|
NLRP10
NLRP10, short for NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 10, is an intracellular protein of mammals that functions in apoptosis and the immune system. It is also known as NALP10, NOD8, PAN5, Pynod, and CLR11.1, and is one of 14 pyrin domain containing members of the NOD-like receptor family of cytoplasmic receptors, although it differs from other NOD-like receptors by lacking the characteristic leucine-rich repeat domain. It is also believed that it helps regulate the inflammatory response. NLRP10 reduces inflammatory and innate immune responses by inhibiting the activity of two proteins associated with the inflammasome; caspase-1 and PYCARD PYCARD, often referred to as ASC (Apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD), is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''PYCARD'' gene. It is localized mainly in the nucleus of monocytes and macrophages. In case of pathogen in .... References Further reading * * * * * * * * * LRR proteins NOD-like r ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
NOD-like Receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response. They are found in lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species (APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R protein). Structure NLRs contain 3 domains – central NACHT (NOD or NBD – nucleotide-binding domain) domai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrin Domain
A pyrin domain (PYD, also known as PAAD/DAPIN) is a protein domain and a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold, the 4th and most recently discovered member of the death domain superfamily (DDF). It was originally discovered in the pyrin protein, or marenostrin, encoded by MEFV. The mutation of the MEFV gene is the cause of the disease known as Familial Mediterranean Fever. The domain is encoded in 23 human proteins and at least 31 mouse genes. Proteins containing a pyrin domain are frequently involved in programmed cell death processes including pyroptosis and apoptosis. Proteins that possess a pyrin domain interact with the pyrin domains in other proteins to form of multi-protein complexes called inflammasomes and to trigger downstream immune responses. Structure Pyrin domains are a ~90 amino acid motif present only at the N-terminus of proteins. The core is made of highly conserved hydrophobic residues surrounded by five or six alpha helices with α1→2 linkage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intracellular
This glossary of biology terms is a list of definitions of fundamental terms and concepts used in biology, the study of life and of living organisms. It is intended as introductory material for novices; for more specific and technical definitions from sub-disciplines and related fields, see Glossary of genetics, Glossary of evolutionary biology, Glossary of ecology, and Glossary of scientific naming, or any of the organism-specific glossaries in :Glossaries of biology. A B C D E ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apoptosis
Apoptosis (from grc, ἀπόπτωσις, apóptōsis, 'falling off') is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Biochemical events lead to characteristic cell changes (morphology) and death. These changes include blebbing, cell shrinkage, nuclear fragmentation, chromatin condensation, DNA fragmentation, and mRNA decay. The average adult human loses between 50 and 70 billion cells each day due to apoptosis. For an average human child between eight and fourteen years old, approximately twenty to thirty billion cells die per day. In contrast to necrosis, which is a form of traumatic cell death that results from acute cellular injury, apoptosis is a highly regulated and controlled process that confers advantages during an organism's life cycle. For example, the separation of fingers and toes in a developing human embryo occurs because cells between the digits undergo apoptosis. Unlike necrosis, apoptosis produces cell fragments called apoptotic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Immune System
The immune system is a network of biological processes that protects an organism from diseases. It detects and responds to a wide variety of pathogens, from viruses to parasitic worms, as well as cancer cells and objects such as wood splinters, distinguishing them from the organism's own healthy tissue. Many species have two major subsystems of the immune system. The innate immune system provides a preconfigured response to broad groups of situations and stimuli. The adaptive immune system provides a tailored response to each stimulus by learning to recognize molecules it has previously encountered. Both use molecules and cells to perform their functions. Nearly all organisms have some kind of immune system. Bacteria have a rudimentary immune system in the form of enzymes that protect against virus infections. Other basic immune mechanisms evolved in ancient plants and animals and remain in their modern descendants. These mechanisms include phagocytosis, antimicrobial pe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cytoplasm
In cell biology, the cytoplasm is all of the material within a eukaryotic cell, enclosed by the cell membrane, except for the cell nucleus. The material inside the nucleus and contained within the nuclear membrane is termed the nucleoplasm. The main components of the cytoplasm are cytosol (a gel-like substance), the organelles (the cell's internal sub-structures), and various cytoplasmic inclusions. The cytoplasm is about 80% water and is usually colorless. The submicroscopic ground cell substance or cytoplasmic matrix which remains after exclusion of the cell organelles and particles is groundplasm. It is the hyaloplasm of light microscopy, a highly complex, polyphasic system in which all resolvable cytoplasmic elements are suspended, including the larger organelles such as the ribosomes, mitochondria, the plant plastids, lipid droplets, and vacuoles. Most cellular activities take place within the cytoplasm, such as many metabolic pathways including glycolysis, and proces ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine-rich Repeat
A leucine-rich repeat (LRR) is a protein structural motif that forms an α/β horseshoe fold. It is composed of repeating 20–30 amino acid stretches that are unusually rich in the hydrophobic amino acid leucine. These tandem repeats commonly fold together to form a solenoid protein domain, termed leucine-rich repeat domain. Typically, each repeat unit has beta strand- turn-alpha helix structure, and the assembled domain, composed of many such repeats, has a horseshoe shape with an interior parallel beta sheet and an exterior array of helices. One face of the beta sheet and one side of the helix array are exposed to solvent and are therefore dominated by hydrophilic residues. The region between the helices and sheets is the protein's hydrophobic core and is tightly sterically packed with leucine residues. Leucine-rich repeats are frequently involved in the formation of protein–protein interactions. Examples Leucine-rich repeat motifs have been identified in a large numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammation
Inflammation (from la, wikt:en:inflammatio#Latin, inflammatio) is part of the complex biological response of body tissues to harmful stimuli, such as pathogens, damaged cells, or Irritation, irritants, and is a protective response involving immune cells, blood vessels, and molecular mediators. The function of inflammation is to eliminate the initial cause of cell injury, clear out necrotic cells and tissues damaged from the original insult and the inflammatory process, and initiate tissue repair. The five cardinal signs are heat, pain, redness, swelling, and Functio laesa, loss of function (Latin ''calor'', ''dolor'', ''rubor'', ''tumor'', and ''functio laesa''). Inflammation is a generic response, and therefore it is considered as a mechanism of innate immune system, innate immunity, as compared to adaptive immune system, adaptive immunity, which is specific for each pathogen. Too little inflammation could lead to progressive tissue destruction by the harmful stimulus (e.g. b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innate Immune System
The innate, or nonspecific, immune system is one of the two main immunity strategies (the other being the adaptive immune system) in vertebrates. The innate immune system is an older evolutionary defense strategy, relatively speaking, and is the dominant immune system response found in plants, fungi, insects, and primitive multicellular organisms (see Beyond vertebrates).. The major functions of the innate immune system are to: * recruit immune cells to infection sites by producing chemical factors, including chemical mediators called cytokines * activate the complement cascade to identify bacteria, activate cells, and promote clearance of antibody complexes or dead cells * identify and remove foreign substances present in organs, tissues, blood and lymph, by specialized white blood cells * activate the adaptive immune system through antigen presentation * act as a physical and chemical barrier to infectious agents; via physical measures such as skin and chemical measures such a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme Inhibition
An enzyme inhibitor is a molecule that binds to an enzyme and blocks its activity. Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions necessary for life, in which substrate molecules are converted into products. An enzyme facilitates a specific chemical reaction by binding the substrate to its active site, a specialized area on the enzyme that accelerates the most difficult step of the reaction. An enzyme inhibitor stops ("inhibits") this process, either by binding to the enzyme's active site (thus preventing the substrate itself from binding) or by binding to another site on the enzyme such that the enzyme's catalysis of the reaction is blocked. Enzyme inhibitors may bind reversibly or irreversibly. Irreversible inhibitors form a chemical bond with the enzyme such that the enzyme is inhibited until the chemical bond is broken. By contrast, reversible inhibitors bind non-covalently and may spontaneously leave the enzyme, allowing the enzyme to resume its function. Rever ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
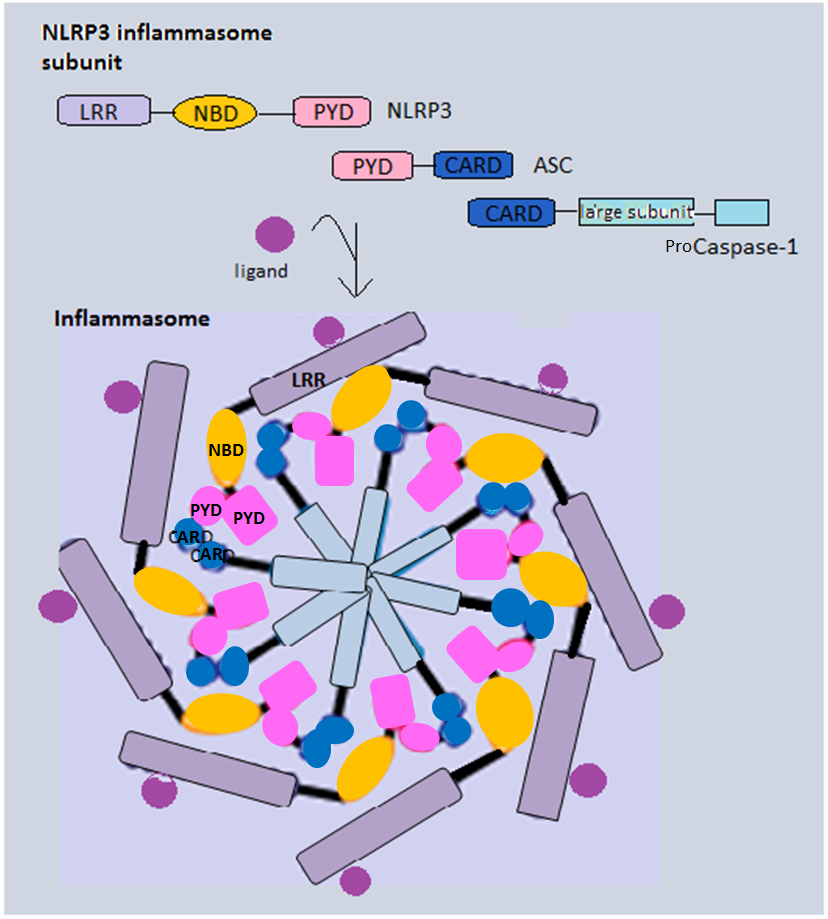
Inflammasome
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein oligomers of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes proteolytic cleavage, maturation and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as cleavage of Gasdermin-D. The N-terminal fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, and is responsible for secretion of the mature cytokines, presumably through the formation of pores in the plasma membrane. Inflammasome activation is initiated by different kinds of cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) that respond to either microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) or danger-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) generated by the host cell. Pattern recognition receptors involved in inflammasomes comprise NLRs (nucleoti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase-1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the precursors of the inflammatory cytokines interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells. Cellular expression Caspase-1 is evolutionarily conserved in many eukaryotes of the Kingdom Animalia. Due to its role in the inflammatory immune ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |