manusc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Palestine (region)
Palestine ( el, Παλαιστίνη, ; la, Palaestina; ar, فلسطين, , , ; he, פלשתינה, ) is a geographic region in Western Asia. It is usually considered to include Israel and the State of Palestine (i.e. West Bank and Gaza Strip), though some definitions also include part of northwestern Jordan. The first written records to attest the name of the region were those of the Twentieth dynasty of Egypt, which used the term "Peleset" in reference to the neighboring people or land. In the 8th century, Assyrian inscriptions refer to the region of "Palashtu" or "Pilistu". In the Hellenistic period, these names were carried over into Greek, appearing in the Histories of Herodotus in the more recognizable form of "Palaistine". The Roman Empire initially used other terms for the region, such as Judaea, but renamed the region Syria Palaestina after the Bar Kokhba revolt. During the Byzantine period, the region was split into the provinces of Palaestina Prima, Palaestin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)


