|
Mathematical Syntaxis
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it canonized a geocentric model of the Universe that was accepted for more than 1,200 years from its origin in Hellenistic Alexandria, in the medieval Byzantine and Islamic worlds, and in Western Europe through the Middle Ages and early Renaissance until Copernicus. It is also a key source of information about ancient Greek astronomy. Ptolemy set up a public inscription at Canopus, Egypt, in 147 or 148. N. T. Hamilton found that the version of Ptolemy's models set out in the ''Canopic Inscription'' was earlier than the version in the ''Almagest''. Hence the ''Almagest'' could not have been completed before about 150, a quarter-century after Ptolemy began observing. Names The name comes from Arabic ', with ' meaning "the", and ''magesti'' bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Definite Article
An article is any member of a class of dedicated words that are used with noun phrases to mark the identifiability of the referents of the noun phrases. The category of articles constitutes a part of speech. In English, both "the" and "a(n)" are articles, which combine with nouns to form noun phrases. Articles typically specify the grammatical definiteness of the noun phrase, but in many languages, they carry additional grammatical information such as gender, number, and case. Articles are part of a broader category called determiners, which also include demonstratives, possessive determiners, and quantifiers. In linguistic interlinear glossing, articles are abbreviated as . Types Definite article A definite article is an article that marks a definite noun phrase. Definite articles such as English ''the'' are used to refer to a particular member of a group. It may be something that the speaker has already mentioned or it may be otherwise something uniquely specified. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Equinox
A solar equinox is a moment in time when the Sun crosses the Earth's equator, which is to say, appears directly above the equator, rather than north or south of the equator. On the day of the equinox, the Sun appears to rise "due east" and set "due west". This occurs twice each year, around 20 March and 23 September. More precisely, an equinox is traditionally defined as the time when the plane of Earth's equator passes through the geometric center of the Sun's disk. Equivalently, this is the moment when Earth's rotation axis is directly perpendicular to the Sun-Earth line, tilting neither toward nor away from the Sun. In modern times, since the Moon (and to a lesser extent the planets) causes Earth's orbit to vary slightly from a perfect ellipse, the equinox is officially defined by the Sun's more regular ecliptic longitude rather than by its declination. The instants of the equinoxes are currently defined to be when the apparent geocentric longitude of the Sun is 0° a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gnomon
A gnomon (; ) is the part of a sundial that casts a shadow. The term is used for a variety of purposes in mathematics and other fields. History A painted stick dating from 2300 BC that was excavated at the astronomical site of Taosi is the oldest gnomon known in China. The gnomon was widely used in ancient China from the second century BC onward in order to determine the changes in seasons, orientation, and geographical latitude. The ancient Chinese used shadow measurements for creating calendars that are mentioned in several ancient texts. According to the collection of Zhou Chinese poetic anthologies ''Classic of Poetry'', one of the distant ancestors of King Wen of the Zhou dynasty used to measure gnomon shadow lengths to determine the orientation around the 14th century BC. The ancient Greek philosopher Anaximander (610–546 BC) is credited with introducing this Babylonian instrument to the Ancient Greeks. The ancient Greek mathematician and astronomer Oenopides used the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north pole, with 0° at the Equator. Lines of constant latitude, or ''parallels'', run east–west as circles parallel to the equator. Latitude and ''longitude'' are used together as a coordinate pair to specify a location on the surface of the Earth. On its own, the term "latitude" normally refers to the ''geodetic latitude'' as defined below. Briefly, the geodetic latitude of a point is the angle formed between the vector perpendicular (or ''normal'') to the ellipsoidal surface from the point, and the plane of the equator. Background Two levels of abstraction are employed in the definitions of latitude and longitude. In the first step the physical surface is modeled by the geoid, a surface which approximates the mean sea level over the ocean ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
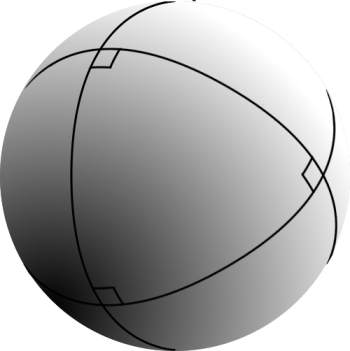
Spherical Trigonometry
Spherical trigonometry is the branch of spherical geometry that deals with the metrical relationships between the sides and angles of spherical triangles, traditionally expressed using trigonometric functions. On the sphere, geodesics are great circles. Spherical trigonometry is of great importance for calculations in astronomy, geodesy, and navigation. The origins of spherical trigonometry in Greek mathematics and the major developments in Islamic mathematics are discussed fully in History of trigonometry and Mathematics in medieval Islam. The subject came to fruition in Early Modern times with important developments by John Napier, Delambre and others, and attained an essentially complete form by the end of the nineteenth century with the publication of Todhunter's textbook ''Spherical trigonometry for the use of colleges and Schools''. Since then, significant developments have been the application of vector methods, quaternion methods, and the use of numerical methods. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ecliptic
The ecliptic or ecliptic plane is the orbital plane of the Earth around the Sun. From the perspective of an observer on Earth, the Sun's movement around the celestial sphere over the course of a year traces out a path along the ecliptic against the background of stars. The ecliptic is an important reference plane and is the basis of the ecliptic coordinate system. Sun's apparent motion The ecliptic is the apparent path of the Sun throughout the course of a year. Because Earth takes one year to orbit the Sun, the apparent position of the Sun takes one year to make a complete circuit of the ecliptic. With slightly more than 365 days in one year, the Sun moves a little less than 1° eastward every day. This small difference in the Sun's position against the stars causes any particular spot on Earth's surface to catch up with (and stand directly north or south of) the Sun about four minutes later each day than it would if Earth did not orbit; a day on Earth is therefore 24 hours ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy's Table Of Chords
The table of chords, created by the Greek astronomer, geometer, and geographer Ptolemy in Egypt during the 2nd century AD, is a trigonometric table in Book I, chapter 11 of Ptolemy's ''Almagest'', a treatise on mathematical astronomy. It is essentially equivalent to a table of values of the sine function. It was the earliest trigonometric table extensive enough for many practical purposes, including those of astronomy (an earlier table of chords by Hipparchus gave chords only for arcs that were multiples of ). Centuries passed before more extensive trigonometric tables were created. One such table is the '' Canon Sinuum'' created at the end of the 16th century. The chord function and the table A chord of a circle is a line segment whose endpoints are on the circle. Ptolemy used a circle whose diameter is 120 parts. He tabulated the length of a chord whose endpoints are separated by an arc of ''n'' degrees, for ''n'' ranging from to 180 by increments o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chord (geometry)
A chord of a circle is a straight line segment whose endpoints both lie on a circular arc. The infinite line extension of a chord is a secant line, or just ''secant''. More generally, a chord is a line segment joining two points on any curve, for instance, an ellipse. A chord that passes through a circle's center point is the circle's diameter. The word ''chord'' is from the Latin ''chorda'' meaning '' bowstring''. In circles Among properties of chords of a circle are the following: # Chords are equidistant from the center if and only if their lengths are equal. # Equal chords are subtended by equal angles from the center of the circle. # A chord that passes through the center of a circle is called a diameter and is the longest chord of that specific circle. # If the line extensions (secant lines) of chords AB and CD intersect at a point P, then their lengths satisfy AP·PB = CP·PD (power of a point theorem). In conics The midpoints of a set of parallel chords of a coni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Planets
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a young protostar orbited by a protoplanetary disk. Planets grow in this disk by the gradual accumulation of material driven by gravity, a process called accretion. The Solar System has at least eight planets: the terrestrial planets Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars, and the giant planets Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune. These planets each rotate around an axis tilted with respect to its orbital pole. All of them possess an atmosphere, although that of Mercury is tenuous, and some share such features as ice caps, seasons, volcanism, hurricanes, tectonics, and even hydrology. Apart from Venus and Mars, the Solar System planets generate magnetic fields, and all except Venus and Mercury have natural satellites. The giant planets bear ring syst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fixed Stars
In astronomy, fixed stars ( la, stellae fixae) is a term to name the full set of glowing points, astronomical objects actually and mainly stars, that appear not to move relative to one another against the darkness of the night sky in the background, unlike the few lights visible at naked eye, including comets, which appear to move slowly between those "fixed" stars along days, weeks or months on the foreground. Generally speaking, the fixed stars comprise all visible stars other than the Sun, plus the faint strip of the Milky Way. Due to their star-like appareance when sighted at naked eye, individual nebulae and other deep-sky objects also are counted among the fixed stars, despite the fact they are not true stars. The term is actually a misnomer due to the fact that those celestial objects are not really fixed with respect to one another; this is only a perceptual illusion, as stars and other extrasolar astronomical objects are so far away from Earth that human vision is unab ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristotle
Aristotle (; grc-gre, Ἀριστοτέλης ''Aristotélēs'', ; 384–322 BC) was a Greek philosopher and polymath during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. Taught by Plato, he was the founder of the Peripatetic school of philosophy within the Lyceum and the wider Aristotelian tradition. His writings cover many subjects including physics, biology, zoology, metaphysics, logic, ethics, aesthetics, poetry, theatre, music, rhetoric, psychology, linguistics, economics, politics, meteorology, geology, and government. Aristotle provided a complex synthesis of the various philosophies existing prior to him. It was above all from his teachings that the West inherited its intellectual lexicon, as well as problems and methods of inquiry. As a result, his philosophy has exerted a unique influence on almost every form of knowledge in the West and it continues to be a subject of contemporary philosophical discussion. Little is known about his life. Aristotle was born in th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |