|
Ospedale Degli Incurabili, Venice
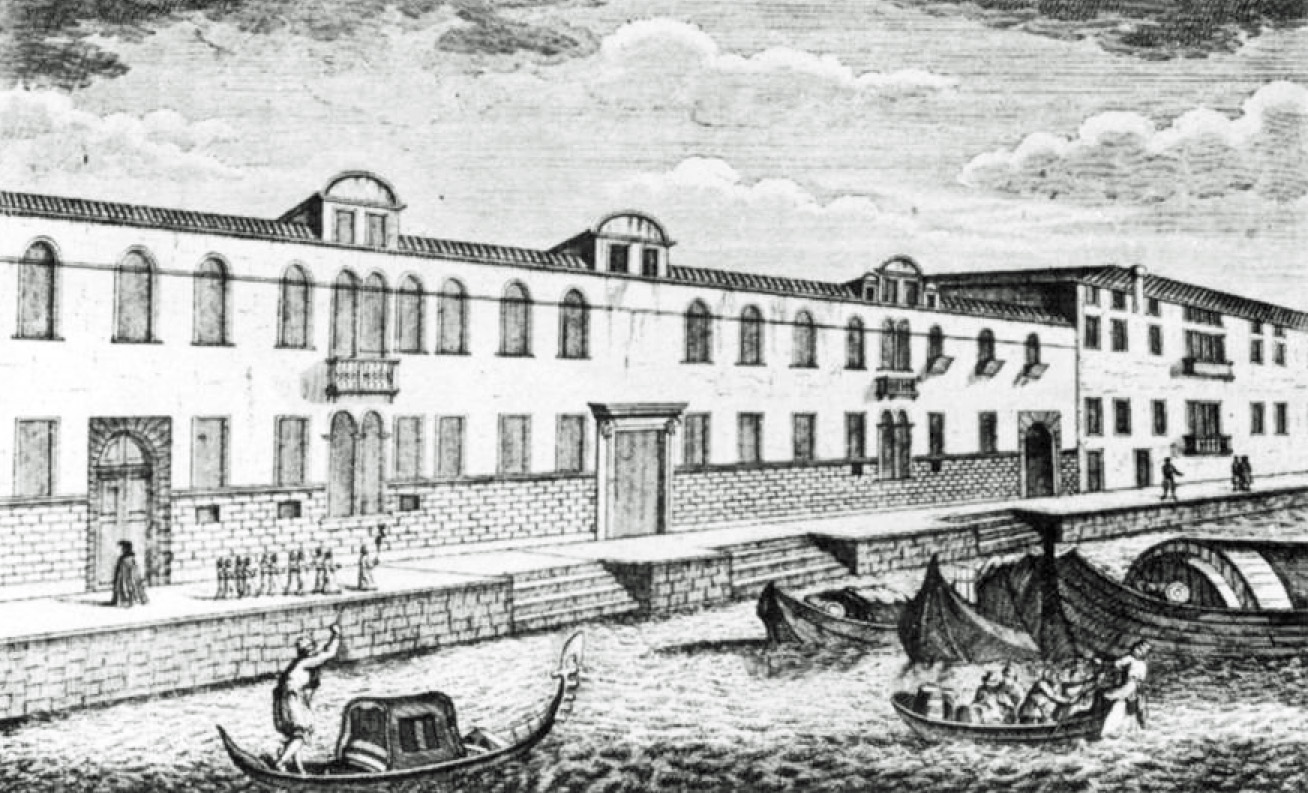
The Ospedale degli Incurabili is a large sixteenth-century hospital building on the , in the sestiere of Dorsoduro, in Venice in north-eastern Italy. Today it is occupied by the Accademia di Belle Arti di Venezia. It was built in the second half of the sixteenth century; the church – which no longer exists – may have been designed by Jacopo Sansovino. History The Ospedale degli Incurabili dates from the early sixteenth century; the first documented mention of it is from 1522. It was established by Gaetano da Thiene with money donated by two noblewomen, Maria Grimani and Maria Malipiero. It was at first intended to accommodate those with incurable diseases such as syphilis, but later – like several other Venetian institutions – became an orphanage. The first structure was probably of wood. From about 1565 – when a request for funds was made to the Senate – until his death in 1597, Antonio da Ponte was responsible for the construction of a substantial building ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fondamenta Delle Zattere
Fondamente (; oc, Fondamenta) is a Communes of France, commune in the Aveyron Departments of France, department in southern France. Geography The village lies on the right bank of the Sorgues River, Sorgues, which flows west-southwest through the northern part of the commune. Population See also *Communes of the Aveyron department References Communes of Aveyron Aveyron communes articles needing translation from French Wikipedia {{Aveyron-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader who rose to prominence during the French Revolution and led successful campaigns during the Revolutionary Wars. He was the ''de facto'' leader of the French Republic as First Consul from 1799 to 1804, then Emperor of the French from 1804 until 1814 and again in 1815. Napoleon's political and cultural legacy endures to this day, as a highly celebrated and controversial leader. He initiated many liberal reforms that have persisted in society, and is considered one of the greatest military commanders in history. His wars and campaigns are studied by militaries all over the world. Between three and six million civilians and soldiers perished in what became known as the Napoleonic Wars. Napoleon was born on the island of Corsica, not long af ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ospedale Della Pietà
The Ospedale della Pietà was a convent, orphanage, and music school in Venice. Like other Venetian ''ospedali'', the Pietà was first established as a hospice for the needy. A group of Venetian nuns, called the Consorelle di Santa Maria dell’Umiltà, established this charitable institution for orphans and abandoned girls in the fourteenth century. By the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries the Pietà – along with the three other charitable Ospedali Grandi – was well known for its all-female musical ensembles that attracted tourists and patrons from around Europe. Musical activity Infants could be left at the Pietà via the ''scaffetta'', a window only large enough to admit infants. Not all infants were female, nor were they necessarily orphans. Through the seventeenth century all four of the surviving ''ospedali'' gained increasing attention through the performances of sacred music by their female musicians, known as ''figlie di coro''. Formal rules for the training of ''fi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ospedali Grandi
The four great Venetian Ospedali (Ospedali Grandi, also referred to as the Ospedali Maggiori) - the Ospedale della Pietà, the Ospedale degl'Incurabili, the Ospedale di Santa Maria dei Derelitti, and the Ospedale di San Lazzaro dei Mendicanti - were charitable hospices, which provided a wide range of services for the needy of Venice. They are most famously recognized for educating select female pupils (called ''figlie del coro'') to professional levels of musicianship and attracting many European tourists to hear their all-female ensembles perform religious services and special concerts throughout the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries. The musical training in the Ospedali Grandi is often thought of as a precursor to the training in European conservatories of the 19th century. Historical background Venice had a long history of caring for its sick, homeless, poor, and orphaned before the four Ospedali became recognized as a group musical institutions. The Ospedale degl’Incurabil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Francesco Saverio
Francis Xavier (born Francisco de Jasso y Azpilicueta; Latin: ''Franciscus Xaverius''; Basque: ''Frantzisko Xabierkoa''; French: ''François Xavier''; Spanish: ''Francisco Javier''; Portuguese: ''Francisco Xavier''; 7 April 15063 December 1552), venerated as Saint Francis Xavier, was a Spanish Catholic missionary and saint who was a co-founder of the Society of Jesus. Born in Javier (Xavier in Old Spanish and in Navarro-Aragonese, or Xabier, a Basque word meaning "new house"), in the Kingdom of Navarre (in present-day Spain), he was a companion of Ignatius of Loyola and one of the first seven Jesuits who took vows of poverty and chastity at Montmartre, Paris in 1534. He led an extensive mission into Asia, mainly the Portuguese Empire in the East, and was influential in evangelisation work, most notably in early modern India. He was extensively involved in the missionary activity in Portuguese India. In 1546, Francis Xavier proposed the establishment of the Goan Inquisition in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerolamo Miani
Gerolamo Emiliani, CRS ( it, Gerolamo Emiliani also Jerome Aemilian, Hiëronymus Emiliani) (1486 – 8 February 1537) was an Italian humanitarian, founder of the Somaschi Fathers, and is considered a saint by the Catholic Church. Born in Venice, he spent some time in the military, and later served as a magistrate. Emiliani provided for the sick, the hungry, and orphans; and persuaded others to do likewise. Through his good offices a number of hospitals and orphanages were established in several northern Italian towns. He was canonized in 1767 and is the patron saint of orphans. Biography Jerome was born in Venice, the son of Angelo Emiliani (popularly called Miani) and Eleonore Mauroceni. His father died when he was a teenager and Jerome ran away at the age of 15 to join the army. In 1508, he participated in the defense of Castelnuovo against the League of Cambray (this was two years before Pope Julius II joined the Venetians). He was appointed governor of a fortress in the m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ignazio Da Loyola
Ignatius of Loyola, S.J. (born Íñigo López de Oñaz y Loyola; eu, Ignazio Loiolakoa; es, Ignacio de Loyola; la, Ignatius de Loyola; – 31 July 1556), venerated as Saint Ignatius of Loyola, was a Spanish Catholic priest and theologian, who, with Peter Faber and Francis Xavier, founded the religious order of the Society of Jesus (The Jesuits), and became its first Superior General, in Paris in 1541. He envisioned the purpose of the Society of Jesus to be missionary work and teaching. In addition to the vows of chastity, obedience and poverty of other religious orders in the church, Loyola instituted a fourth vow for Jesuits of obedience to the Pope, to engage in projects ordained by the pontiff. Jesuits were instrumental in leading the Counter-Reformation. As a former soldier, Ignatius paid particular attention to the spiritual formation of his recruits and recorded his method in the ''Spiritual Exercises'' (1548). In time, the method has become known as Ignatian spiritua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paolo Veronese
Paolo Caliari (152819 April 1588), known as Paolo Veronese ( , also , ), was an Italian Renaissance painter based in Venice, known for extremely large history paintings of religion and mythology, such as ''The Wedding at Cana'' (1563) and ''The Feast in the House of Levi'' (1573). Included with Titian, a generation older, and Tintoretto, a decade senior, Veronese is one of the "great trio that dominated Venetian painting of the ''cinquecento''" and the Late Renaissance in the 16th century.Rosand, 107 Known as a supreme colorist, and after an early period with Mannerism, Paolo Veronese developed a naturalist style of painting, influenced by Titian. His most famous works are elaborate narrative cycles, executed in a dramatic and colorful style, full of majestic architectural settings and glittering pageantry. His large paintings of biblical feasts, crowded with figures, painted for the refectories of monasteries in Venice and Verona are especially famous, and he was also the leadi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tintoretto
Tintoretto ( , , ; born Jacopo Robusti; late September or early October 1518Bernari and de Vecchi 1970, p. 83.31 May 1594) was an Italian painter identified with the Venetian school. His contemporaries both admired and criticized the speed with which he painted, and the unprecedented boldness of his brushwork. For his phenomenal energy in painting he was termed Il Furioso ("The Furious"). His work is characterised by his muscular figures, dramatic gestures and bold use of perspective, in the Mannerist style. Life The years of apprenticeship Tintoretto was born in Venice in 1518. His father, Battista, was a dyer, or ''tintore''; hence the son got the nickname of Tintoretto, "little dyer", or "dyer's boy". Tintoretto is known to have had at least one sibling, a brother named Domenico, although an unreliable 17th-century account says his siblings numbered 22. The family was believed to have originated from Brescia, in Lombardy, then part of the Republic of Venice. Older studies ga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sante Peranda
Sante Peranda (1566–1638) was an Italian painter of the late-Renaissance period. He was a pupil of the painter Leonardo Corona and later Palma il Giovane. Also known as ''Santo Peranda''. He painted a ''Descent from the cross'' for San Procolo in Venice. He painted ''The defeat of the Saracens'' for the Ducal Palace of Modena. He painted the ''Gathering of the Manna'' for the church of the San Bartolome. In 1623 he finished ''Glorious Mysteries'' for the church of San Nicolò in Treviso Treviso ( , ; vec, Trevixo) is a city and '' comune'' in the Veneto region of northern Italy. It is the capital of the province of Treviso and the municipality has 84,669 inhabitants (as of September 2017). Some 3,000 live within the Ven .... Among his pupils were Francesco Maffei, Matteo Ponzone, and Filippo Zaniberti.Hobbes et al. p 194 References * * 1566 births 1638 deaths 16th-century Italian painters Italian male painters 17th-century Italian painters Pai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |




_Casa_di_Tintoretto.jpg)