|
Nabataean Art
Nabataean art is the art of the Nabataeans of North Arabia. They are known for finely-potted painted ceramics, which became dispersed among Greco-Roman world, as well as contributions to sculpture and Nabataean architecture. Nabataean art is most well known for the archaeological sites in Petra, specifically monuments such as Al Khazneh and Ad Deir. Ceramics Nabataean pottery is characterised by its thin walls and floral motifs. The exclusive use of floral patterns links back to Nabataean aniconism in their religious practices. The designs on the wares are generally painted on or pressed into the surface with stamps and rouletting wheels. To put a finish on the pieces, the makers burnished them or used a sintering process. Most of the wares are pinkish in color, much like the cliffs surrounding the city. This is because Nabataean potters used local clay bodies in their work. Nabataean wares take many forms, and can be classified by their thickness, rim shape, bases, and deco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nabataeans
The Nabataeans or Nabateans (; Nabataean Aramaic: , , vocalized as ; Arabic language, Arabic: , , singular , ; compare grc, Ναβαταῖος, translit=Nabataîos; la, Nabataeus) were an ancient Arab people who inhabited northern Arabian Peninsula, Arabia and the southern Levant. Their settlements—most prominently the assumed capital city of Petra, Raqmu (present-day Petra, Jordan)—gave the name ''Nabatene'' ( grc, Ναβατηνή, translit=Nabatēnḗ) to the Arabian borderland that stretched from the Euphrates to the Red Sea. The Nabateans emerged as a distinct civilization and political entity between the 4th and 2nd centuries BCE,Taylor, Jane (2001). ''Petra and the Lost Kingdom of the Nabataeans''. London: I.B.Tauris. pp. 14, 17, 30, 31. . Retrieved 8 July 2016. with Nabataean Kingdom, their kingdom centered around a loosely controlled trading network that brought considerable wealth and influence across the ancient world. Described as fiercely independent by cont ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
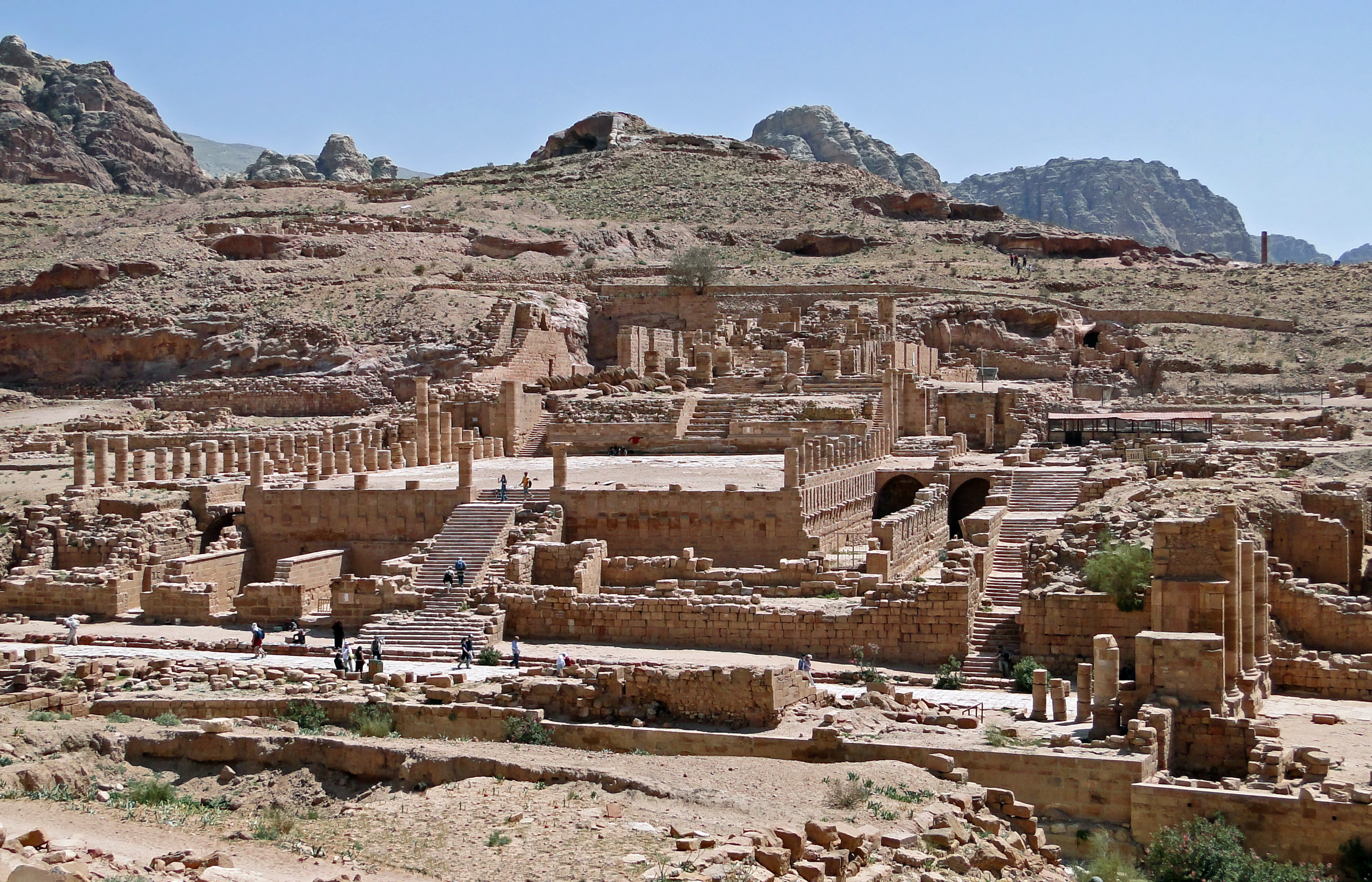
Great Temple (Petra)
The Great Temple at Petra is a grand monumental complex that lies south of the Colonnaded Street at Petra. It covers an area of ~7,560 m2. The complex was probably completed in the early first century CE, under the rule of Nabataean king Aretas IV, as suggested by architectural and sculptural details. The "Great Temple" occupied a prime spot in ancient Petra: from its ruins one can now see the Siq to the Southeast, the Qasr al-Bint to the West, and the Lower Market/Petra Pool Complex to the East. It is unclear whether the complex was a religious or administrative building, and – if it was indeed religious – how exactly it functioned or to what deity it was dedicated. History of research In the 1890s, the ruins were superficially explored by German archaeologists R. E. Brünnow and A. von Domaszewski. Walter Bachmann then surveyed Petra as a member of the Preservation branch of the German-Turkish army, and was the first scholar to identify the monument by its current ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baetylus
Baetylus (also Baetyl, Bethel, or Betyl, from Semitic ''bet el'' "house of god"; compare Bethel, Beit El) are sacred stones that were supposedly endowed with life, or gave access to a deity. According to ancient sources, at least some of these objects of worship were meteorites, which were dedicated to the gods or revered as symbols of the gods themselves. Other accounts suggest that contact with them could give access to epiphanic experiences of the deity. The baetyl has been described by Wendy Doniger as "the parent form for altars and iconic statuary". In general the baetyl was believed to have something inherent in its own nature that made it sacred, rather than becoming sacred by human intervention, such as carving it into a cult image. Some baetyls were left in their natural state, but others were worked on by sculptors. The exact definition of a baetyl, as opposed to other types of sacred stones, "cult stones" and so on, is rather vague both in ancient and modern sourc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Basel 2012-08 Mattes 1 (215)
, french: link=no, Bâlois(e), it, Basilese , neighboring_municipalities= Allschwil (BL), Hégenheim (FR-68), Binningen (BL), Birsfelden (BL), Bottmingen (BL), Huningue (FR-68), Münchenstein (BL), Muttenz (BL), Reinach (BL), Riehen (BS), Saint-Louis (FR-68), Weil am Rhein (DE-BW) , twintowns = Shanghai, Miami Beach , website = www.bs.ch Basel ( , ), also known as Basle ( ),french: Bâle ; it, Basilea ; rm, label=Sutsilvan, Basileia; other rm, Basilea . is a city in northwestern Switzerland on the river Rhine. Basel is Switzerland's third-most-populous city (after Zürich and Geneva) with about 175,000 inhabitants. The official language of Basel is (the Swiss variety of Standard) German, but the main spoken language is the local Basel German dialect. Basel is commonly considered to be the cultural capital of Switzerland and the city is famous for its many museums, including the Kunstmuseum, which is the first collection of art accessible to the public ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
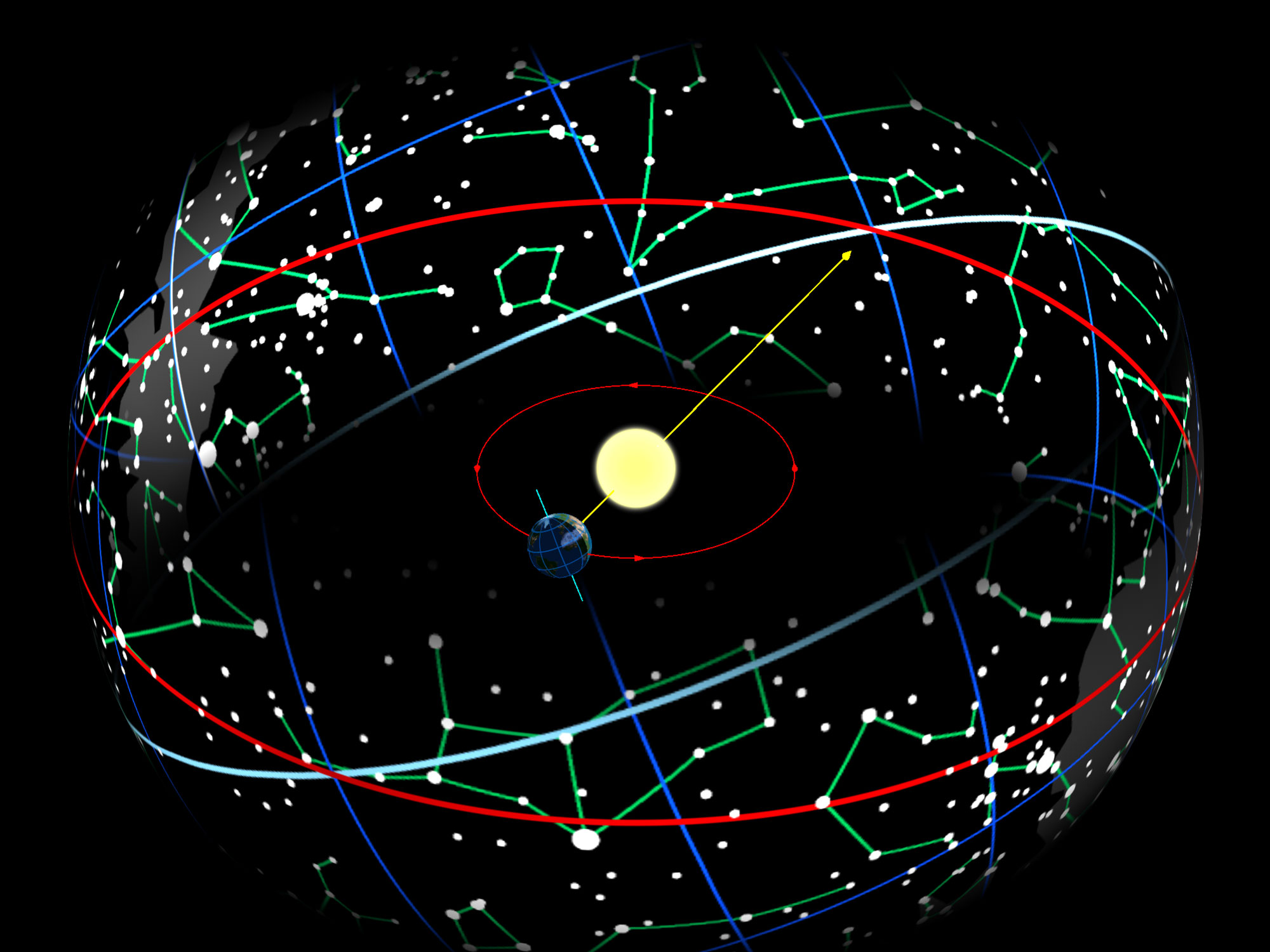
Zodiacs
The zodiac is a belt-shaped region of the sky that extends approximately 8° north or south (as measured in celestial latitude) of the ecliptic, the apparent path of the Sun across the celestial sphere over the course of the year. The paths of the Moon and visible planets are within the belt of the zodiac. In Western astrology, and formerly astronomy, the zodiac is divided into twelve signs, each occupying 30° of celestial longitude and roughly corresponding to the following star constellations: Aries, Taurus, Gemini, Cancer, Leo, Virgo, Libra, Scorpio, Sagittarius, Capricorn, Aquarius, and Pisces. These astrological signs form a celestial coordinate system, or more specifically an ecliptic coordinate system, which takes the ecliptic as the origin of latitude and the Sun's position at vernal equinox as the origin of longitude. Name The English word ' derives from , the Latinized form of the Ancient Greek ( ), meaning "cycle or circle of little animals". () ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nike (mythology)
In Greek mythology, Nike (; grc, Νίκη, lit=victory, ancient: , modern: ) was a goddess who personified victory in any field including art, music, war, and athletics. She is often portrayed in Greek art as Winged Victory in the motion of flight; however, she can also appear without wings as "Wingless Victory" when she is being portrayed as an attribute of another deity such as Athena.Suidas. ''The Suda on Line: Byzantine Lexicography''. Translated by Whitehead, David, et al. (2014). Accessed 9 December 2022. https://www.cs.uky.edu/~raphael/sol/sol-html/ In Greek literature Nike is described as both an attribute and attendant to the gods Zeus and Athena. Nike gained this honored role beside Zeus during the Titanomachy where she was one of the first gods to offer her allegiance to Zeus. At Athens, Nike became a servant to Athena as well as an attribute of her due to the prominent status Athena held in her patron city. The fusion of the two goddesses at Athens has contributed to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Kutbay
Al-Kutba' ( ar, الكتبي) was a north Arabian god. The name means, roughly, "the scribe"; it comes from the Semitic root ''K-T-B'' which means 'to write.' A carving at the foot of Jebal Rumm in Jordan, discovered in 1959 by J. Strugell, is dedicated to al-Kutbay. Another inscription in Wadi Es Siyyagh, on the way to the main spring of Petra contains the phrase "in front of Kutbay, this very god." Other sites around Arabia contain inscriptions dedicated to him. Kutba' is represented as a betyl in Wadi Rum alongside al-'Uzza. The gender of this god is disputed. Because of the god's name originating from the root word ''K-T-B'' or "to write", it is considered that Kutba' was a god of intellect including writing. Nabataeans and other mercantile Arab tribes brought the worship of al-Kutbay from Petra in Jordan to Egypt. A temple to the god has been discovered at Qasr Gheit, built in characteristic Egyptian style. An altar-base in this temple, is inscribed with the Nabataean ded ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Al-Uzza
Al-ʻUzzā ( ar, العزى or Old Arabic l ʕuzzeː was one of the three chief goddesses of Arabian religion in pre-Islamic times and she was worshiped by the pre-Islamic Arabs along with al-Lāt and Manāt. A stone cube at Nakhla (near Mecca) was held sacred as part of her cult. She is mentioned in Qur'an 53:19 as being one of the goddesses who people worshiped. Al-ʻUzzā, like Hubal, was called upon for protection by the pre-Islamic Quraysh. "In 624 at the ' battle called Uhud', the war cry of the Qurayshites was, "O people of Uzzā, people of Hubal!". Al-‘Uzzá also later appears in Ibn Ishaq's account of the alleged Satanic Verses. The temple dedicated to al-ʻUzzā and the statue was destroyed by Khalid ibn al Walid in Nakhla in 630 AD."He sent Khal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khirbet Et-Tannur
Khirbet et-Tannur (Arabic: خربة التنور) is an ancient Nabataean temple situated on top of Jebel Tannur, in today's Jordan. Based on the cults statues iconography, whether the temple was dedicated to the fertility goddess Atargatis and Zeus-Hadad, or perhaps other gods of their own in that form is not yet certain. The only inscription which mentioned a deity was in reference to the Edomite god Qos, who was the equivalent of the Arab god Quzah, the god of the sky. History The remains of Khirbet et-Tannur consists only of the temple complex on isolated mountain top, which indicate a site solely functioning as a religious high place similar to those in other Nabataean regions. While no dating is established, the temple went through three different phases. The earliest phase of the temple is usually dated around 8-7 BC on the account of an inscription engraved on a small stone block. The final phase was dated by Glueck judging from the temple's sculptures and architectural ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dionysus
In ancient Greek religion and myth, Dionysus (; grc, Διόνυσος ) is the god of the grape-harvest, winemaking, orchards and fruit, vegetation, fertility, insanity, ritual madness, religious ecstasy, festivity, and theatre. The Romans called him Bacchus ( or ; grc, Βάκχος ) for a frenzy he is said to induce called ''bakkheia''. As Dionysus Eleutherios ("the liberator"), his wine, music, and ecstatic dance free his followers from self-conscious fear and care, and subvert the oppressive restraints of the powerful. His ''thyrsus'', a fennel-stem sceptre, sometimes wound with ivy and dripping with honey, is both a beneficent wand and a weapon used to destroy those who oppose his cult and the freedoms he represents. Those who partake of his mysteries are believed to become possessed and empowered by the god himself. His origins are uncertain, and his cults took many forms; some are described by ancient sources as Thracian, others as Greek. In Orphic religion, he wa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dushara
Dushara, (Nabataean Arabic: 𐢅𐢈𐢝𐢛𐢀 ''dwšrʾ'') also transliterated as Dusares, is a pre-Islamic Arabian god worshipped by the Nabataeans at Petra and Madain Saleh (of which city he was the patron). Safaitic inscriptions imply he was the son of Al-Lat, and that he assembled in the heavens with other gods. He is called "Dushara from Petra" in one inscription. Dushara was expected to bring justice if called by the correct ritual. Etymology Dushara is known first from epigraphic Nabataean sources who invariably spell the name ''dwsrʾ'', the Nabataean script denoting only consonants. He appears in Classical Greek sources Δουσάρης (''Dousárēs'') and in Latin as ''Dusares''. The original meaning is disputed, but early Muslim historian Ibn al-Kalbi in his "Book of Idols" explains the name as ''Dhū l-Šarā'' ( ar, ذو الشرى), meaning likely "The One from Shara", Shara being a mountain range south-east of the Dead Sea. If this interpretation is correct ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Camel And Riders MET Me31 67 2
A camel (from: la, camelus and grc-gre, κάμηλος (''kamēlos'') from Hebrew or Phoenician: גָמָל ''gāmāl''.) is an even-toed ungulate in the genus ''Camelus'' that bears distinctive fatty deposits known as "humps" on its back. Camels have long been domesticated and, as livestock, they provide food (milk and meat) and textiles (fiber and felt from hair). Camels are working animals especially suited to their desert habitat and are a vital means of transport for passengers and cargo. There are three surviving species of camel. The one-humped dromedary makes up 94% of the world's camel population, and the two-humped Bactrian camel makes up 6%. The Wild Bactrian camel is a separate species and is now critically endangered. The word ''camel'' is also used informally in a wider sense, where the more correct term is "camelid", to include all seven species of the family Camelidae: the true camels (the above three species), along with the "New World" camelids: the llam ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)