|
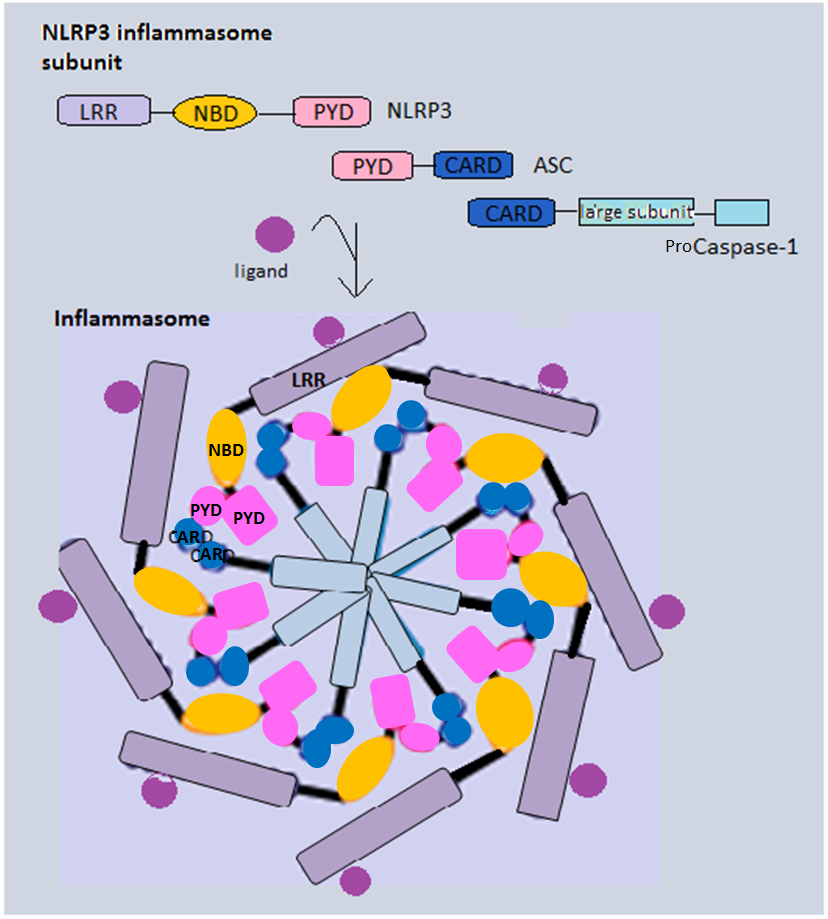
Inflammasome
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein complexes of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses and cell death. They are formed as a result of specific cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) sensing microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from the host cell, or homeostatic disruptions. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes the activation of caspase-1, which then proteolytically cleaves pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as the pore-forming molecule gasdermin D ( GSDMD). The N-terminal GSDMD fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, which is responsible for the release of mature cytokines. Additionally, inflammasomes can act as integral components of larger cell death-inducing complexes ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Inflammasome Final1
Inflammasomes are cytosolic multiprotein complexes of the innate immune system responsible for the activation of inflammatory responses and cell death. They are formed as a result of specific cytosolic pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) sensing microbe-derived pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) from the host cell, or homeostatic disruptions. Activation and assembly of the inflammasome promotes the activation of caspase-1, which then proteolytically cleaves pro-inflammatory cytokines, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18), as well as the pore-forming molecule gasdermin D ( GSDMD). The N-terminal GSDMD fragment resulting from this cleavage induces a pro-inflammatory form of programmed cell death distinct from apoptosis, referred to as pyroptosis, which is responsible for the release of mature cytokines. Additionally, inflammasomes can act as integral components of larger cell death-inducing complexes called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyroptosis
Pyroptosis is a highly inflammatory form of lytic programmed cell death that occurs most frequently upon infection with intracellular pathogens and is likely to form part of the antimicrobial response. This process promotes the rapid clearance of various bacterial, viral, fungal and protozoan infections by removing intracellular replication niches and enhancing the host's defensive responses. Pyroptosis can take place in immune cells and is also reported to occur in keratinocytes and some epithelial cells. The process is initiated by formation of a large supramolecular complex termed the inflammasome (also known as a pyroptosome) upon intracellular danger signals. The inflammasome activates a different set of caspases as compared to apoptosis, for example, caspase-1/4/5 in humans and caspase-11 in mice. These caspases contribute to the maturation and activation of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18, as well as the pore-forming protein gasdermin D. Formation of pores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GSDMD
Gasdermin D (GSDMD, from combination of ''gastro'' and ''dermato'', referencing the locations where its family of proteins were originally found to be primarily expressed) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''GSDMD'' gene on chromosome 8. It belongs to the gasdermin family which is conserved among vertebrates and comprises six members in humans, GSDMA, GSDMB, GSDMC, GSDMD, GSDME (DFNA5) and DFNB59 (Pejvakin). Members of the gasdermin family are expressed in a variety of cell types including epithelial cells and immune cells. GSDMA, GSDMB, GSDMC, GSDMD and GSDME have been suggested to act as tumour suppressors. Structure The structure of full-length GSDMD consists of two domains, the 31 kDa N-terminal (GSDMD-N) and 22 kDa C-terminal (GSDMD-C) domains, separated by a linker region. GSDMD-C can be divided into four subdomains and is composed of 10 α-helices and two β-strands, forming a compact globular fold. The linker helix contacts the two helix-repe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pyrin Domain
A pyrin domain (PYD, also known as PAAD/DAPIN) is a protein domain and a subclass of protein motif known as the death fold, the 4th and most recently discovered member of the death domain superfamily (DDF). It was initially discovered in the pyrin protein, also known as marenostrin, which is encoded by MEFV. The mutation of the MEFV gene is the cause of the disease known as Familial Mediterranean fever, Familial Mediterranean Fever. The domain is encoded in 23 human proteins and at least 31 mouse genes. Proteins containing a pyrin domain are frequently involved in programmed cell death processes, including pyroptosis and apoptosis. Proteins that possess a pyrin domain interact with the pyrin domains of other proteins to form multi-protein complexes called inflammasomes, triggering downstream immune responses. Structure Pyrin domains are a ~90 amino acid Protein motif, motif present only at the N-terminus of proteins. The core is composed of highly conserved hydrophobic residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
PANoptosis
PANoptosis is a prominent innate immune, inflammatory, and lytic cell death pathway initiated by innate immune sensors and driven by caspases and receptor-interacting protein kinases (RIPKs) through multiprotein PANoptosome complexes. The assembly of the PANoptosome cell death complex occurs in response to germline-encoded pattern-recognition receptors (PRRs) sensing pathogens, including bacterial, viral, and fungal infections, as well as pathogen-associated molecular patterns, damage-associated molecular patterns, and cytokines that are released during infections, inflammatory conditions, and cancer. Several PANoptosome complexes, such as the ZBP1-, AIM2-, RIPK1-, NLRP3 and NLRC5- and NLRP12-PANoptosomes, have been characterized so far. Emerging genetic, molecular, and biochemical studies have identified extensive crosstalk among the molecular components across various cell death pathways in response to a variety of pathogens and innate immune triggers. Historically, inflamm ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 11
Murine caspase-11, and its human homologs caspase-4 and caspase-5, are mammalian intracellular receptor proteases activated by TLR4 and TLR3 signaling during the innate immune response. Caspase-11, also termed the non-canonical inflammasome, is activated by TLR3/TLR4- TRIF signaling and directly binds cytosolic lipopolysaccharide (LPS), a major structural element of Gram-negative bacterial cell walls. Activation of caspase-11 by LPS is known to cause the activation of other caspase proteins, leading to septic shock, pyroptosis, and often organismal death. History LPS is a known activator of innate immune responses. Extracellular LPS binds specifically to the cell surface receptor TLR4. LPS binding to TLR4 subsequently causes initiation of the MyD88 and TRIF signaling pathways, leading to expression of pro- inflammatory molecules and cytokines. These inflammatory mediators cause host toxic shock and sepsis as a result of an overactive immune response to LPS. Until recentl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caspase 1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolysis, proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the Protein precursor, precursors of the inflammatory cytokines Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β and interleukin 18 as well as the pyroptosis inducer Gasdermin D, into active mature peptides. It plays a central role in cell immunity as an inflammatory response initiator. Once activated through formation of an inflammasome complex, it initiates a proinflammatory response through the cleavage and thus activation of the two inflammatory cytokines, Interleukin 1 beta, interleukin 1β (IL-1β) and interleukin 18 (IL-18) as well as pyroptosis, a programmed lytic cell death pathway, through cleavage of Gasdermin D. The two inflammatory cytokines activated by Caspase-1 are excreted from the cell to further induce the inflammatory response in neighboring cells. Cellular expression Caspase-1 is evolutionarily conserved in many eukaryot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jürg Tschopp
Jürg Tschopp (born 1951 in Basel — died 22 March 2011 in the Swiss Alps) was a Swiss biochemist, known for his research on apoptosis and the immunology of inflammation. His greatest achievement was perhaps his team's discovery and scientific description of the inflammasome (which he named). Biography Tschopp studied chemistry with his 1974 ''Diplom'' thesis supervised by Joachim Seelig at the Biozentrum University of Basel. There Tschopp received in 1979 his doctorate in biophysics under the supervision of Jürgen Engel. As a postdoc Tschopp was supervised by Hans J. Müller-Eberhard at the Scripps Research Institute in La Jolla. There with colleagues he showed "that the lytic pore of complement was formed by C9 multimers." At the University of Lausanne, Tschopp became an assistant professor in 1982, an associate professor in 1987, and a full professor in 1990 in the biochemistry department. Since 2003 he was a co-director of the biochemistry department. He and his colleag ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cell Death
Cell death is the event of a biological cell ceasing to carry out its functions. This may be the result of the natural process of old cells dying and being replaced by new ones, as in programmed cell death, or may result from factors such as diseases, localized injury, or the death of the organism of which the cells are part. Apoptosis or Type I cell-death, and Autophagy (cellular), autophagy or Type II cell-death are both forms of programmed cell death, while necrosis is a non-physiological process that occurs as a result of infection or injury. The term "cell necrobiology" has been used to describe the life processes associated with morphological, biochemical, and molecular changes which predispose, precede, and accompany cell death, as well as the consequences and tissue response to cell death. The word is derived from the Greek language, Greek νεκρό meaning "death", βìο meaning "life", and logos, λόγος meaning "the study of". The term was initially coined to bro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pattern Recognition Receptor
Pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) play a crucial role in the proper function of the innate immune system. PRRs are germline-encoded host sensors, which detect molecules typical for the pathogens. They are proteins expressed mainly by cells of the innate immune system, such as dendritic cells, macrophages, monocytes, neutrophils, as well as by epithelial cells, to identify two classes of molecules: pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs), which are associated with microbial pathogens, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), which are associated with components of host's cells that are released during cell damage or death. They are also called primitive pattern recognition receptors because they evolved before other parts of the immune system, particularly before adaptive immunity. PRRs also mediate the initiation of antigen-specific adaptive immune response and release of inflammatory cytokines. PRRs are regulated through a variety of pathways ensure optimal im ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
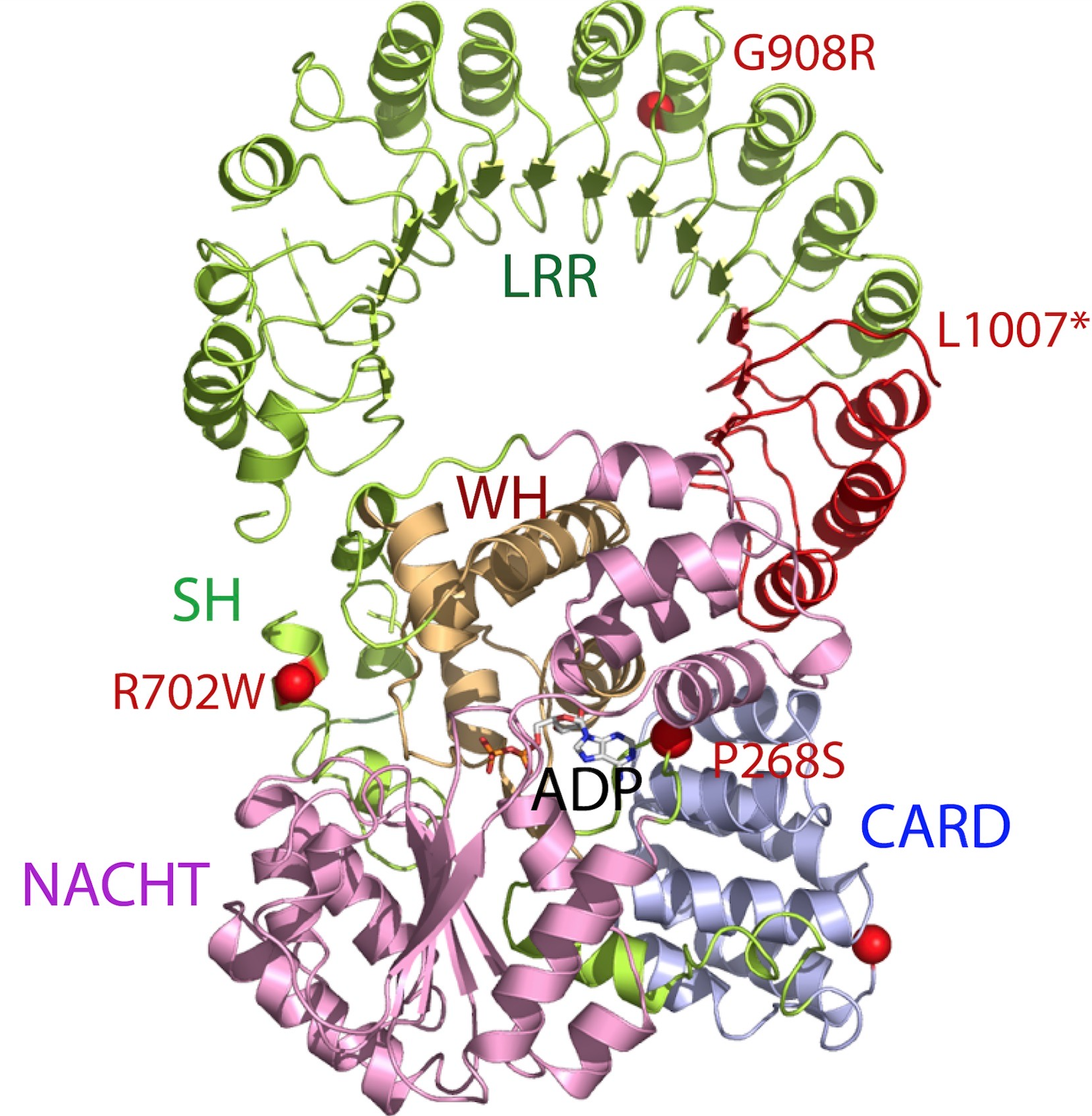
NOD-like Receptor
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response. NLRs primarily recognize Gram-positive bacteria, whereas TLRs primarily recognize Gram-negative bacteria. They are found in lymphocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species ( APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R pr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
AIM2
Interferon-inducible protein AIM2 also known as absent in melanoma 2 or simply AIM2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''AIM2'' gene. AIM2 is a cytoplasmic sensor found in hematopoietic cells that recognizes the presence of double-stranded DNA (dsDNA) of microbial or host cellular origin. AIM2-like receptor (ALR) family was founded on AIM2 and now consists of four members in human genome. Activated AIM2 recruits apoptosis-associated speck-like protein containing a CARD (ASC), resulting in caspase-1 binding, and forming of AIM2 inflammasome. This signaling contributes to the defense against bacterial and viral DNA. The AIM2 inflammasome can also be an integral component of the AIM2-PANoptosome to drive PANoptosis. Structure Proteins belonging to ALR family usually contain an N-terminal pyrin (PYD) domain, and one or two HIN domains. AIM2 consists of two domains connected through a long linker: an N-terminal PYD domain (amino acids 1-87), and a C-terminal HIN-200 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |