|
Negative Elongation Factor
In molecular biology, the NELF (negative elongation factor) is a four-subunit protein complex (NELF-A, NELF-B, NELF-C/NELF-D, and NELF-E) that negatively impacts transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II) by pausing about 20-60 nucleotides downstream from the transcription start site (TSS). Structure The NELF has four subunits within its complex which are the following: NELF-A, NELF-B, NELF-C/NELF-D, and NELF-E. The NELF-A subunit is encoded by the gene WHSC2 (Wolf-Hirschhorn syndrome candidate 2). Micro-sequencing analysis demonstrated that NELF-B was the protein previously identified as being encoded by the gene COBRA1. It is unknown whether or not NELF-C and NELF-D are peptides resulting from the same mRNA with different translation initiation sites; possibly differing only in an extra 9 amino acids for NELF-C at the N-terminus, or peptides from different mRNAs entirely. A single NELF complex consists of either NELF-C or NELF-D, but not both. NELF-E is also known as RDBP. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PDB 2bz2 EBI
PDB may refer to: * Chess Problem Database Server (PDB Server) * 1,4-Dichlorobenzene (paradichlorobenzene) * Party of German-speaking Belgians, (German: '), a political party and predecessor of the ProDG * PDB (Palm OS), a container format for record databases in Palm OS, Garnet OS and Access Linux Platform * ''Pee Dee Belemnite'', a standard for stable Carbon-13 and Oxygen-18 isotopes; see * Pluggable database, such as an Oracle Database in a multitenancy environment * Potato dextrose broth, a common microbiological growth media * Pousette-Dart Band * President's Daily Brief or Briefing or Bulletin, a top-secret intelligence document produced each morning for the U.S. President * Program database, a file format for storing debugging information * Promised Day Brigade, an Iraqi Shia organisation * Protein Data Bank * Protein Data Bank (file format) * Python Debugger, see Python (programming language) Python is a high-level, general-purpose programming language. Its design phil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
DSIF
In gene expression, DSIF (DRB Sensitivity Inducing Factor) is a protein that can either negatively or positively affect transcription by RNA polymerase II (Pol II). In one case of negative regulation, it can interact with negative elongation factor (NELF) to promote the stalling of Pol II at some genes. This stalling is relieved by P-TEFb. In humans, DSIF is composed of hSPT4 and hSPT5 (SPT4 and SPT5 are homologs in yeast). The complex locks the RNAP clamp into a closed state to prevent the elongation complex (EC) from dissociating. The Spt5 NGN domain helps anneal the two strands of DNA upstream. The single KOW domain Kow or KOW may refer to: * Kow (bull), a legendary bull in Meitei mythology of Manipur * Ganzhou Huangjin Airport, IATA code KOW * Ganzhou Huangjin Airport (former), IATA code KOW until replaced by new airport in 2008 * Kow Swamp, Victoria, ... in bacteria and archaea anchors a ribosome to the RNAP. In bacteria, the homologous complex only contains ''N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tumorigenesis
Carcinogenesis, also called oncogenesis or tumorigenesis, is the formation of a cancer, whereby normal cells are transformed into cancer cells. The process is characterized by changes at the cellular, genetic, and epigenetic levels and abnormal cell division. Cell division is a physiological process that occurs in almost all tissues and under a variety of circumstances. Normally, the balance between proliferation and programmed cell death, in the form of apoptosis, is maintained to ensure the integrity of tissues and organs. According to the prevailing accepted theory of carcinogenesis, the somatic mutation theory, mutations in DNA and epimutations that lead to cancer disrupt these orderly processes by interfering with the programming regulating the processes, upsetting the normal balance between proliferation and cell death. This results in uncontrolled cell division and the evolution of those cells by natural selection in the body. Only certain mutations lead to can ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
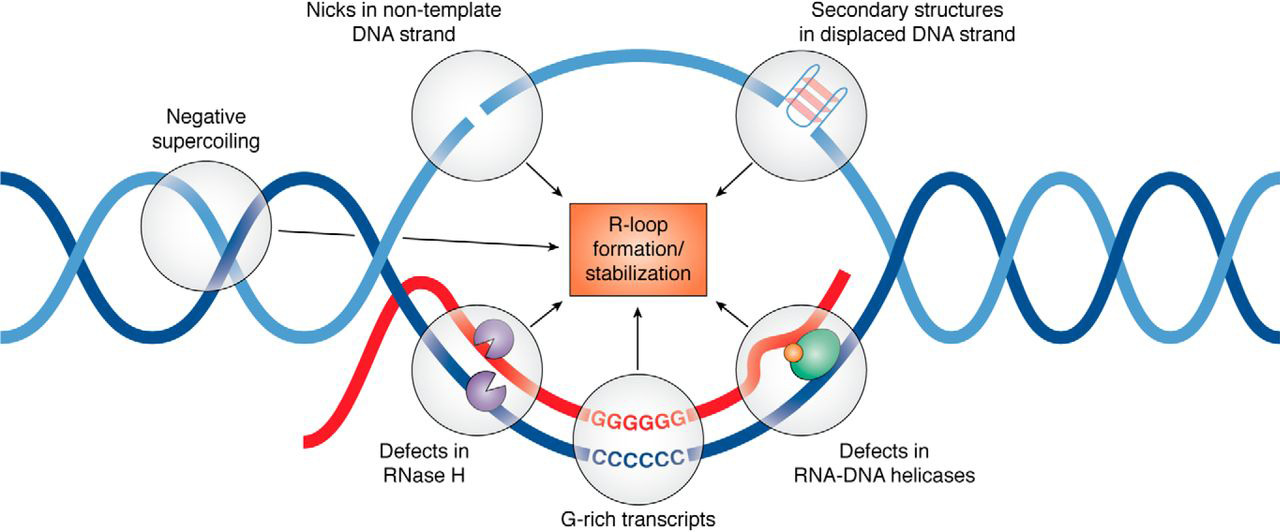
R-loop
An R-loop is a three-stranded nucleic acid structure, composed of a DNA:RNA hybrid and the associated non-template single-stranded DNA. R-loops may be formed in a variety of circumstances, and may be tolerated or cleared by cellular components. The term "R-loop" was given to reflect the similarity of these structures to D-loops; the "R" in this case represents the involvement of an RNA moiety. In the laboratory, R-loops may also be created by the hybridization of mature mRNA with double-stranded DNA under conditions favoring the formation of a DNA-RNA hybrid; in this case, the intron regions (which have been spliced out of the mRNA) form single-stranded DNA loops, as they cannot hybridize with complementary sequence in the mRNA. History R-looping was first described in 1976. Independent R-looping studies from the laboratories of Richard J. Roberts and Phillip A. Sharp showed that protein coding adenovirus genes contained DNA sequences that were not present in the mature ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chromosome 4
Chromosome 4 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 4 spans more than 186 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 6 and 6.5 percent of the total DNA in cell (biology), cells. Genomics The chromosome is ~191 megabases in length. In a 2012 paper, 775 protein-encoding genes were identified on this chromosome.Chen LC, Liu MY, Hsiao YC, Choong WK, Wu HY, Hsu WL, Liao PC, Sung TY, Tsai SF, Yu JS, Chen YJ (2012) Decoding the disease-associated proteins encoded in the human chromosome 4. J Proteome Res 211 (27.9%) of these coding sequences did not have any experimental evidence at the protein level, in 2012. 271 appear to be membrane proteins. 54 have been classified as cancer-associated proteins. Genes Number of genes The following are some of the gene count estimates of human chromosome 4. Because researchers use different approaches to genome annotation their predictions of the num ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Subtypes Of HIV
The subtypes of HIV include two major types, HIV type 1 (HIV-1) and HIV type 2 (HIV-2). HIV-1 is related to viruses found in chimpanzees and gorillas living in western Africa, while HIV-2 viruses are related to viruses found in the sooty mangabey, a vulnerable West African primate. HIV-1 viruses can be further divided into groups M, N, O and P. The HIV-1 group M viruses predominate and are responsible for the AIDS pandemic. Group M can be further subdivided into subtypes based on genetic sequence data. Some of the subtypes are known to be more virulent or are resistant to different medications. Likewise, HIV-2 viruses are thought to be less virulent and transmissible than HIV-1 M group viruses, although HIV-2 is also known to cause AIDS. One of the obstacles to treatment of the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is its high genetic variability. Major types HIV-1 HIV-1 is the most common and pathogenic strain of the virus. Over 2 million such infections occur annually. Scientists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BRCA1
Breast cancer type 1 susceptibility protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''BRCA1'' () gene. Orthologs are common in other vertebrate species, whereas invertebrate genomes may encode a more distantly related gene. ''BRCA1'' is a human tumor suppressor gene (also known as a caretaker gene) and is responsible for repairing DNA. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' are unrelated proteins, but both are normally expressed in the cells of breast and other tissue, where they help repair damaged DNA, or destroy cells if DNA cannot be repaired. They are involved in the repair of chromosomal damage with an important role in the error-free repair of DNA double-strand breaks. If ''BRCA1'' or ''BRCA2'' itself is damaged by a BRCA mutation, damaged DNA is not repaired properly, and this increases the risk for breast cancer. ''BRCA1'' and ''BRCA2'' have been described as "breast cancer susceptibility genes" and "breast cancer susceptibility proteins". The predominant allele has a normal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metazoan
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage in which their body consists of a hollow sphere of cells, the blastula, during embryonic development. Over 1.5 million living animal species have been described—of which around 1 million are insects—but it has been estimated there are over 7 million animal species in total. Animals range in length from to . They have complex interactions with each other and their environments, forming intricate food webs. The scientific study of animals is known as zoology. Most living animal species are in Bilateria, a clade whose members have a bilaterally symmetric body plan. The Bilateria include the protostomes, containing animals such as nematodes, arthropods, flatworms, annelids and molluscs, and the deuterostomes, containing the echinoderms ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immediate Early Gene
Immediate early genes (IEGs) are genes which are activated transiently and rapidly in response to a wide variety of cellular stimuli. They represent a standing response mechanism that is activated at the transcription level in the first round of response to stimuli, before any new proteins are synthesized. IEGs are distinct from "late response" genes, which can only be activated later, following the synthesis of early response gene products. Thus IEGs have been called the "gateway to the genomic response". The term can describe viral regulatory proteins that are synthesized following viral infection of a host cell, or cellular proteins that are made immediately following stimulation of a resting cell by extracellular signals. In their role as "gateways to genomic response", many IEG products are natural transcription factors or other DNA-binding proteins. However, other important classes of IEG products include secreted proteins, cytoskeletal proteins, and receptor subunits. Ne ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Messenger RNA
In molecular biology, messenger ribonucleic acid (mRNA) is a single-stranded molecule of RNA that corresponds to the genetic sequence of a gene, and is read by a ribosome in the process of synthesizing a protein. mRNA is created during the process of transcription, where an enzyme (RNA polymerase) converts the gene into primary transcript mRNA (also known as pre-mRNA). This pre-mRNA usually still contains introns, regions that will not go on to code for the final amino acid sequence. These are removed in the process of RNA splicing, leaving only exons, regions that will encode the protein. This exon sequence constitutes mature mRNA. Mature mRNA is then read by the ribosome, and, utilising amino acids carried by transfer RNA (tRNA), the ribosome creates the protein. This process is known as translation. All of these processes form part of the central dogma of molecular biology, which describes the flow of genetic information in a biological system. As in DNA, genet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enhancer RNA
Enhancer RNAs (eRNAs) represent a class of relatively long non-coding RNA molecules (50-2000 nucleotides) transcribed from the DNA sequence of enhancer regions. They were first detected in 2010 through the use of genome-wide techniques such as RNA-seq and ChIP-seq. eRNAs can be subdivided into two main classes: 1D eRNAs and 2D eRNAs, which differ primarily in terms of their size, polyadenylation state, and transcriptional directionality. The expression of a given eRNA correlates with the activity of its corresponding enhancer in target genes. Increasing evidence suggests that eRNAs actively play a role in transcriptional regulation in cis and in trans, and while their mechanisms of action remain unclear, a few models have been proposed. Discovery Enhancers as sites of extragenic transcription were initially discovered in genome-wide studies that identified enhancers as common regions of RNA polymerase II (RNA pol II) binding and non-coding RNA transcription. The level of RNA pol ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regulation Of Transcription In Metazoans (animals)
Regulation is the management of complex systems according to a set of rules and trends. In systems theory, these types of rules exist in various fields of biology and society, but the term has slightly different meanings according to context. For example: * in biology, gene regulation and metabolic regulation allow living organisms to adapt to their environment and maintain homeostasis; * in government, typically regulation means stipulations of the delegated legislation which is drafted by subject-matter experts to enforce primary legislation; * in business, industry self-regulation occurs through self-regulatory organizations and trade associations which allow industries to set and enforce rules with less government involvement; and, * in psychology, self-regulation theory is the study of how individuals regulate their thoughts and behaviors to reach goals. Social Regulation in the social, political, psychological, and economic domains can take many forms: legal restriction ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |