|
Oghuz Khagan
Oghuz Khagan or Oghuz Khan ( tk, Oguz Han or Oguz Kagan ; tr, Oğuz Kağan or Oğuz Han; Azerbaijani: Oğuz Xan or Oğuz Xaqan) is a legendary khan of the Turkic people and an eponymous ancestor of Oghuz Turks. Some Turkic cultures use the legend of Oghuz Khan to describe their ethnic and tribal origins. The various versions of the narrative preserved in many different manuscripts has been published in numerous languages as listed below in the references. The narratives about him are often entitled Oghuzname, of which there are several traditions, describing his many feats and conquests, some of these tend to overlap with other Turkic epic traditions such as Seljukname and The Book of Dede Korkut. The name of Oghuz Khan has been associated with Maodun, also known as Mete Han; the reason being that there is a remarkable similarity between the biography of Oghuz Khagan in the Turkic mythology and the biography of Maodun found in the Chinese historiography, which was first noti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zulqarnayn
, ( ar, ذُو ٱلْقَرْنَيْن, Ḏū l-Qarnayn, ; "He of the Two Horns") appears in the Quran, Surah Al-Kahf (18), Ayahs 83–101 as one who travels to east and west and sets up a barrier between a certain people and Gog and Magog (called Ya'juj and Ma'juj). Elsewhere the Quran tells how the end of the world will be signaled by the release of Gog and Magog from behind the barrier. Other apocalyptic writings predict that their destruction by God in a single night will usher in the Day of Resurrection (''Yawm al-Qiyāmah)''. Early Muslim commentators and historians variously identified , most notably as Alexander the Great and as the South-Arabian Himyarite king al-Ṣaʿb bin Dhī Marāthid. Some modern scholars have argued that the origin of the Quranic story may be found in the ''Syriac Alexander Legend,'' but others disagree. Although some favor identification of with Cyrus the Great, the majority of modern scholars and commentators still prefer Alexander the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chinese Historiography
Chinese historiography is the study of the techniques and sources used by historians to develop the recorded history of China. Overview of Chinese history The recording of events in Chinese history dates back to the Shang dynasty (c. 1600–1046 BC). Many written examples survive of ceremonial inscriptions, divinations and records of family names, which were carved or painted onto tortoise shell or bones.William G. Boltz, Early Chinese Writing, World Archaeology, Vol. 17, No. 3, Early Writing Systems. (Feb., 1986), pp. 420–436 (436). The first conscious attempt to record history in China may have been the inscription on the Zhou dynasty bronze Shi Qiang ''pan''. The oldest surviving history texts of China were compiled in the ''Book of Documents (Shujing)''. The '' Spring and Autumn Annals (Chunqiu)'', the official chronicle of the State of Lu, cover the period from 722 to 481 BC and are among the earliest surviving Chinese historical texts to be arranged as annals. The co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-Ghazi Bahadur
Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur ( uz, Abulgʻozi Bahodirxon, Abulgazi, Ebulgazi, Abu-l-Ghazi, August 24, 1603 – 1663) was Khan of Khiva from 1643 to 1663. He spent ten years in Persia before becoming khan, and was very well educated, writing two historical works in the Khiva dialect of the Chagatai language. He was a descendant of Genghis Khan. Life He was born in Urgench, Khanate of Khiva, the son of ruler 'Arab Muhammad Khan. He fled to the Safavid court in Isfahan after a power struggle arose among him and his brothers. He lived there in exile from 1629 until 1639 studying Persian and Arabic history. In 1644 or 1645 he acceded to the throne, a position he would hold for twenty years. He died in Khiva in 1663. Abu al-Ghazi is known as the author of two historical works: "Genealogy of the Turkmen" '' Shajara-i Tarākima'' finished in 1661 and "Genealogy of the Turks" '' Shajara-i Turk'' finished in 1665. These are important sources for modern knowledge of Central Asian history. The ' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal member of the large family of Mongolic peoples. The Oirats in Western Mongolia as well as the Buryats and Kalmyks of Russia are classified either as distinct ethno-linguistic groups or subgroups of Mongols. The Mongols are bound together by a common heritage and ethnic identity. Their indigenous dialects are collectively known as the Mongolian language. The ancestors of the modern-day Mongols are referred to as Proto-Mongols. Definition Broadly defined, the term includes the Mongols proper (also known as the Khalkha Mongols), Buryats, Oirats, the Kalmyk people and the Southern Mongols. The latter comprises the Abaga Mongols, Abaganar, Aohans, Baarins, Chahars, Eastern Dorbets, Gorlos Mongols, Jalaids, Jaruud, Kharchins, Khishigt ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Islamization
Islamization, Islamicization, or Islamification ( ar, أسلمة, translit=aslamāh), refers to the process through which a society shifts towards the religion of Islam and becomes largely Muslim. Societal Islamization has historically occurred over the course of many centuries since the spread of Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula through the early Muslim conquests, with notable shifts occurring in the Levant, Iran, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, West Africa, Central Asia, South Asia (in Afghanistan, Maldives, Pakistan, and Bangladesh), Southeast Asia (in Malaysia, Brunei, and Indonesia), Southeastern Europe (in Albania, Bosnia and Herzegovina, and Kosovo, among others), Eastern Europe (in the Caucasus, Crimea, and the Volga), and Southern Europe (in Spain, Portugal, and Sicily prior to re-Christianizations). In contemporary usage, it may refer to the perceived imposition of an Islamist social and political system on a society with an indige ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paul Pelliot
Paul Eugène Pelliot (28 May 187826 October 1945) was a French Sinologist and Orientalist best known for his explorations of Central Asia and his discovery of many important Chinese texts such as the Dunhuang manuscripts. Early life and career Paul Pelliot was born on 28 May 1878 in Paris, France, and initially intended to pursue a career as a foreign diplomat. Accordingly, he studied English as a secondary school student at La Sorbonne, then studied Mandarin Chinese at the École des Langues Orientales Vivantes (School of Living Oriental Languages). Pelliot was a gifted student, and completed the school's three-year Mandarin course in only two years. His rapid progress and accomplishments attracted the attention of the Sinologist Édouard Chavannes, the chair of Chinese at the Collège de France, who befriended Pelliot and began mentoring him. Chavannes also introduced Pelliot to the Collège's Sanskrit chair, Sylvain Lévi. Pelliot began studying under the two men ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
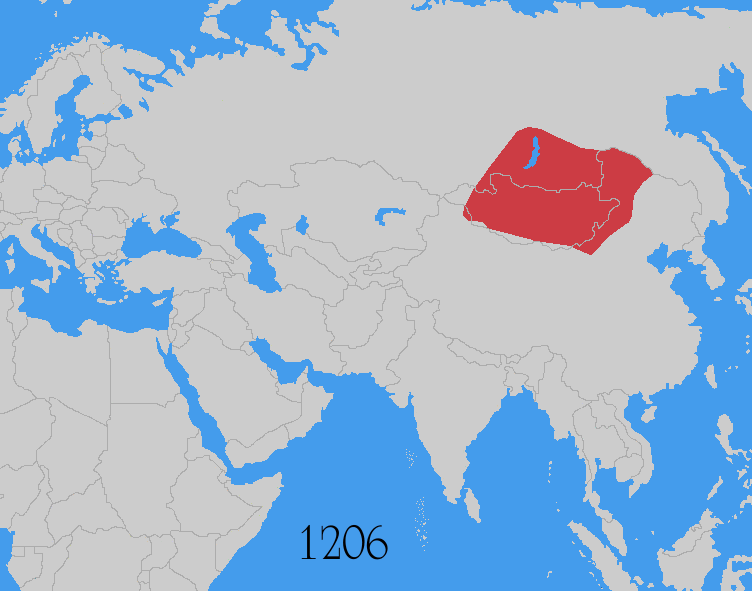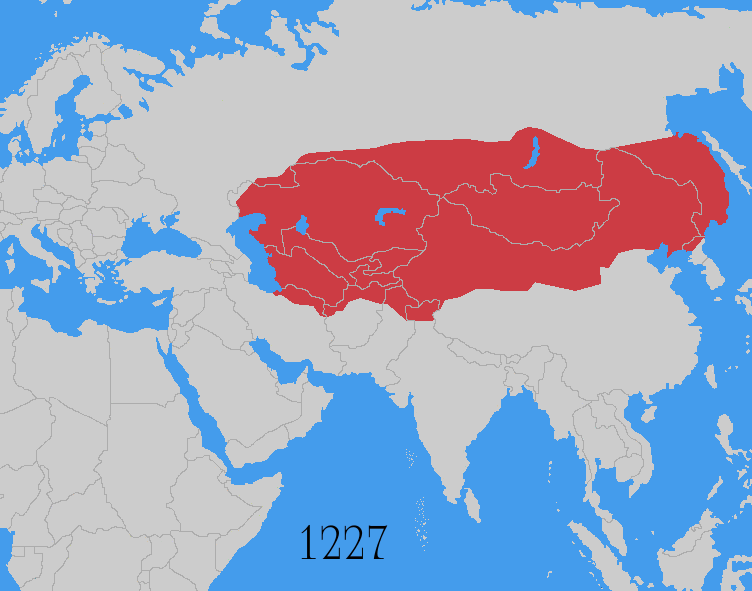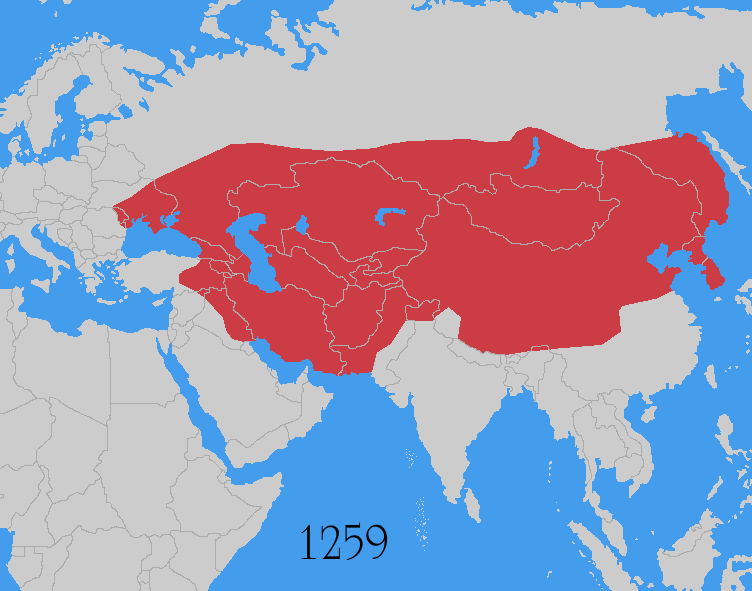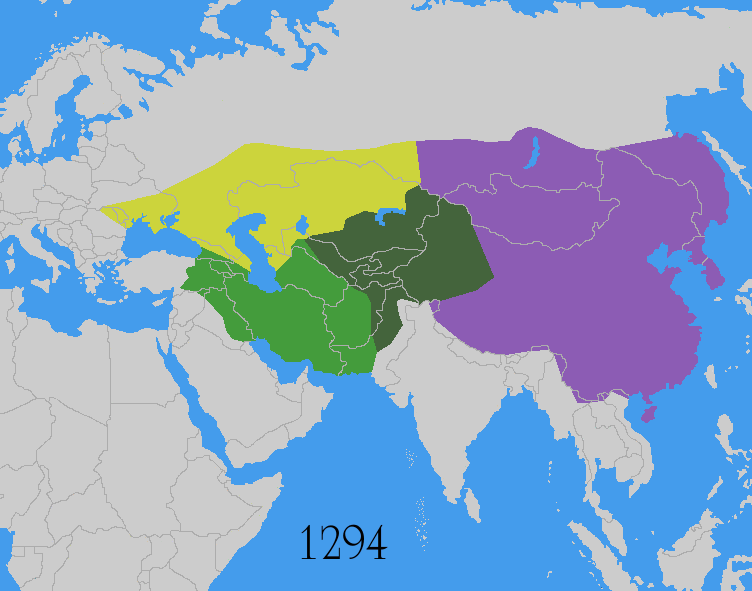
Mongol Conquest
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation as one of the deadliest episodes in history. In addition, Mongol expeditions may have spread the bubonic plague across much of Eurasia, helping to spark the Black Death of the 14th century. The Mongol Empire developed in the course of the 13th century through a series of victorious campaigns throughout Asia, reaching Eastern Europe by the 1240s. In contrast with later "empires of the sea" such as European colonial powers, the Mongol Empire was a land power, fueled by the grass-foraging Mongol cavalry and cattle. Thus most Mongol conquest and plundering took place during the warmer seasons, when there was sufficient grazing for their herds. The rise of the Mongols was preceded by 15 years of wet and warm weather conditions from 1211 to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced in some indirect or automated way. More recently, the term has come to be understood to further include ''any'' written, typed, or word-processed copy of an author's work, as distinguished from the rendition as a printed version of the same. Before the arrival of printing, all documents and books were manuscripts. Manuscripts are not defined by their contents, which may combine writing with mathematical calculations, maps, music notation, explanatory figures, or illustrations. Terminology The study of the writing in surviving manuscripts, the "hand", is termed palaeography (or paleography). The traditional abbreviations are MS for manuscript and MSS for manuscripts, while the forms MS., ms or ms. for singular, and MSS., mss or mss. f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Since the 17th century, Paris has been one of the world's major centres of finance, diplomacy, commerce, fashion, gastronomy, and science. For its leading role in the arts and sciences, as well as its very early system of street lighting, in the 19th century it became known as "the City of Light". Like London, prior to the Second World War, it was also sometimes called the capital of the world. The City of Paris is the centre of the Île-de-France region, or Paris Region, with an estimated population of 12,262,544 in 2019, or about 19% of the population of France, making the region France's primate city. The Paris Region had a GDP of €739 billion ($743 billion) in 2019, which is the highest in Europe. According to the Economis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Uyghur Script
Uyghur is a Turkic language with a long literary tradition spoken in Xinjiang, China by the Uyghurs. Today, the Uyghur Arabic alphabet is the official writing system used for Uyghur in Xinjiang, whereas other alphabets like the Uyghur Latin and Uyghur Cyrillic alphabets are still in use outside China, especially in Central Asia. History Old Uyghur and Modern Uyghur The Old Uyghur language and Modern Uyghur are distinct Turkic languages and are not different stages of the same language. The Old Uyghur language is ancestral to Western Yugur, while modern Uyghur is descended from one of the Karluk languages. Old Uyghur alphabets 5th to 18th century In the 5th century Old Uyghur was written for the first time using the Sogdian alphabet. This fell out of use during the 10th century, when it evolved into the Old Uyghur alphabet, although it was taken into use again between the 15th and 16th century. While the Sogdian alphabet was still in use, it was written with the Old Turkic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkic Peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West Asia, West, Central Asia, Central, East Asia, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to the Turkic subfamily...". "The Turkic peoples represent a diverse collection of ethnic groups defined by the Turkic languages." According to historians and linguists, the Proto-Turkic language originated in Central-East Asia region, potentially in Mongolia or Tuva. Initially, Proto-Turkic speakers were potentially both hunter-gatherers and farmers, but later became nomadic Pastoralism, pastoralists. Early and Post-classical history, medieval Turkic groups exhibited a wide range of both East Asian and West-Eurasian physical appearances and genetic origins, in part through long-term contact with neighboring peoples such as Iranian peoples, Iranian, Mongolic peoples, Mongolic, Tocharians, Yeniseian people, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hyacinth (Bichurin)
Nikita Yakovlevich Bichurin (Никита Яковлевич Бичурин) (29 August 1777 – 11 May 1853, St. Petersburg), better known under his archimandrite monastic name Hyacinth (sometimes rendered as Joacinth), or Iakinf (Иакинф), was one of the founding fathers of Russian Sinology. He translated many works from Chinese into Russian, which were then translated into other European languages. Biography Bichurin was born in Akulevo to a Russian half- Chuvash priest named Iakov and Russian mother Akulina Stepanova. He studied at a church choir school in Sviiazhsk and later at the Kazan Theological Seminary. He also studied Latin, Greek and French and his abilities were noticed by Archbishop Amvrosij Podobedov of the Russian Orthodox Church. He taught in Kazan Theological Seminary from 1799 and was anointed a monk in 1800 with the name of ''Iakinf'' or ''Hyacinth'' and tonsured, sent to promote Christianity in Beijing, where he spent the next 14 years. The genuin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |