|
Shotgun Proteomics
Shotgun proteomics refers to the use of bottom-up proteomics techniques in identifying proteins in complex mixtures using a combination of high performance liquid chromatography combined with mass spectrometry. The name is derived from shotgun sequencing of DNA which is itself named after the rapidly expanding, quasi-random firing pattern of a shotgun. The most common method of shotgun proteomics starts with the proteins in the mixture being protease, digested and the resulting peptides are separated by liquid chromatography. Tandem mass spectrometry is then used to identify the peptides. Selected reaction monitoring, Targeted proteomics using SRM and data-independent acquisition methods are often considered alternatives to shotgun proteomics in the field of bottom-up proteomics. While shotgun proteomics uses data-dependent selection of precursor ions to generate fragment ion scans, the aforementioned methods use a deterministic method for acquisition of fragment ion scans. History ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bottom-up Proteomics
Bottom-up proteomics is a common method to identify proteins and characterize their amino acid sequences and post-translational modifications by proteolytic digestion of proteins prior to analysis by mass spectrometry. The major alternative workflow used in proteomics is called top-down proteomics where intact proteins are purified prior to digestion and/or fragmentation either within the mass spectrometer or by 2D electrophoresis. Essentially, bottom-up proteomics is a relatively simple and reliable means of determining the protein make-up of a given sample of cells, tissues, etc. In bottom-up proteomics, the crude protein extract is enzymatically digested, followed by one or more dimensions of separation of the peptides by liquid chromatography coupled to mass spectrometry, a technique known as shotgun proteomics. By comparing the masses of the proteolytic peptides or their tandem mass spectra with those predicted from a sequence database or annotated peptide spectral in a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
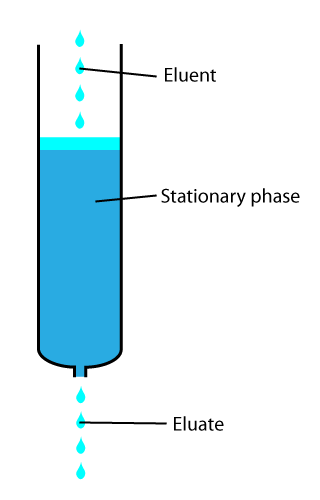
Elute
In analytical and organic chemistry, elution is the process of extracting one material from another by washing with a solvent; as in washing of loaded ion-exchange resins to remove captured ions. In a liquid chromatography experiment, for example, an analyte is generally adsorbed, or "bound to", an adsorbent in a liquid chromatography column. The adsorbent, a solid phase (stationary phase), is a powder which is coated onto a solid support. Based on an adsorbent's composition, it can have varying affinities to "hold" onto other molecules—forming a thin film on the surface of its particles. Elution then is the process of removing analytes from the adsorbent by running a solvent, called an "eluent", past the adsorbent/analyte complex. As the solvent molecules "elute", or travel down through the chromatography column, they can either pass by the adsorbent/analyte complex or they can displace the analyte by binding to the adsorbent in its place. After the solvent molecules displac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hep G2
Hep G2 (or HepG2) is a human liver cancer cell line. Hep G2 is an immortal cell line which was derived in 1975 from the liver tissue of a 15-year-old Caucasian male from Argentina with a well-differentiated hepatocellular carcinoma. These cells are epithelial in morphology, have a modal chromosome number of 55, and are not tumorigenic in nude mice. The cells secrete a variety of major plasma proteins, e.g., albumin, and the acute-phase proteins fibrinogen, alpha 2-macroglobulin, alpha 1-antitrypsin, transferrin and plasminogen. They have been grown successfully in large-scale cultivation systems. Hepatitis B virus surface antigens have not been detected. Hep G2 will respond to stimulation with human growth hormone. Hep G2 cells are a suitable ''in vitro'' model system for the study of polarized human hepatocytes. Another well-characterized polarized hepatocyte cell line is the rat hepatoma-derived hybrid cell line WIF-B. With the proper culture conditions, H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hsp90
Hsp90 (heat shock protein 90) is a chaperone protein that assists other proteins to fold properly, stabilizes proteins against heat stress, and aids in protein degradation. It also stabilizes a number of proteins required for tumor growth, which is why Hsp90 inhibitors are investigated as anti-cancer drugs. Heat shock proteins, as a class, are among the most highly expressed cellular proteins across all species. As their name implies, heat shock proteins protect cells when stressed by elevated temperatures. They account for 1–2% of total protein in unstressed cells. However, when cells are heated, the fraction of heat shock proteins increases to 4–6% of cellular proteins. Heat shock protein 90 (Hsp90) is one of the most common of the heat-related proteins. The "90" comes from the fact that it has a mass of roughly 90 kilodaltons. A 90 kDa protein is considered fairly large for a non-fibrous protein. Hsp90 is found in bacteria and all branches of eukarya, but ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heterogeneous Ribonucleoprotein Particle
Heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoproteins (hnRNPs) are complexes of RNA and protein present in the cell nucleus during gene transcription and subsequent post-transcriptional modification of the newly synthesized RNA (pre-mRNA). The presence of the proteins bound to a pre-mRNA molecule serves as a signal that the pre-mRNA is not yet fully processed and therefore not ready for export to the cytoplasm. Since most mature RNA is exported from the nucleus relatively quickly, most RNA-binding protein in the nucleus exist as heterogeneous ribonucleoprotein particles. After splicing has occurred, the proteins remain bound to spliced introns and target them for degradation. hnRNPs are also integral to the 40s subunit of the ribosome and therefore important for the translation of mRNA in the cytoplasm. However, hnRNPs also have their own nuclear localization sequences (NLS) and are therefore found mainly in the nucleus. Though it is known that a few hnRNPs shuttle between the cytoplasm and nucle ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
High-density Lipoprotein
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) is one of the five major groups of lipoproteins. Lipoproteins are complex particles composed of multiple proteins which transport all fat molecules ( lipids) around the body within the water outside cells. They are typically composed of 80–100 proteins per particle (organized by one, two or three ApoA. HDL particles enlarge while circulating in the blood, aggregating more fat molecules) and transporting up to hundreds of fat molecules per particle. Overview Lipoproteins are divided into five subgroups, by density/size (an inverse relationship), which also correlates with function and incidence of cardiovascular events. Unlike the larger lipoprotein particles, which deliver fat molecules to cells, HDL particles remove fat molecules from cells. The lipids carried include cholesterol, phospholipids, and triglycerides, amounts of each are variable. Increasing concentrations of HDL particles are associated with decreasing accumulation of atheroscl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transmembrane Domain
A transmembrane domain (TMD) is a membrane-spanning protein domain. TMDs generally adopt an alpha helix topological conformation, although some TMDs such as those in porins can adopt a different conformation. Because the interior of the lipid bilayer is hydrophobic, the amino acid residues in TMDs are often hydrophobic, although proteins such as membrane pumps and ion channels can contain polar residues. TMDs vary greatly in length, sequence, and hydrophobicity, adopting organelle-specific properties. Functions of transmembrane domains Transmembrane domains are known to perform a variety of functions. These include: * Anchoring transmembrane proteins to the membrane. *Facilitating molecular transport of molecules such as ions and proteins across biological membranes; usually hydrophilic residues and binding sites in the TMDs help in this process. *Signal transduction across the membrane; many transmembrane proteins, such as G protein-coupled receptors, receive extracel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Protein Kinases
A protein kinase is a kinase which selectively modifies other proteins by covalently adding phosphate, phosphates to them (Protein phosphorylation, phosphorylation) as opposed to kinases which modify lipids, carbohydrates, or other molecules. Phosphorylation usually results in a functional change of the target protein (substrate (biochemistry), substrate) by changing enzyme catalysis, activity, cellular location, or association with other proteins. The human genome contains about 500 protein kinase genes and they constitute about 2% of all human genes. There are two main types of protein kinase. The great majority are Serine/threonine-specific protein kinase, serine/threonine kinases, which phosphorylate the hydroxyl groups of serines and threonines in their targets and most of the others are Tyrosine kinase, tyrosine kinases, although additional types exist. Protein kinases are also found in bacteria and plants. Up to 30% of all human proteins may be modified by kinase activity, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Transcription Factors
In molecular biology, a transcription factor (TF) (or sequence-specific DNA-binding factor) is a protein that controls the rate of transcription of genetic information from DNA to messenger RNA, by binding to a specific DNA sequence. The function of TFs is to regulate—turn on and off—genes in order to make sure that they are expressed in the desired cells at the right time and in the right amount throughout the life of the cell and the organism. Groups of TFs function in a coordinated fashion to direct cell division, cell growth, and cell death throughout life; cell migration and organization (body plan) during embryonic development; and intermittently in response to signals from outside the cell, such as a hormone. There are up to 1600 TFs in the human genome. Transcription factors are members of the proteome as well as regulome. TFs work alone or with other proteins in a complex, by promoting (as an activator), or blocking (as a repressor) the recruitment of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saccharomyces Cerevisiae
''Saccharomyces cerevisiae'' () (brewer's yeast or baker's yeast) is a species of yeast (single-celled fungus microorganisms). The species has been instrumental in winemaking, baking, and brewing since ancient times. It is believed to have been originally isolated from the skin of grapes. It is one of the most intensively studied eukaryotic model organisms in molecular and cell biology, much like ''Escherichia coli'' as the model bacterium. It is the microorganism behind the most common type of fermentation. ''S. cerevisiae'' cells are round to ovoid, 5–10 μm in diameter. It reproduces by budding. Many proteins important in human biology were first discovered by studying their homologs in yeast; these proteins include cell cycle proteins, signaling proteins, and protein-processing enzymes. ''S. cerevisiae'' is currently the only yeast cell known to have Berkeley bodies present, which are involved in particular secretory pathways. Antibodies against ''S. cerevis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paralog
Sequence homology is the biological homology between DNA, RNA, or protein sequences, defined in terms of shared ancestry in the evolutionary history of life. Two segments of DNA can have shared ancestry because of three phenomena: either a speciation event (orthologs), or a duplication event (paralogs), or else a horizontal (or lateral) gene transfer event (xenologs). Homology among DNA, RNA, or proteins is typically inferred from their nucleotide or amino acid sequence similarity. Significant similarity is strong evidence that two sequences are related by evolutionary changes from a common ancestral sequence. Alignments of multiple sequences are used to indicate which regions of each sequence are homologous. Identity, similarity, and conservation The term "percent homology" is often used to mean "sequence similarity”, that is the percentage of identical residues (''percent identity''), or the percentage of residues conserved with similar physicochemical properties ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mascot (software)
Mascot is a software search engine that uses mass spectrometry data to identify proteins from peptide sequence databases. Mascot is widely used by research facilities around the world. Mascot uses a probabilistic scoring algorithm for protein identification that was adapted from the MOWSE algorithm. Mascot is freely available to use on the website of Matrix Science. A license is required for in-house use where more features can be incorporated. History means MOWSE was one of the first algorithms developed for protein identification using peptide mass fingerprinting. It was originally developed in 1993 as a collaboration between Darryl Pappin of the Imperial Cancer Research Fund (ICRF) and Alan Bleasby of the Science and Engineering Research Council (SERC). MOWSE stood apart from other protein identification algorithms in that it produced a probability-based score for identification. It was also the first to take into account the non-uniform distribution of peptide sizes, ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.png)