|
Nycteroleteridae
Nycteroleteridae is a family of procolophonian parareptilians (extinct early reptiles) from the Middle to Late Permian of Russia and North America. They are sometimes classified as a sister group to pareiasaurids (but see ''Classification)''. The group includes the genera ''Macroleter'', '' Bashkyroleter'', ''"Bashkyroleter" mesensis'', ''Nycteroleter'', ''Emeroleter'', and probably ''Rhipaeosaurus''. They were carnivorous, and occasionally ate insects. The group was most common in European Russia, with only a few fossils in North America. One fossil has also been found in Africa, but this is the only one from Gondwana. Classification Nycteroleteridae is sometimes considered a sister group to the Pareiasauridae, but Bayesian inference suggests that it was in fact paraphyletic, with ''Rhipaeosaurus'' a basal member of the Pareiasauridae and other members of the Nycteroleteridae as outgroups. This is supported by the appearance of ''Rhipaeosaurus skull and teeth - it had tricuspi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Procolophonia
The Procolophonia are a suborder of herbivorous reptiles that lived from the Middle Permian till the end of the Triassic period. They were originally included as a suborder of the Cotylosauria (later renamed Captorhinida Carroll 1988) but are now considered a clade of Parareptilia. They are closely related to other generally lizard-like Permian reptiles such as the Millerettidae, Bolosauridae, Acleistorhinidae, and Lanthanosuchidae, all of which are included under the Anapsida or "Parareptiles" (as opposed to the Eureptilia). Classification There are two main groups of Procolophonia, the small, lizard-like Procolophonoidea, and the Pareiasauroidea, which include the large, armoured Pareiasauridae. According to the traditional classification of Carroll 1988 as well as recent phylogenetic analyses, smaller groups like Rhipaeosauridae (now a synonym of Nycteroleteridae) and Sclerosauridae are classified with the pareiasaurs and with the procolophonids, respectively. The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nycteroleter
''Nycteroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the Middle Permian of European Russia. Fossils were first found in the Mezen River, near to Arkhangelsk. Within the Nycteroleteridae, it is considered most closely related to '' Emeroleter.'' However, its legs were shorter than those of ''Emeroleter'' and its skull was flatter. ''Nycteroleter'' was insectivorous, and may have been nocturnal. It was a small animal, less than a metre long. Classification ''Nycteroleter'' is classified as a primitive procolophonian, related to the Pareisauridae. It is not certain whether the nycteroleterids formed a monophyletic or polyphyletic group, as '' Rhipaeosaurus'' seems to be more similar to pareisaurids than to other nycteroleterids. Previously, it was uncertain whether nycteroleterids were parareptiles Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids ( reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
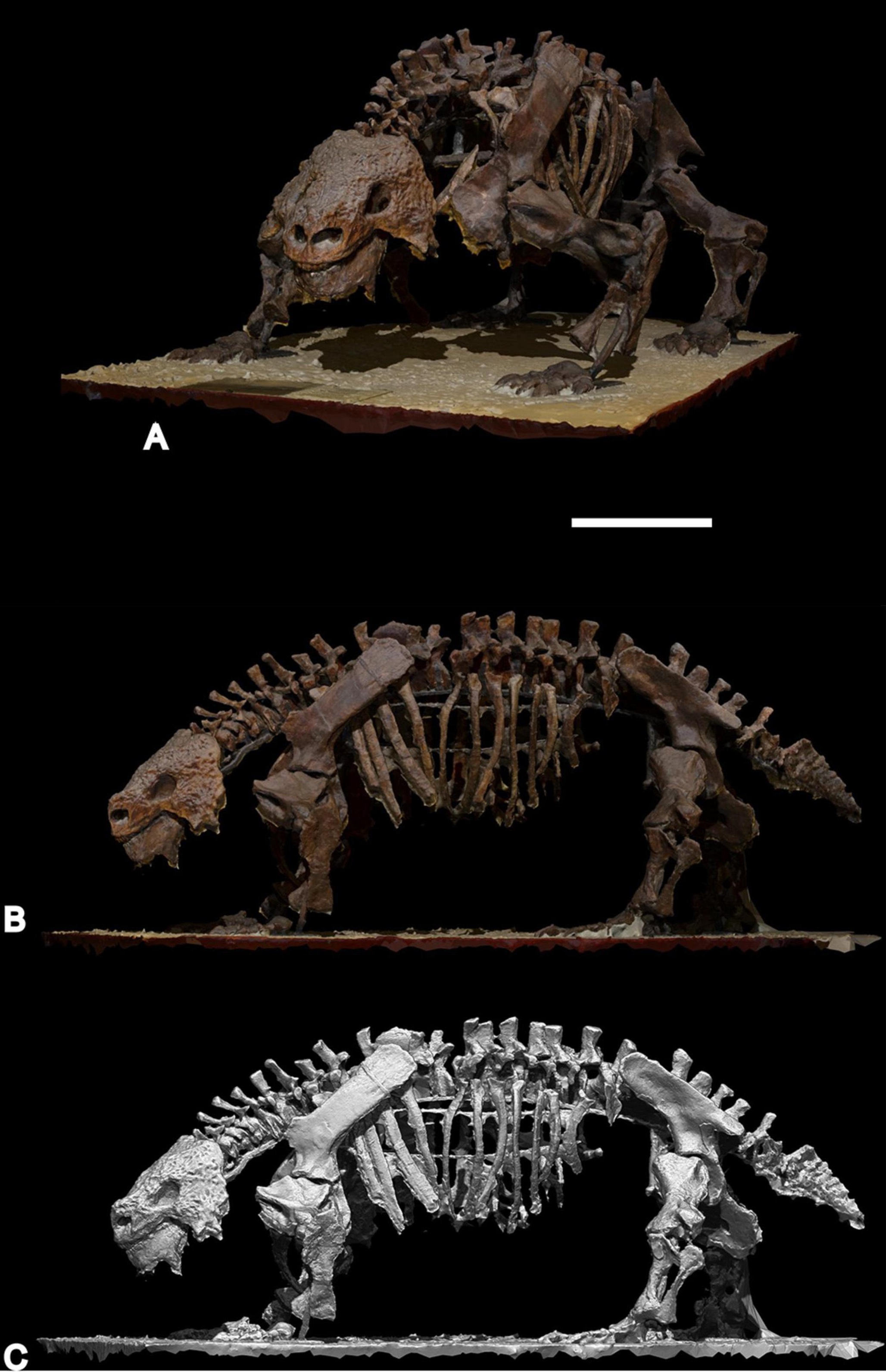
Rhipaeosaurus
''Rhipaeosaurus'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from an articulated skeleton from the mid Middle Permian of European Russia. It contained a single species, ''Rhipaeosaurus tricuspidens''. A bayesian analysis suggests that it is more closely related to pareiasaurs than to the other nycteroleterids, due to skull and tooth features. For this reason, "Nycteroleteridae" may be a grade rather than a clade, unless redefined to exclude ''Rhipaeosaurus''. Description ''Rhipaeosaurus'' is around a meter long, larger than any other "nycteroleterids" and closer in size to later pareiasaurs. Postcranial remains were similar to ''Macroleter'', though the limbs were more robust and the ankle bones were unfused. The teeth were flattened and tricuspid (possessing three cusps), seemingly intermediate in form between the one- or two-cusped teeth of earlier nycteroleterids and the multi-cusped teeth of pareiasaurs. Many components of the partial skull and skeleton (wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tokosaurus
''Macroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in Oklahoma and Russia during the upper Permian period. It was a quite generalized primitive reptile, in many ways resembling their amphibian ancestors. It was first named by paleontologists Tverdochlebova and Ivachnenko in 1984. According to classification by Michel Laurin and Robert R. Reisz, the genus is a parareptile, belonging to the same branch as Millerettidae, Procolophonidae and other generalized anapsid reptiles. The type species is ''Macroleter poezicus'' from Upper Permian of Russia. ''Macroleter'' had an 8 cm skull, and an overall length of 75 cm. It was generally lizard-like in build with a rather flat and broad skull. The teeth were small and pointy, indication it predominantly hunted insects and other small invertebrates. ''Seymouria agilis'' (Olson, 1980) that is known from only one specimen (holotype UCMP 143 277) was originally thought to be a reptile-like amphibian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parareptilia
Parareptilia ("at the side of reptiles") is a subclass or clade of basal sauropsids (reptiles), typically considered the sister taxon to Eureptilia (the group that likely contains all living reptiles and birds). Parareptiles first arose near the end of the Carboniferous period and achieved their highest diversity during the Permian period. Several ecological innovations were first accomplished by parareptiles among reptiles. These include the first reptiles to return to marine ecosystems (mesosaurs), the first bipedal reptiles ( bolosaurids such as ''Eudibamus''), the first reptiles with advanced hearing systems ( nycteroleterids and others), and the first large herbivorous reptiles (the pareiasaurs). The only parareptiles to survive into the Triassic period were the procolophonoids, a group of small generalists, omnivores, and herbivores. The largest family of procolophonoids, the procolophonids, rediversified in the Triassic, but subsequently declined and became extinct by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reptiles
Reptiles, as most commonly defined are the animals in the Class (biology), class Reptilia ( ), a paraphyletic grouping comprising all sauropsid, sauropsids except birds. Living reptiles comprise turtles, crocodilians, Squamata, squamates (lizards and snakes) and rhynchocephalians (tuatara). As of March 2022, the Reptile Database includes about 11,700 species. In the traditional Linnaean taxonomy, Linnaean classification system, birds are considered a separate class to reptiles. However, crocodilians are more closely related to birds than they are to other living reptiles, and so modern Cladistics, cladistic classification systems include birds within Reptilia, redefining the term as a clade. Other cladistic definitions abandon the term reptile altogether in favor of the clade Sauropsida, which refers to all amniotes more closely related to modern reptiles than to mammals. The study of the traditional reptile Order (biology), orders, historically combined with that of modern amphi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macroleter
''Macroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile which existed in Oklahoma and Russia during the upper Permian period. It was a quite generalized primitive reptile, in many ways resembling their amphibian ancestors. It was first named by paleontologists Tverdochlebova and Ivachnenko in 1984. According to classification by Michel Laurin and Robert R. Reisz, the genus is a parareptile, belonging to the same branch as Millerettidae, Procolophonidae and other generalized anapsid reptiles. The type species is ''Macroleter poezicus'' from Upper Permian of Russia. ''Macroleter'' had an 8 cm skull, and an overall length of 75 cm. It was generally lizard-like in build with a rather flat and broad skull. The teeth were small and pointy, indication it predominantly hunted insects and other small invertebrates. ''Seymouria agilis'' (Olson, 1980) that is known from only one specimen (holotype UCMP 143 277) was originally thought to be a reptile-like amphibian a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Emeroleter
''Emeroleter'' is an extinct genus of nycteroleterid parareptile known from the early Late Permian Late may refer to: * LATE, an acronym which could stand for: ** Limbic-predominant age-related TDP-43 encephalopathy, a proposed form of dementia ** Local-authority trading enterprise, a New Zealand business law ** Local average treatment effect, ... of European Russia. It was a long-legged lizard-like small animal with a length about 30 cm. References Permian reptiles of Europe Pareiasauromorphs Fossil taxa described in 1997 Prehistoric reptile genera {{paleo-reptile-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Permian
The Guadalupian is the second and middle series/epoch of the Permian. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lopingian. It is named after the Guadalupe Mountains of New Mexico and Texas, and dates between 272.95 ± 0.5 – 259.1 ± 0.4 Mya. The series saw the rise of the therapsids, a minor extinction event called Olson's Extinction and a significant mass extinction called the end-Capitanian extinction event. The Guadalupian was previously known as the Middle Permian. Name and background The Guadalupian is the second and middle series or epoch of the Permian. Previously called Middle Permian, the name of this epoch is part of a revision of Permian stratigraphy for standard global correlation. The name "Guadalupian" was first proposed in the early 1900s, and approved by the International Subcommission on Permian Stratigraphy in 1996. References to the Middle Permian still exist. The Guadalupian was preceded by the Cisuralian and followed by the Lop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tooth
A tooth ( : teeth) is a hard, calcified structure found in the jaws (or mouths) of many vertebrates and used to break down food. Some animals, particularly carnivores and omnivores, also use teeth to help with capturing or wounding prey, tearing food, for defensive purposes, to intimidate other animals often including their own, or to carry prey or their young. The roots of teeth are covered by gums. Teeth are not made of bone, but rather of multiple tissues of varying density and hardness that originate from the embryonic germ layer, the ectoderm. The general structure of teeth is similar across the vertebrates, although there is considerable variation in their form and position. The teeth of mammals have deep roots, and this pattern is also found in some fish, and in crocodilians. In most teleost fish, however, the teeth are attached to the outer surface of the bone, while in lizards they are attached to the inner surface of the jaw by one side. In cartilaginous fish, s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scutosaurus
''Scutosaurus'' ("shield lizard") is an extinct genus of pareiasaur parareptiles. Its genus name refers to large plates of armor scattered across its body. It was a large anapsid reptile that, unlike most reptiles, held its legs underneath its body to support its great weight. Fossils have been found in the Sokolki Assemblage Zone of the Malokinelskaya Formation in European Russia, close to the Ural Mountains, dating to the late Permian (Lopingian) between 264 and 252 million years ago. Research history The first fossils were uncovered by Russian paleontologist Vladimir Prokhorovich Amalitskii while documenting plant and animal species in the Upper Permian sediments in the Northern Dvina River, Arkhangelsk District, Northern European Russia. Amalitskii had discovered the site in 1899, and he and his wife Anne Amalitskii continued to oversee excavation until 1914, recovering numerous nearly complete and articulated (in their natural position) skeletons belonging to a menage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Otic Notch
Otic notches are invaginations in the posterior margin of the skull roof, one behind each orbit. Otic notches are one of the features lost in the evolution of amniotes from their tetrapod ancestors. The notches have been interpreted as part of an auditory structure and are often reconstructed as holding a tympanum similar to those seen in modern anurans. Analysis of the ''columella'' (the stapes in amphibians and reptiles) of labyrinthodonts however indicates that it did not function in transmitting low-energy vibrations, thus rendering these animals effectively deaf to airborne sound. The otic notch instead functioned as a spiracle, at least in the early forms.Laurin, M. (1996)Hearing in Stegocephalians from the Tree of Life Web Project The Tree of Life Web Project is an Internet project providing information about the diversity and phylogeny of life on Earth. This collaborative peer reviewed project began in 1995, and is written by biologists from around the world. The site ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |