|
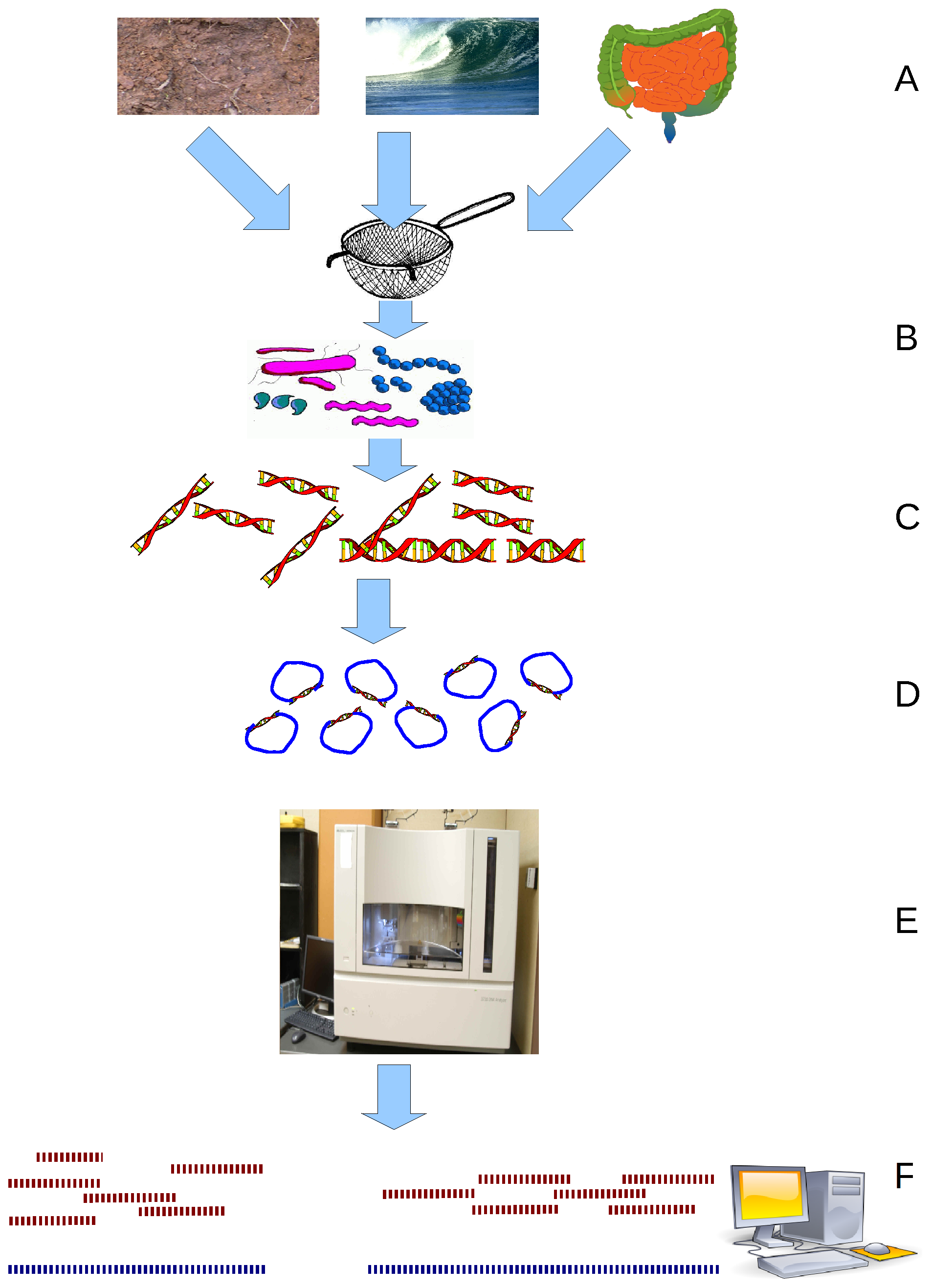
Metaproteomics
Metaproteomics (also Community Proteomics, Environmental Proteomics, or Community Proteogenomics) is an umbrella term for experimental approaches to study all proteins in microbial communities and microbiomes from environmental sources. Metaproteomics is used to classify experiments that deal with all proteins identified and quantified from complex microbial communities. Metaproteomics approaches are comparable to gene-centric environmental genomics, or metagenomics. Origin of the term The term "metaproteomics" was proposed by Francisco Rodríguez-Valera to describe the genes and/or proteins most abundantly expressed in environmental samples. The term was derived from "metagenome". Wilmes and Bond proposed the term "metaproteomics" for the large-scale characterization of the entire protein complement of environmental microbiota at a given point in time. At the same time, the terms "microbial community proteomics" and "microbial community proteogenomics" are sometimes used interch ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Microbiota
Microbiota are the range of microorganisms that may be commensal, symbiotic, or pathogenic found in and on all multicellular organisms, including plants. Microbiota include bacteria, archaea, protists, fungi, and viruses, and have been found to be crucial for immunologic, hormonal, and metabolic homeostasis of their host. The term ''microbiome'' describes either the collective genomes of the microbes that reside in an ecological niche or within the microbes themselves. The microbiome and host emerged during evolution as a synergistic unit from epigenetics and genetic characteristics, sometimes collectively referred to as a holobiont. The presence of microbiota in human and other metazoan guts has been critical for understanding the co-evolution between metazoans and bacteria. Microbiota play key roles in the intestinal immune and metabolic responses via their fermentation product (short-chain fatty acid), acetate. Introduction All plants and animals, from simple life fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metagenomics
Metagenomics is the study of genetic material recovered directly from environmental or clinical samples by a method called sequencing. The broad field may also be referred to as environmental genomics, ecogenomics, community genomics or microbiomics. While traditional microbiology and microbial genome sequencing and genomics rely upon cultivated clonal cultures, early environmental gene sequencing cloned specific genes (often the 16S rRNA gene) to produce a profile of diversity in a natural sample. Such work revealed that the vast majority of microbial biodiversity had been missed by cultivation-based methods. Because of its ability to reveal the previously hidden diversity of microscopic life, metagenomics offers a powerful lens for viewing the microbial world that has the potential to revolutionize understanding of the entire living world. As the price of DNA sequencing continues to fall, metagenomics now allows microbial ecology to be investigated at a much greater scale ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
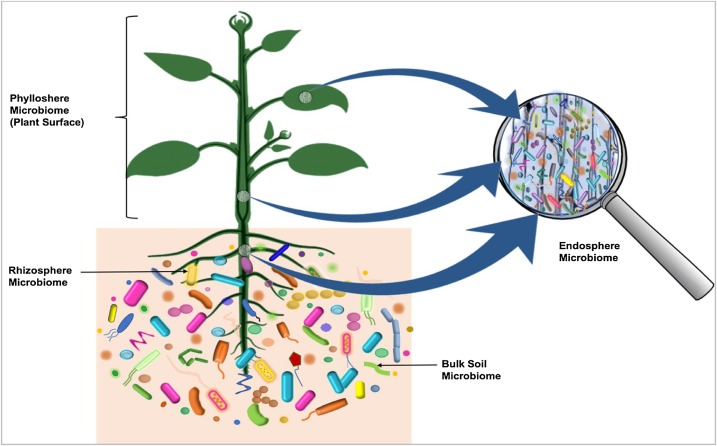
Microbiome
A microbiome () is the community of microorganisms that can usually be found living together in any given habitat. It was defined more precisely in 1988 by Whipps ''et al.'' as "a characteristic microbial community occupying a reasonably well-defined habitat which has distinct physio-chemical properties. The term thus not only refers to the microorganisms involved but also encompasses their theatre of activity". In 2020, an international panel of experts published the outcome of their discussions on the definition of the microbiome. They proposed a definition of the microbiome based on a revival of the "compact, clear, and comprehensive description of the term" as originally provided by Whipps ''et al.'', but supplemented with two explanatory paragraphs. The first explanatory paragraph pronounces the dynamic character of the microbiome, and the second explanatory paragraph clearly separates the term ''microbiota'' from the term ''microbiome''. The microbiota consists of all ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, responding to stimuli, providing structure to cells and organisms, and transporting molecules from one location to another. Proteins differ from one another primarily in their sequence of amino acids, which is dictated by the nucleotide sequence of their genes, and which usually results in protein folding into a specific 3D structure that determines its activity. A linear chain of amino acid residues is called a polypeptide. A protein contains at least one long polypeptide. Short polypeptides, containing less than 20–30 residues, are rarely considered to be proteins and are commonly called peptides. The individual amino acid residues are bonded together by peptide bonds and adjacent amino acid residues. The sequence of amino acid residue ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Top-down Proteomics
Top-down proteomics is a method of protein identification that either uses an ion trapping mass spectrometer to store an isolated protein ion for mass measurement and tandem mass spectrometry (MS/MS) analysis or other protein purification methods such as two-dimensional gel electrophoresis in conjunction with MS/MS. Top-down proteomics is capable of identifying and quantitating unique proteoforms through the analysis of intact proteins. The name is derived from the similar approach to DNA sequencing. During mass spectrometry intact proteins are typically ionized by electrospray ionization and trapped in a Fourier transform ion cyclotron resonance (Penning trap), quadrupole ion trap (Paul trap) or Orbitrap mass spectrometer. Fragmentation for tandem mass spectrometry is accomplished by electron-capture dissociation or electron-transfer dissociation. Effective fractionation is critical for sample handling before mass-spectrometry-based proteomics. Proteome analysis routinely involves ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metatranscriptomics
Metatranscriptomics is the science that studies gene expression of microbes within natural environments, i.e., the metatranscriptome. It also allows to obtain whole gene expression profiling of complex microbial communities. While metagenomics focuses on studying the genomic content and on identifying which microbes are present within a community, metatranscriptomics can be used to study the diversity of the active genes within such community, to quantify their expression levels and to monitor how these levels change in different conditions (e.g., physiological vs. pathological conditions in an organism). The advantage of metatranscriptomics is that it can provide information about differences in the active functions of microbial communities which appear to be the same in terms of microbe composition. Introduction The microbiome has been defined as a microbial community occupying a well-defined habitat. They are ubiquitous and extremely relevant for the maintenance of” the chara ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gut Microbiome
Gut microbiota, gut microbiome, or gut flora, are the microorganisms, including bacteria, archaea, fungi, and viruses that live in the digestive tracts of animals. The gastrointestinal metagenome is the aggregate of all the genomes of the gut microbiota. The gut is the main location of the human microbiome. The gut microbiota has broad impacts, including effects on colonization, resistance to pathogens, maintaining the intestinal epithelium, metabolizing dietary and pharmaceutical compounds, controlling immune function, and even behavior through the gut–brain axis. The microbial composition of the gut microbiota varies across regions of the digestive tract. The colon contains the highest microbial density recorded in any habitat on Earth, representing between 300 and 1000 different species. Bacteria are the largest and to date, best studied component and 99% of gut bacteria come from about 30 or 40 species. Up to 60% of the dry mass of feces is bacteria. Over 99% of the bacter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shotgun Proteomics
Shotgun proteomics refers to the use of bottom-up proteomics techniques in identifying proteins in complex mixtures using a combination of high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry. The name is derived from shotgun sequencing of DNA which is itself named after the rapidly expanding, quasi-random firing pattern of a shotgun. The most common method of shotgun proteomics starts with the proteins in the mixture being digested and the resulting peptides are separated by liquid chromatography. Tandem mass spectrometry is then used to identify the peptides. Targeted proteomics using SRM and data-independent acquisition methods are often considered alternatives to shotgun proteomics in the field of bottom-up proteomics. While shotgun proteomics uses data-dependent selection of precursor ions to generate fragment ion scans, the aforementioned methods use a deterministic method for acquisition of fragment ion scans. History Shotgun proteomics arose from t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Structure
Protein structure is the three-dimensional arrangement of atoms in an amino acid-chain molecule. Proteins are polymers specifically polypeptides formed from sequences of amino acids, the monomers of the polymer. A single amino acid monomer may also be called a ''residue'' indicating a repeating unit of a polymer. Proteins form by amino acids undergoing condensation reactions, in which the amino acids lose one water molecule per reaction in order to attach to one another with a peptide bond. By convention, a chain under 30 amino acids is often identified as a peptide, rather than a protein. To be able to perform their biological function, proteins fold into one or more specific spatial conformations driven by a number of non-covalent interactions such as hydrogen bonding, ionic interactions, Van der Waals forces, and hydrophobic packing. To understand the functions of proteins at a molecular level, it is often necessary to determine their three-dimensional structure. This is t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gene Expression
Gene expression is the process by which information from a gene is used in the synthesis of a functional gene product that enables it to produce end products, protein or non-coding RNA, and ultimately affect a phenotype, as the final effect. These products are often proteins, but in non-protein-coding genes such as transfer RNA (tRNA) and small nuclear RNA (snRNA), the product is a functional non-coding RNA. Gene expression is summarized in the central dogma of molecular biology first formulated by Francis Crick in 1958, further developed in his 1970 article, and expanded by the subsequent discoveries of reverse transcription and RNA replication. The process of gene expression is used by all known life—eukaryotes (including multicellular organisms), prokaryotes (bacteria and archaea), and utilized by viruses—to generate the macromolecular machinery for life. In genetics, gene expression is the most fundamental level at which the genotype gives rise to the phenotype, '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom-up Proteomics
Bottom-up proteomics is a common method to identify proteins and characterize their amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications by proteolytic digestion of proteins prior to analysis by mass spectrometry. The major alternative workflow used in proteomics is called top-down proteomics where intact proteins are purified prior to digestion and/or fragmentation either within the mass spectrometer or by 2D electrophoresis. Essentially, bottom-up proteomics is a relatively simple and reliable means of determining the protein make-up of a given sample of cells, tissues, etc. In bottom-up proteomics, the crude protein extract is enzymatically digested, followed by one or more dimensions of separation of the peptides by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry, a technique known as shotgun proteomics. By comparing the masses of the proteolytic peptides or their tandem mass spectra with those predicted from a sequence database or annotated peptide spectral in a p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis
Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) is a technique widely used in biochemistry, forensic chemistry, genetics, molecular biology and biotechnology to separate biological macromolecules, usually proteins or nucleic acids, according to their electrophoretic mobility. Electrophoretic mobility is a function of the length, conformation, and charge of the molecule. Polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis is a powerful tool used to analyze RNA samples. When polyacrylamide gel is denatured after electrophoresis, it provides information on the sample composition of the RNA species. Hydration of acrylonitrile results in formation of acrylamide molecules () by nitrile hydratase. Acrylamide monomer is in a powder state before addition of water. Acrylamide is toxic to the human nervous system, therefore all safety measures must be followed when working with it. Acrylamide is soluble in water and upon addition of free-radical initiators it polymerizes resulting in formation of polyacrylamide. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |