NOD-like receptor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via
PTHR14074filter for human
{{Portal bar, Biology Intracellular receptors LRR proteins NOD-like receptors Immune system
 The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via
The nucleotide-binding oligomerization domain-like receptors, or NOD-like receptors (NLRs) (also known as nucleotide-binding leucine-rich repeat receptors), are intracellular sensors of pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) that enter the cell via phagocytosis
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell (biology), cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs ph ...
or pores, and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) that are associated with cell stress. They are types of pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and play key roles in the regulation of innate immune response. NLRs can cooperate with toll-like receptors (TLRs) and regulate inflammatory and apoptotic response.
NLRs primarily recognize Gram-positive bacteria
In bacteriology, gram-positive bacteria are bacteria that give a positive result in the Gram stain test, which is traditionally used to quickly classify bacteria into two broad categories according to their type of cell wall.
The Gram stain ...
, whereas TLRs primarily recognize Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
. They are found in lymphocyte
A lymphocyte is a type of white blood cell (leukocyte) in the immune system of most vertebrates. Lymphocytes include T cells (for cell-mediated and cytotoxic adaptive immunity), B cells (for humoral, antibody-driven adaptive immunity), an ...
s, macrophage
Macrophages (; abbreviated MPhi, φ, MΦ or MP) are a type of white blood cell of the innate immune system that engulf and digest pathogens, such as cancer cells, microbes, cellular debris and foreign substances, which do not have proteins that ...
s, dendritic cell
A dendritic cell (DC) is an antigen-presenting cell (also known as an ''accessory cell'') of the mammalian immune system. A DC's main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system ...
s and also in non-immune cells, for example in epithelium
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is a thin, continuous, protective layer of cells with little extracellular matrix. An example is the epidermis, the outermost layer of the skin. Epithelial ( mesothelial) tissues line the outer surfaces of man ...
. NLRs are highly conserved through evolution. Their homologs have been discovered in many different animal species ( APAF1) and also in the plant kingdom ( disease-resistance R protein).
Structure
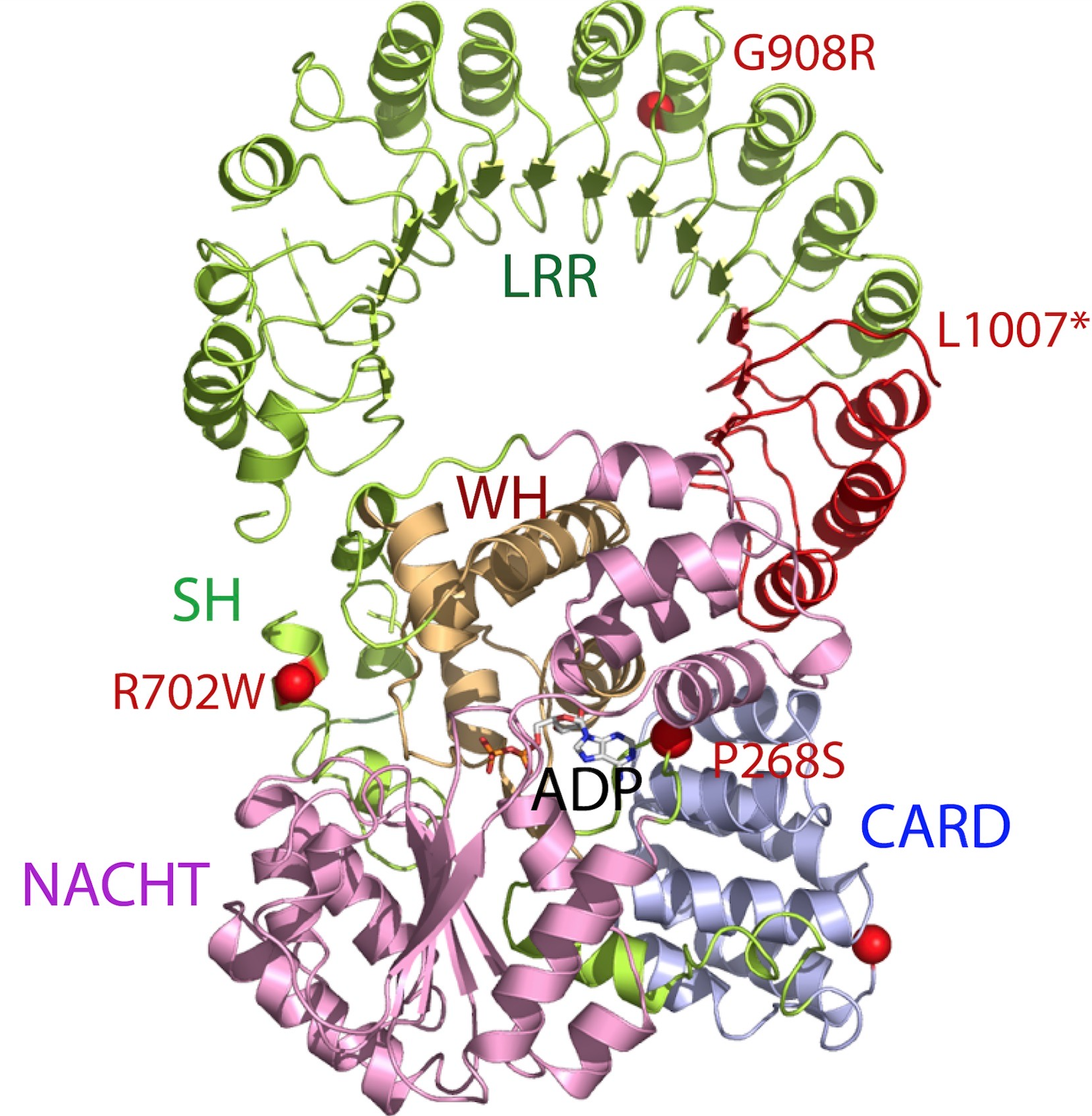
NLRs contain 3 domains – central NACHT (NOD or NBD – nucleotide-binding domain) domain, which is common to all NLRs, most of NLRs have also C-terminalleucine-rich repeat
A leucine-rich repeat (LRR) is a protein structural motif that forms an α/β horseshoe tertiary structure, fold. It is composed of repeating 20–30 amino acid stretches that are unusually rich in the hydrophobic amino acid leucine. These Pr ...
(LRR) and variable N-terminal interaction domain. NACHT domain mediates ATP-dependent self-oligomerization and LRR senses the presence of ligand. N-terminal domain is responsible for homotypic protein-protein interaction and it can consist of caspase recruitment domain (CARD), pyrin domain (PYD), acidic transactivating domain or baculovirus inhibitor repeats (BIRs).
Nomenclature and system
Names as CATERPILLER, NOD, NALP, PAN, NACHT, PYPAF were used to describe the NLRs family. The nomenclature was unified by theHUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee
The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC) is a committee of the Human Genome Organisation (HUGO) that sets the standards for human gene nomenclature. The HGNC approves a ''unique'' and ''meaningful'' name for every known human gene, based on a ...
in 2008. The family was characterized as NLRs to provide description of the families features – NLR means nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat containing gene family.
This system divides NLRs into 4 subfamilies based on the type of N-terminal domain:
*NLRA (A for acidic transactivating domain): CIITA
CIITA is a human gene which encodes a protein called the class II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator. Mutations in this gene are responsible for the bare lymphocyte syndrome in which the immune system is severely compromised and c ...
*NLRB (B for BIRs): NAIP
*NLRC (C for CARD
Card or The Card may refer to:
Common uses
* Plastic cards of various types:
**Bank card
**Credit card
**Debit card
**Payment card
* Playing card, used in games
* Printed circuit board, or card
* Greeting card, given on special occasions
Arts an ...
): NOD1, NOD2, NLRC3, NLRC4
NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRC4'' gene.
Structure
The NLRC4 protein is highly conserved across mammalian species. It bears homology to the ''C. elegans'' Ced4 protein. It conta ...
, NLRC5
*NLRP (P for PYD): NLRP1
NLRP1 encodes NACHT, LRR, FIIND, CARD domain and PYD domains-containing protein 1 in humans. NLRP1 was the first protein shown to form an inflammasome. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution ...
, NLRP2, NLRP3, NLRP4, NLRP5, NLRP6, NLRP7, NLRP8, NLRP9, NLRP10, NLRP11, NLRP12, NLRP13, NLRP14
There is also an additional subfamily NLRX which doesn't have significant homology to any N-terminal domain. A member of this subfamily is NLRX1.
On the other hand, NLRs can be divided into 3 subfamilies with regard to their phylogenetic relationships:
*NODs: NOD1, NOD2, NOD3 ( NLRC3), NOD4 ( NLRC5), NOD5 ( NLRX1), CIITA
CIITA is a human gene which encodes a protein called the class II, major histocompatibility complex, transactivator. Mutations in this gene are responsible for the bare lymphocyte syndrome in which the immune system is severely compromised and c ...
*NLRPs (also called NALPs): NLRP1
NLRP1 encodes NACHT, LRR, FIIND, CARD domain and PYD domains-containing protein 1 in humans. NLRP1 was the first protein shown to form an inflammasome. Material was copied from this source, which is available under Creative Commons Attribution ...
, NLRP2, NLRP3, NLRP4, NLRP5, NLRP6, NLRP7, NLRP8, NLRP9, NLRP10, NLRP11, NLRP12, NLRP13, NLRP14
*IPAF: IPAF (NLRC4
NLR family CARD domain-containing protein 4 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''NLRC4'' gene.
Structure
The NLRC4 protein is highly conserved across mammalian species. It bears homology to the ''C. elegans'' Ced4 protein. It conta ...
), NAIP
Subfamily NODs
NODs subfamily consists of NOD1, NOD2, NOD3, NOD4 with CARD domain, CIITA containing acidic transactivator domain and NOD5 without any N-terminal domain.Signalling
The well-described receptors are NOD1 and NOD2. The recognition of their ligands recruits oligomerization of NACHT domain and CARD-CARD interaction with CARD-containing serine-threonin kinase RIP2 which leads to activation of RIP2. RIP2 mediates the recruitment of kinase TAK1 which phosphorylates and activates IκB kinase. The activation of IκB kinase results in the phosphorylation of inhibitor IκB which releasesNF-κB
Nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NF-κB) is a family of transcription factor protein complexes that controls transcription (genetics), transcription of DNA, cytokine production and cell survival. NF-κB is found i ...
and its nuclear translocation. NF-κB then activates expression of inflammatory cytokines.
Mutations in NOD2 are associated with Crohn's disease
Crohn's disease is a type of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that may affect any segment of the gastrointestinal tract. Symptoms often include abdominal pain, diarrhea, fever, abdominal distension, and weight loss. Complications outside of the ...
or Blau syndrome.
Ligands
NOD1 and NOD2 recognizepeptidoglycan
Peptidoglycan or murein is a unique large macromolecule, a polysaccharide, consisting of sugars and amino acids that forms a mesh-like layer (sacculus) that surrounds the bacterial cytoplasmic membrane. The sugar component consists of alternating ...
motifs from bacterial cell which consists of N-acetylglucosamine and N-acetylmuramic acid. These sugar chains are cross-linked by peptide chains that can be sensed by NODs. NOD1 recognizes a molecule called meso-diaminopimelic acid (meso-DAP) mostly found in Gram-negative bacteria
Gram-negative bacteria are bacteria that, unlike gram-positive bacteria, do not retain the Crystal violet, crystal violet stain used in the Gram staining method of bacterial differentiation. Their defining characteristic is that their cell envelo ...
(for example ''Helicobacter pylori
''Helicobacter pylori'', previously known as ''Campylobacter pylori'', is a gram-negative, Flagellum#bacterial, flagellated, Bacterial cellular morphologies#Helical, helical bacterium. Mutants can have a rod or curved rod shape that exhibits l ...
'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
''). NOD2 proteins can sense intracellular muramyl dipeptide (MDP), typical for bacteria such as '' Streptococcus pneumoniae'' or ''Mycobacterium tuberculosis
''Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (M. tb), also known as Koch's bacillus, is a species of pathogenic bacteria in the family Mycobacteriaceae and the causative agent of tuberculosis.
First discovered in 1882 by Robert Koch, ''M. tuberculosis'' ha ...
''.
Subfamilies NLRPs and IPAF
NLRPs subfamily contains NLRP1-NLRP14 that are characterized by the presence of PYD domain. IPAF subfamily has two members – IPAF with CARD domain and NAIP with BIR domain.Signalization
NLRPs and IPAF subfamilies are involved in the formation of the inflammasome. The best characterized inflammasome is NLRP3, the activation through PAMPs or DAMPs leads to the oligomerization. The pyrin domain of NLRs binds to an adaptor protein ASC (PYCARD) via PYD-PYD interaction. ASC contains PYD and CARD domain and links the NLRs to inactive form ofcaspase 1
Caspase-1/Interleukin-1 converting enzyme (ICE) is an evolutionarily conserved enzyme that proteolysis, proteolytically cleaves other proteins, such as the Protein precursor, precursors of the inflammatory cytokines Interleukin 1 beta, interleuki ...
through the CARD domain.
All these protein-protein interaction form a complex called the inflammasome. The aggregation of the pro-caspase-1 causes the autocleavage and formation of an active enzyme. Caspase-1 is important for the proteolytic processing of the pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β and IL-18.
NLRP3 mutations are responsible for the autoinflammatory disease familial cold autoinflammatory syndrome or Muckle–Wells syndrome.
Ligands
There are three well-characterized inflammasomes – NLRP1, NLRP3 and IPAF. The formation of NLRP3 inflammasome can be activated by PAMPs such as microbial toxins (for example alpha-toxin of ''Staphylococcus aureus
''Staphylococcus aureus'' is a Gram-positive spherically shaped bacterium, a member of the Bacillota, and is a usual member of the microbiota of the body, frequently found in the upper respiratory tract and on the skin. It is often posi ...
'') or whole pathogens, for instance '' Candida albicans'', ''Saccharomyces cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungal microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have be ...
'', Sendai virus
''Murine respirovirus'', formerly ''Sendai virus'' (SeV) and previously also known as murine parainfluenza virus type 1 or hemagglutinating virus of Japan (HVJ), is an Viral envelope, enveloped, 150-200 nm–diameter, negative sense, single ...
, Influenza
Influenza, commonly known as the flu, is an infectious disease caused by influenza viruses. Symptoms range from mild to severe and often include fever, runny nose, sore throat, muscle pain, headache, coughing, and fatigue. These sympto ...
. NLRP3 recognize also DAMPs which indicate stress in the cell. The danger molecule can be extracellular ATP, extracellular glucose, monosodium urate (MSU) crystals, calcium pyrophosphate dihydrate (CPPD), alum
An alum () is a type of chemical compound, usually a hydrated double salt, double sulfate salt (chemistry), salt of aluminium with the general chemical formula, formula , such that is a valence (chemistry), monovalent cation such as potassium ...
, cholesterol
Cholesterol is the principal sterol of all higher animals, distributed in body Tissue (biology), tissues, especially the brain and spinal cord, and in Animal fat, animal fats and oils.
Cholesterol is biosynthesis, biosynthesized by all anima ...
or environmental irritants – silica
Silicon dioxide, also known as silica, is an oxide of silicon with the chemical formula , commonly found in nature as quartz. In many parts of the world, silica is the major constituent of sand. Silica is one of the most complex and abundant f ...
, asbestos
Asbestos ( ) is a group of naturally occurring, Toxicity, toxic, carcinogenic and fibrous silicate minerals. There are six types, all of which are composed of long and thin fibrous Crystal habit, crystals, each fibre (particulate with length su ...
, UV irradiation and skin irritants. The presence of these molecules causes a production of ROS and K+ efflux. NLRP1 recognizes lethal toxin from '' Bacillus anthracis'' and muramyl dipeptide. IPAF senses flagellin
Flagellins are a family of proteins present in flagellated bacteria which arrange themselves in a hollow cylinder to form the filament in a bacterial flagellum. Flagellin has a mass on average of about 40,000 daltons. Flagellins are the princi ...
from '' Salmonella typhimurium'', ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common Bacterial capsule, encapsulated, Gram-negative bacteria, Gram-negative, Aerobic organism, aerobic–facultative anaerobe, facultatively anaerobic, Bacillus (shape), rod-shaped bacteria, bacterium that can c ...
'', '' Listeria monocytogenes''.
See also
*Toll-like receptor
Toll-like receptors (TLRs) are a class of proteins that play a key role in the innate immune system. They are single-pass membrane protein, single-spanning receptor (biochemistry), receptors usually expressed on sentinel cells such as macrophages ...
* Inflammasome
* RIG-I-like receptor
References
External links
PTHR14074
{{Portal bar, Biology Intracellular receptors LRR proteins NOD-like receptors Immune system