|
Nabataeans
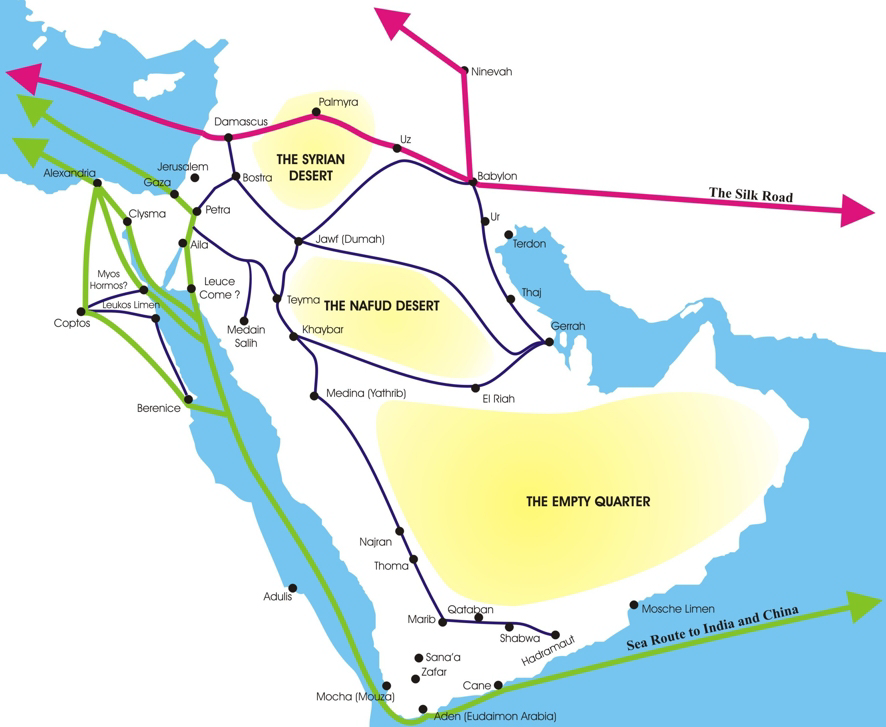
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic language, Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Petra, Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Kingdom
The Nabataean Kingdom (Nabataean Aramaic: 𐢕𐢃𐢋𐢈 ''Nabāṭū''), also named Nabatea (), was a political state of the Arab Nabataeans during classical antiquity. The Nabataean Kingdom controlled many of the trade routes of the region, amassing large wealth and drawing the envy of its neighbors. It stretched south along the Red Sea coast into the Hejaz, up as far north as Damascus, which it controlled for a short period (85–71 BC). Nabataea remained an independent political entity from the mid-3rd century BC until it was annexed in AD 106 by the Roman Empire, which renamed it Arabia Petraea. History Nabataeans The Nabataeans were one among several nomadic Bedouin tribes that roamed the Arabian Desert and moved with their herds to wherever they could find pasture and water. They became familiar with their area as seasons passed, and they struggled to survive during bad years when seasonal rainfall diminished. Although the Nabataeans were initially embedded in Aramaic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Religion
The Nabataean religion was a form of Arab polytheism practiced in Nabataea, an ancient Arab nation which was well settled by the third century BCE and lasted until the Roman annexation in 106 CE.Patrich, Joseph. The Formation of Nabataean Art: Prohibition of a Graven Image Among the Nabateans. Jerusalem: Magnes, 1990. Print. The Nabateans were polytheistic and worshipped a wide variety of local gods as well as Baalshamin, Isis, and Greco-Roman gods such as Tyche and Dionysus. They worshipped their gods at temples, high places, and betyls. They were mostly aniconic and preferred to decorate their sacred places with geometric designs. Much knowledge of the Nabataeans’ grave goods has been lost due to extensive looting throughout history. They made sacrifices to their gods, performed other rituals and believed in an afterlife. Gods and goddesses Most of the deities in Nabataean religion were part of the pre-Islamic Arab pantheon, with the addition of foreign deities such as Isis an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Petra
Petra ( ar, ٱلْبَتْرَاء, Al-Batrāʾ; grc, Πέτρα, "Rock", Nabataean Aramaic, Nabataean: ), originally known to its inhabitants as Raqmu or Raqēmō, is an historic and archaeological city in southern Jordan. It is adjacent to the mountain of Jebel al-Madhbah, Jabal Al-Madbah, in a Depression (geology), basin surrounded by mountains forming the eastern flank of the Arabah valley running from the Dead Sea to the Gulf of Aqaba. The area around Petra has been inhabited from as early as 7000 BC, and the Nabataeans might have settled in what would become the capital city of Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom as early as the 4th century BC. Archaeological work has only discovered evidence of Nabataean presence dating back to the second century BC, by which time Petra had become their capital. The Nabataeans were nomadic Arabs who invested in Petra's proximity to the incense trade routes by establishing it as a major regional trading hub. The trading business gained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Religion In Pre-Islamic Arabia
Religion in pre-Islamic Arabia included indigenous Arabian polytheism, ancient Semitic religions, Christianity, Judaism, Mandaeism, and Iranian religions such as Zoroastrianism, and Manichaeism, and rarely Buddhism. Arabian polytheism, the dominant form of religion in pre-Islamic Arabia, was based on veneration of deities and spirits. Worship was directed to various gods and goddesses, including Hubal and the goddesses al-Lāt, al-‘Uzzā, and Manāt, at local shrines and temples such as the Kaaba in Mecca. Deities were venerated and invoked through a variety of rituals, including pilgrimages and divination, as well as ritual sacrifice. Different theories have been proposed regarding the role of Allah in Meccan religion. Many of the physical descriptions of the pre-Islamic gods are traced to idols, especially near the Kaaba, which is said to have contained up to 360 of them. Other religions were represented to varying, lesser degrees. The influence of the adjacent Roman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan River. Jordan is bordered by Saudi Arabia to the south and east, Iraq to the northeast, Syria to the north, and the Palestinian West Bank, Israel, and the Dead Sea to the west. It has a coastline in its southwest on the Gulf of Aqaba's Red Sea, which separates Jordan from Egypt. Amman is Jordan's capital and largest city, as well as its economic, political, and cultural centre. Modern-day Jordan has been inhabited by humans since the Paleolithic period. Three stable kingdoms emerged there at the end of the Bronze Age: Ammon, Moab and Edom. In the third century BC, the Arab Nabataeans established their Kingdom with Petra as the capital. Later rulers of the Transjordan region include the Assyrian, Babylonian, Roman, Byzantine, Rashidun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Aramaic
Nabataean Aramaic is the Aramaic variety used in inscriptions by the Nabataeans of the East Bank of the Jordan River, the Negev, and the Sinai Peninsula. Compared to other varieties of Aramaic, it is notable for the occurrence of a number of loanwords and grammatical borrowings from Arabic or other North Arabian languages.Butts, Aaron M"North Arabian Features in the Nabataean Aramaic Inscriptions from Madāʼin Ṣāliḥ: A Contact-Linguistic Analysis" in G.J. Brooke et al. (eds), ''Near Eastern and Arabian Essays: Studies in Honour of John F. Healey'' (Journal of Semitic Studies Supplement 41; Oxford: Oxford University Press), 39–57. Attested in several dozen longer dedicatory and funerary inscriptions and a few legal documents from the period of the Nabataean Kingdom, Nabataean Aramaic remained in use for several centuries after the kingdom's annexation by the Roman Empire in 106 AD. Over time, the distinctive Nabataean script was increasingly used to write texts in the Arab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arabs
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western List of islands in the Indian Ocean, Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Arabs in Turkey, Turkey, Arab Indonesians, Indonesia, and Iranian Arabs, Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both Arab identity, carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, and the western Indian Ocean islands (including the Comoros). An Arab diaspora is also present around the world in significant numbers, most notably in the Americas, Western Europe, Turkey, Indonesia, and Iran. In modern usage, the term "Arab" tends to refer to those who both carry that ethnic identity and speak Arabic as their native language. This contrasts with the narrower traditional definition, which refers to the descendants of the tribes of Arabia. The religion of Islam was developed in Arabia, and Classical Arabic serves as the language of Islamic literature. 93 percent of Arabs are Muslims (the remainder consisted mostly of Arab Christians), while Arab Muslims are only 20 percent of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nebaioth
Nebaioth ( ''Nəḇāyōṯ'') or Nebajoth is mentioned at least five times in the Hebrew Bible, according to which he was the firstborn son of Ishmael, and the name appears as the name of one of the wilderness tribes mentioned in the Book of Genesis 25:13, and in the Book of Isaiah 60:7. Biblical occurrences In the Book of Genesis, Nebaioth is listed as the firstborn son of Ishmael: :...Now these are the generations of Ishmael, Abraham's son, whom Hagar the Egyptian, Sarah's handmaid, bore unto Abraham. And these are the names of the sons of Ishmael, by their names, according to their generations: the first-born of Ishmael, Nebaioth; and Kedar, and Adbeel, and Mibsam, and Mishma, and Dumah, and Massa; Hadad, and Tema, Jetur, Naphish, and Kedem; these are the sons of Ishmael, and these are their names, by their villages, and by their encampments; twelve princes according to their nations... (Book of Genesis 25:12-16) Nebaioth is portrayed as the brother of Mahalath, one of Esau's w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataean Arabic
Nabataean Arabic was the dialect of Arabic spoken by the Nabataeans in antiquity. In the 1st century AD, the Nabataeans wrote their inscriptions, such as the legal texts carved on the façades of the monumental tombs at Mada'in Salih, ancient Ḥegrā, in Nabataean Aramaic. It is probable, however, that some or all of them, possibly in varying proportion depending on the region of the Nabataean Kingdom where they lived, spoke Arabic. Phonology Consonants : These consonants were probably voiceless, in contrast with Old Higazi Old Hijazi, or Old Higazi, is a variety of Old Arabic attested in Hejaz (the western part of Saudi Arabia) from about the 1st century to the 7th century. It is the variety thought to underlie the Quranic Consonantal Text (QCT) and in its later ..., where they may have been voiced It is clear that in southern Syria the two sounds had not merged and that they remained voiceless. The evidence from Nessana, on the other hand, suggests that both refl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
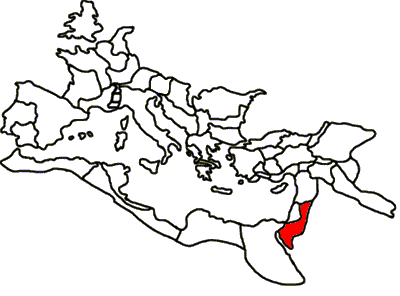
Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province ( la, Provincia Arabia; ar, العربية البترائية; grc, Ἐπαρχία Πετραίας Ἀραβίας) or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Empire beginning in the 2nd century. It consisted of the former Nabataean Kingdom in Jordan, southern Levant, the Sinai Peninsula and northwestern Arabian Peninsula. Its capital was Petra. It was bordered on the north by Syria, on the west by Judaea (merged with Syria from AD 135) and Egypt, and on the south and east by the rest of Arabia, known as Arabia Deserta and Arabia Felix. The territory was annexed by Emperor Trajan, like many other eastern frontier provinces of the Roman Empire, but held onto, unlike Armenia, Mesopotamia and Assyria, well after Trajan's rule, its desert frontier being called the Limes Arabicus. It produced the Emperor Philippus, who was born around 204. As a frontier province, it included a desert populated by Arabic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Voiced Palatal Approximant
The voiced palatal approximant, or yod, is a type of consonant used in many spoken languages. The symbol in the International Phonetic Alphabet that represents this sound is . The equivalent X-SAMPA symbol is j, and in the Americanist phonetic notation it is . Because the English name of the letter J, ''jay'', starts with (voiced palato-alveolar affricate), the approximant is sometimes instead called ''yod'' (jod), as in the phonological history terms yod-dropping and yod-coalescence. The palatal approximant can often be considered the semivowel, semivocalic equivalent of the close front unrounded vowel . They alternation (linguistics), alternate with each other in certain languages, such as French language, French, and in the diphthongs of some languages as and , with the non-syllabic diacritic used in different phonetic transcription systems to represent the same sound. Some languages, however, have a palatal approximant that is unspecified for rounding and so cannot be consi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |