|
Oronce Finé
Oronce Finé (or Fine; Latin: ''Orontius Finnaeus'' or ''Finaeus''; it, Oronzio Fineo; 20 December 1494 – 8 August 1555) was a French mathematician, cartographer, editor and book illustrator. Life Born in Briançon, the son and grandson of physicians, he was educated in Paris ( Collège de Navarre) and obtained a degree in medicine in 1522. Fine grew up in an academic household and his parents contribution to sciences was notable in France at the time. Much of Fines early childhood was shaped by his fathers involvement and support of sciences. Fine's father in addition to being a physician was a strong student in astronomy. He had created many astronomical instruments and published a treatise which was one of the few astronomical incunabula of French origin. Fine's university was known as a leading center at Paris for the study of scholastic philosophy and theology. There he fostered his editing ability and later printed many editions of writings from scholars. It is believ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Briançon
Briançon (, ) is the sole subprefecture of the Hautes-Alpes department in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region in Southeastern France. It is the highest city in France at an altitude of , based on the national definition as a community containing more than 2,000 inhabitants. Its most recent population estimate is 11,084 (as of 2018) for the commune. Briançon has been part of the Fortifications of Vauban UNESCO World Heritage Sites since they were established in 2008. History Briançon was the ''Brigantium'' of the Romans and formed part of the kingdom of King Cottius. Brigantium was marked as the first place in Gallia after Alpis Cottia (Mont Genèvre). At Brigantium the road branched, to the west through Grenoble to ''Vienna'' (modern Vienne), on the Rhone; to the south through ''Ebrodunum'' (modern Embrun), to ''Vapincum'' (modern Gap). Both the Antonine Itinerary and the Table give the route from Brigantium to Vapincum. The Table places Brigantium 6 M.P. from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ivory
Ivory is a hard, white material from the tusks (traditionally from elephants) and teeth of animals, that consists mainly of dentine, one of the physical structures of teeth and tusks. The chemical structure of the teeth and tusks of mammals is the same, regardless of the species of origin, but ivory contains structures of mineralised collagen. The trade in certain teeth and tusks other than elephant is well established and widespread; therefore, "ivory" can correctly be used to describe any mammalian teeth or tusks of commercial interest which are large enough to be carved or scrimshawed. Besides natural ivory, ivory can also be produced synthetically, hence (unlike natural ivory) not requiring the retrieval of the material from animals. Tagua nuts can also be carved like ivory. The trade of finished goods of ivory products has its origins in the Indus Valley. Ivory is a main product that is seen in abundance and was used for trading in Harappan civilization. Finished iv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf Of Mexico
The Gulf of Mexico ( es, Golfo de México) is an ocean basin and a marginal sea of the Atlantic Ocean, largely surrounded by the North American continent. It is bounded on the northeast, north and northwest by the Gulf Coast of the United States; on the southwest and south by the Mexican states of Tamaulipas, Veracruz, Tabasco, Campeche, Yucatan, and Quintana Roo; and on the southeast by Cuba. The Southern U.S. states of Texas, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, and Florida, which border the Gulf on the north, are often referred to as the " Third Coast" of the United States (in addition to its Atlantic and Pacific coasts). The Gulf of Mexico took shape approximately 300 million years ago as a result of plate tectonics.Huerta, A.D., and D.L. Harry (2012) ''Wilson cycles, tectonic inheritance, and rifting of the North American Gulf of Mexico continental margin.'' Geosphere. 8(1):GES00725.1, first published on March 6, 2012, The Gulf of Mexico basin is roughly ov ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
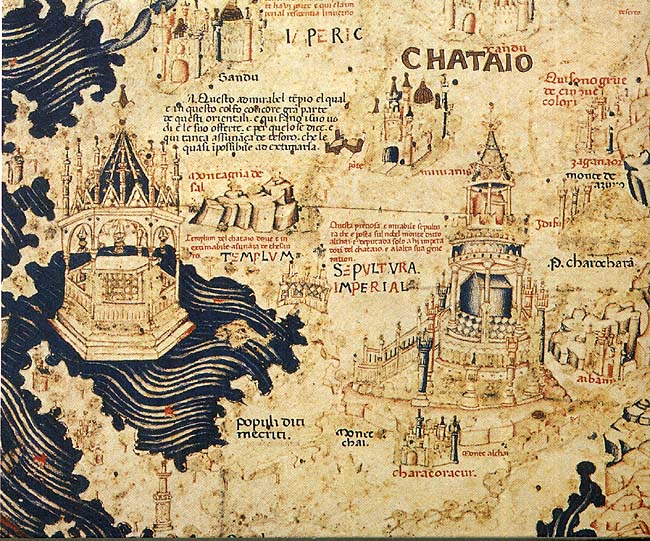
Cathay
Cathay (; ) is a historical name for China that was used in Europe. During the early modern period, the term ''Cathay'' initially evolved as a term referring to what is now Northern China, completely separate and distinct from China, which was a reference to southern China. As knowledge of East Asia increased, Cathay came to be seen as the same polity as China as a whole. The term ''Cathay'' became a poetic name for China. The name ''Cathay'' originates from the word '' Khitan'', a name of a para-Mongolic nomadic people who ruled the Liao dynasty in northern China from 916 to 1125, and who later migrated west after they were overthrown by the Jin dynasty to form the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) for another century thereafter. Originally, this name was the name applied by Central and Western Asians and Europeans to northern China; the name was also used in Marco Polo's book on his travels in Yuan dynasty China (he referred to southern China as '' Mangi''). Od ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tangut People
The Tangut people ( Tangut: , ''mjɨ nja̱'' or , ''mji dzjwo''; ; ; mn, Тангуд) were a Tibeto-Burman tribal union that founded and inhabited the Western Xia dynasty. The group initially lived under Tuyuhun authority, but later submitted to the Tang dynasty, prior to their establishment of the Western Xia. They spoke the Tangut language, which was previously believed to be one of the Qiangic languages or Yi languages that belong to the Tibeto-Burman family. Phylogenetic and historical linguistic accounts, however, reveal that Tangut belonged to the Gyalrongic languages. Language The Tangut language, otherwise known as ''Fan'', belongs to the Tibeto-Burman branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. Like many other Sino-Tibetan languages, it is a tonal language with predominantly mono-syllabic roots, but it shares certain grammatical traits central to the Tibeto-Burman branch. It is still debated as to whether Tangut belongs to the Yi or Qiangic subdivision of Tibeto- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Names Of China
The names of China include the many contemporary and historical appellations given in various languages for the East Asian country known as ''Zhōngguó'' (/, "middle country") in its national language, Standard Mandarin. China, the name in English for the country, was derived from Portuguese in the 16th century, and became common usage in the West in the subsequent centuries. It is believed to be a borrowing from Middle Persian, and some have traced it further back to Sanskrit. It is also thought that the ultimate source of the name China is the Chinese word "Qin" (), the name of the Qin dynasty, dynasty that unified China but also existed as a Qin (state), state for many centuries prior. There are, however, other alternative suggestions for the origin of the word. Chinese names for China, aside from ''Zhongguo'', include ''Zhonghua minzu, Zhōnghuá'' (/, "central beauty"), ''Huaxia, Huáxià'' (/, "beautiful grandness"), ''Shénzhōu'' (, "divine state") and ''Jiǔzhōu'' (, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Marco Polo
Marco Polo (, , ; 8 January 1324) was a Venetian merchant, explorer and writer who travelled through Asia along the Silk Road between 1271 and 1295. His travels are recorded in '' The Travels of Marco Polo'' (also known as ''Book of the Marvels of the World '' and ''Il Milione'', ), a book that described to Europeans the then mysterious culture and inner workings of the Eastern world, including the wealth and great size of the Mongol Empire and China in the Yuan Dynasty, giving their first comprehensive look into China, Persia, India, Japan and other Asian cities and countries. Born in Venice, Marco learned the mercantile trade from his father and his uncle, Niccolò and Maffeo, who travelled through Asia and met Kublai Khan. In 1269, they returned to Venice to meet Marco for the first time. The three of them embarked on an epic journey to Asia, exploring many places along the Silk Road until they reached Cathay (China). They were received by the royal court of Kublai Kha ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toponymy
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' ( proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of any geographical feature, and full scope of the term also includes proper names of all cosmographical features. In a more specific sense, the term ''toponymy'' refers to an inventory of toponyms, while the discipline researching such names is referred to as ''toponymics'' or ''toponomastics''. Toponymy is a branch of onomastics, the study of proper names of all kinds. A person who studies toponymy is called ''toponymist''. Etymology The term toponymy come from grc, τόπος / , 'place', and / , 'name'. The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' records ''toponymy'' (meaning "place name") first appearing in English in 1876. Since then, ''toponym'' has come to replace the term ''place-name'' in professional discourse among geographers. Topo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importance to later Byzantine, Islamic, and Western European science. The first is the astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', although it was originally entitled the ''Mathēmatikē Syntaxis'' or ''Mathematical Treatise'', and later known as ''The Greatest Treatise''. The second is the ''Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ''Apotelesmatika'' (lit. "On the Effects") but more commonly known as the '' Tetrábiblos'', from the Koine Greek meaning "Four Books", or by its Latin equivalent ''Qua ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
New World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. 33: "[16c: from the feminine of ''Americus'', the Latinized first name of the explorer Amerigo Vespucci (1454–1512). The name ''America'' first appeared on a map in 1507 by the German cartographer Martin Waldseemüller, referring to the area now called Brazil]. Since the 16c, a name of the western hemisphere, often in the plural ''Americas'' and more or less synonymous with ''the New World''. Since the 18c, a name of the United States of America. The second sense is now primary in English: ... However, the term is open to uncertainties: ..." The term gained prominence in the early 16th century, during Europe's Age of Discovery, shortly after the Italian explorer Amerigo Vespucci concluded that America (now often called ''th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gerardus Mercator
Gerardus Mercator (; 5 March 1512 – 2 December 1594) was a 16th-century geographer, cosmographer and cartographer from the County of Flanders. He is most renowned for creating the 1569 world map based on a new projection which represented sailing courses of constant bearing (rhumb lines) as straight lines—an innovation that is still employed in nautical charts. Mercator was a highly influential pioneer in the history of cartography. Monmonier, Mark: ''Rhumb Lines and Map Wars: A Social History of the Mercator Projection''. (Chicago: University of Chicago Press, 2004)Van der Krogt, Peter (2015), 'Chapter 6: Gerhard Mercator and his Cosmography: How the 'Atlas' became an Atlas,'; in: Gerhard Holzer, et al. (eds.), ''A World of Innovation: Cartography in the Time of Gerhard Mercator''. (Newcastle upon Tyne: Cambridge Scholars Publishing, 2015), pp. 112–130 Along with Gemma Frisius and Abraham Ortelius, he is generally considered one of the founders of the Netherlandish ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
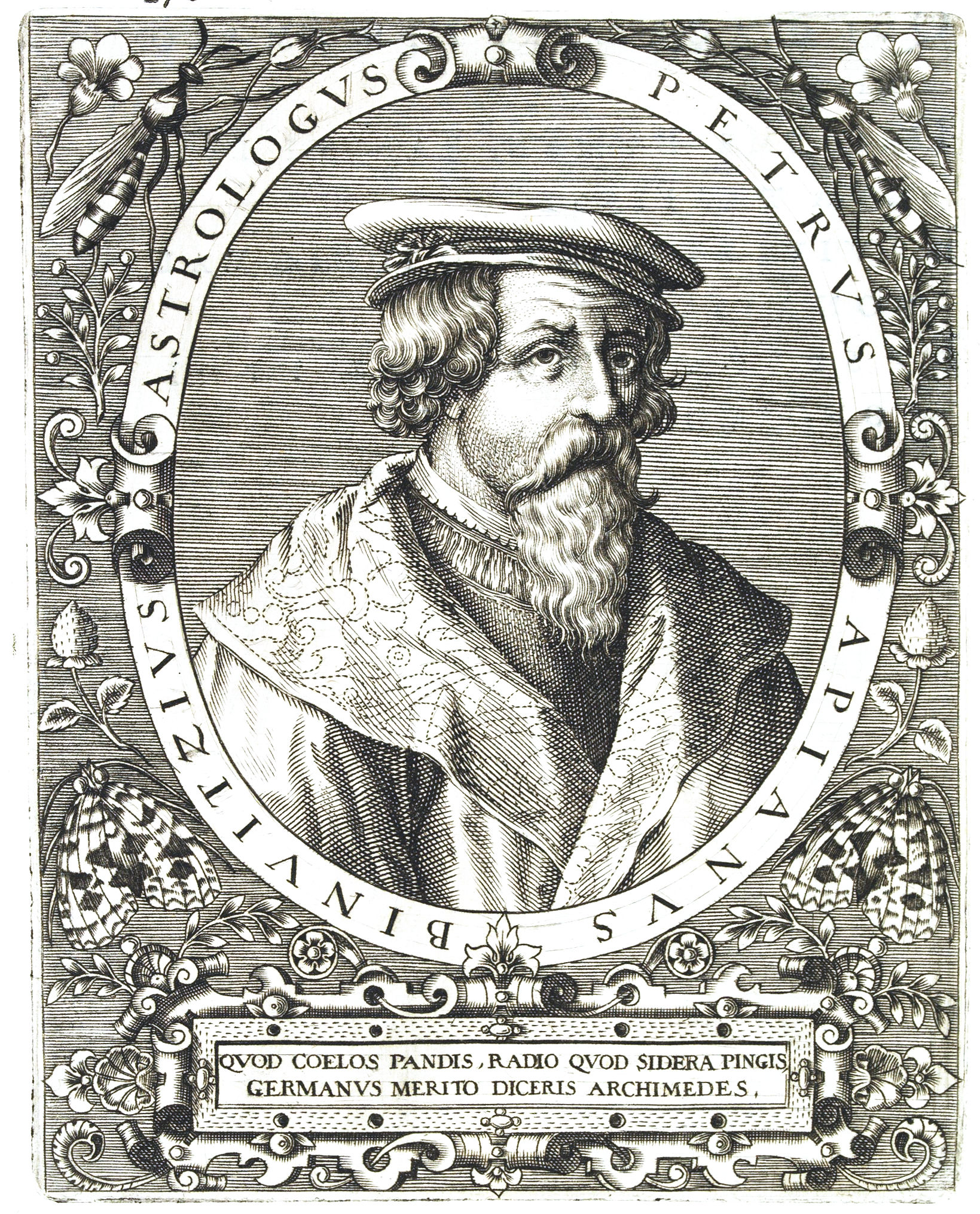
Peter Apian
Petrus Apianus (April 16, 1495 – April 21, 1552), also known as Peter Apian, Peter Bennewitz, and Peter Bienewitz, was a German humanist, known for his works in mathematics, astronomy and cartography. His work on " cosmography", the field that dealt with the earth and its position in the universe, was presented in his most famous publications, '' Astronomicum Caesareum'' (1540) and ''Cosmographicus liber'' (1524). His books were extremely influential in his time, with the numerous editions in multiple languages being published until 1609. The lunar crater '' Apianus'' and asteroid 19139 Apian are named in his honour. Life and work Apianus was born as Peter Bienewitz (or Bennewitz) in Leisnig in Saxony; his father, Martin, was a shoemaker. The family was relatively well off, belonging to the middle-class citizenry of Leisnig. Apianus was educated at the Latin school in Rochlitz. From 1516 to 1519 he studied at the University of Leipzig; during this time, he Latin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)