|
Medvyezhi Islands
The Medvezhyi Islands, or Bear Islands (russian: Медве́жьи острова́; sah, Эhэлээх арыылар, ''Eheleex Arıılar'') is an uninhabited group of islands at the western end of the Kolyma Gulf of the East Siberian Sea. History The first recorded European to report the existence of the Medvezhyi Islands was Russian explorer Yakov Permyakov in 1710. While sailing from the Lena to the Kolyma River, Permyakov observed the silhouette of the unknown island group in the then little explored East Siberian Sea. In 1820-1824, during Ferdinand Wrangel's Arctic expedition to the East Siberian Sea and the Chukchi Sea, Arctic explorer Fyodor Matyushkin surveyed and mapped Chetyryokhstolbovoy Island in the Medvezhyi group. On September 3, 1878, Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld recorded that he sailed close to the island group in the steamship ''Vega''. This report was made during the famous expedition that made the whole length of the Northeast passage for the first ti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island in a river or a lake island may be called an eyot or ait, and a small island off the coast may be called a holm. Sedimentary islands in the Ganges delta are called chars. A grouping of geographically or geologically related islands, such as the Philippines, is referred to as an archipelago. There are two main types of islands in the sea: continental and oceanic. There are also artificial islands, which are man-made. Etymology The word ''island'' derives from Middle English ''iland'', from Old English ''igland'' (from ''ig'' or ''ieg'', similarly meaning 'island' when used independently, and -land carrying its contemporary meaning; cf. Dutch ''eiland'' ("island"), German ''Eiland'' ("small island")). However, the spelling of the word ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vega (ship)
SS ''Vega'' was a Swedish barque, built in Bremerhaven, Germany in 1872. The Vega was the first ship to complete a voyage through the Northeast Passage, and the first vessel to circumnavigate the Eurasian continent, during the Vega expedition. Initially a troubled enterprise, the successful expedition is considered to be among the highest achievements in the history of Swedish science. Construction Though a sailing ship, the Vega had a 60 hp auxiliary steam engine. The hull was of wood measuring 150 ft. in length (45.72 m), a capacity of 357 DWT. Arctic exploration Constructed as a whaler, the vessel was acquired and rebuilt for Arctic exploration by Nils Adolf Erik Nordenskiöld with financial assistance from King Oscar II of Sweden and others.Aho, Marie''A.E. Nordenskiöld Collection included in the Unesco Memory of the World Program'' Tietolinja News (National Library of Finland), January 1999 On 22 June 1878 the ship set out from Karlskrona, Sweden through the Northea ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
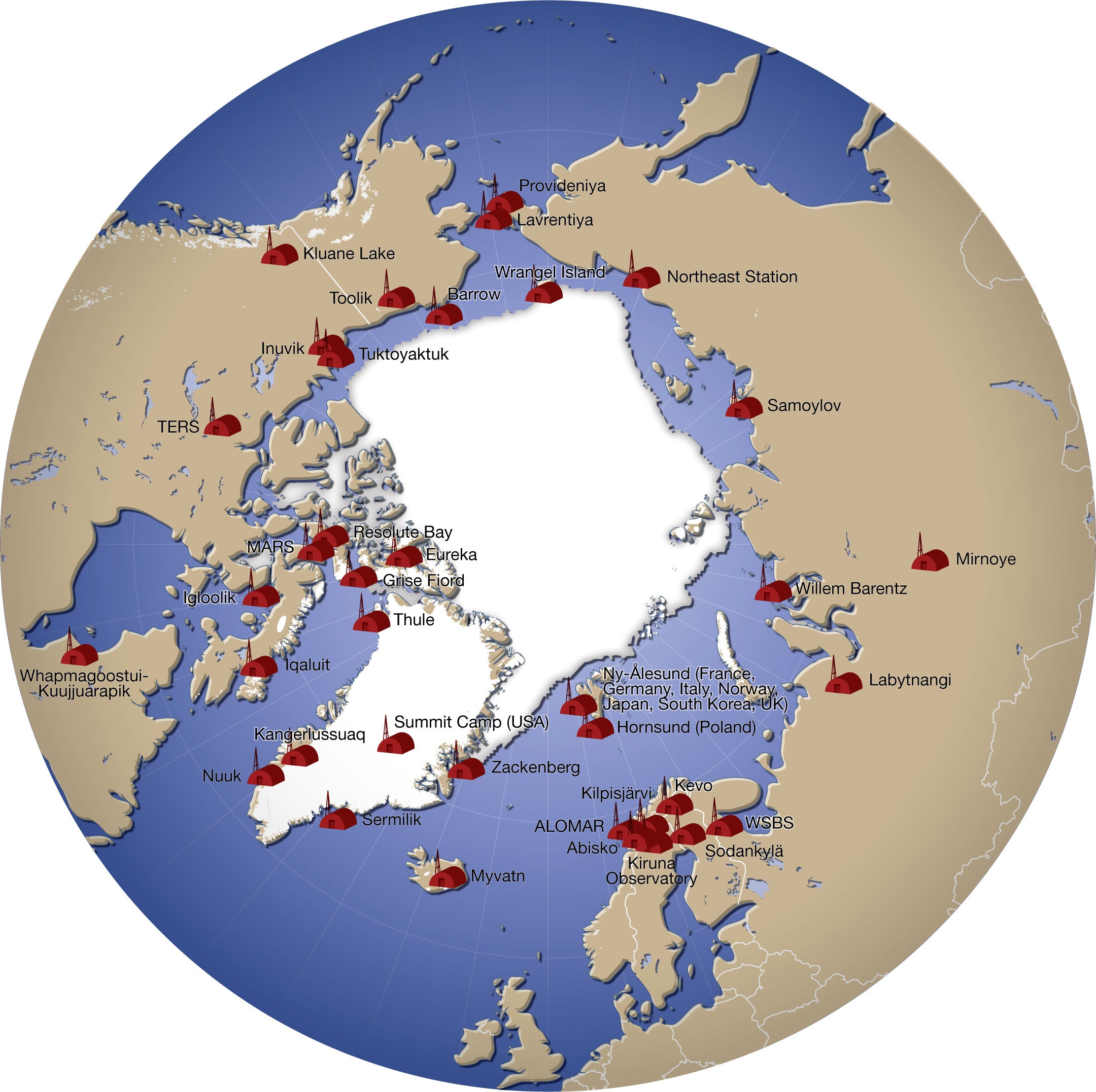
List Of Research Stations In The Arctic
A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research stations have been permanent. Most of them were temporary, being abandoned after the completion of the project or owing to lack of funding to continue the research. Some of these were military or intelligence stations (listening posts) created as a result of the proximity of the U.S. and Soviet Union to each other's landmass across the polar region. Ice stations are constructed on land or on ice that rests on land, while others are drifting ice stations built on the sea ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. Research stations Drifting ice stations *Fletcher's Ice Island, US (1952 - 1978) In fiction *Ice Station Zebra (novel), by Alistair MacLean **Ice Station Zebra (1968 film) **Ice Station Zebra a song by Jack White on Boar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kigilyakh
Kigilyakh or kisiliyakh ( rus, кигиляхи; sah, киһилээх, meaning "stone person") are tall, pillar-like natural rock formations looking like tall monoliths standing more or less isolated. Usually they are composed of granite or sandstone shaped as a result of cryogenic weathering. Most kigilyakhs formed during the Cretaceous period and are about 120 million years old. Cultural significance and etymology These anthropomorphic rock pillars are an important feature in Yakut culture. Often they are slightly scattered, protruding from the surface of smooth mountains and giving the impression of a standing crowd of people. According to Yakut legends kigilyakhs originated in very ancient people. The Yakut word ''"kisiliy"'' means "a place where there are people". ''Kisilyakh'' means "mountain having a man" or "mountain married". The term "kigilyakh" is a distorted form of the original Yakut ''"kisilyakh"''. Locations Such stones are found in different places of Sakha ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
National Oceanic And Atmospheric Administration
The National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (abbreviated as NOAA ) is an United States scientific and regulatory agency within the United States Department of Commerce that forecasts weather, monitors oceanic and atmospheric conditions, charts the seas, conducts deep sea exploration, and manages fishing and protection of marine mammals and endangered species in the U.S. exclusive economic zone. Purpose and function NOAA's specific roles include: * ''Supplying Environmental Information Products''. NOAA supplies to its customers and partners information pertaining to the state of the oceans and the atmosphere, such as weather warnings and forecasts via the National Weather Service. NOAA's information services extend as well to climate, ecosystems, and commerce. * ''Providing Environmental Stewardship Services''. NOAA is a steward of U.S. coastal and marine environments. In coordination with federal, state, local, tribal and international authorities, NOAA manages the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tundra
In physical geography, tundra () is a type of biome where tree growth is hindered by frigid temperatures and short growing seasons. The term ''tundra'' comes through Russian (') from the Kildin Sámi word (') meaning "uplands", "treeless mountain tract". There are three regions and associated types of tundra: Arctic tundra, alpine tundra, and Antarctic tundra. Tundra vegetation is composed of dwarf shrubs, sedges, grasses, mosses, and lichens. Scattered trees grow in some tundra regions. The ecotone (or ecological boundary region) between the tundra and the forest is known as the tree line or timberline. The tundra soil is rich in nitrogen and phosphorus. The soil also contains large amounts of biomass and decomposed biomass that has been stored as methane and carbon dioxide in the permafrost, making the tundra soil a carbon sink. As global warming heats the ecosystem and causes soil thawing, the permafrost carbon cycle accelerates and releases much of these soil-contained g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Station
A number of governments maintain permanent research stations in the Arctic. Also known as Arctic bases, polar stations or ice stations, these bases are widely distributed across the northern polar region of Earth. Historically few research stations have been permanent. Most of them were temporary, being abandoned after the completion of the project or owing to lack of funding to continue the research. Some of these were military or intelligence stations (listening posts) created as a result of the proximity of the U.S. and Soviet Union to each other's landmass across the polar region. Ice stations are constructed on land or on ice that rests on land, while others are drifting ice stations built on the sea ice of the high latitudes of the Arctic Ocean. Research stations Drifting ice stations *Fletcher's Ice Island, US (1952 - 1978) In fiction *Ice Station Zebra (novel), by Alistair MacLean **Ice Station Zebra (1968 film) **Ice Station Zebra a song by Jack White on Boardi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polar Bear
The polar bear (''Ursus maritimus'') is a hypercarnivorous bear whose native range lies largely within the Arctic Circle, encompassing the Arctic Ocean, its surrounding seas and surrounding land masses. It is the largest extant bear species, as well as the largest extant land carnivore. A boar (adult male) weighs around , while a sow (adult female) is about half that size. Although it is the sister species of the brown bear, it has evolved to occupy a narrower ecological niche, with many body characteristics adapted for cold temperatures, for moving across snow, ice and open water, and for hunting seals, which make up most of its diet. Although most polar bears are born on land, they spend most of their time on the sea ice. Their scientific name means "maritime bear" and derives from this fact. Polar bears hunt their preferred food of seals from the edge of sea ice, often living off fat reserves when no sea ice is present. Because of their dependence on the sea ice, polar be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of Russia since the latter half of the 16th century, after the Russians conquered lands east of the Ural Mountains. Siberia is vast and sparsely populated, covering an area of over , but home to merely one-fifth of Russia's population. Novosibirsk, Krasnoyarsk and Omsk are the largest cities in the region. Because Siberia is a geographic and historic region and not a political entity, there is no single precise definition of its territorial borders. Traditionally, Siberia extends eastwards from the Ural Mountains to the Pacific Ocean, and includes most of the drainage basin of the Arctic Ocean. The river Yenisey divides Siberia into two parts, Western and Eastern. Siberia stretches southwards from the Arctic Ocean to the hills of north-ce ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
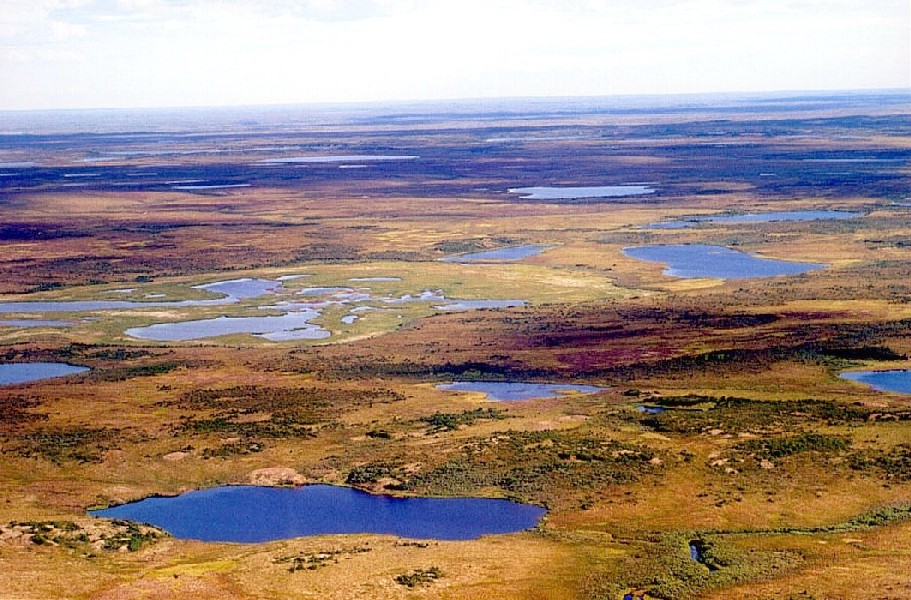
East Siberian Lowland
The East Siberian Lowland ( rus, Восточно-Сибирская низменность), also known as Yana-Kolyma Lowland,Oleg Leonidovič Kryžanovskij, ''A Checklist of the Ground-beetles of Russia and Adjacent Lands.'' p. 16 is a vast plain in Northeastern Siberia, Russia.Yana-Indigirka and Kolyma lowlands (physical map, scale 1: 2 500 000) // National Atlas of Russia . - M .: Roskartografiya, 2004. - T. 1. - S. 260—261. - 496 p. - The territory of the lowland is one of the . Administratively it is part of the |
Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition
The Arctic Ocean Hydrographic Expedition (GESLO) (1910–1915) was a scientific expedition organized by Russia for the purpose of the development of the Northern Sea Route. This expedition accomplished its goal of exploring the uncharted areas of the continental side of the Northern Sea Route in what was seen as the culmination of the Great Northern Expedition, an ambitious enterprise initially conceived by emperor Peter I the Great to map the whole of the northern coast of Russia to the east. Expedition Two icebreaking steamers Vaigach and Taimyr were used for the venture. The plan of the expedition was developed with the active participation of A.V. Kolchak and F. A. Matisen. The 32 man expedition was headed by Boris A. Vilkitsky and was staffed with military seamen and hydrographers, such as Konstantin Neupokoev. The biological and geological collections were performed by military doctors L. M. Starokadomsky on icebreaker "Taimyr" and E. E. Arnold on icebreaker "Vay ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpg)




