|
Orbiting Carbon Observatory 3
The Orbiting Carbon Observatory-3 (OCO-3) is a NASA- JPL instrument designed to measure carbon dioxide in Earth's atmosphere. The instrument is mounted on the Japanese Experiment Module-Exposed Facility on board the International Space Station (ISS). OCO-3 was scheduled to be transported to space by a SpaceX Dragon from a Falcon 9 rocket on 30 April 2019, but the launch was delayed to 3 May, due to problems with the space station's electrical power system. This launch was further delayed to 4 May due to electrical issues aboard Of Course I Still Love You (OCISLY), the barge used to recover the Falcon 9’s first stage. OCO-3 was launched as part of CRS-17 on 4 May 2019 at 06:48 UTC. The nominal mission lifetime is ten years. OCO-3 was assembled using spare materials from the Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 satellite. Because the OCO-3 instrument is similar to the OCO-2 instrument, it is expected to have similar performance with its measurements used to quantify to 1 ppm precisi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil space program, aeronautics research, and space research. NASA was established in 1958, succeeding the National Advisory Committee for Aeronautics (NACA), to give the U.S. space development effort a distinctly civilian orientation, emphasizing peaceful applications in space science. NASA has since led most American space exploration, including Project Mercury, Project Gemini, the 1968-1972 Apollo Moon landing missions, the Skylab space station, and the Space Shuttle. NASA supports the International Space Station and oversees the development of the Orion spacecraft and the Space Launch System for the crewed lunar Artemis program, Commercial Crew spacecraft, and the planned Lunar Gateway space station. The agency is also responsible for the Launch Services Program, which provides oversight of launch operations and countdown management f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vandenberg Air Force Base
Vandenberg may refer to: * Vandenberg (surname), including a list of people with the name * USS General Harry Taylor (AP-145), USNS ''General Hoyt S. Vandenberg'' (T-AGM-10), transport ship in the United States Navy, sank as an artificial reef in Key West, Florida * Vandenberg Space Force Base, a United States military installation with a spaceport * Vandenberg (band), a Dutch hard rock band ** Vandenberg (album), ''Vandenberg'' (album), their 1982 debut album * Vandenberg resolution, a United States Congress resolution passed in 1948 {{disambig ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Photosynthesis
Photosynthesis is a process used by plants and other organisms to convert light energy into chemical energy that, through cellular respiration, can later be released to fuel the organism's activities. Some of this chemical energy is stored in carbohydrate molecules, such as sugars and starches, which are synthesized from carbon dioxide and water – hence the name ''photosynthesis'', from the Greek ''phōs'' (), "light", and ''synthesis'' (), "putting together". Most plants, algae, and cyanobacteria perform photosynthesis; such organisms are called photoautotrophs. Photosynthesis is largely responsible for producing and maintaining the oxygen content of the Earth's atmosphere, and supplies most of the energy necessary for life on Earth. Although photosynthesis is performed differently by different species, the process always begins when energy from light is absorbed by proteins called reaction centers that contain green chlorophyll (and other colored) pigments/chromoph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solar Induced Fluorescence
Solar may refer to: Astronomy * Of or relating to the Sun ** Solar telescope, a special purpose telescope used to observe the Sun ** A device that utilizes solar energy (e.g. "solar panels") ** Solar calendar, a calendar whose dates indicate the position of the Earth on its revolution around the Sun * Solar Maximum Mission, a satellite * SOLAR (ISS), an observatory on International Space Station Music * "Solar" (composition), attributed to Miles Davis * ''Solar'' (Red Garland album), 1962 * ''Solar'' (Taeyang album), 2010 * ''Solar'', a 2011 album by Rubik * "Solar", a song by Northlane from ''Mesmer'', 2017 * SOLAR Records, a record label Geography * Solar (Spanish term), a type of urban site * Solar, County Antrim, Northern Ireland, United Kingdom * Solar, Erode, India * Solar, Iran, Iran Companies * Solar Entertainment Corporation, a Philippines television and radio media company * Solar TV, a former TV channel * Solar Television Network, Inc., a former name of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Terrestrial Ecosystem
Terrestrial ecosystems are ecosystems which are found on land. Examples include tundra, taiga, temperate deciduous forest, tropical rain forest, grassland, deserts. Terrestrial ecosystems differ from aquatic ecosystems by the predominant presence of soil rather than water at the surface and by the extension of plants above this soil/water surface in terrestrial ecosystems. There is a wide range of water availability among terrestrial ecosystems (including water scarcity in some cases), whereas water is seldom a limiting factor to organisms in aquatic ecosystems. Because water buffers temperature fluctuations, terrestrial ecosystems usually experience greater diurnal and seasonal temperature fluctuations than do aquatic ecosystems in similar climates. Terrestrial ecosystems are of particular importance especially in meeting Sustainable Development Goal 15 that targets the conservation-restoration and sustainable use of terrestrial ecosystems. Organisms and processes Organis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GEDI
Gedi or GEDI may refer to: People * Ali Mohamed Gedi (born 1952), Prime Minister of Somalia, 2004–2007 * Bashir Nur Gedi (died 2007), Somalian dissident journalist who was murdered * Ahmed Jimale Gedi, Somalian Chief of Army, 2010–2011 * Mohamed Omar Gedi, Somalian vice minister in the Cabinet of Somalia * Gedi Sibony, American artist who exhibited in the 2006 Whitney Biennial * Gedi Ugas Madhar, Somalian leader of a faction of the Somali Patriotic Movement * Gedi, a subtribe of the Daizangi (Hazara tribe) in Afghanistan Places * Gedi, Saurashtra, a village on the Saurashtra Peninsula, Gujarat, India * Gedi State, a former princely state with seat in the above town * Gedi, Kutch, a village in Kutch district, Gujarat, India * Gedi, Kenya, a town in Kilifi County, Kenya ** Gedi Ruins, a historical and archaeological site adjacent to the town * Gedi Township, in Yonghe County, Linfen, Shanxi Province, China * Gedi, a rural village in Changshan County, Quzhou, Zhejian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
ECOSTRESS
ECOSTRESS (Ecosystem Spaceborne Thermal Radiometer Experiment on Space Station) is an ongoing scientific experiment in which a radiometer mounted on the International Space Station (ISS) measures the temperature of plants growing in specific locations on Earth over the course of a solar year. These measurements give scientists insight into the effects of events like heat waves and droughts on crops. ECOSTRESS radiometer The instrument that collects this data is a multispectral thermal infrared radiometer. It measures temperatures on the surface of the Earth, rather than surface air temperature. Dr. Simon Hook is the principal investigator of the ECOSTRESS mission and Dr. Joshua Fisher is the Science lead; both are located at NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL). ECOSTRESS data is archived at the Land Processes Distributed Active Archive Center (LP DAAC), which is a data center managed by the United States Geological Survey (USGS). ECOSTRESS data is discoverable through vari ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Electromagnetic Spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies. The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging from below one hertz to above 1025 hertz, corresponding to wavelengths from thousands of kilometers down to a fraction of the size of an atomic nucleus. This frequency range is divided into separate bands, and the electromagnetic waves within each frequency band are called by different names; beginning at the low frequency (long wavelength) end of the spectrum these are: radio waves, microwaves, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, X-rays, and gamma rays at the high-frequency (short wavelength) end. The electromagnetic waves in each of these bands have different characteristics, such as how they are produced, how they interact with matter, and their practical applications. There is no known limit for long and short wavelengths. Extreme ultr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Near-infrared Spectroscopy
Near-infrared spectroscopy (NIRS) is a spectroscopic method that uses the near-infrared region of the electromagnetic spectrum (from 780 nm to 2500 nm). Typical applications include medical and physiological diagnostics and research including blood sugar, pulse oximetry, functional neuroimaging, sports medicine, elite sports training, ergonomics, rehabilitation, neonatal research, brain computer interface, urology (bladder contraction), and neurology (neurovascular coupling). There are also applications in other areas as well such as pharmaceutical, food and agrochemical quality control, atmospheric chemistry, combustion research and astronomy. Theory Near-infrared spectroscopy is based on molecular overtone and combination vibrations. Such transitions are forbidden by the selection rules of quantum mechanics. As a result, the molar absorptivity in the near-IR region is typically quite small. (NIR absorption bands are typically 10–100 times weaker than the correspond ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
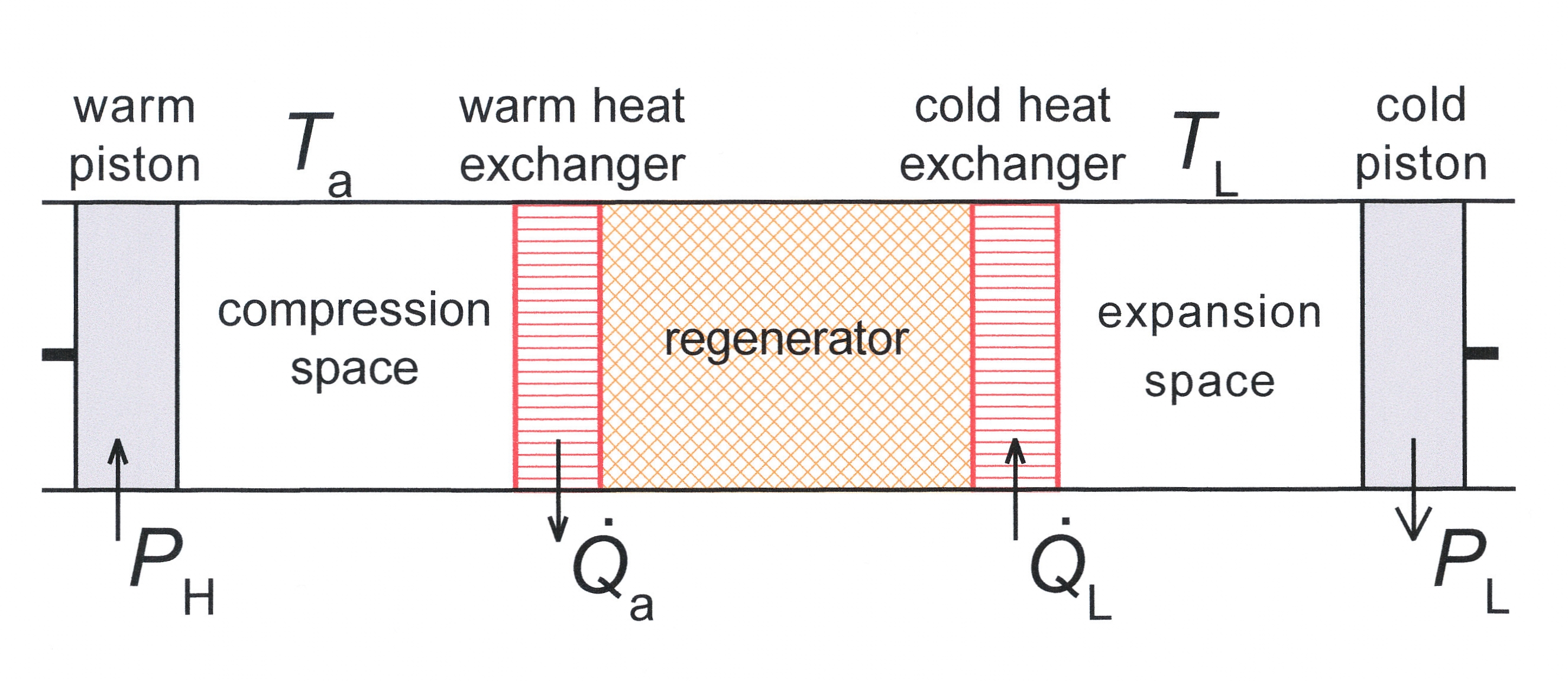
Cryocooler
A refrigerator designed to reach cryogenic temperatures (below ) is often called a cryocooler. The term is most often used for smaller systems, typically table-top size, with input powers less than about 20 kW. Some can have input powers as low as 2–3 W. Large systems, such as those used for cooling the superconducting magnets in particle accelerators are more often called cryogenic refrigerators. Their input powers can be as high as 1 MW. In most cases cryocoolers use a cryogenic fluid as the working substance and employ moving parts to cycle the fluid around a thermodynamic cycle. The fluid is typically compressed at room temperature, precooled in a heat exchanger, then expanded at some low temperature. The returning low-pressure fluid passes through the heat exchanger to precool the high-pressure fluid before entering the compressor intake. The cycle is then repeated. __TOC__ Ideal heat exchangers and regenerators Heat exchangers are important components of all cry ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orbiting Carbon Observatory 2
Orbiting Carbon Observatory-2 (OCO-2) is an American environmental science satellite which launched on 2 July 2014. A NASA mission, it is a replacement for the Orbiting Carbon Observatory which was lost in a launch failure in 2009. It is the second successful high-precision (better than 0.3%) observing satellite, after GOSAT. Mission overview The OCO-2 satellite was built by Orbital Sciences Corporation, based around the LEOStar-2 bus. The spacecraft is being used to study carbon dioxide concentrations and distributions in the atmosphere. OCO-2 was ordered after the original OCO spacecraft failed to achieve orbit. During the first satellite's launch atop a Taurus-XL in February 2009, the payload fairing failed to separate from around the spacecraft and the rocket did not have sufficient power to enter orbit with its additional mass. Although a Taurus launch was initially contracted for the reflight, the launch contract was cancelled after the same malfunction occurred on the l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cape Canaveral Air Force Station
Cape Canaveral Space Force Station (CCSFS) is an installation of the United States Space Force's Space Launch Delta 45, located on Cape Canaveral in Brevard County, Florida. Headquartered at the nearby Patrick Space Force Base, the station is the primary launch site for the Space Force's Eastern RangeCAST 1999, p. 1-12. with three launch pads currently active (Space Launch Complexes 37B, 40, and 41). The facility is south-southeast of NASA's Kennedy Space Center on adjacent Merritt Island, with the two linked by bridges and causeways. The Cape Canaveral Space Force Station Skid Strip provides a runway close to the launch complexes for military airlift aircraft delivering heavy and outsized payloads to the Cape. A number of American space exploration pioneers were launched from CCSFS, including the first U.S. Earth satellite (1958), first U.S. astronaut (1961), first U.S. astronaut in orbit (1962), first two-man U.S. spacecraft (1965), first U.S. unmanned lunar lan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
