|
IκB Kinase
The IκB kinase (IkappaB kinase or IKK) is an enzyme complex that is involved in propagating the cellular response to inflammation, specifically the regulation of lymphocytes. The IκB kinase enzyme complex is part of the upstream NF-κB signal transduction cascade. The IκBα (inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa B) protein inactivates the NF-κB transcription factor by masking the nuclear localization signals (NLS) of NF-κB proteins and keeping them sequestered in an inactive state in the cytoplasm. Specifically, IKK phosphorylates the inhibitory IκBα protein. This phosphorylation results in the dissociation of IκBα from NF-κB. NF-κB, which is now free, migrates into the nucleus and activates the expression of at least 150 genes; some of which are anti-apoptotic. Catalyzed reaction In enzymology, an IκB kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the chemical reaction: :ATP + IκB protein \rightleftharpoons ADP + IκB phosphoprotein Thus, the two substrates of this enzy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Enzyme
An enzyme () is a protein that acts as a biological catalyst by accelerating chemical reactions. The molecules upon which enzymes may act are called substrate (chemistry), substrates, and the enzyme converts the substrates into different molecules known as product (chemistry), products. Almost all metabolism, metabolic processes in the cell (biology), cell need enzyme catalysis in order to occur at rates fast enough to sustain life. Metabolic pathways depend upon enzymes to catalyze individual steps. The study of enzymes is called ''enzymology'' and the field of pseudoenzyme, pseudoenzyme analysis recognizes that during evolution, some enzymes have lost the ability to carry out biological catalysis, which is often reflected in their amino acid sequences and unusual 'pseudocatalytic' properties. Enzymes are known to catalyze more than 5,000 biochemical reaction types. Other biocatalysts include Ribozyme, catalytic RNA molecules, also called ribozymes. They are sometimes descr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Serine
Serine (symbol Ser or S) is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α- amino group (which is in the protonated − form under biological conditions), a carboxyl group (which is in the deprotonated − form under biological conditions), and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It can be synthesized in the human body under normal physiological circumstances, making it a nonessential amino acid. It is encoded by the codons UCU, UCC, UCA, UCG, AGU and AGC. Occurrence This compound is one of the proteinogenic amino acids. Only the L- stereoisomer appears naturally in proteins. It is not essential to the human diet, since it is synthesized in the body from other metabolites, including glycine. Serine was first obtained from silk protein, a particularly rich source, in 1865 by Emil Cramer. Its name is derived from the Latin for silk, '' sericum''. Serine's structure was established in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lipopolysaccharide
Lipopolysaccharide (LPS), now more commonly known as endotoxin, is a collective term for components of the outermost membrane of the cell envelope of gram-negative bacteria, such as '' E. coli'' and ''Salmonella'' with a common structural architecture. Lipopolysaccharides are large molecules consisting of three parts: an outer core polysaccharide termed the O-antigen, an inner core oligosaccharide and Lipid A (from which toxicity is largely derived), all covalently linked. In current terminology, the term endotoxin is often used synonymously with LPS, although there are a few endotoxins (in the original sense of toxins that are inside the bacterial cell that are released when the cell disintegrates) that are not related to LPS, such as the so-called delta endotoxin proteins produced by '' Bacillus thuringiensis''. Lipopolysaccharides can have substantial impacts on human health, primarily through interactions with the immune system. LPS is a potent activator of the immune syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zinc Finger
A zinc finger is a small protein structural motif that is characterized by the coordination of one or more zinc ions (Zn2+) which stabilizes the fold. The term ''zinc finger'' was originally coined to describe the finger-like appearance of a hypothesized structure from the African clawed frog (''Xenopus laevis'') transcription factor IIIA. However, it has been found to encompass a wide variety of differing protein structures in eukaryotic cells. '' Xenopus laevis'' TFIIIA was originally demonstrated to contain zinc and require the metal for function in 1983, the first such reported zinc requirement for a gene regulatory protein followed soon thereafter by the Krüppel factor in ''Drosophila''. It often appears as a metal-binding domain in multi-domain proteins. Proteins that contain zinc fingers (zinc finger proteins) are classified into several different structural families. Unlike many other clearly defined supersecondary structures such as Greek keys or β hairpins, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
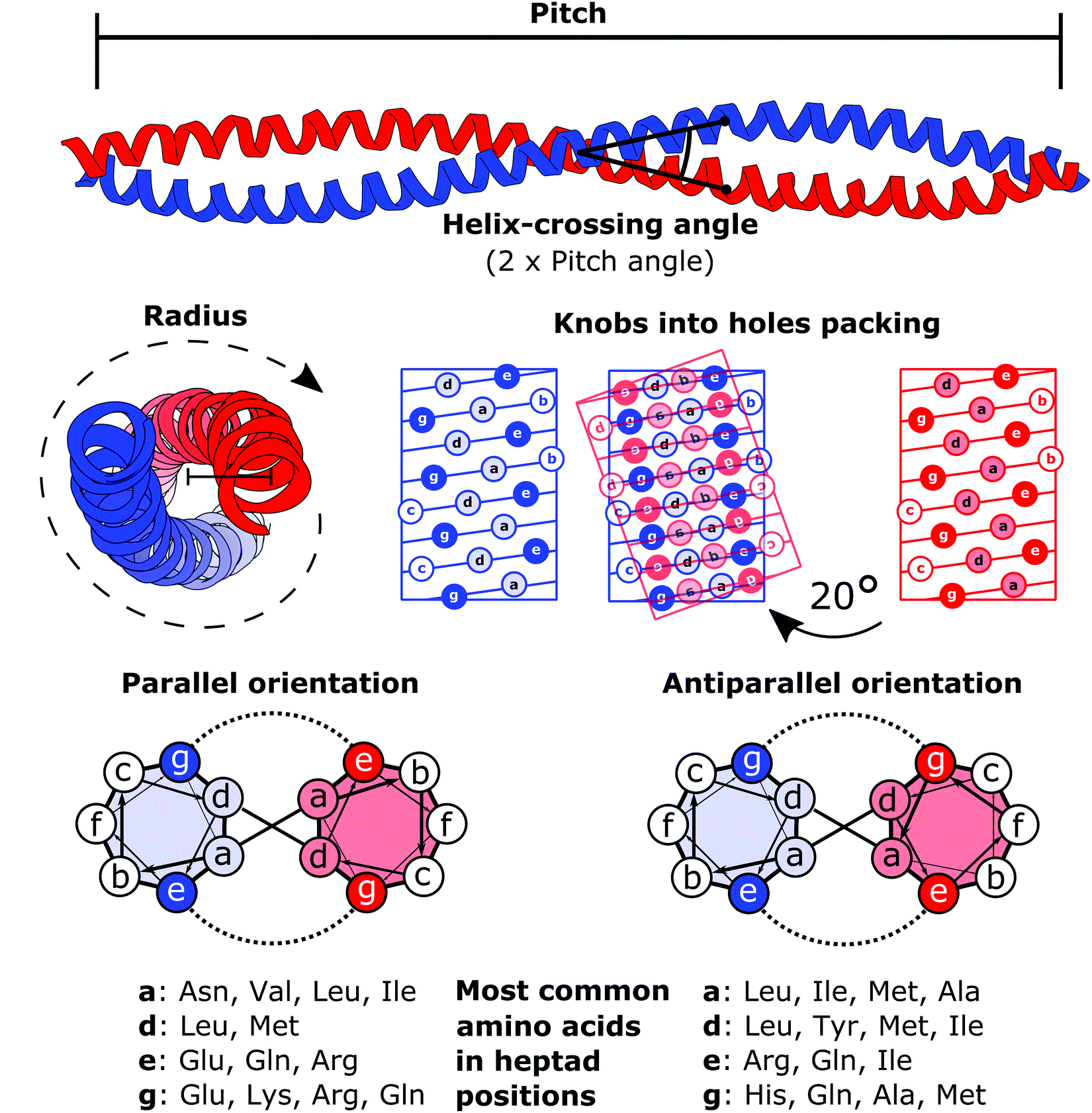
Coiled Coil
A coiled coil is a structural motif in proteins in which two to seven alpha-helices are coiled together like the strands of a rope. ( Dimers and trimers are the most common types.) They have been found in roughly 5-10% of proteins and have a variety of functions. They are one of the most widespread motifs found in protein-protein interactions. To aid protein study, several tools have been developed to predict coiled-coils in protein structures. Many coiled coil-type proteins are involved in important biological functions, such as the regulation of gene expression — e.g., transcription factors. Notable examples are the oncoproteins c-Fos and c-Jun, as well as the muscle protein tropomyosin. Discovery The possibility of coiled coils for α-keratin was initially somewhat controversial. Linus Pauling and Francis Crick independently came to the conclusion that this was possible at about the same time. In the summer of 1952, Pauling visited the laboratory in England where C ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leucine Zipper
A leucine zipper (or leucine scissors) is a common three-dimensional structural motif in proteins. They were first described by Landschulz and collaborators in 1988 when they found that an enhancer binding protein had a very characteristic 30-amino acid segment and the display of these amino acid sequences on an idealized alpha helix revealed a periodic repetition of leucine residues at every seventh position over a distance covering eight helical turns. The polypeptide segments containing these periodic arrays of leucine residues were proposed to exist in an alpha-helical conformation and the leucine side chains from one alpha helix interdigitate with those from the alpha helix of a second polypeptide, facilitating dimerization. Leucine zippers are a dimerization motif of the BZIP domain, bZIP (Basic-region leucine zipper) class of eukaryotic transcription factors. The bZIP domain is 60 to 80 amino acids in length with a highly conserved DNA binding basic region and a more divers ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kinase
In biochemistry, a kinase () is an enzyme that catalyzes the transfer of phosphate groups from high-energy, phosphate-donating molecules to specific substrates. This process is known as phosphorylation, where the high-energy ATP molecule donates a phosphate group to the substrate molecule. As a result, kinase produces a phosphorylated substrate and ADP. Conversely, it is referred to as dephosphorylation when the phosphorylated substrate donates a phosphate group and ADP gains a phosphate group (producing a dephosphorylated substrate and the high energy molecule of ATP). These two processes, phosphorylation and dephosphorylation, occur four times during glycolysis. Kinases are part of the larger family of phosphotransferases. Kinases should not be confused with phosphorylases, which catalyze the addition of inorganic phosphate groups to an acceptor, nor with phosphatases, which remove phosphate groups (dephosphorylation). The phosphorylation state of a molecule, whether it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IKBKG
NF-kappa-B essential modulator (NEMO) also known as inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit gamma (IKK-γ) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IKBKG'' gene. NEMO is a subunit of the IκB kinase complex that activates NF-κB. The human gene for IKBKG is located on the chromosome band Xq28. Multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. Function NEMO (IKK-γ) is the regulatory subunit of the inhibitor of IκB kinase (IKK) complex, which activates NF-κB resulting in activation of genes involved in inflammation, immunity, cell survival, and other pathways. Clinical significance Mutations in the IKBKG gene results in incontinentia pigmenti, hypohidrotic ectodermal dysplasia, and several other types of immunodeficiencies. Incontinentia Pigmenti (IP) is an X-linked dominant disease caused by a mutation in the IKBKG gene. Since IKBKG helps activate NF-κB, which protects cells against TNF-alpha induced apop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
IKK2
IKK-β also known as inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit beta is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''IKBKB'' (inhibitor of kappa light polypeptide gene enhancer in B-cells, kinase beta) gene. Function IKK-β is an enzyme that serves as a protein subunit of IκB kinase, which is a component of the cytokine-activated intracellular signaling pathway involved in triggering immune responses. IKK's activity causes activation of a transcription factor In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription (genetics), transcription of genetics, genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding t ... known as Nuclear Transcription factor kappa-B or NF-κB. Activated IKK-β phosphorylates a protein called the '' inhibitor of NF-κB'', IκB ( IκBα), which binds NF-κB to inhibit its function. Phosphorylated IκB is degraded via the ubiquitination pat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
CHUK
Inhibitor of nuclear factor kappa-B kinase subunit alpha (IKK-α) also known as IKK1 or conserved helix-loop-helix ubiquitous kinase (CHUK) is a protein kinase that in humans is encoded by the ''CHUK'' gene. IKK-α is part of the IκB kinase complex that plays an important role in regulating the NF-κB transcription factor. However, IKK-α has many additional cellular targets, and is thought to function independently of the NF-κB pathway to regulate epidermal differentiation. Function NF-κB response IKK-α is a member of the serine/threonine protein kinase family and forms a complex in the cell with IKK-β and NEMO. NF-κB transcription factors are normally held in an inactive state by the inhibitory proteins IκBs. IKK-α and IKK-β phosphorylate the IκB proteins, marking them for degradation via ubiquitination and allowing NF-κB transcription factors to go into the nucleus. Once activated, NF-κB transcription factors regulate genes that are implicated in m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Enzymes
Enzymes are listed here by their classification in the International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology's Enzyme Commission (EC) numbering system: :Oxidoreductases (EC 1) ( Oxidoreductase) * Dehydrogenase * Luciferase * DMSO reductase :EC 1.1 (act on the CH-OH group of donors) * :EC 1.1.1 (with NAD+ or NADP+ as acceptor) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NAD) ** Alcohol dehydrogenase (NADP) ** Homoserine dehydrogenase ** Aminopropanol oxidoreductase ** Diacetyl reductase ** Glycerol dehydrogenase ** Propanediol-phosphate dehydrogenase ** glycerol-3-phoshitiendopene dehydrogenase (NAD+) ** D-xylulose reductase ** L-xylulose reductase ** Lactate dehydrogenase ** Malate dehydrogenase ** Isocitrate dehydrogenase ** HMG-CoA reductase * :EC 1.1.2 (with a cytochrome as acceptor) * :EC 1.1.3 (with oxygen as acceptor) ** Glucose oxidase ** L-gulonolactone oxidase ** Thiamine oxidase ** Xanthine oxidase * EC 1.1.4 (with a disulfide as accep ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |