|
Maglev June2005
Maglev (derived from ''magnetic levitation''), is a system of train transportation that uses two sets of electromagnets: one set to repel and push the train up off the track, and another set to move the elevated train ahead, taking advantage of the lack of friction. Such trains rise approximately off the track. There are both high speed, intercity maglev systems (over ), and low speed, urban maglev systems ( to ) being built and under construction and development. With maglev technology, the train travels along a guideway of electromagnets which control the train's stability and speed. While the propulsion and levitation require no moving parts, the bogies can move in relation to the main body of the vehicle and some technologies require support by retractable wheels at low speeds under . This compares with electric multiple units that may have several dozen parts per bogie. Maglev trains can therefore in some cases be quieter and smoother than conventional trains and have th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Series L0
Series may refer to: People with the name * Caroline Series (born 1951), English mathematician, daughter of George Series * George Series (1920–1995), English physicist Arts, entertainment, and media Music * Series, the ordered sets used in serialism including tone rows * Harmonic series (music) * Serialism, including the twelve-tone technique Types of series in arts, entertainment, and media * Anime series * Book series * Comic book series * Film series * Manga series * Podcast series * Radio series * Television series * "Television series", the Australian, British, and a number of others countries' equivalent term for the North American "television season", a set of episodes produced by a television serial * Video game series * Web series Mathematics and science * Series (botany), a taxonomic rank between genus and species * Series (mathematics), the sum of a sequence of terms * Series (stratigraphy), a stratigraphic unit deposited during a certain interval of geologic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shanghai Pudong International Airport
Shanghai Pudong International Airport is one of two international airports serving Shanghai and a major aviation hub of East Asia. Pudong Airport serves both international flights and a smaller number of domestic fights, while the city's other major airport, Shanghai–Hongqiao, mainly serves domestic and regional flights in East Asia. Located about east of the city center, Pudong Airport occupies a site adjacent to the coastline in eastern Pudong. The airport is operated by Shanghai Airport Authority (). The airport is the main hub for China Eastern Airlines and Shanghai Airlines, and a major international hub for Air China, as well as a secondary hub for China Southern Airlines. It is also the hub for privately owned Juneyao Airlines and Spring Airlines, and an Asia-Pacific cargo hub for FedEx, UPS and DHL. The DHL hub, opened in July 2012, is reportedly the largest express hub in Asia. Pudong Airport had two main passenger terminals, flanked on both sides by four op ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Birmingham
Birmingham ( ) is a city and metropolitan borough in the metropolitan county of West Midlands in England. It is the second-largest city in the United Kingdom with a population of 1.145 million in the city proper, 2.92 million in the West Midlands metropolitan county, and approximately 4.3 million in the wider metropolitan area. It is the largest UK metropolitan area outside of London. Birmingham is known as the second city of the United Kingdom. Located in the West Midlands region of England, approximately from London, Birmingham is considered to be the social, cultural, financial and commercial centre of the Midlands. Distinctively, Birmingham only has small rivers flowing through it, mainly the River Tame and its tributaries River Rea and River Cole – one of the closest main rivers is the Severn, approximately west of the city centre. Historically a market town in Warwickshire in the medieval period, Birmingham grew during the 18th century during the Midla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
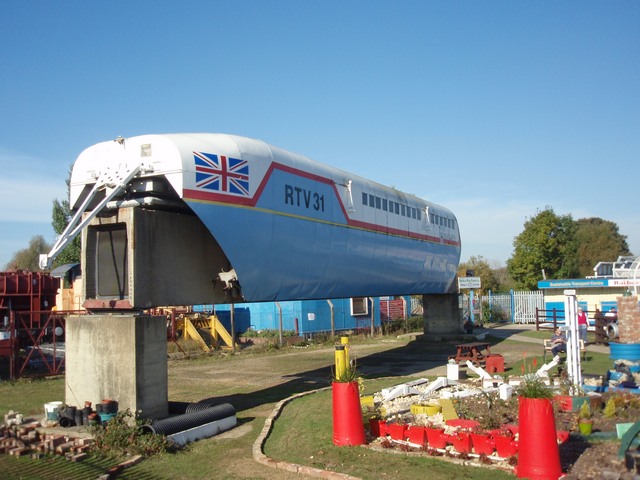
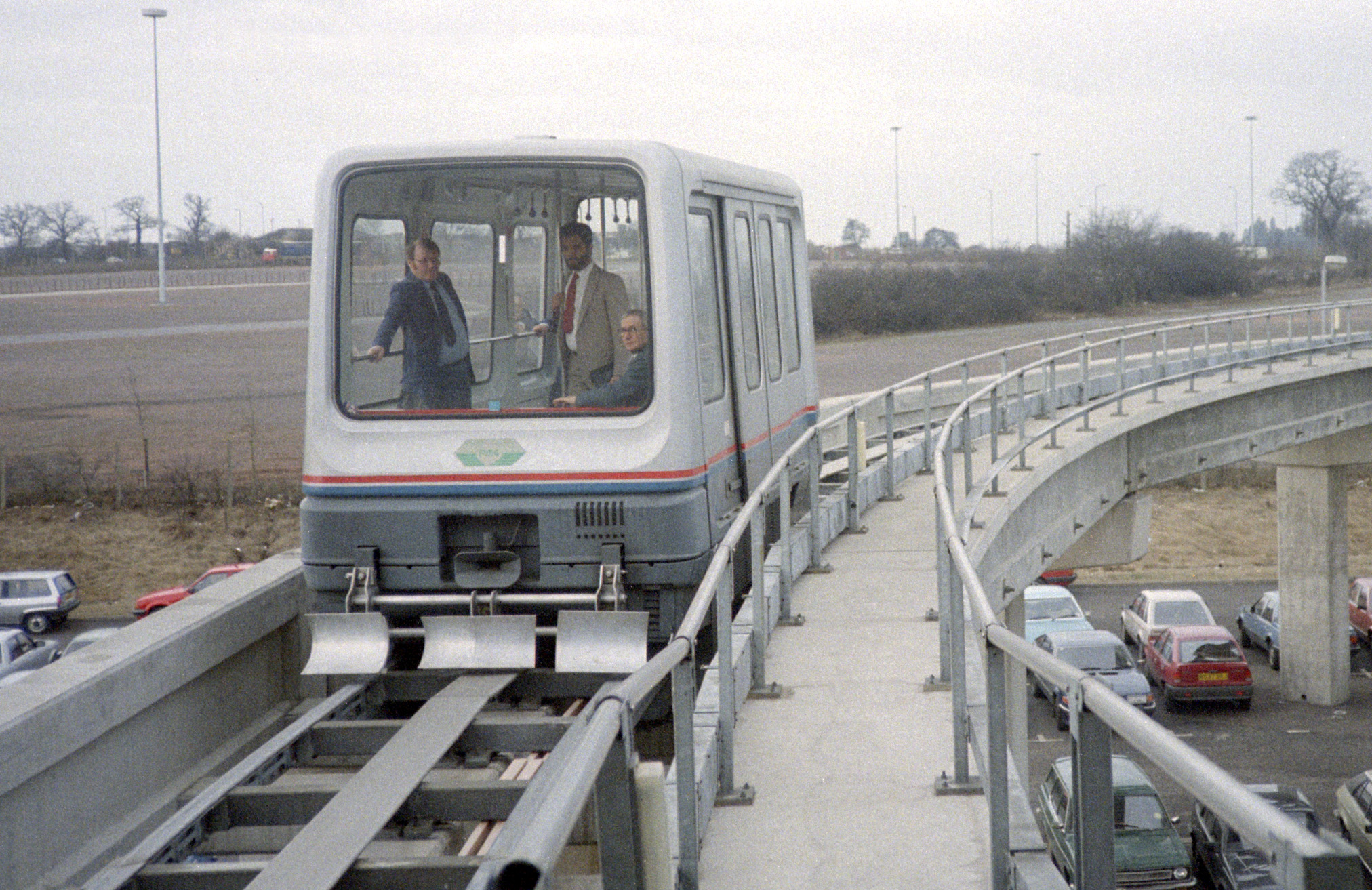
AirRail Link
The Air-Rail Link is a people mover linking Birmingham Airport with Birmingham International railway station and the National Exhibition Centre in England. The current system, originally known as SkyRail, replaced the earlier Birmingham Maglev system in 2003. The current system is a fully automated cable-hauled system that opened in 2003 and has a length of . It takes passengers between the high-level railway station concourse and the airport terminal buildings. It is free to use, and handles three million passengers per year. The Birmingham Maglev was opened in 1984 and was the first commercial Maglev transport system in the world. It operated up until 1995. The system was fully automated and used an elevated concrete guideway, much of which has been reused for the current Air-Rail Link system. Maglev Initial feasibility studies for a link from the airport to the railway station and exhibition centre were started in 1979 by the owners of the airport at that time, West Midl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
People Mover
A people mover or automated people mover (APM) is a type of small scale automated guideway transit system. The term is generally used only to describe systems serving relatively small areas such as airports, downtown districts or theme parks. The term was originally applied to three different systems, developed roughly at the same time. One was Skybus, an automated mass transit system prototyped by the Westinghouse Electric Corporation beginning in 1964. The second, alternately called the People Mover and Minirail, opened in Montreal at Expo 67. Finally the last, called PeopleMover or WEDway PeopleMover, was an attraction that was originally presented by Goodyear Tire and Rubber Company and that opened at Disneyland in 1967. Now, however, the term "people mover" is generic, and may use technologies such as monorail, rail tracks or maglev. Propulsion may involve conventional on-board electric motors, linear motors or cable traction. Generally speaking, larger APMs are refe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Derby
Derby ( ) is a city and unitary authority area in Derbyshire, England. It lies on the banks of the River Derwent in the south of Derbyshire, which is in the East Midlands Region. It was traditionally the county town of Derbyshire. Derby gained city status in 1977, the population size has increased by 5.1%, from around 248,800 in 2011 to 261,400 in 2021. Derby was settled by Romans, who established the town of Derventio, later captured by the Anglo-Saxons, and later still by the Vikings, who made their town of one of the Five Boroughs of the Danelaw. Initially a market town, Derby grew rapidly in the industrial era. Home to Lombe's Mill, an early British factory, Derby has a claim to be one of the birthplaces of the Industrial Revolution. It contains the southern part of the Derwent Valley Mills World Heritage Site. With the arrival of the railways in the 19th century, Derby became a centre of the British rail industry. Derby is a centre for advanced transport manufactur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
British Rail Research Division
The British Rail Research Division was established in 1964 directly under the control of the British Railways Board, moving into purpose-built premises at the Railway Technical Centre in Derby. The intention was to improve railway reliability and efficiency, while reducing costs and improving revenue. In so doing it became recognised as a centre of excellence and, in time, was providing consultancy to other railways around the world. While it became famous for the Advanced Passenger Train (APT), its activities extended into every area of railway operation. The theoretical rigour of its approach to railway engineering superseded the ad hoc methods that had prevailed previously. Work The Research Division brought together personnel and expertise from all over the country, including the LMS Scientific Research Laboratory. Its remit was not simply the improvement of existing equipment, or the solution of existing problems, but fundamental research from first principles, into railway ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Magnetic River
Magnetic river is an electrodynamic magnetic levitation (maglev) system designed by Fredrick Eastham and Eric Laithwaite in 1974. It consists of a thin conductive plate on an AC linear induction motor. Due to the transverse flux and the geometry, this gives it lift, stability and propulsion as well as being relatively efficient. The name refers to the action that provides stability along the longitudinal axis, which acts similar to the flow of water in a river. Linear motors A linear induction motor (LIM) is essentially a conventional induction motor with its primary "unwound" and laid out flat. The rotor, normally consisting of a series of conductors wound onto a form of some sort, is replaced by a sheet of magnetically susceptible metal. Due to its good conductance to weight ratio, aluminium is almost always used for this "stator plate". When the primaries are fed current, they induce a magnetic field in the stator plate, which generates forces away from the plate and along it. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tracked Hovercraft
Tracked Hovercraft was an experimental high speed train developed in the United Kingdom during the 1960s. It combined two British inventions, the hovercraft and linear induction motor, in an effort to produce a train system that would provide inter-city service with lowered capital costs compared to other high-speed solutions. Substantially similar to the French Aérotrain and other hovertrain systems of the 1960s, Tracked Hovercraft suffered a similar fate to these projects when it was cancelled as a part of wide budget cuts in 1973. History Genesis at Hovercraft Development It was noticed early on in the development of the hovercraft that the energy needed to lift a vehicle was directly related to the smoothness of the surface on which it travelled. This was not entirely surprising; the air trapped under the hovercraft will remain there except where it leaks out where the lifting surface contacts the ground — if this interface is smooth, the amount of leaked air will b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
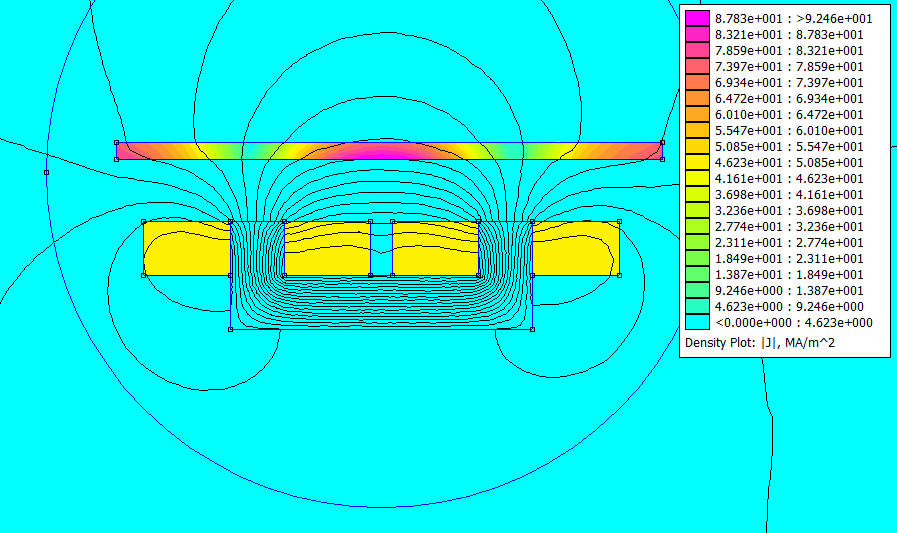
Linear Motor
A linear motor is an electric motor that has had its stator and rotor "unrolled", thus, instead of producing a torque (rotation), it produces a linear force along its length. However, linear motors are not necessarily straight. Characteristically, a linear motor's active section has ends, whereas more conventional motors are arranged as a continuous loop. A typical mode of operation is as a Lorentz-type actuator, in which the applied force is linearly proportional to the current and the magnetic field (\vec F = I \vec L \times \vec B). Linear motors are by far most commonly found in high accuracy engineering applications. It is a thriving field of applied research with dedicated scientific conferences and engineering text books. Many designs have been put forward for linear motors, falling into two major categories, low-acceleration and high-acceleration linear motors. Low-acceleration linear motors are suitable for maglev trains and other ground-based transportation applicat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperial College London
Imperial College London (legally Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine) is a public research university in London, United Kingdom. Its history began with Prince Albert, consort of Queen Victoria, who developed his vision for a cultural area that included the Royal Albert Hall, Victoria & Albert Museum, Natural History Museum and royal colleges. In 1907, Imperial College was established by a royal charter, which unified the Royal College of Science, Royal School of Mines, and City and Guilds of London Institute. In 1988, the Imperial College School of Medicine was formed by merging with St Mary's Hospital Medical School. In 2004, Queen Elizabeth II opened the Imperial College Business School. Imperial focuses exclusively on science, technology, medicine, and business. The main campus is located in South Kensington, and there is an innovation campus in White City. Facilities also include teaching hospitals throughout London, and with Imperial College Healthcare ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eric Laithwaite
Eric Roberts Laithwaite (14 June 1921 – 27 November 1997) was a British electrical engineer, known as the "Father of Maglev" for his development of the linear induction motor and maglev rail system. Biography Eric Roberts Laithwaite was born in Atherton, Lancashire, on 14 June 1921, raised in the Fylde, Lancashire and educated at Kirkham Grammar School. He joined the Royal Air Force in 1941. Through his service in World War II, he rose to the rank of Flying Officer, becoming a test engineer for autopilot technology at the Royal Aircraft Establishment in Farnborough. On demobilization in 1946, he attended the University of Manchester to study electrical engineering. His work on the Manchester Mark I computer earned him his master's degree. His subsequent doctoral work started his interest in linear induction motors. He derived an equation for " goodness" which parametrically describes the efficiency of a motor in general terms, and showed that it tended to imply that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |



.jpg)